Identification and expression analysis of VQ family genes in Lolium perenne L.
-
摘要:
VQ(Valine-glutamine)是植物特有的一类蛋白,在植物生长发育及抵御生物与非生物胁迫中发挥着重要作用,但在多年生黑麦草(Lolium perenne L.)中鲜有VQ基因的相关研究报道。本研究利用生物信息学方法在多年生黑麦草基因组中鉴定了52个LpVQ基因,其不均匀地分布于7条染色体上。亚细胞定位结果显示,LpVQ蛋白主要定位于细胞核,仅LpVQ45定位于细胞膜。系统进化分析表明,LpVQ基因被分为7个亚家族,与拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh.)只存在4对直系同源基因。基因结构分析结果表明,46个LpVQ基因无内含子。荧光定量PCR分析结果显示,从各亚家族中随机选取的21个LpVQ基因不同程度地响应黑暗、高温及盐胁迫,且在胁迫早期快速响应。
Abstract:Valine-glutamine (VQ) is a plant-specific protein, which plays an important role in plant growth, development, and resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses. To date, however, little research has been conducted on the VQ gene family in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). In this study, 52 LpVQ genes were identified in the perennial ryegrass genome, which were unevenly distributed on seven chromosomes. Subcellular localization prediction indicated that LpVQ proteins were mainly located in the nucleus, with only LpVQ45 located in the cell membrane. Phylogenetic analysis showed that LpVQ genes were divided into seven subfamilies and there were only four pairs of lineal homologous genes with Arabidopsis. Based on gene structure analysis of the LpVQ gene family, 88.46% of LpVQ genes had no intron. Finally, three LpVQ genes were randomly from each subfamily to observe the responses to dark, high temperature, and salt stress. The qRT-PCR analysis LpVQ genes responded quickly in early stages of stress. This study provides a theoretical foundation for further study on VQ family genes of perennial ryegrass under abiotic stress.
-
Keywords:
- Lolium perenne /
- VQ family /
- Abiotic stress /
- Expression analysis
-
VQ(Valine-glutamine)是植物特有的一类蛋白,因其包含一个特有的保守基序FxxxVQxLTG而得名(F:苯丙氨酸,V:缬氨酸,Q:谷氨酰胺,L:亮氨酸,T:苏氨酸,G:甘氨酸,x 代表任意氨基酸)[1-3]。首个VQ蛋白SIB1(SIGMA FACTOR-BINDING PROTEIN1)在拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh.)中被发现[4],随后,从拟南芥中又陆续鉴定出33个VQ蛋白。目前,科研人员已在茶(Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Ktze. )[2]、大豆(Glycine max (L.) Merr.)[5]、小麦(Triticum aestivum L.)[6]及烟草(Nicotiana tabacum L.)[3]中分别鉴定出25、75、113和59个VQ基因。
VQ蛋白在植物应答生物与非生物胁迫中发挥着重要作用[7, 8],其作用机制主要有两种。一是通过与WRKY转录因子相互作用发挥功能,如AtVQ23和AtVQ16通过与WRKY33的WRKY结构域结合,增强后者与靶基因的结合能力,从而影响植物的抗病能力[9]。而AtVQ9与WRKY8互作抑制了WRKY8与W-box的结合活性,从而负调控植物的抗盐性[10]。在番茄(Solanum lycopersicum L.)叶片中,SlVQ7与SlWRKY37互作可提高后者的稳定性,并转录激活其下游靶基因,从而正调控茉莉酸及黑暗诱导的叶片衰老[11]。二是作为丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)家族的磷酸化底物发挥作用[12-14]。如拟南芥MKS1(AtVQ21)作为AtMPK4的底物,与WRKY25和WRKY33相互作用,有助于激活MPK4调节的病原体防御反应[3]。
多年生黑麦草(Lolium perenne L.)为禾本科早熟禾亚科黑麦草属植物,是世界上广泛种植的冷季型草坪草及牧草[15],具有分蘖多、成坪速度快、粗蛋白含量高、耐牧性好等优点。多年生黑麦草在生长发育过程中常面临高温、盐碱、荫蔽等非生物胁迫,严重影响草坪质量和牧草品质。因此,鉴定多年生黑麦草VQ基因,探究其在应答非生物胁迫中的作用十分必要。然而,目前尚未见相关报道。本研究系统鉴定了多年生黑麦草VQ蛋白家族成员,并对其保守结构域、进化关系、共线性、亚细胞定位及其在高温、盐碱、黑暗等非生物胁迫下的表达模式进行了分析,研究结果旨在为进一步探讨VQ蛋白在多年生黑麦草生长发育及应答非生物逆境胁迫中的作用奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
本研究以多年生黑麦草品种‘百灵鸟’为实验材料。黑麦草种子于营养土(基质∶蛭石=1∶1)中萌发,萌发后转移至光照培养箱,光周期为16 h / 8 h(光 / 黑暗),温度为25 ℃ / 22 ℃(光 / 黑暗)。待植株生长1个月后进行黑暗、高温和NaCl处理。黑暗处理的条件为:25 ℃ / 22 ℃,24 h黑暗,分别于处理0、2、8 d后取样。高温处理的条件为:42 ℃,光周期16 h / 8 h,分别于处理0、1、24 h后取样。NaCl处理的条件为:25 ℃ / 22 ℃,光周期16 h / 8 h,使用200 mL 200 mmol/L的NaCl溶液进行浇灌,分别于盐处理0、3、38 h后取样。
1.2 多年生黑麦草VQ基因家族成员的鉴定
以Pfam数据库中VQ结构域(PF05678)的隐马尔可夫模型(HMM)图谱作为查询,通过HMMER搜索多年生黑麦草基因组,鉴定了可能的VQ蛋白序列。使用Pfam数据库(http://pfam.xfam.org/)进一步确认了这些序列。在拟南芥基因组数据库(TAIR)中下载拟南芥全基因组序列及其注释信息。
1.3 多年生黑麦草VQ家族成员的理化性质及亚细胞定位
使用在线网站(https://web.expasy.org/compute_pi/)分析多年生黑麦草VQ蛋白的理化性质。使用BIOINF(http://www.csbio.sjtu.edu.cn/bioinf/Cell-PLoc-)在线工具对多年生黑麦草VQ家族成员进行亚细胞定位预测。
1.4 多年生黑麦草VQ家族基因系统发育树构建
使用MEGAX(http://www.megasoftware.net)软件的ML法构建系统发育树,进行系统发育分析,并用iTOL(https://itol.embl.de/)网站进行美化。
1.5 多年生黑麦草VQ保守基序及基因结构分析
利用MEME(https://meme-suite.org/meme/tools/meme)网站对VQ蛋白的氨基酸序列进行保守基序分析。结合植物基因组序列和注释文件,用TBtools提取VQ基因的基因组序列及CDS序列,用TBtools软件工具中的Gene Structure View进行可视化。
1.6 VQ基因染色体分布及种内共线性分析
结合植物基因组序列和注释文件,使用TBtools软件工具中的Amazing Gene Location From GFF3/GTF File进行可视化,使用TBtools软件工具中的one step MCScanX进行种内基因组比对,并用Multiple Synreny Plot进行可视化。
1.7 胁迫条件下多年生黑麦草VQ基因的表达模式分析
利用Trizol试剂(Takara,大连)提取多年生黑麦草在不同非生物胁迫处理后的总RNA。使用反转录试剂盒Hifair® Ⅲ 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis SuperMix for qPCR(gDNA digester plus)(Yeasen,上海)合成cDNA。利用Hieff® qPCR SYBR Green Master Mix(High Rox Plus)试剂盒(Yeasen,上海)在Step One Plus Real-Time PCR Systems系统上进行qRT-PCR反应。反应体系总体积为20 μL,包括2 μL cDNA,上、下游引物各0.8 μL,10 μL SYBR,用ddH2O补足体积。反应程序为:95 ℃预变性5 min;95 ℃变性10 s,60 ℃退火20 s,72 ℃延伸20 s,40个循环,系统自带熔解曲线。引物序列见附表1
1 ,由擎科公司(擎科,武汉)合成,多年生黑麦草eEF1A(s)为内参基因。采用2−△△Ct方法计算候选基因的相对表达量,实验设3次重复。利用TBtools绘制热图,进行表达模式分析。2. 结果与分析
2.1 LpVQ家族成员鉴定
为了系统分析多年生黑麦草的VQ基因,以VQ结构域(PF05678)为参考,从全基因组水平挖掘其VQ家族基因。结果显示,多年生黑麦草中共存在52个VQ基因。对这些基因的编码产物LpVQ家族成员进行理化性质分析,发现LpVQs的氨基酸长度介于118~427 aa,蛋白分子量范围为11.67~43.84 kD,等电点在5.01~11.6。通过BIOINF在线网站对LpVQ家族成员进行亚细胞定位预测,发现48个蛋白定位在细胞核中,LpVQ22为叶绿体与细胞核共定位,LpVQ33为细胞壁与细胞核共定位,LpVQ37为细胞膜与细胞核共定位,而LpVQ45预测定位在细胞膜中(附表2
1 )。2.2 LpVQ家族系统进化树分析
为了分析LpVQs的进化关系,利用多年生黑麦草的52个LpVQ蛋白和拟南芥的34个AtVQ蛋白共同构建系统进化树。结果显示,拟南芥与多年生黑麦草的VQ家族成员可划分为7个亚家族(Ⅰ~Ⅶ),分别包含5、8、6、11、12、6和4个LpVQ蛋白。亚家族Ⅰ中只包含LpVQs,亚家族Ⅳ、Ⅴ和Ⅵ中含有较多的LpVQ家族成员,而AtVQ家族成员则更多地归类于亚家族Ⅱ、Ⅲ和Ⅶ(图1)。进一步分析发现,多年生黑麦草与拟南芥的VQ家族间存在4对直系同源基因,分别是LpVQ6 / AtVQ7、LpVQ11 / AtVQ9、LpVQ50 / AtVQ32和LpVQ5 / AtVQ31。
2.3 LpVQ家族成员保守基序和基因结构分析
为了研究蛋白的结构多样性,利用MEME在线软件对52个LpVQ蛋白的保守基序进行分析,结果发现17%的LpVQs含有1个Motif,48%的LpVQs含有两个Motif,19%的LpVQs含有3个Motif,6%的LpVQs含有4个Motif,10%的LpVQs含有5个Motif。所有家族成员均具有Motif1,表明它是LpVQ家族的核心保守结构域(图2)。
此外,本研究用TBtools工具对LpVQs进行了基因结构分析。结果发现,46个LpVQ基因没有内含子,5个LpVQ基因含有1个内含子(LpVQ24、LpVQ29、LpVQ31、LpVQ32、LpVQ52),仅有1个基因(LpVQ161)含有两个内含子(附图1
1 )。2.4 LpVQ家族成员染色体定位以及共线性分析
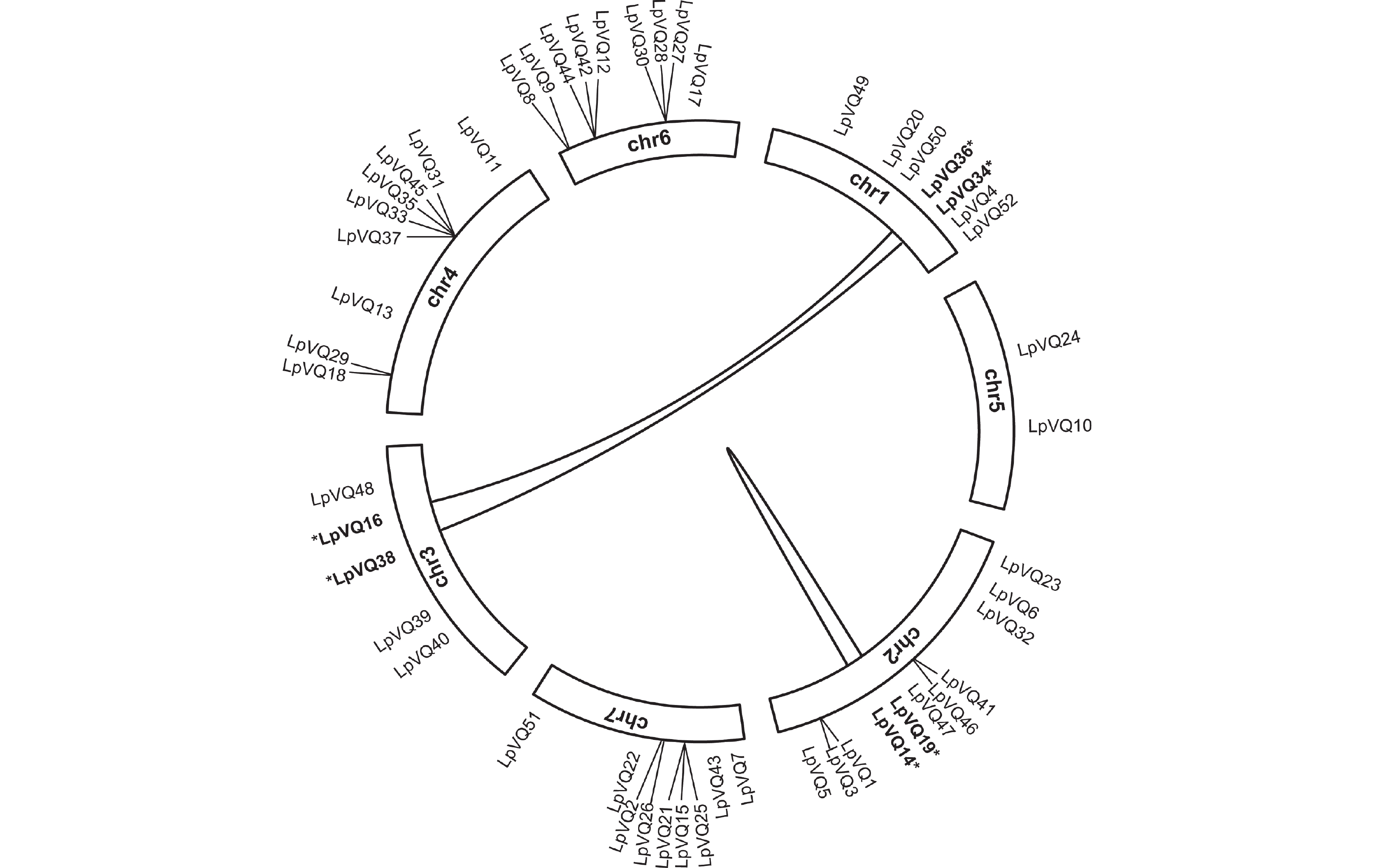
染色体定位分析结果表明,LpVQ基因分布在多年生黑麦草的7条染色体上,其中分布在chr1上的有7个,占13%,分布在chr2上的最多,为11个,占21%,分布在chr3上的为5个,占10%,分布在chr4、chr6和chr7上的基因均各有9个,各占17%,而分布在chr5上的最少,仅有2个,占4%(图3)。
为了了解LpVQ基因之间的进化关系,本研究对VQ家族成员进行了种内共线性分析。结果表明,3对VQ基因之间存在共同进化关系,分别是LpVQ16与LpVQ36、LpVQ34与LpVQ38以及LpVQ14与LpVQ19(图4)。
2.5 LpVQ基因响应非生物胁迫的表达模式分析
从7个亚家族中分别随机选取3个LpVQ基因,检测其在黑暗、高温以及盐胁迫下多年生黑麦草中的表达量变化。结果显示,黑暗处理后,只有4个LpVQ基因的表达持续上调。大部分LpVQ基因的表达量在黑暗处理2 d后下降,其中,LpVQ2、LpVQ8、LpVQ14、LpVQ22及LpVQ38的表达量在黑暗处理8 d后又显著上升(图5:A)。
![]() 图 5 LpVQ基因响应黑暗、高温及NaCl胁迫的表达模式分析A:黑暗处理;B:高温处理;C:NaCl处理。红色、蓝色和黄色分别代表上调、下调和没有表达差异的基因。Figure 5. Expression analyses of LpVQs under dark, high temperature and NaCl treatmentsA: Dark treatment; B: Heat treatment; C: NaCl treatment. Red, blue, and yellow represent up-regulated, down-regulated, and no differential genes, respectively.
图 5 LpVQ基因响应黑暗、高温及NaCl胁迫的表达模式分析A:黑暗处理;B:高温处理;C:NaCl处理。红色、蓝色和黄色分别代表上调、下调和没有表达差异的基因。Figure 5. Expression analyses of LpVQs under dark, high temperature and NaCl treatmentsA: Dark treatment; B: Heat treatment; C: NaCl treatment. Red, blue, and yellow represent up-regulated, down-regulated, and no differential genes, respectively.42 ℃高温处理后,LpVQ的表达模式被分为3类。LpVQ18、LpVQ8、LpVQ28、LpVQ2、LpVQ7、LpVQ4及LpVQ12受1 h高温处理的显著诱导,而高温处理24 h后,其表达又显著下调。LpVQ9、LpVQ22、LpVQ15、LpVQ3、LpVQ42、LpVQ6、LpVQ10、LpVQ1、LpVQ38的表达量在1 h和24 h高温处理后均显著下降。LpVQ5、LpVQ27、LpVQ34、LpVQ14和LpVQ44的表达量只在24 h高温处理后下降(图5:B)。
NaCl处理3 h后,13个LpVQ基因显著上调表达,其中LpVQ4的表达上升了13倍。而NaCl处理38 h后,大部分基因的表达明显下调。仅有3个基因的表达受盐诱导持续上调,分别是 LpVQ8、LpVQ10和LpVQ38(图5:C)。
3. 讨论
近年来,VQ基因已经在多种植物中被发掘鉴定,包括拟南芥、水稻(Oryza sativa L.)、大豆和葡萄(Vitis vinifera L.)等[16-19],而关于多年生黑麦草VQ家族基因的鉴定和分析还鲜见报道。本研究通过全基因组鉴定,得到52个多年生黑麦草LpVQ基因,并系统分析了其理化特性、蛋白结构、基因结构、共线性、进化关系以及响应逆境胁迫的表达模式。
基因结构分析发现,88.46%的LpVQ基因无内含子,与之类似,在拟南芥[16]、水稻[17]、玉米(Zea mays L.)[20]和马铃薯(Solanum tuberosum L.)[21]中,无内含子的VQ基因分别占88.2%、92.5%、88.5%和91.89%。而苔藓(Bryophyta)[22]中无内含子的VQ基因比例则远低于以上物种,仅为28.0%,说明VQ基因可能在长期进化过程中丢失了内含子。
系统进化分析结果显示,多年生黑麦草和拟南芥的VQ家族成员可被分为7个亚家族,且LpVQs与AtVQs亲缘关系较远,只存在4对直系同源基因,分别是LpVQ6 / AtVQ7、LpVQ11 / AtVQ9、LpVQ50 / AtVQ32和LpVQ5 / AtVQ31。根据拟南芥VQ基因的功能,可以推测多年生黑麦草中其直系同源VQ基因的功能。有研究指出,AtVQ9作为AtWRKY8的抑制子,能提高拟南芥的耐盐性[9],由此推测,其直系同源基因LpVQ11可能也在多年生黑麦草抵御盐胁迫中发挥重要作用。
VQ基因在植物响应非生物胁迫中发挥着重要作用。如,过表达PtVQ1基因显著增强了转基因拟南芥的耐盐性[23];而过表达MdVQ37则提高了转基因苹果(Malus pumila Mill.)对高温胁迫的敏感性[24]。本研究对黑暗、高温及盐胁迫处理下多年生黑麦草的VQ表达量进行了分析。结果显示,LpVQ基因广泛响应黑暗、高温及盐胁迫,且大部分LpVQ基因均在胁迫初期即做出快速响应,这与西葫芦(Cucurbita pepo L.)[8]、黄瓜(Cucumis sativus L.)[25]等物种中的研究结果相类似。然而,LpVQ基因的表达模式在不同胁迫处理下也存在差异。如,LpVQ1在黑暗胁迫处理后持续下调表达,而在高温和盐胁迫下持续上调表达,推测该基因可能在不同胁迫中发挥着不同的作用。尽管LpVQ可能参与多年生黑麦草对黑暗、高温及盐等胁迫响应的调控,但其具体功能还需要进一步验证。
综上所述,本研究对多年生黑麦草VQ基因家族成员进行了系统鉴定与分析,为后续验证VQ家族成员在多年生黑麦草应答生物或非生物胁迫中的功能提供了基础。
1 1~3)如需查阅附件内容请登录《植物科学学报》网站(http://www.plantscience.cn)查看本期文章。 -
图 5 LpVQ基因响应黑暗、高温及NaCl胁迫的表达模式分析
A:黑暗处理;B:高温处理;C:NaCl处理。红色、蓝色和黄色分别代表上调、下调和没有表达差异的基因。
Figure 5. Expression analyses of LpVQs under dark, high temperature and NaCl treatments
A: Dark treatment; B: Heat treatment; C: NaCl treatment. Red, blue, and yellow represent up-regulated, down-regulated, and no differential genes, respectively.
-
[1] Wang YJ,Liu HL,Zhu DY,Gao YM,Yan HW,Xiang Y. Genome-wide analysis of VQ motif-containing proteins in Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis)[J]. Planta,2017,246(1):165−181. doi: 10.1007/s00425-017-2693-9
[2] Guo JH,Chen JF,Yang JK,Yu YB,Yang YJ,Wang WD. Identification,characterization and expression analysis of the VQ motif-containing gene family in tea plant (Camellia sinensis)[J]. BMC Genomics,2018,19(1):710. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5107-x
[3] Andreasson E,Jenkins T,Brodersen P,Thorgrimsen S,Petersen NHT,et al. The MAP kinase substrate MKS1 is a regulator of plant defense responses[J]. EMBO J,2005,24(14):2579−2589. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600737
[4] Morikawa K,Shiina T,Murakami S,Toyoshima Y. Novel nuclear-encoded proteins interacting with a plastid sigma factor,Sig1,in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. FEBS Lett,2002,514(2-3):300−304. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(02)02388-8
[5] Wang YB,Jiang ZF,Li ZX,Zhao YL,Tan WW,et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the VQ gene family in soybean (Glycine max)[J]. PeerJ,2019,7:e7509. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7509
[6] Zhang LL,Wang KK,Han YX,Yan LY,Zheng Y,et al. Genome-wide analysis of the VQ motif-containing gene family and expression profiles during phytohormones and abiotic stresses in wheat (Triticum aestivum L. )[J]. BMC Genomics,2022,23(1):292. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08519-3
[7] Jiang SY,Sevugan M,Ramachandran S. Valine-glutamine (VQ) motif coding genes are ancient and non-plant-specific with comprehensive expression regulation by various biotic and abiotic stresses[J]. BMC Genomics,2018,19(1):342. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4733-7
[8] Xu K,Wang P. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the VQ gene family in Cucurbita pepo L.[J]. PeerJ,2022,10:e12827. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12827
[9] Lai ZB,Li Y,Wang F,Cheng Y,Fan BF,et al. Arabidopsis sigma factor binding proteins are activators of the WRKY33 transcription factor in plant defense[J]. Plant Cell,2011,23(10):3824−3841. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.090571
[10] Hu YR,Chen LG,Wang HP,Zhang LP,Wang F,Yu DQ. Arabidopsis transcription factor WRKY8 functions antagonistically with its interacting partner VQ9 to modulate salinity stress tolerance[J]. Plant J,2013,74(5):730−745. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12159
[11] Wang ZR,Gao M,Li YF,Zhang JL,Su H,et al. The transcription factor SlWRKY37 positively regulates jasmonic acid- and dark-induced leaf senescence in tomato[J]. J Exp Bot,2022,73(18):6207−6225. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac258
[12] Yuan GB,Qian Y,Ren Y,Guan YL,Wu XX,et al. The role of plant-specific VQ motif-containing proteins:an ever-thickening plot[J]. Plant Physiol Biochem,2021,159:12−16. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.12.005
[13] Ding HD,Yuan GB,Mo SR,Qian Y,Wu Y,et al. Genome-wide analysis of the plant-specific VQ motif-containing proteins in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and characterization of SlVQ6 in thermotolerance[J]. Plant Physiol Biochem,2019,143:29−39. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.08.019
[14] Jing YJ,Lin RC. The VQ motif-containing protein family of plant-specific transcriptional regulators[J]. Plant Physiol,2015,169(1):371−378. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00788
[15] Han SJ,Li XN,Amombo E,Fu JM,Xie Y. Cadmium tolerance of perennial ryegrass induced by Aspergillus aculeatus[J]. Front Microbiol,2018,9:1579. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01579
[16] Cheng Y,Zhou Y,Yang Y,Chi YJ,Zhou J,et al. Structural and functional analysis of VQ motif-containing proteins in Arabidopsis as interacting proteins of WRKY transcription factors[J]. Plant Physiol,2012,159(2):810−825. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.196816
[17] Zhou Y,Yang Y,Zhou XJ,Chi YJ,Fan BF,Chen ZX. Structural and functional characterization of the VQ protein family and VQ protein variants from soybean[J]. Sci Rep,2016,6:34663. doi: 10.1038/srep34663
[18] Hao ZY,Tian JF,Fang H,Fang L,Xu X,et al. A VQ-motif-containing protein fine-tunes rice immunity and growth by a hierarchical regulatory mechanism[J]. Cell Rep,2022,40(7):111235. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111235
[19] Wang M,Vannozzi A,Wang G,Zhong Y,Corso M,et al. A comprehensive survey of the grapevine VQ gene family and its transcriptional correlation with WRKY proteins[J]. Front Plant Sci,2015,6:417.
[20] Song WB,Zhao HM,Zhang XB,Lei L,Lai JS. Genome-wide identification of VQ motif-containing proteins and their expression profiles under abiotic stresses in maize[J]. Front Plant Sci,2016,6:1177.
[21] 翟明明,刘娜,徐任园,李欢欢,王倩,等. 马铃薯VQ基因家族鉴定与表达分析[J]. 农业生物技术学报,2022,30(1):25−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7968.2022.01.003 Zhai MM,Liu N,Xu RY,Li HH,Wang Q,et al. Identification and expression analysis of VQ gene family in Solanum tuberosum[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology,2022,30(1):25−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7968.2022.01.003
[22] 严涵薇,陈风,潘枫,项艳. 双子叶植物VQ基因家族的全基因组鉴定与盐胁迫下的表达模式分析[J]. 安徽农业大学学报,2018,45(5):921−931. Yan HW,Chen F,Pan F,Xiang Y. Genome-wide identification and expression pattern on salt stress of VQ gene family in dicots[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University,2018,45(5):921−931.
[23] Liu SF,Wang ZC,Wu J,Wu CJ,Xiong R,et al. The poplar VQ1 gene confers salt tolerance and pathogen resistance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants via changes in hormonal signaling[J]. G3 (Bethesda)
,2022,12(4):jkac044. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac044 [24] Dong QL,Duan DY,He JL,Zheng WQ,Huang D,et al. Overexpression of MdVQ37 reduces salt stress tolerance in Malus domestica[J]. Sci Hortic,2022,300:111077. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2022.111077
[25] Shan N,Xiang ZJ,Sun JY,Zhu QL,Xiao Y,et al. Genome-wide analysis of valine-glutamine motif-containing proteins related to abiotic stress response in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L. )[J]. BMC Plant Biol,2021,21(1):492. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03242-9
-
其他相关附件
-
PDF格式
王阳附件 点击下载(440KB)
-




 下载:
下载: