Enrichment and migration of heavy metals in the soil-plant system of the riparian zone in the Fuzhou section of the Minjiang River
-
摘要:
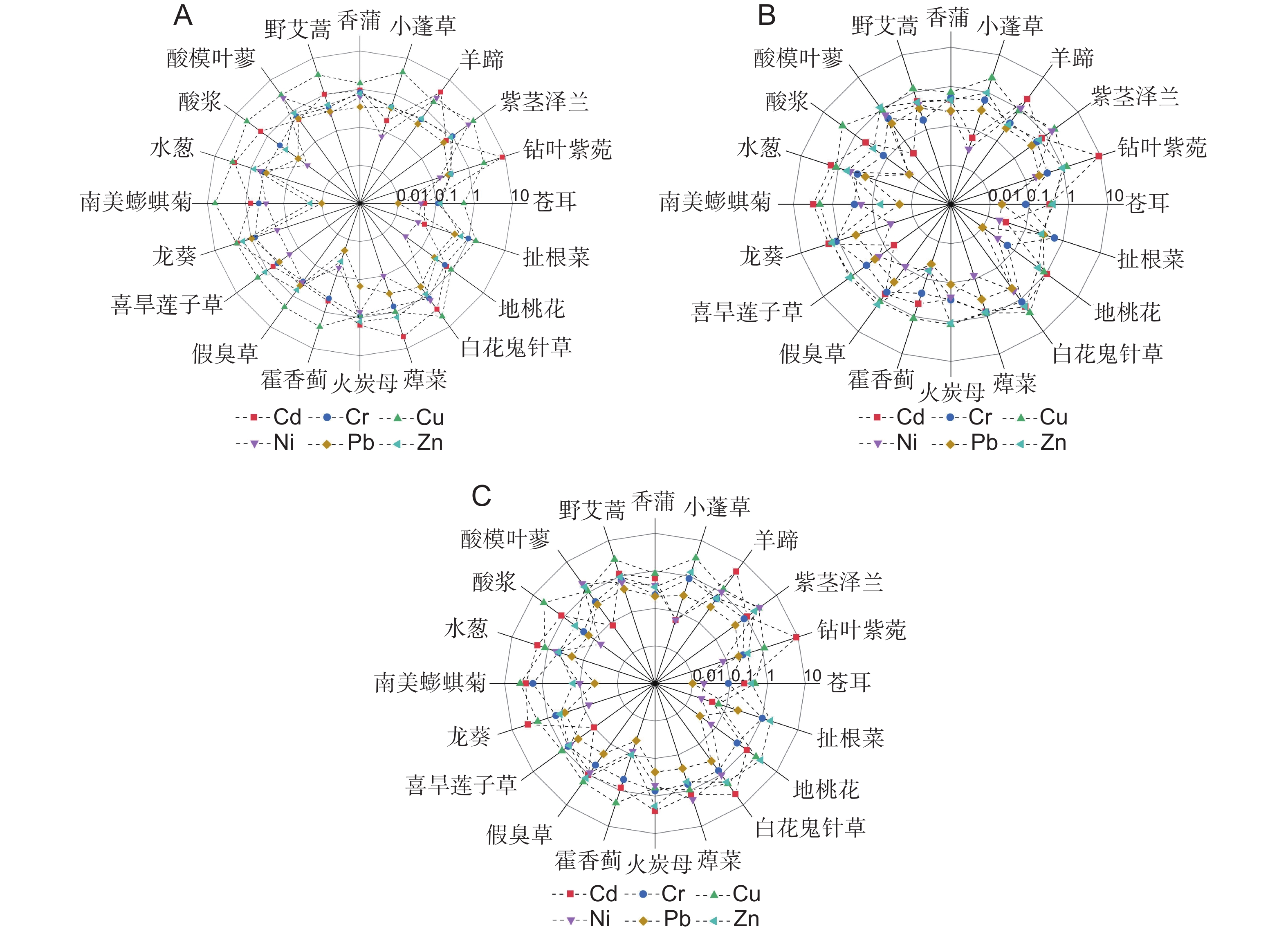
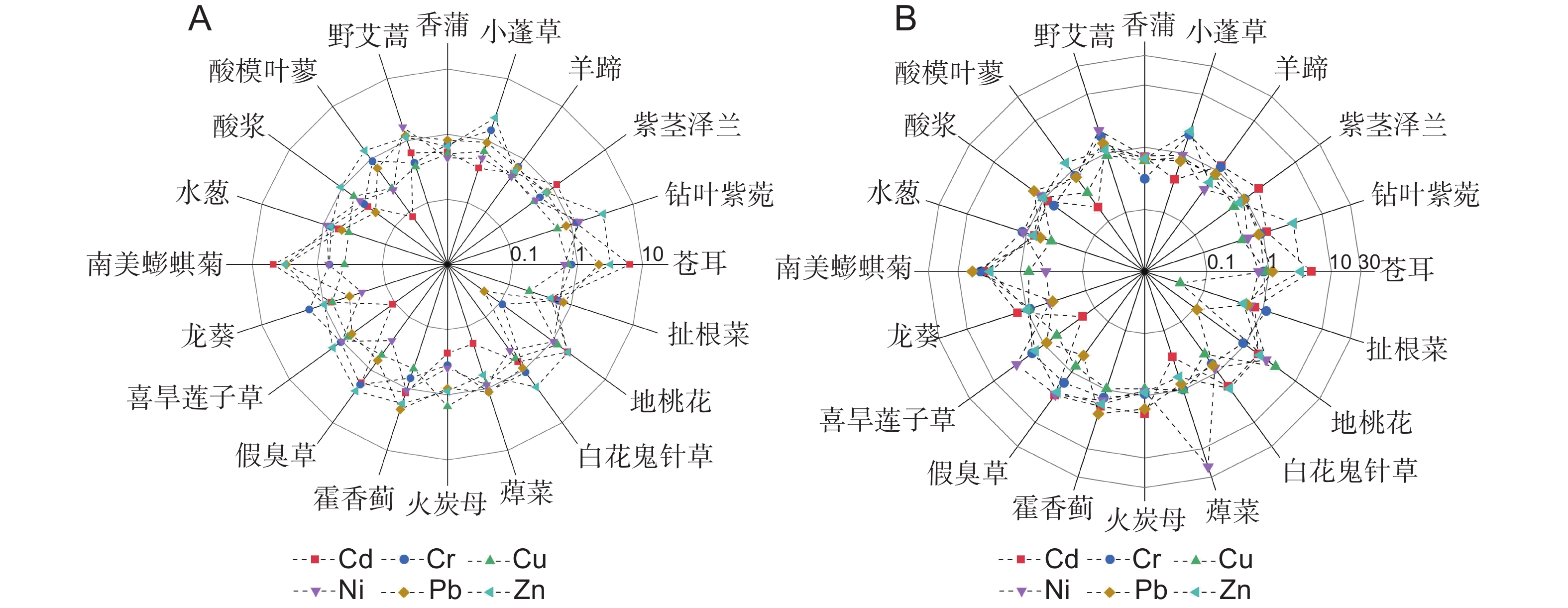
本研究分析了闽江福州段河岸带20种优势草本植物根茎叶和根际土壤的Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb和Zn含量,评估了该区域土壤重金属污染状况以及植物的重金属富集能力,并比较了植物不同器官对重金属富集和转运的差异。结果显示:(1)研究区域土壤除Pb含量低于背景值,其余元素均超背景值1.05~1.5倍,Cd是主要危害元素;(2)20种植物对Cd和Cu的富集能力较强,对Pb的富集能力最弱;(3)根和叶对重金属的富集能力强于茎,叶对重金属的转运能力强于茎;(4)白花鬼针草(Bidens pilosa L.)、紫茎泽兰(Ageratina adenophora R. M. King & H. Robinson)和龙葵(Solanum nigrum L.)的重金属综合富集能力排名前三,重金属生物富集系数分别为0.686、0.662和0.470,而苍耳(Xanthium strumarium L.)对土壤重金属的规避性较强。
Abstract:To elucidate the characteristics of heavy metal migration and enrichment within the soil-plant system of riparian zones, we analyzed the concentrations of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn in the roots, stems, leaves, and rhizosphere soil of 20 plants along the Fuzhou section of the Minjiang River. Soil heavy metal pollution levels and plant accumulation capacities were evaluated, alongside comparisons of heavy metal accumulation and translocation among plant organs. Results indicated that: (1) Pb levels in the riparian soil of the Fuzhou section were lower than background values, while Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, and Zn levels exceeded background values by 1.05 to 1.5 times, with Cd being the primary hazardous element; (2) Plants exhibited pronounced capabilities for Cd and Cu accumulation, but showed minimal accumulation of Pb; (3) Roots and leaves showed greater capacities for heavy metal accumulation than stems, with leaves also demonstrating a higher translocation ability for heavy metals than stems; (4) Among the 20 plant species studied, Bidens pilosa L., Ageratina adenophora R. M. King & H. Robinson, and Solanum nigrum L. demonstrated the highest heavy metal accumulation capacities, with comprehensive bio-concentration indices of 0.686, 0.662, and 0.470, respectively. Xanthium strumarium L. exhibited a strong tendency for heavy metal avoidance in soil.
-
Keywords:
- Minjiang River /
- Riparian zone /
- Soil /
- Herbaceous plant /
- Heavy metal enrichment /
- Heavy metal migration
-
高寒草地是青藏高原最主要的生态系统,是维护国家生态安全和改善青藏高原地区农牧民生活质量的重要保障[1]。在过去几十年里,受人类活动和自然因素的影响,高寒草地的生产和生态功能急剧下降,造成大面积土地裸露和草畜不平衡等诸多问题[2]。最近,经过相关领域学者们的不断探索实践,我国高寒草地退化的趋势明显改善,植被覆盖度大幅提升,水土流失和荒漠化基本遏制[3]。然而,青藏高原地区气候寒冷,有机质分解较慢,土壤微生物活性较低[4],导致退化草地治理周期较长,草畜矛盾仍未能有效解决。因此,在退化草地恢复的同时,建植多年生人工草地便成为满足生产和生态功能需求的重要手段。在实践中发现,多年生高寒栽培草地在建植2~3年后地上生物量达到峰值,第4年开始其地上生物量逐年下降,且饲草品质普遍较低[5]。究其原因,与青藏高原地区土壤氮限制密切相关[6]。青藏高原地区土壤氮限制极其严重,加之气温较低,严重抑制了与氮有关的功能微生物的活性,导致生产力较低[6]。此外,多年生牧草常年吸收土壤中的营养物质,导致土壤养分贫瘠,进而造成草地减产[7]。综合两方面的原因,氮添加成为提升多年生栽培草地生产功能的直接手段。
氮素形态和施氮水平是草地氮肥管理的两项重要内容,对植物生长发育起着关键调节作用。根据化合物形态可将氮肥分为铵态氮肥(A)、酰胺态氮肥(U)和硝态氮肥(N)等多种类型,不同形态氮肥均能促进植物的生长,但在土壤中的转化机制不同,导致植物的干物质分配和营养积累存在差异[8]。植物可以吸收利用的土壤氮素主要为硝态氮和铵态氮,氮素形态对不同植物生长发育的影响存在差异,氮肥形态是影响肥效的主要因素之一[9]。施用不同形态氮素会影响作物的根系发育及碳氮代谢等生理进程,进而影响植株生物量的积累。同时,氮素形态还会影响糖、激素、维生素和生物碱等各种化学物质的合成,进而影响植物的品质[10]。向雪梅等[11]在高寒区的施氮研究表明,酰胺态氮能保证植物较高的氮素利用率和较低的氮损失率,是提高植物生产力最佳的氮素形态,而Guo等[12]研究发现,硝态氮能促进野牛草(Buchloe dactyloides (Nutt.) Engelm.)的营养繁殖和品质积累。两种结果不一致的主要原因是不同植物对氮素形态的需求存在差异,故应根据植物类型和生存环境设置合理的氮源。对于青藏高原地区多年生高寒栽培草地而言,哪种氮素形态更有利于生产力和营养品质的积累不得而知。此外,研究施氮水平对植物生产性能的影响并确定合理的氮添加量也是科学添加氮肥的关键[13]。以往研究证实,合理的氮添加量是保证植物生产力和营养品质的关键[14],但关于具体氮添加量始终没有形成统一的结论,这是因为施氮水平应符合环境状况,不同区域氮素水平的阈值存在显著差异,氮限制比较严重的土壤环境可能需要施加更多的氮肥来满足植物的生长需求[15]。但过量的氮添加不仅造成氮肥利用率下降,也会对生态环境构成威胁。因此,确定最佳施氮量也是维持多年生高寒栽培草地生产力和营养品质的核心目标。
鉴于此,本研究以4年龄人工草地为研究对象,设置3个氮素形态和4个施氮水平,通过比较不同处理植物的地上生物量和饲草营养品质等参数,探究不同氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草生产性能和营养品质的影响,通过灰色关联度综合分析,进一步筛选出最佳的氮素形态和施氮水平,以期为高寒地区优质饲草的生产提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验区概况
试验区位于青海省海南藏族自治州共和县巴卡台农牧场(36°17'N,100°55'E),平均海拔3 300 m,年均降水量为300 mm,年蒸发量在2 000~2 400 mm,年平均气温为4.1 ℃。试验区冬季寒冷漫长,夏季温和短暂,年内干旱少雨且温度偏低,气温垂直分布明显,太阳辐射强,属高原大陆性气候特征。降水季节性分布不均,主要集中在7-10月。试验地土壤为高山草甸土和黄绵土[16]。
1.2 试验设计
于2022年6月,以2019年建植的青海草地早熟禾(Poa pratensis L. cv. Qinghai)+青海中华羊茅(Festuca sinensis L. cv. Qinghai)混播草地为研究对象,两个物种的混播比例为1∶1,建植面积为15 m×150 m。设置小区时,为避免边际效应,选取整块地中间较均匀的地段,采用随机区组设计,设置3个氮素形态,分别为尿素(酰胺态氮,U)、硫酸铵(铵态氮,A)和硝酸钙(硝态氮,N);参照中国氮沉降分布格局(青海地区干湿沉降率7.55 kg·hm−2·yr−1)确定氮素添加剂量,设4个施氮梯度,分别为青海省干湿氮沉降的0、3、6、9倍,浓度依次为0(T0,CK)、22.5(T1)、45(T2)、67.5 kg·hm−2·a−1(T3),各处理见表1。每个处理3个重复,共30个小区,小区面积为4 m×4 m,小区之间间隔5 m。将称好的肥料分为两等份,分别于6月上旬和下旬加到2 L水中溶解,摇匀后装入喷壶,均匀喷洒在相应的小区内,CK处理喷洒相同体积的水。
表 1 氮素形态和施氮水平设置Table 1. Nitrogen forms and nitrogen level settings施肥处理
Fertilization treatment氮素形态
Nitrogen form施氮水平
Nitrogen level / kg·hm−2·a−1T0(CK) − 0.0 UT1 酰胺态氮 22.5 UT2 45.0 UT3 67.5 AT1 铵态氮 22.5 AT2 45.0 AT3 67.5 NT1 硝态氮 22.5 NT2 45.0 NT3 67.5 1.3 样品采集与分析
1.3.1 样品采集与处理
于2022年8月上旬(植物生长旺期)对各试验小区进行调查与样品采集。采用样方法,设置50 cm×50 cm的样方,齐地面刈割后带回实验室称取鲜重,后转移至105 ℃烘箱中杀青30 min,然后在75 ℃烘干至恒重,称取地上生物量。之后将烘干草样用粉碎机粉碎,过1 mm筛备用。
1.3.2 牧草品质测定方法
利用元素分析仪测定植物粗蛋白含量[17],利用索氏抽提法测定粗脂肪含量[18],使用马弗炉灼烧法测定粗灰分含量[18],中性洗涤纤维含量和酸性洗涤纤维含量采用范式纤维洗涤法进行测定[19],并根据童永尚等[19]的方法计算相对饲喂价值。
1.3.3 数据处理与分析
采用Excel 2010软件进行原始数据整理和灰色关联度分析,具体参见童永尚等[19]的方法。运用SPSS 27.0软件进行双因素方差分析和聚类分析。在Origin 2022软件中绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草生产性能的影响
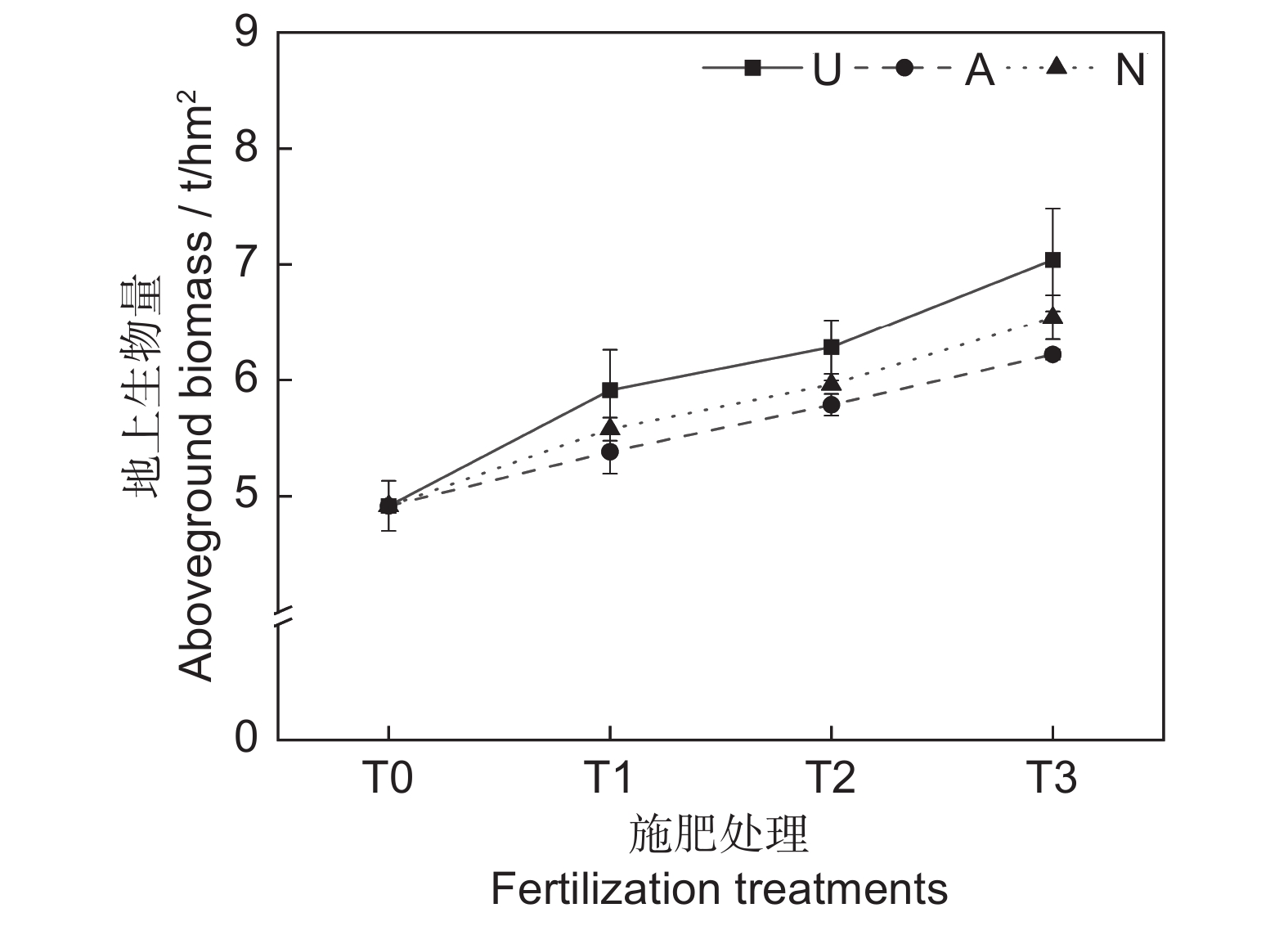
由表2可知,氮素形态对多年生高寒栽培草地的地上生物量影响显著(P<0.05),施氮水平对地上生物量的影响极显著(P<0.001),氮素形态和施氮水平交互作用对地上生物量影响不显著。氮添加整体上提高了群落地上生物量,且随着施氮水平的提高呈递增趋势,UT3、AT3和NT3处理分别较CK处理提高43.22%、26.54%和33.11%。同等氮水平相比较,对地上生物量的促进作用表现为U>N>A(图1)。
表 2 氮素形态和施氮水平的双因素方差分析Table 2. Two factor analysis of variance for nitrogen forms and nitrogen application levels影响因素
Influence factor氮素形态
Nitrogen form (F)施氮水平
Nitrogen level (L)氮素形态×施氮水平
F×LF P F P F P 地上生物量 5.622 <0.05 14.056 <0.001 0.153 0.959 粗蛋白 18.073 <0.001 38.120 <0.001 1.748 0.184 粗脂肪 39.829 <0.001 5.377 <0.05 1.183 0.351 粗灰分 0.020 0.980 0.576 0.572 1.714 0.191 中性洗涤纤维 1.979 0.167 1.423 0.267 1.422 0.267 酸性洗涤纤维 1.153 0.338 0.718 0.501 1.555 0.229 相对饲喂价值 1.275 0.304 1.284 0.301 1.909 0.153 2.2 氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草营养品质的影响
2.2.1 对饲草粗蛋白含量的影响
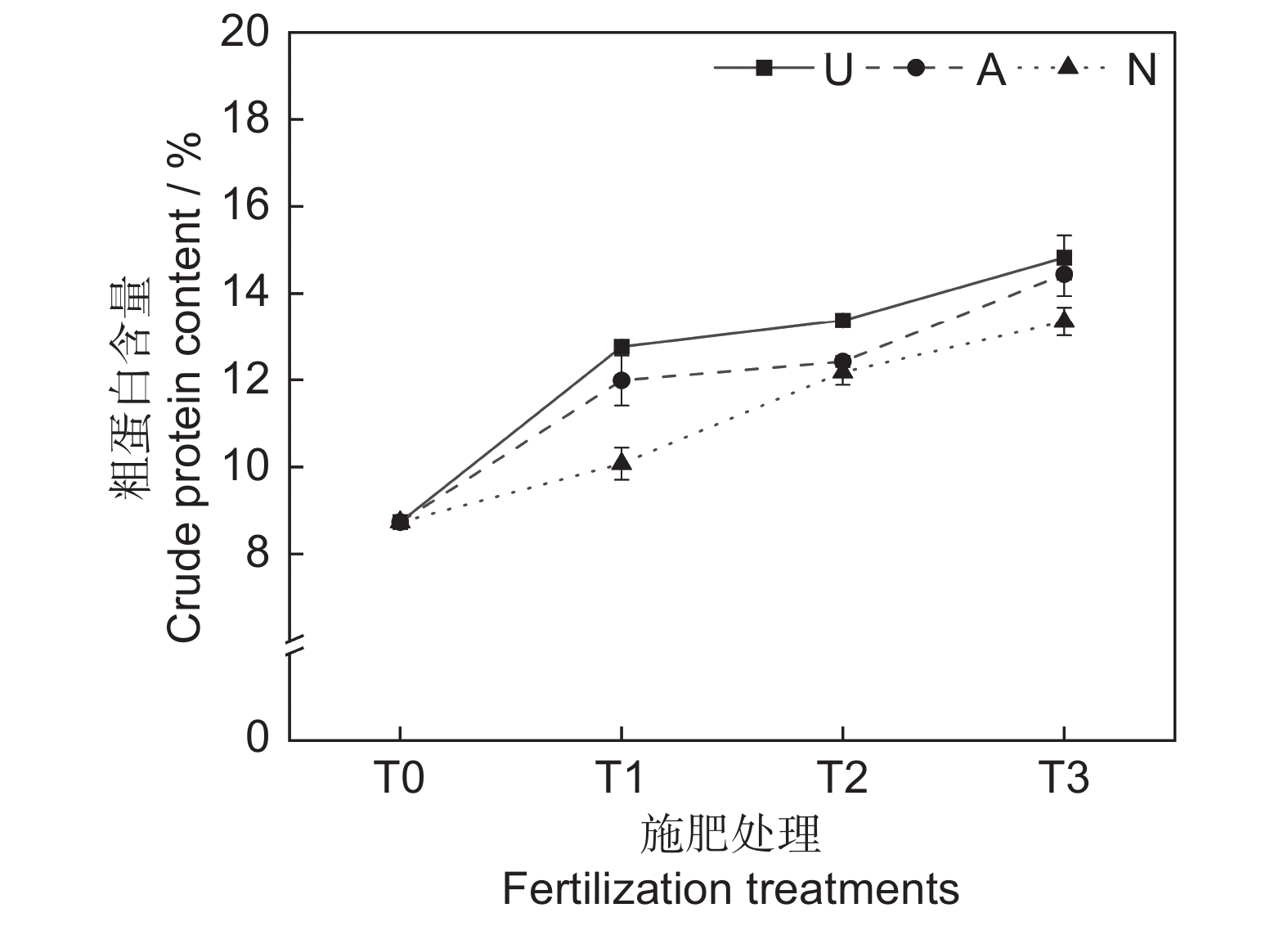
由表2和图2可知,氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草粗蛋白含量均具有极显著影响(P<0.001),氮素形态和施氮水平交互作用对饲草粗蛋白含量影响不显著。氮添加整体上提高了植物的粗蛋白含量,且随着施氮水平的提高呈递增趋势,UT3、AT3和NT3处理分别较CK处理提高了69.76%、65.41%和52.86%。同等氮水平相比较,对饲草粗蛋白含量的促进作用表现为U>A>N。
2.2.2 对饲草粗脂肪含量的影响
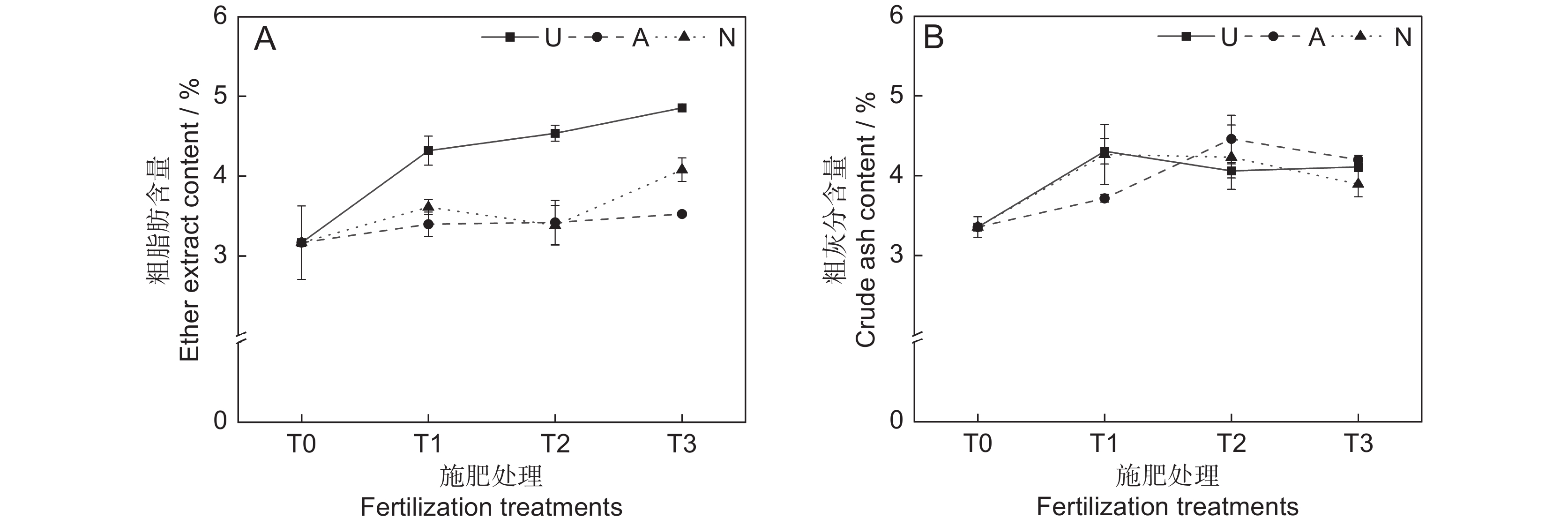
氮素形态对饲草粗脂肪含量具有极显著影响(P<0.001),施氮水平对饲草粗脂肪含量具有显著影响(P<0.05),氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草粗脂肪含量没有明显的交互作用(表2)。氮添加整体上提高了植物的粗脂肪含量,不同施氮水平对饲草粗脂肪含量的促进作用因氮素形态不同而有所差异。饲草粗脂肪含量随着酰胺态氮施肥水平的提高而增加,铵态氮施肥水平的增加对植物粗脂肪含量的影响较小。3种氮素形态下,饲草的粗脂肪含量均在T3水平时达到峰值,UT3、AT3和NT3处理分别较CK提高了53.30%、11.34%和28.86%。同等氮水平相比较,对地上生物量的促进作用表现为U>N>A(图3:A)。
2.2.3 对饲草粗灰分含量的影响
由表2可知,氮素形态、施氮水平及二者交互作用对饲草粗灰分含量的影响均不显著。氮添加整体上提高了植物的粗灰分含量(P<0.05),AT2处理下植物的粗灰分含量最高,为4.46%。同一氮素形态下不同施氮水平相比较,A和N处理均在T1水平时达到最大粗灰分含量,分别为4.31%和4.26%(图3:B)。
2.2.4 对饲草中性洗涤纤维含量的影响
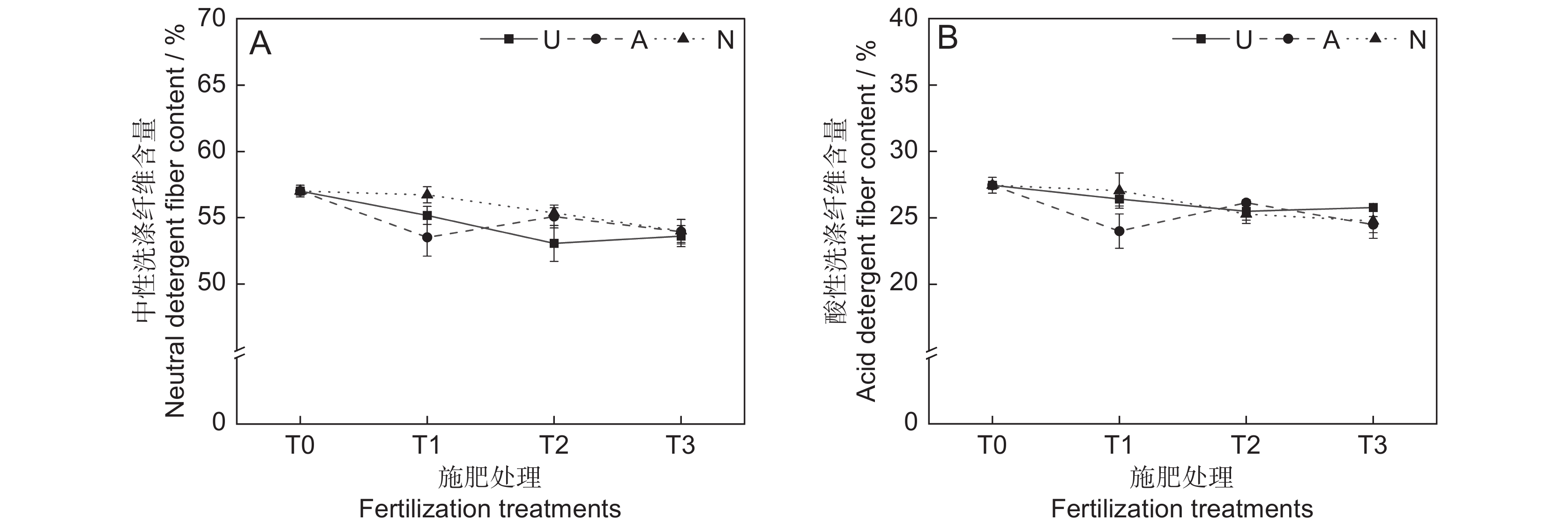
本研究发现,氮素形态、施氮水平及二者交互作用对饲草中性洗涤纤维含量均未产生显著影响(表2)。氮添加整体上降低了植物的中性洗涤纤维含量(P<0.05)。随着硝态氮施肥水平的提高,植物中性洗涤纤维含量逐渐降低(图4:A)。3种氮肥在T3水平时的中性洗涤纤维含量趋于一致,介于63.6%~64.0%。
2.2.5 对饲草酸性洗涤纤维含量的影响
由表2可知,氮素形态、施氮水平、氮素形态和施氮水平交互作用对饲草酸性洗涤纤维含量的影响均不显著。氮添加整体上降低了植物的酸性洗涤纤维含量(图4:B)。T2水平时,3种氮肥对植物酸性洗涤纤维含量的影响不明显。总体来看,T1水平时,施用铵态氮肥对植物酸性洗涤纤维含量的降低效果最为明显。
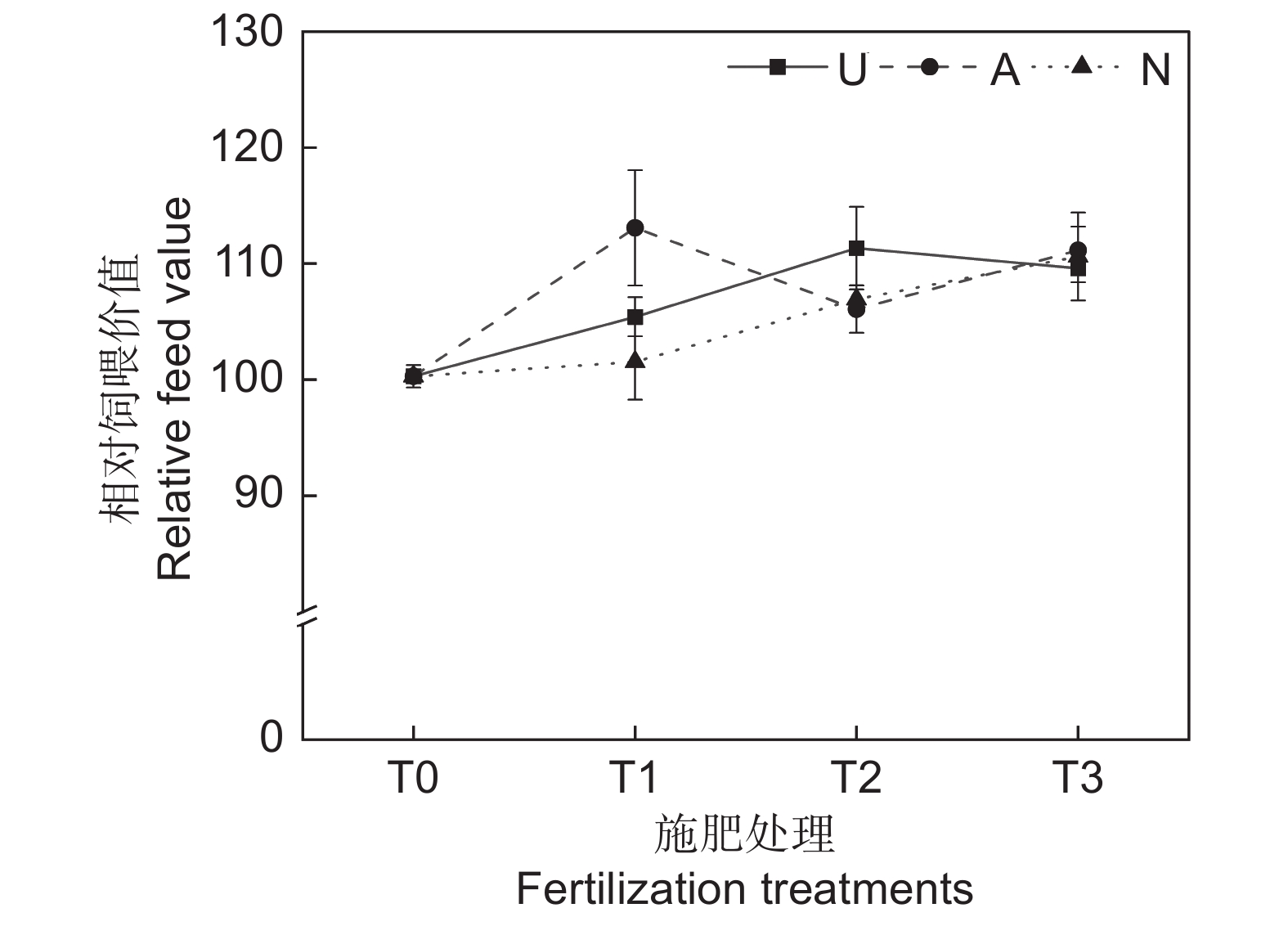
2.2.6 对饲草相对饲喂价值的影响
由表2可知,氮素形态、施氮水平及二者交互作用对饲草相对饲喂价值均未产生显著影响。如图5所示,氮添加整体上提高了饲草的相对饲喂价值,不同氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草相对饲喂价值的影响较大。随着硝态氮肥施氮水平的提高,饲草的相对饲喂价值逐渐提高。T3水平时,3种氮肥对饲草相对饲喂价值的提升效果接近。不同氮肥形态相比较,T1水平时,施用铵态氮肥的饲草其相对饲喂价值最高,为113.08;T2水平时,施用酰胺态氮肥时饲草的相对饲喂价值最高,为113.34。
2.3 灰色关联度评价和聚类分析
将植物地上生物量、粗蛋白含量和中性洗涤纤维含量等7个指标纳入评价体系,对不同氮素形态和施肥水平共10个处理进行灰色关联度综合评价。由表3可知,CK处理排序第9,说明氮添加普遍提高了饲草的综合性能。综合排名前4位的处理分别是UT3、UT2、NT3和AT3。不同酰胺态氮肥处理的综合排名依次为UT3>UT2>UT1,不同铵态氮肥处理的综合排名依次为AT3>AT1>AT2,不同硝态氮肥处理的综合排名依次为NT3>NT2>NT1。
表 3 不同处理的灰色关联度综合评价Table 3. Comprehensive evaluation of gray correlation degree for different treatments施肥处理
Fertilization treatment等权关联度
Gray correlative排序
Rank权重系数
Weight coefficient加权关联度
Weighted gray correlative加权关联度排序
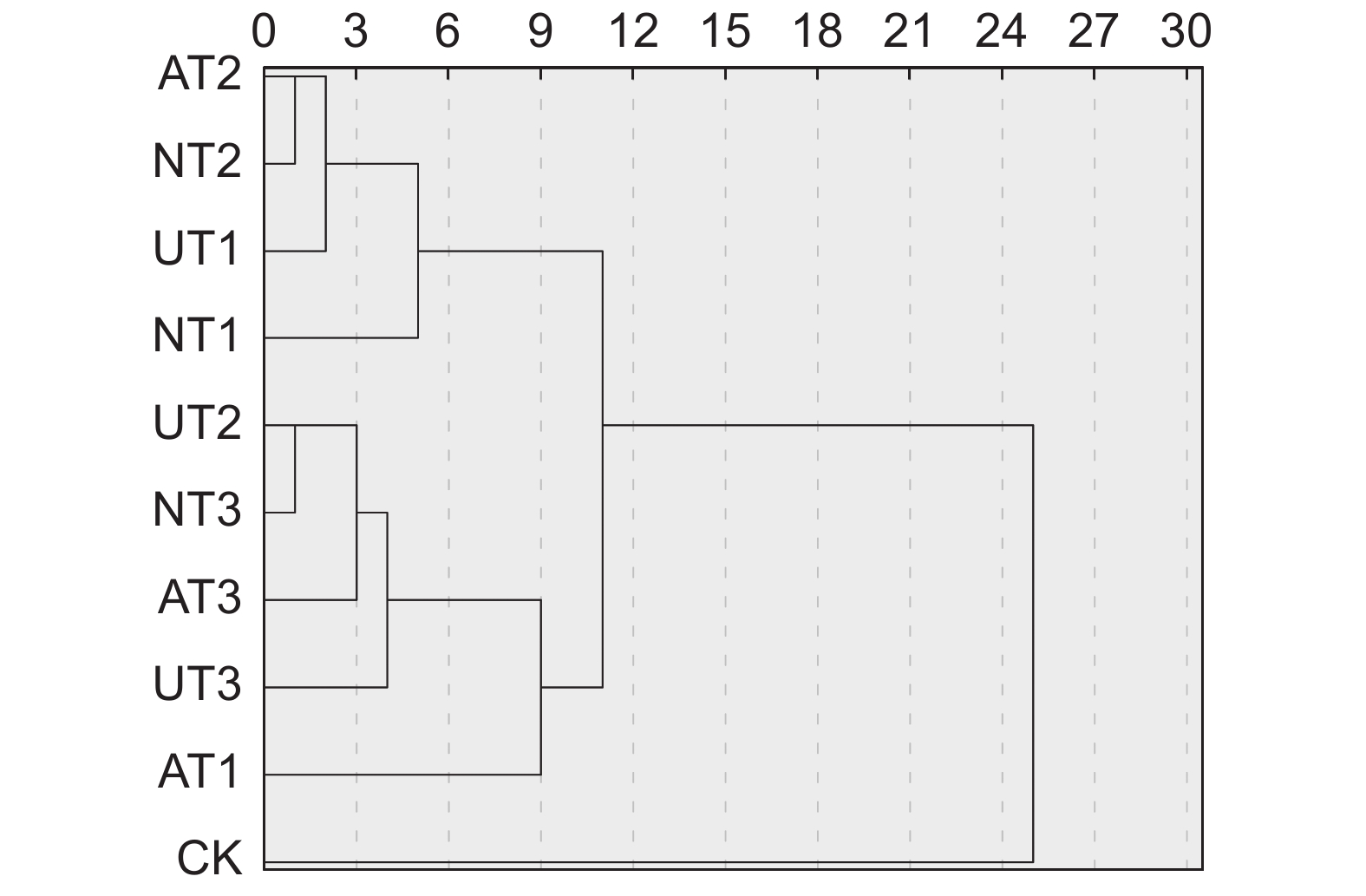
Rank of weighted gray correlativeUT3 0.871 4 1 0.126 3 0.110 0 1 UT2 0.763 3 2 0.110 6 0.084 4 2 NT3 0.753 6 3 0.109 2 0.082 3 3 AT3 0.746 1 4 0.108 1 0.080 7 4 AT1 0.718 6 5 0.104 1 0.074 8 5 UT1 0.654 1 6 0.094 8 0.062 0 6 NT2 0.633 7 7 0.091 8 0.058 2 7 AT2 0.613 0 8 0.088 8 0.054 5 8 CK 0.589 1 9 0.085 4 0.050 3 9 NT1 0.557 0 10 0.080 7 0.045 0 10 本试验将10个处理的地上生物量和营养品质进行了聚类分析,运用SPSS 27.0软件构建树形图(图6),在欧式距离为9处,可将其分为4大类。第Ⅰ类仅包括CK处理,其产量和营养品质均表现最差;第Ⅱ类只有AT1处理,其地上生物量略高于CK处理;第Ⅲ类包括UT2、UT3、AT3和NT3处理,其产量和营养品质均表现最好;第Ⅳ类包括UT1、NT1、NT2和AT2处理,其产量和营养品质仅次于第Ⅲ类。
3. 讨论
3.1 氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草生产性能的影响
众所周知,氮添加可以提高植物的生产力,但不同环境的氮添加量应有所差异[20]。施氮量较低时,土壤养分仍然不能满足植物生长,施氮量过多又会导致土壤中产生有毒的亚硝酸盐[21],进而阻碍植物生长,因此栽培草地施氮量应根据土壤氮素含量来确定。在以往的研究中,关于氮添加水平对植物地上生物量的调节作用有两种结论,第1种是地上生物量随施氮量增加而增加[22];第2种是地上生物量随施氮量的增加会出现一个峰值,然后逐渐降低[15],这是因为氮添加量有一定的环境阈值,存在一个最适施氮量,以最适施氮量为对称轴,植物的地上生物量随施氮量增加呈抛物线变化。本研究中,施氮水平对地上生物量具有极显著影响,氮添加显著提高了群落地上生物量,且随着施氮水平的提高呈递增趋势,在施氮量为67.5 kg·hm−2·a−1时达到峰值,说明本研究中设置的施氮量可能过低,在后期的试验中需要加大施氮梯度。此外,氮素形态对植物的地上生物量也产生显著影响,对地上生物量的促进作用表现为U>N>A。说明在短期内,酰胺态氮对植物生物量的促进效果更为明显,而硝态氮和铵态氮的效果相对较差,这与向雪梅等[11]和芦光新等[23]在高寒草地中的研究结论相似。尽管施加铵态氮肥补充了土壤养分,一定程度上促进了植物生长,但铵态氮肥抑制了植物对K+和Ca2+的吸收,导致NH4+的积累并产生氨害,从而限制了植物的生长[12, 24]。硝态氮肥的促产作用介于酰胺态和铵态氮肥之间。硝态氮同样也会对植物的生长产生不利影响,在还原过程中,硝态氮会消耗较多的能量。另外,在弱光条件下,植物对硝态氮的吸收也有可能会受到抑制,从而导致氮素供应不足。相比铵态氮肥和硝态氮肥,含氮量较高的酰胺态氮肥为土壤补充了充足的养分[16],更能满足植物的生长需求。由于氮素形态和氮素水平的设置还与牧草栽培方式、施氮时间和气候条件等因素相关,后期还应针对以上干扰因素设置控制试验,进行深入研究。
3.2 氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草营养品质的影响
在高寒地区,老龄人工草地牧草的营养品质较差是一个普遍现象。究其原因,土壤中营养元素含量较低,导致植物对氮、磷等元素的吸收利用效率较低。研究表明,氮素添加可迅速补充植物中的全氮含量,满足植物对营养元素的需求,进而恢复草地生产力,改善草地群落结构和植物的营养品质[25]。粗蛋白和粗脂肪含量是评价牧草营养价值的重要指标,其含量高则表明牧草营养品质较高,而粗纤维和粗灰分含量越高,则表明牧草可消化养分低,品质下降[26]。宋建超等[27]在高寒区的研究表明,氮添加显著提高了垂穗披碱草(Elymus nutans Griseb.)的粗蛋白和粗脂肪含量,与本研究结论一致。本研究中,所有施氮处理均显著提高了饲草的粗蛋白和粗脂肪含量。此外,我们还发现不同氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草的粗蛋白和粗脂肪含量具有显著影响,施用酰胺态氮肥更有利于粗蛋白和粗脂肪的积累,且高氮水平的促进作用更加明显。该现象一方面说明了高寒区氮限制非常严重,改善牧草的营养品质可能需要投入更多的氮肥;另一方面,由于不同的植物或生育期对氮肥的需求量和氮素形态具有明显差异,所以应根据实际情况选择适宜的氮素形态和施氮量。适宜的氮素形态是提高氮素利用率以及植物蛋白质含量的重要途径之一[28]。本研究中,酰胺态氮对植物粗蛋白和粗脂肪的促进效果明显高于铵态氮和硝态氮,这可能与植物的选择吸收能力以及不同氮肥的供氮能力等因素有关[29]。此外,本研究中的3种氮肥均不同程度地提高了饲草的粗灰分含量,降低了饲草的中性洗涤纤维及酸性洗涤纤维含量,与前人研究结论相似[30]。聚类分析将10个处理分为4大类,通过对比试验数据发现,这4大类可划分饲草生产性能和营养品质的优劣,基本对应了不施氮、低氮、中氮和高氮4种属性,因此,施氮水平对饲草生产性能和营养品质的影响是显而易见的。最后,本研究通过灰色关联度分析得出,选用酰胺态氮肥,施氮量为67.5 kg·hm−2·a−1时,多年生栽培草地饲草的生产性能和营养品质综合表现最优,研究结果可为青藏高原环青海湖地区人工草地生产力及营养品质的提高提供参考。
4. 结论
氮素形态和施氮水平对多年生高寒栽培草地饲草的生产性能和营养品质具有显著影响。选择酰胺态氮肥,施氮量为67.5 kg·hm−2·a−1时,多年生栽培草地饲草的生产性能和营养品质综合表现最优,说明适宜的氮肥管理制度对提高研究区饲草生产性能和营养价值具有促进作用。
1 如需查阅附图内容请登录《植物科学学报》网站(http://www.plantscience.cn)查看本期文章。 -
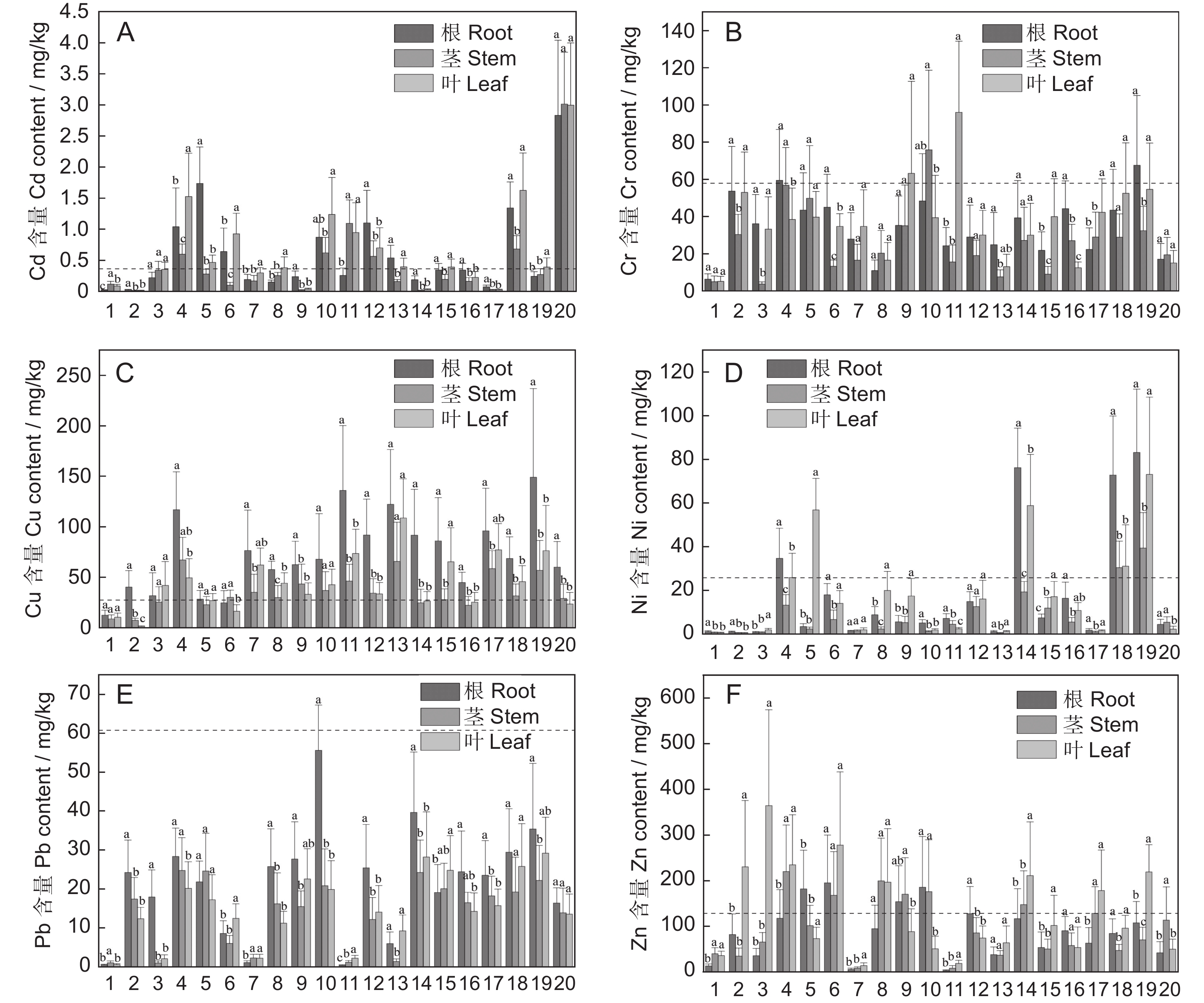
图 1 植物不同器官中的重金属含量
不同小写字母表示同种植物不同部位重金属含量差异显著,P<0.05;虚线表示土壤重金属含量均值。1:苍耳;2:扯根菜;3:地桃花;4:白花鬼针草;5:蔊菜;6:火炭母;7:藿香蓟;8:假臭草;9:喜旱莲子草;10:龙葵;11:南美蟛蜞菊;12:水葱;13:酸浆;14:酸模叶蓼;15:野艾蒿;16:香蒲;17:小蓬草;18:羊蹄;19:紫茎泽兰;20:钻叶紫菀。
Figure 1. Heavy metal content in different plant organs
Different lowercase letters indicate different parts of the same plant, P<0.05. Black underlines indicate mean heavy metal content in soil. 1: Xanthium strumarium L.; 2: Penthorum chinense Pursh; 3: Urena lobata L.; 4: Bidens pilosa L.; 5: Rorippa indica Hiern; 6: Persicaria chinensis H. Gross; 7: Ageratum conyzoides L.; 8: Praxelis clematidea Cassini; 9: Alternanthera philoxeroides Griseb.; 10: Solanum nigrum L.; 11: Sphagneticola trilobata Pruski; 12: Schoenoplectus tabernaemontani Palla; 13: Alkekengi officinarum Moench; 14: Persicaria lapathifolia S. F. Gray; 15: Artemisia lavandulifolia Candolle; 16: Typha orientalis Presl; 17: Erigeron canadensis L.; 18: Rumex japonicus Houtt.; 19: Ageratina adenophora R. M. King & H. Robinson; 20: Symphyotrichum subulatum G. L. Nesom.
表 1 样地信息
Table 1 Information of sample sites
样地
Site地理坐标
Coordinate海拔
Altitude / mM1 26°12′42″N,119°02′14″E 29 M2 26°11′36″N,119°04′10″E 20 M3 26°09′46″N,119°07′01″E 11 M4 26°07′02″N,119°11′27″E 11 M5 26°06′48″N,119°10′38″E 6 M6 26°08′07″N,119°08′43″E 15 B7 26°05′06″N,119°14′53″E 5 B8 26°04′40″N,119°15′08″E 4 N9 26°01′55″N,119°14′14″E 2 N10 26°01′36″N,119°14′24″E 6 N11 25°58′46″N,119°15′54″E 5 N12 25°38′41″N,119°18′20″E 6 表 2 土壤重金属含量
Table 2 Contents of soil heavy metals
重金属
Heavy metal均值
Mean / mg/kg标准差
SD变异系数
CV / %背景值
Background value / mg/kg超标率
Over-standard rate / %Cd 0.36 0.07 19.45 0.24 100 Cr 57.85 25.35 43.83 53 52.86 Cu 27.32 9.01 32.98 23 63.21 Ni 25.65 7.34 28.62 23 58.21 Pb 60.76 14.63 24.07 66 26.07 Zn 128.20 53.79 41.96 122 46.43 表 3 植物重金属含量平均值
Table 3 Average value of heavy metal content in plants
植物
Species重金属Heavy metal/ mg/kg Cd Cr Cu Ni Pb Zn 苍耳Xanthium strumarium L. 0.07 5.44 10.46 0.73 0.69 29.44 扯根菜Penthorum chinense Pursh 0.02 45.61 16.25 0.63 17.96 115.70 地桃花Urena lobata L. 0.30 24.29 33.03 1.11 6.96 154.77 白花鬼针草Bidens pilosa L. 1.05 51.55 77.72 24.51 24.37 190.71 蔊菜Rorippa indica Hiern 0.83 44.29 25.98 20.79 21.17 118.63 火炭母Persicaria chinensis H. Gross 0.55 30.95 23.64 12.85 8.99 213.63 藿香蓟Ageratum conyzoides L. 0.22 26.31 57.82 1.60 1.84 9.09 假臭草Praxelis clematidea Cassini 0.26 15.87 43.91 10.32 17.66 163.60 喜旱莲子草Alternanthera philoxeroides Griseb. 0.10 44.45 46.23 9.35 21.87 137.33 龙葵Solanum nigrum L. 0.91 54.51 49.10 2.66 32.06 137.20 南美蟛蜞菊Sphagneticola trilobata Pruski 0.76 45.27 85.19 4.68 1.25 9.71 水葱Schoenoplectus tabernaemontani Palla 0.79 25.98 53.09 14.41 17.19 95.66 酸浆Alkekengi officinarum Moench 0.36 15.13 98.70 0.92 5.48 46.00 酸模叶蓼Persicaria lapathifolia S. F. Gray 0.08 32.09 47.48 51.35 30.64 158.32 野艾蒿Artemisia lavandulifolia Candolle 0.31 23.56 59.64 12.07 21.27 68.45 香蒲Typha orientalis Presl 0.24 27.86 30.80 10.83 18.33 67.10 小蓬草Erigeron canadensis L. 0.04 31.14 77.16 1.36 19.11 123.23 羊蹄Rumex japonicus Houtt. 1.22 41.60 48.52 44.69 24.79 75.55 紫茎泽兰Ageratina adenophora R. M. King & H. Robinson 0.30 51.52 93.98 65.14 28.88 132.21 钻叶紫菀Symphyotrichum subulatum G. L. Nesom 2.95 17.15 37.48 3.99 14.57 68.33 注:加粗数字表示高于土壤重金属平均含量。 Note: Bold numbers indicate higher than average heavy metal content in soil. 表 4 植物重金属综合生物富集指数
Table 4 CBCI for heavy metals in plants
植物
Species隶属函数u(xi) 综合生物富集指数
CBCI排名
RankCd Cr Cu Ni Zn 白花鬼针草 Bidens pilosa L. 0.33 1.00 0.72 0.38 1.00 0.686 1 紫茎泽兰 Ageratina adenophora R. M. King & H. Robinson 0.09 0.74 0.71 1.00 0.78 0.662 2 龙葵 Solanum nigrum L. 0.29 0.79 0.42 0.03 0.82 0.470 3 酸模叶蓼 Persicaria lapathifolia S. F. Gray 0.02 0.49 0.36 0.68 0.79 0.468 4 南美蟛蜞菊 Sphagneticola trilobata Pruski 0.24 0.78 1.00 0.07 0.01 0.420 5 羊蹄 Rumex japonicus Houtt. 0.41 0.43 0.25 0.62 0.32 0.405 6 火炭母 Persicaria chinensis H. Gross 0.16 0.57 0.12 0.18 0.98 0.403 7 钻叶紫菀 Symphyotrichum subulatum G. L. Nesom 1.00 0.25 0.34 0.05 0.37 0.401 8 小蓬草 Erigeron canadensis L. 0.01 0.59 0.78 0.01 0.62 0.400 9 蔊菜 Rorippa indica Hiern 0.25 0.66 0.13 0.25 0.62 0.382 10 假臭草 Praxelis clematidea Cassini 0.07 0.40 0.36 0.17 0.77 0.353 11 野艾蒿 Artemisia lavandulifolia Candolle 0.10 0.41 0.58 0.19 0.44 0.343 12 喜旱莲子草 Alternanthera philoxeroides Griseb. 0.03 0.47 0.30 0.12 0.76 0.334 13 水葱 Schoenoplectus tabernaemontani Palla 0.23 0.35 0.39 0.21 0.41 0.317 14 地桃花 Urena lobata L. 0.10 0.30 0.23 0.01 0.90 0.306 15 扯根菜 Penthorum chinense Pursh 0.00 0.80 0.05 0.00 0.59 0.289 16 酸浆 Alkekengi officinarum Moench 0.12 0.16 0.94 0.01 0.18 0.281 17 香蒲 Typha orientalis Presl 0.07 0.46 0.15 0.16 0.34 0.236 18 藿香蓟 Ageratum conyzoides L. 0.06 0.31 0.42 0.02 0.00 0.161 19 苍耳 Xanthium strumarium L. 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.17 0.038 20 注:加粗字体表示入侵植物。 Note: Bold fonts indicate invasive plants. -
[1] 周晓声,娄厦,Radnaeva LD,Nikitina E,汪豪. 植物对土壤重金属富集特性研究进展[J]. 生态毒理学报,2022,17(3):400−410. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20210803001 Zhou XS,Lou S,Radnaeva LD,Nikitina E,Wang H. Advances in heavy metal accumulation characteristics of plants in soil[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology,2022,17(3):400−410. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20210803001
[2] Hu BF,Wang JY,Jin B,Li Y,Shi Z. Assessment of the potential health risks of heavy metals in soils in a coastal industrial region of the Yangtze River Delta[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res,2017,24(24):19816−19826. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9516-1
[3] Gao Q,Li Y,Cheng QY,Yu MX,Hu B,et al. Analysis and assessment of the nutrients,biochemical indexes and heavy metals in the Three Gorges Reservoir,China,from 2008 to 2013[J]. Water Res,2016,92:262−274. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.12.055
[4] Bai JH,Jia J,Zhang GL,Zhao QQ,Lu QQ,et al. Spatial and temporal dynamics of heavy metal pollution and source identification in sediment cores from the short-term flooding riparian wetlands in a Chinese delta[J]. Environ Pollut,2016,219:379−388. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.05.016
[5] 曾欢,张华,丁明军,王鹏,黄高翔,等. 鄱阳湖典型湿地土壤-植物系统重金属沿湖向富集及迁移转换特征分析[J]. 环境科学,2023,44(2):781−795. Zeng H,Zhang H,Ding MJ,Wang P,Huang GX,et al. Enrichments,migrations,and conversions of heavy metal in the soil/sediment-plant system towards the lake in typical Poyang Lake wetland[J]. Environmental Science,2023,44(2):781−795.
[6] 杨阳,周正朝,王欢欢,张越,曹睿,王若丹. 沣河沿岸土壤和优势植物重金属富集特征和潜在生态风险[J]. 生态学报,2013,33(21):6834−6843. doi: 10.5846/stxb201206150859 Yang Y,Zhou ZC,Wang HH,Zhang Y,Cao R,Wang RD. Enrichment and ecological risk of heavy metal in soils and dominant plants in the riparian of the Fenghe River[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2013,33(21):6834−6843. doi: 10.5846/stxb201206150859
[7] 李洋,陈卫锋,魏然,杨柳明,彭园珍,倪进治. 闽江福州段沉积物中重金属的分布特征及其毒性和生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报,2016,36(5):1792−1799. Li Y,Chen WF,Wei R,Yang LM,Peng YZ,Ni JZ. Distribution characteristics,toxicity and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Minjiang River in Fuzhou City[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2016,36(5):1792−1799.
[8] Sun ZG,Li JB,He T,Ren P,Zhu H,et al. Spatial variation and toxicity assessment for heavy metals in sediments of intertidal zone in a typical subtropical estuary (Min River) of China[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res,2017,24(29):23080−23095. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9897-1
[9] Li X,Sun ZG,Tian LP,He T,Li J,et al. Effects of spatial expansion between Phragmites australis and Cyperus malaccensis on variations of arsenic and heavy metals in decomposing litters in a typical subtropical estuary (Min River),China[J]. Chemosphere,2020,204:124965.
[10] 陶长铸,李林鑫,张婷,李娜娜,曹越,等. 湿地公园芦苇重金属富集能力分析——以闽江流域乌龙江段为例[J]. 生态学杂志,2023,42(7):1678−1686. Tao CZ,Li LX,Zhang T,Li NN,Cao Y,et al. Heavy metal accumulation capacity of Phragmites australis in wetland parks:a case study of Wulong River in Minjiang River basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2023,42(7):1678−1686.
[11] 李刚,高明远,诸堃. 微波消解-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定植物样品中微量元素[J]. 岩矿测试,2010,29(1):17−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2010.01.005 Li G,Gao YM,Zhu K. Determination of micro-amount of elements in plant samples by inductively coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry with microwave digestion[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis,2010,29(1):17−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2010.01.005
[12] 刘属灵,吴梅,刘志远,刘双燕,刘永林,等. 四川盆地典型农耕区土壤重金属含量、污染及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学,2023,44(1):347−355. Liu SL,Wu M,Liu ZY,Liu SY,Liu YL,et al. Soil heavy metal content,pollution,and influencing factors in typical farming area of Sichuan basin[J]. Environmental Science,2023,44(1):347−355.
[13] 成晓梦,赵辰,吴超,孙彬彬,曾道明,贺灵. 典型硫铁矿区农田土壤-作物系统重金属生态风险及迁移富集特征[J]. 环境科学,2023,44(11):6309−6318. Cheng XM,Zhao C,Wu C,Sun BB,Zeng DM,He L. Ecological risk assessment and migration and accumulation characteristics of heavy metals in farmland soil-crop system from typical pyrite mining area[J]. Environmental Science,2023,44(11):6309−6318.
[14] Zhao XL,Liu JF,Xia XL,Chu JM,Wei Y,et al. The evaluation of heavy metal accumulation and application of a comprehensive bio-concentration index for woody species on contaminated sites in Hunan,China[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res,2014,21(7):5076−5085. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-2393-3
[15] 成杭新,李括,李敏,杨柯,刘飞,成晓梦. 中国城市土壤化学元素的背景值与基准值[J]. 地学前缘,2014,21(3):265−306. Cheng HX,Li K,Li M,Yang K,Liu F,Cheng XM. Geochemical background and baseline value of chemical elements in urban soil in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2014,21(3):265−306.
[16] 牛学奎,吴学勇,王薇,艾志敏,王舒婷,等. 典型鼓风炉铅冶炼废渣堆场周边优势植物重金属富集特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报,2021,30(6):1293−1298. Niu XK,Wu XY,Wang W,Ai ZM,Wang ST,et al. Study on enrichment characteristics of heavy metals from dominant plants around the waste slag yard of lead smelting in a typical blast furnace[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2021,30(6):1293−1298.
[17] 何东,邱波,彭尽晖,彭亮,胡凌雪,胡瑶. 湖南下水湾铅锌尾矿库优势植物重金属含量及富集特征[J]. 环境科学,2013,34(9):3595−3600. He D,Qiu B,Peng JH,Peng L,Hu LX,Hu Y. Heavy metal contents and enrichment characteristics of dominant plants in a lead-zinc tailings in Xiashuiwan of Hunan Province[J]. Environmental Science,2013,34(9):3595−3600.
[18] 徐华伟,张仁陟,谢永. 铅锌矿区先锋植物野艾蒿对重金属的吸收与富集特征[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2009,28(6):1136−1141. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2009.06.008 Xu HW,Zhang RZ,Xie Y. Accumulation and distribution of heavy metals in Artemisia lavandulaefolia at lead-zinc mining area[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2009,28(6):1136−1141. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2009.06.008
[19] 施翔,陈益泰,王树凤,李江川. 废弃尾矿库15种植物对重金属Pb、Zn的积累和养分吸收[J]. 环境科学,2012,33(6):2021−2027. Shi X,Chen YT,Wang SF,Li JC. Pb,Zn accumulation and nutrient uptake of 15 plant species grown in abandoned mine tailings[J]. Environmental Science,2012,33(6):2021−2027.
[20] Abdel-Sabour MF,Mortvedt JJ,Kelsoe JJ. Cadmium-zinc interactions in plants and extractable cadmium and zinc fractions in soil[J]. Soil Sci,1988,145(6):424−431. doi: 10.1097/00010694-198806000-00004
[21] Yin HB,Deng JC,Shao SG,Gao F,Gao JF,et al. Distribution characteristics and toxicity assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Lake Chaohu,China[J]. Environ Monit Assess,2011,179(1-4):431−442. doi: 10.1007/s10661-010-1746-3
[22] Liu BL,Ai SW,Zhang WY,Huang DJ,Zhang YM. Assessment of the bioavailability,bioaccessibility and transfer of heavy metals in the soil-grain-human systems near a mining and smelting area in NW China[J]. Sci Total Environ,2017,609:822−829. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.215
[23] 弓秋丽,杨剑洲,王振亮,严慧. 海南省琼中县土壤——茶树中重金属的迁移特征及饮茶健康风险[J]. 物探与化探,2023,47(3):826−834. Gong QL,Yang JZ,Wang ZL,Yan H. Migration of heavy metals in the soil-tea plant system and health risks of drinking tea:a case study of Qiongzhong County,Hainan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,2023,47(3):826−834.
[24] 王子诚,陈梦霞,杨毓贤,方项,刘众杰,等. 铜胁迫对植物生长发育影响与植物耐铜机制的研究进展[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报,2021,27(10):1849−1863. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2021164 Wang ZC,Chen MX,Yang YX,Fang X,Liu ZJ,et al. Effects of copper stress on plant growth and advances in the mechanisms of plant tolerance research[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers,2021,27(10):1849−1863. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2021164
[25] 王丹,魏威,梁东丽,王松山,胡斌. 土壤铜、铬(Ⅵ)复合污染重金属形态转化及其对生物有效性的影响[J]. 环境科学,2011,32(10):3113−3120. Wang D,Wei W,Liang DL,Wang SS,Hu B. Transformation of Copper and chromium in Co-contaminated soil and its influence on bioavailability for Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis)[J]. Environmental Science,2011,32(10):3113−3120.
[26] 李俊凯,张丹,周培,刘群录. 南京市铅锌矿采矿场土壤重金属污染评价及优势植物重金属富集特征[J]. 环境科学,2018,39(8):3845−3853. Li JK,Zhang D,Zhou P,Liu QL. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in soil and its bioaccumulation by dominant plants in a lead-zinc mining area,Nanjing[J]. Environmental Science,2018,39(8):3845−3853.
[27] Baker AJM,Brooks RR,Pease AJ,Malaisse F. Studies on copper and cobalt tolerance in three closely related taxa within the genus Silene L. (Caryophyllaceae) from Zaïre[J]. Plant Soil,1983,73(3):377−385. doi: 10.1007/BF02184314
[28] 魏敏,刘新,陈朝琼,余小平,彭晓莉. 攀钢冶炼渣堆土壤与优势植物的重金属含量[J]. 生态学报,2008,28(6):2931−2936. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.06.060 Wei M,Liu X,Chen ZQ,Yu XP,Peng XL. The concentration of heavy metals in soil and dominant plants growing on spoiled heap from steel refinery[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2008,28(6):2931−2936. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.06.060
[29] 袁鑫奇,俞乃琪,郭兆来,汪斯琛,唐春东,等. 会泽铅锌矿区废弃地优势草本植物的重金属富集特征[J]. 生态与农村环境学报,2022,38(3):399−408. Yuan XQ,Yu NQ,Guo ZL,Wang SC,Tang CD,et al. The accumulation characteristics of heavy metals in dominant herbaceous plants in the abandoned Pb-Zn mining area of Huize[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment,2022,38(3):399−408.
[30] 王新帅,林华,俞果,蒋萍萍,刘杰. 桂北典型锰矿区周边土壤重金属污染状况及主要植物富集特征[J]. 广西植物,2022,42(7):1160−1169. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw202110027 Wang XS,Lin H,Yu G,Jiang PP,Liu J. Heavy metal pollution assessment of a typical manganese mine tailing and heavy metal enrichment characteristics of dominant plant species in North Guangxi[J]. Guihaia,2022,42(7):1160−1169. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw202110027
[31] 刘月莉,伍钧,唐亚,杨刚,祝亮. 四川甘洛铅锌矿区优势植物的重金属含量[J]. 生态学报,2009,29(4):2020−2026. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.04.048 Liu YL,Wu J,Tang Y,Yang G,Zhu L. An investigation of heavy-metal concentration in cominant plant species in a zinc-lead mining area in Ganluo County of Sichuan Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2009,29(4):2020−2026. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.04.048
[32] 周启武,杨国琴,张国昌,马引娟,杨国恩. 入侵植物紫茎泽兰对其根际重金属的富集作用研究[J]. 安徽农业科学,2020,48(24):87−90,93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2020.24.024 Zhou QW,Yang GQ,Zhang GC,Ma YJ,Yang GE. Study on the bioaccumulation ability of Eupatorium adenophorum to heavy metal ions in its rhizosphere soil[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2020,48(24):87−90,93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2020.24.024
[33] 白如霞,刘海,王玉书,黄建国. 四川省凉山州紫茎泽兰的重金属含量及其肥用安全性评价[J]. 土壤学报,2018,55(2):432−442. Bai RX,Liu H,Wang YS,Huang JG. Heavy metal contents in Eupatorium adenophorum in Liangshan of Sichuan,and safeness of using the plant as organic manure[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2018,55(2):432−442.
[34] 严莲英,范成五,赵振宇,刘桂华,胡岗,秦松. 黔北轻污染耕地12种优势杂草重金属含量及富集特征[J]. 草业学报,2017,26(10):237−244. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2016499 Yan LY,Fan CW,Zhao ZY,Liu GH,Hu G,Qin S. Heavy metal absorption and enrichment characteristics of dominant weed speciesnaturally growing on farmland in Northern Guizhou[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica,2017,26(10):237−244. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2016499
[35] 陈伟,蒋文艳,杨玉霞,廖洁,王海军,等. 一种新发现的镉超积累植物——钻叶紫菀(Aster subulatus Michx.)[J]. 生态学报,2023,43(13):5592−5599. Chen W,Jiang WY,Yang YX,Liao J,Wang HJ,et al. A newly discovered cadmium hyperaccumulator: Aster subulatus Michx.[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2023,43(13):5592−5599.
-
其他相关附件
-
PDF格式
关永鑫 附图1 点击下载(163KB)
-



 下载:
下载: