Comparison of quantitative research methods for flower scent based on dynamic headspace collection
-
摘要:
由于花气味能够影响植物与传粉者的相互作用并在香水产业中具有重要价值,研究者们开发出了众多收集花气味的方法。其中,通过连续的气流将花气味收集到吸附剂上的动态顶空吸附法是最为常用的方法。但在实验过程中,研究者们使用的具体方案仍不够统一,这可能会对分析结果造成较大影响。在总结已有文献相关方法的基础上,本研究以典型花香成分标准混合物和大花六道木(Abelia×grandiflora (André) Rehder)为研究对象,分别开展了室内和室外实验,对比了活性碳、Tenax TA与Propak Q 3种吸附剂,正己烷、二氯甲烷两种洗脱溶液,以及推拉法、循环法与闭环法3种连接方法的收集效果。结果显示,Propak Q是综合性能最为优秀的吸附剂,活性炭与Tenax TA分别对于苯类物质与脂肪族物质的吸附能力较差。两种洗脱溶液的效果类似,而3种连接方法中推拉法的综合表现最为优秀,同时能够保持植物的自然鲜活状态。在气味成分未知或需要进行群落水平研究时,推荐采用Propak Q吸附剂与推拉法连接方式进行实验。
Abstract:Floral scents play a critical role in mediating plant-pollinator interactions and hold significant commercial value in the perfume industry. To analyze these scents, researchers have developed various collection methods, with dynamic headspace collection-using continuous airflow to capture volatile compounds onto sorbent traps—being the most commonly used. However, the lack of standardized experimental protocols poses challenges in achieving consistent and reliable results. This study systematically evaluated the performance of three sorbent traps (charcoal, Tenax TA, and Propak Q), two elution solvents (hexane and dichloromethane), and three connection methods (push-pull, circulation, and closed-loop) through controlled indoor and outdoor experiments using a standard mixture of floral scent components and Abelia×grandiflora (André) Rehder. Results showed that Propak Q outperformed the other sorbent traps, while charcoal and Tenax TA exhibited relatively poor adsorption capabilities for benzenes and aliphatic compounds, respectively. The effects of the two elution solvents were similar. Among the three connection methods, the push-pull approach delivered the most consistent results, effectively preserving the natural freshness of floral scents. Based on these findings, the study recommends the use of Propak Q as the preferred sorbent trap and the push-pull method for floral scent experiments, particularly in cases where the composition of volatile compounds is unknown or when community-level analyses are required.
-
Keywords:
- Dynamic headspace collection /
- Floral scent /
- Sorbent trap /
- Elution solution /
- Connection method
-
高寒草地是青藏高原最主要的生态系统,是维护国家生态安全和改善青藏高原地区农牧民生活质量的重要保障[1]。在过去几十年里,受人类活动和自然因素的影响,高寒草地的生产和生态功能急剧下降,造成大面积土地裸露和草畜不平衡等诸多问题[2]。最近,经过相关领域学者们的不断探索实践,我国高寒草地退化的趋势明显改善,植被覆盖度大幅提升,水土流失和荒漠化基本遏制[3]。然而,青藏高原地区气候寒冷,有机质分解较慢,土壤微生物活性较低[4],导致退化草地治理周期较长,草畜矛盾仍未能有效解决。因此,在退化草地恢复的同时,建植多年生人工草地便成为满足生产和生态功能需求的重要手段。在实践中发现,多年生高寒栽培草地在建植2~3年后地上生物量达到峰值,第4年开始其地上生物量逐年下降,且饲草品质普遍较低[5]。究其原因,与青藏高原地区土壤氮限制密切相关[6]。青藏高原地区土壤氮限制极其严重,加之气温较低,严重抑制了与氮有关的功能微生物的活性,导致生产力较低[6]。此外,多年生牧草常年吸收土壤中的营养物质,导致土壤养分贫瘠,进而造成草地减产[7]。综合两方面的原因,氮添加成为提升多年生栽培草地生产功能的直接手段。
氮素形态和施氮水平是草地氮肥管理的两项重要内容,对植物生长发育起着关键调节作用。根据化合物形态可将氮肥分为铵态氮肥(A)、酰胺态氮肥(U)和硝态氮肥(N)等多种类型,不同形态氮肥均能促进植物的生长,但在土壤中的转化机制不同,导致植物的干物质分配和营养积累存在差异[8]。植物可以吸收利用的土壤氮素主要为硝态氮和铵态氮,氮素形态对不同植物生长发育的影响存在差异,氮肥形态是影响肥效的主要因素之一[9]。施用不同形态氮素会影响作物的根系发育及碳氮代谢等生理进程,进而影响植株生物量的积累。同时,氮素形态还会影响糖、激素、维生素和生物碱等各种化学物质的合成,进而影响植物的品质[10]。向雪梅等[11]在高寒区的施氮研究表明,酰胺态氮能保证植物较高的氮素利用率和较低的氮损失率,是提高植物生产力最佳的氮素形态,而Guo等[12]研究发现,硝态氮能促进野牛草(Buchloe dactyloides (Nutt.) Engelm.)的营养繁殖和品质积累。两种结果不一致的主要原因是不同植物对氮素形态的需求存在差异,故应根据植物类型和生存环境设置合理的氮源。对于青藏高原地区多年生高寒栽培草地而言,哪种氮素形态更有利于生产力和营养品质的积累不得而知。此外,研究施氮水平对植物生产性能的影响并确定合理的氮添加量也是科学添加氮肥的关键[13]。以往研究证实,合理的氮添加量是保证植物生产力和营养品质的关键[14],但关于具体氮添加量始终没有形成统一的结论,这是因为施氮水平应符合环境状况,不同区域氮素水平的阈值存在显著差异,氮限制比较严重的土壤环境可能需要施加更多的氮肥来满足植物的生长需求[15]。但过量的氮添加不仅造成氮肥利用率下降,也会对生态环境构成威胁。因此,确定最佳施氮量也是维持多年生高寒栽培草地生产力和营养品质的核心目标。
鉴于此,本研究以4年龄人工草地为研究对象,设置3个氮素形态和4个施氮水平,通过比较不同处理植物的地上生物量和饲草营养品质等参数,探究不同氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草生产性能和营养品质的影响,通过灰色关联度综合分析,进一步筛选出最佳的氮素形态和施氮水平,以期为高寒地区优质饲草的生产提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验区概况
试验区位于青海省海南藏族自治州共和县巴卡台农牧场(36°17'N,100°55'E),平均海拔3 300 m,年均降水量为300 mm,年蒸发量在2 000~2 400 mm,年平均气温为4.1 ℃。试验区冬季寒冷漫长,夏季温和短暂,年内干旱少雨且温度偏低,气温垂直分布明显,太阳辐射强,属高原大陆性气候特征。降水季节性分布不均,主要集中在7-10月。试验地土壤为高山草甸土和黄绵土[16]。
1.2 试验设计
于2022年6月,以2019年建植的青海草地早熟禾(Poa pratensis L. cv. Qinghai)+青海中华羊茅(Festuca sinensis L. cv. Qinghai)混播草地为研究对象,两个物种的混播比例为1∶1,建植面积为15 m×150 m。设置小区时,为避免边际效应,选取整块地中间较均匀的地段,采用随机区组设计,设置3个氮素形态,分别为尿素(酰胺态氮,U)、硫酸铵(铵态氮,A)和硝酸钙(硝态氮,N);参照中国氮沉降分布格局(青海地区干湿沉降率7.55 kg·hm−2·yr−1)确定氮素添加剂量,设4个施氮梯度,分别为青海省干湿氮沉降的0、3、6、9倍,浓度依次为0(T0,CK)、22.5(T1)、45(T2)、67.5 kg·hm−2·a−1(T3),各处理见表1。每个处理3个重复,共30个小区,小区面积为4 m×4 m,小区之间间隔5 m。将称好的肥料分为两等份,分别于6月上旬和下旬加到2 L水中溶解,摇匀后装入喷壶,均匀喷洒在相应的小区内,CK处理喷洒相同体积的水。
表 1 氮素形态和施氮水平设置Table 1. Nitrogen forms and nitrogen level settings施肥处理
Fertilization treatment氮素形态
Nitrogen form施氮水平
Nitrogen level / kg·hm−2·a−1T0(CK) − 0.0 UT1 酰胺态氮 22.5 UT2 45.0 UT3 67.5 AT1 铵态氮 22.5 AT2 45.0 AT3 67.5 NT1 硝态氮 22.5 NT2 45.0 NT3 67.5 1.3 样品采集与分析
1.3.1 样品采集与处理
于2022年8月上旬(植物生长旺期)对各试验小区进行调查与样品采集。采用样方法,设置50 cm×50 cm的样方,齐地面刈割后带回实验室称取鲜重,后转移至105 ℃烘箱中杀青30 min,然后在75 ℃烘干至恒重,称取地上生物量。之后将烘干草样用粉碎机粉碎,过1 mm筛备用。
1.3.2 牧草品质测定方法
利用元素分析仪测定植物粗蛋白含量[17],利用索氏抽提法测定粗脂肪含量[18],使用马弗炉灼烧法测定粗灰分含量[18],中性洗涤纤维含量和酸性洗涤纤维含量采用范式纤维洗涤法进行测定[19],并根据童永尚等[19]的方法计算相对饲喂价值。
1.3.3 数据处理与分析
采用Excel 2010软件进行原始数据整理和灰色关联度分析,具体参见童永尚等[19]的方法。运用SPSS 27.0软件进行双因素方差分析和聚类分析。在Origin 2022软件中绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草生产性能的影响
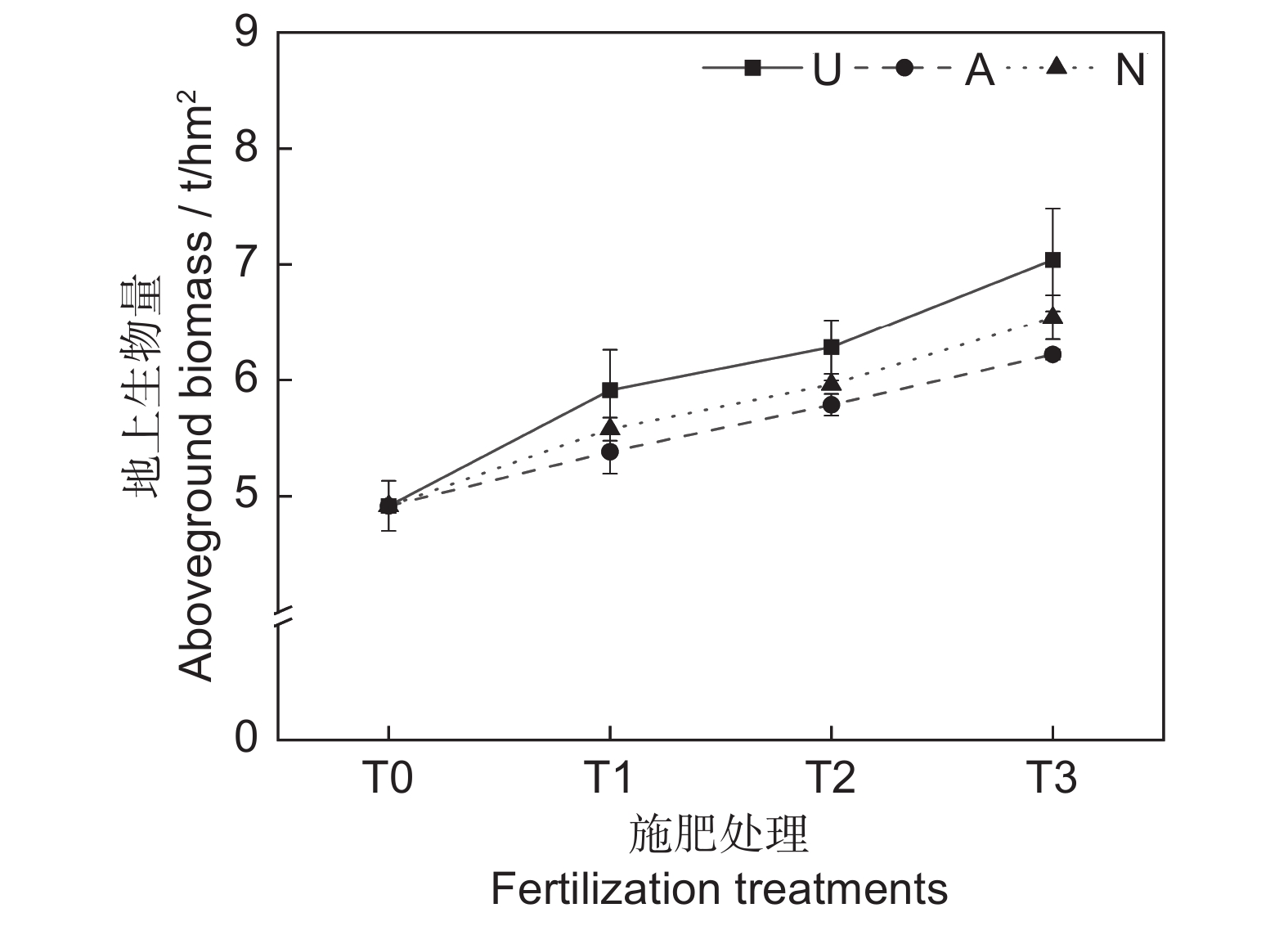
由表2可知,氮素形态对多年生高寒栽培草地的地上生物量影响显著(P<0.05),施氮水平对地上生物量的影响极显著(P<0.001),氮素形态和施氮水平交互作用对地上生物量影响不显著。氮添加整体上提高了群落地上生物量,且随着施氮水平的提高呈递增趋势,UT3、AT3和NT3处理分别较CK处理提高43.22%、26.54%和33.11%。同等氮水平相比较,对地上生物量的促进作用表现为U>N>A(图1)。
表 2 氮素形态和施氮水平的双因素方差分析Table 2. Two factor analysis of variance for nitrogen forms and nitrogen application levels影响因素
Influence factor氮素形态
Nitrogen form (F)施氮水平
Nitrogen level (L)氮素形态×施氮水平
F×LF P F P F P 地上生物量 5.622 <0.05 14.056 <0.001 0.153 0.959 粗蛋白 18.073 <0.001 38.120 <0.001 1.748 0.184 粗脂肪 39.829 <0.001 5.377 <0.05 1.183 0.351 粗灰分 0.020 0.980 0.576 0.572 1.714 0.191 中性洗涤纤维 1.979 0.167 1.423 0.267 1.422 0.267 酸性洗涤纤维 1.153 0.338 0.718 0.501 1.555 0.229 相对饲喂价值 1.275 0.304 1.284 0.301 1.909 0.153 2.2 氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草营养品质的影响
2.2.1 对饲草粗蛋白含量的影响
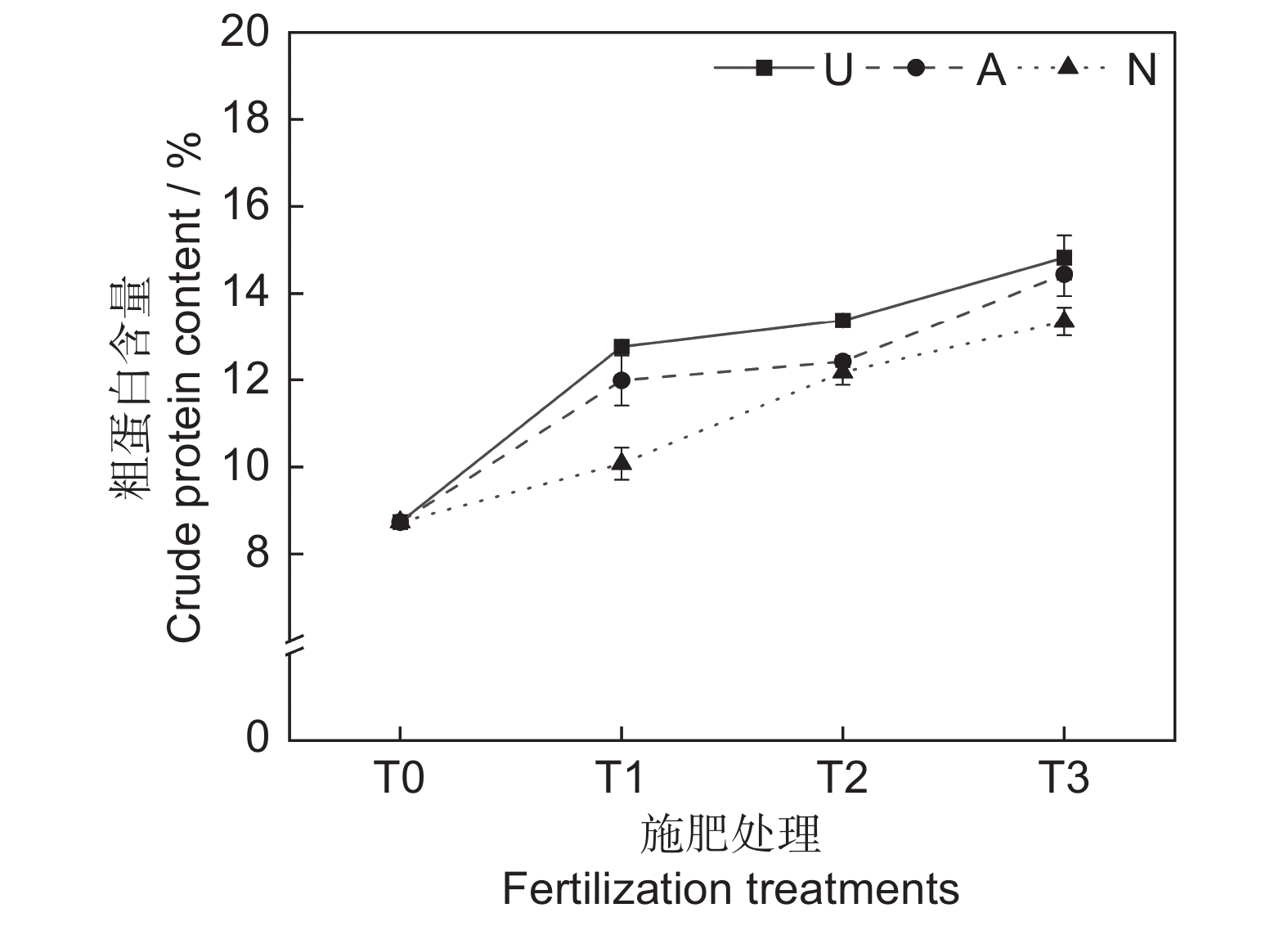
由表2和图2可知,氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草粗蛋白含量均具有极显著影响(P<0.001),氮素形态和施氮水平交互作用对饲草粗蛋白含量影响不显著。氮添加整体上提高了植物的粗蛋白含量,且随着施氮水平的提高呈递增趋势,UT3、AT3和NT3处理分别较CK处理提高了69.76%、65.41%和52.86%。同等氮水平相比较,对饲草粗蛋白含量的促进作用表现为U>A>N。
2.2.2 对饲草粗脂肪含量的影响
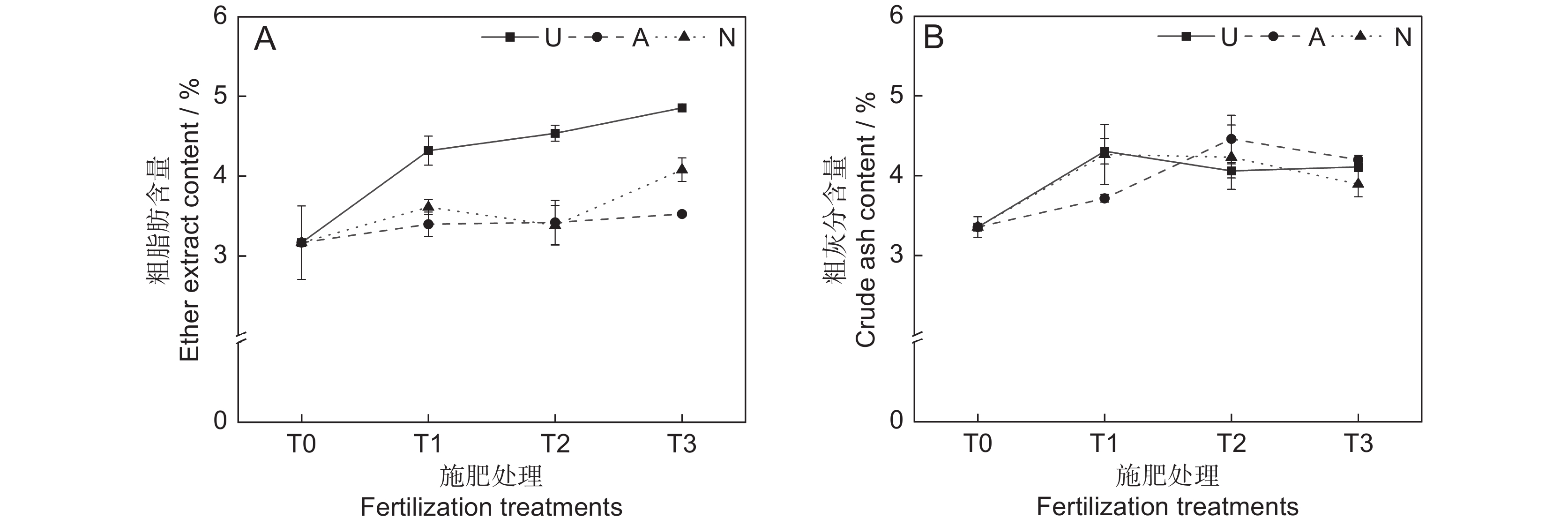
氮素形态对饲草粗脂肪含量具有极显著影响(P<0.001),施氮水平对饲草粗脂肪含量具有显著影响(P<0.05),氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草粗脂肪含量没有明显的交互作用(表2)。氮添加整体上提高了植物的粗脂肪含量,不同施氮水平对饲草粗脂肪含量的促进作用因氮素形态不同而有所差异。饲草粗脂肪含量随着酰胺态氮施肥水平的提高而增加,铵态氮施肥水平的增加对植物粗脂肪含量的影响较小。3种氮素形态下,饲草的粗脂肪含量均在T3水平时达到峰值,UT3、AT3和NT3处理分别较CK提高了53.30%、11.34%和28.86%。同等氮水平相比较,对地上生物量的促进作用表现为U>N>A(图3:A)。
2.2.3 对饲草粗灰分含量的影响
由表2可知,氮素形态、施氮水平及二者交互作用对饲草粗灰分含量的影响均不显著。氮添加整体上提高了植物的粗灰分含量(P<0.05),AT2处理下植物的粗灰分含量最高,为4.46%。同一氮素形态下不同施氮水平相比较,A和N处理均在T1水平时达到最大粗灰分含量,分别为4.31%和4.26%(图3:B)。
2.2.4 对饲草中性洗涤纤维含量的影响
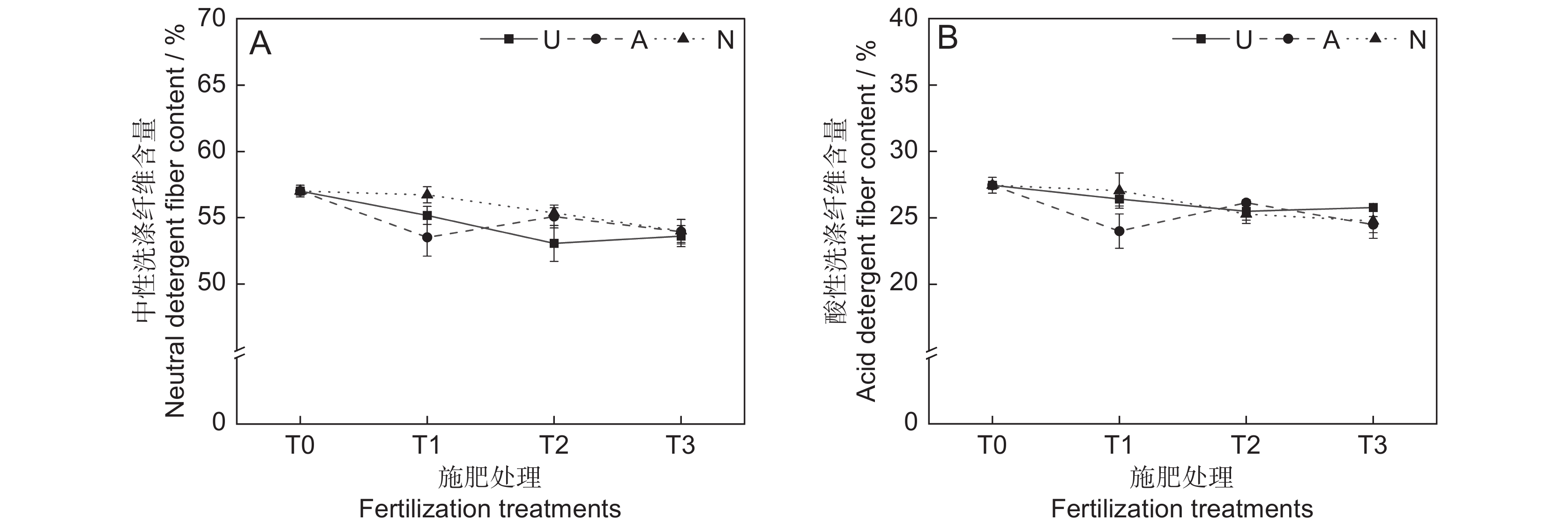
本研究发现,氮素形态、施氮水平及二者交互作用对饲草中性洗涤纤维含量均未产生显著影响(表2)。氮添加整体上降低了植物的中性洗涤纤维含量(P<0.05)。随着硝态氮施肥水平的提高,植物中性洗涤纤维含量逐渐降低(图4:A)。3种氮肥在T3水平时的中性洗涤纤维含量趋于一致,介于63.6%~64.0%。
2.2.5 对饲草酸性洗涤纤维含量的影响
由表2可知,氮素形态、施氮水平、氮素形态和施氮水平交互作用对饲草酸性洗涤纤维含量的影响均不显著。氮添加整体上降低了植物的酸性洗涤纤维含量(图4:B)。T2水平时,3种氮肥对植物酸性洗涤纤维含量的影响不明显。总体来看,T1水平时,施用铵态氮肥对植物酸性洗涤纤维含量的降低效果最为明显。
2.2.6 对饲草相对饲喂价值的影响
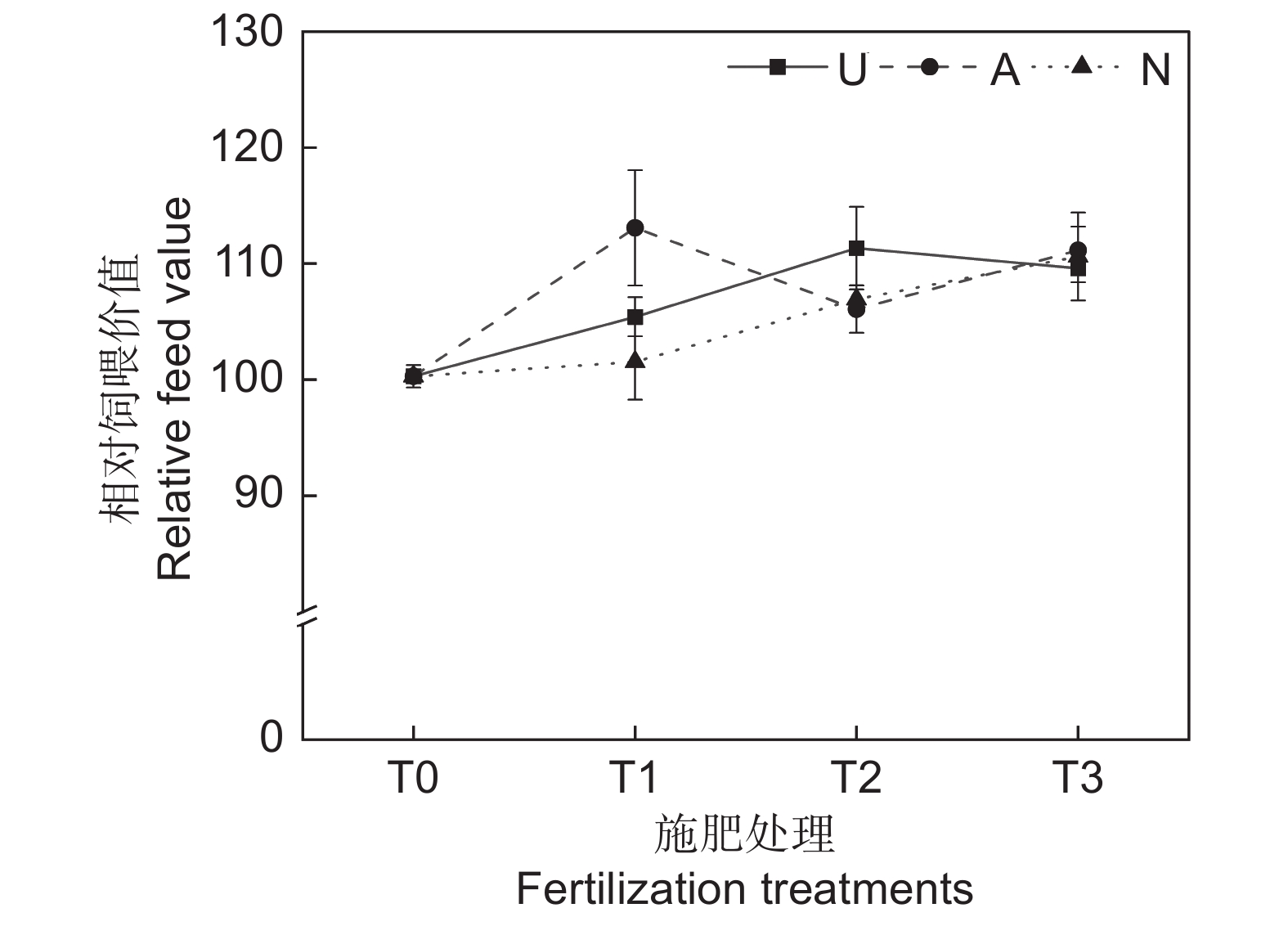
由表2可知,氮素形态、施氮水平及二者交互作用对饲草相对饲喂价值均未产生显著影响。如图5所示,氮添加整体上提高了饲草的相对饲喂价值,不同氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草相对饲喂价值的影响较大。随着硝态氮肥施氮水平的提高,饲草的相对饲喂价值逐渐提高。T3水平时,3种氮肥对饲草相对饲喂价值的提升效果接近。不同氮肥形态相比较,T1水平时,施用铵态氮肥的饲草其相对饲喂价值最高,为113.08;T2水平时,施用酰胺态氮肥时饲草的相对饲喂价值最高,为113.34。
2.3 灰色关联度评价和聚类分析
将植物地上生物量、粗蛋白含量和中性洗涤纤维含量等7个指标纳入评价体系,对不同氮素形态和施肥水平共10个处理进行灰色关联度综合评价。由表3可知,CK处理排序第9,说明氮添加普遍提高了饲草的综合性能。综合排名前4位的处理分别是UT3、UT2、NT3和AT3。不同酰胺态氮肥处理的综合排名依次为UT3>UT2>UT1,不同铵态氮肥处理的综合排名依次为AT3>AT1>AT2,不同硝态氮肥处理的综合排名依次为NT3>NT2>NT1。
表 3 不同处理的灰色关联度综合评价Table 3. Comprehensive evaluation of gray correlation degree for different treatments施肥处理
Fertilization treatment等权关联度
Gray correlative排序
Rank权重系数
Weight coefficient加权关联度
Weighted gray correlative加权关联度排序
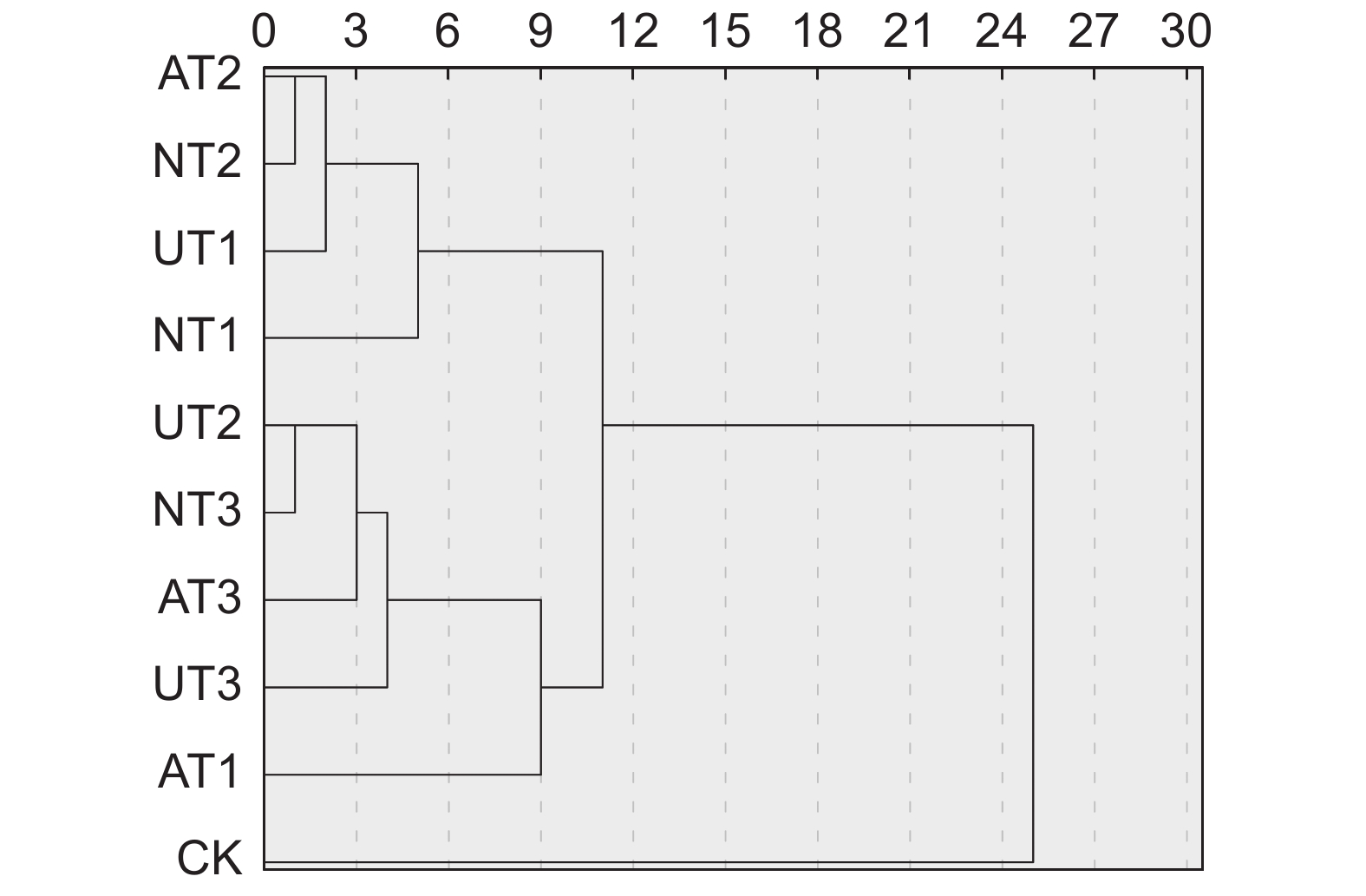
Rank of weighted gray correlativeUT3 0.871 4 1 0.126 3 0.110 0 1 UT2 0.763 3 2 0.110 6 0.084 4 2 NT3 0.753 6 3 0.109 2 0.082 3 3 AT3 0.746 1 4 0.108 1 0.080 7 4 AT1 0.718 6 5 0.104 1 0.074 8 5 UT1 0.654 1 6 0.094 8 0.062 0 6 NT2 0.633 7 7 0.091 8 0.058 2 7 AT2 0.613 0 8 0.088 8 0.054 5 8 CK 0.589 1 9 0.085 4 0.050 3 9 NT1 0.557 0 10 0.080 7 0.045 0 10 本试验将10个处理的地上生物量和营养品质进行了聚类分析,运用SPSS 27.0软件构建树形图(图6),在欧式距离为9处,可将其分为4大类。第Ⅰ类仅包括CK处理,其产量和营养品质均表现最差;第Ⅱ类只有AT1处理,其地上生物量略高于CK处理;第Ⅲ类包括UT2、UT3、AT3和NT3处理,其产量和营养品质均表现最好;第Ⅳ类包括UT1、NT1、NT2和AT2处理,其产量和营养品质仅次于第Ⅲ类。
3. 讨论
3.1 氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草生产性能的影响
众所周知,氮添加可以提高植物的生产力,但不同环境的氮添加量应有所差异[20]。施氮量较低时,土壤养分仍然不能满足植物生长,施氮量过多又会导致土壤中产生有毒的亚硝酸盐[21],进而阻碍植物生长,因此栽培草地施氮量应根据土壤氮素含量来确定。在以往的研究中,关于氮添加水平对植物地上生物量的调节作用有两种结论,第1种是地上生物量随施氮量增加而增加[22];第2种是地上生物量随施氮量的增加会出现一个峰值,然后逐渐降低[15],这是因为氮添加量有一定的环境阈值,存在一个最适施氮量,以最适施氮量为对称轴,植物的地上生物量随施氮量增加呈抛物线变化。本研究中,施氮水平对地上生物量具有极显著影响,氮添加显著提高了群落地上生物量,且随着施氮水平的提高呈递增趋势,在施氮量为67.5 kg·hm−2·a−1时达到峰值,说明本研究中设置的施氮量可能过低,在后期的试验中需要加大施氮梯度。此外,氮素形态对植物的地上生物量也产生显著影响,对地上生物量的促进作用表现为U>N>A。说明在短期内,酰胺态氮对植物生物量的促进效果更为明显,而硝态氮和铵态氮的效果相对较差,这与向雪梅等[11]和芦光新等[23]在高寒草地中的研究结论相似。尽管施加铵态氮肥补充了土壤养分,一定程度上促进了植物生长,但铵态氮肥抑制了植物对K+和Ca2+的吸收,导致NH4+的积累并产生氨害,从而限制了植物的生长[12, 24]。硝态氮肥的促产作用介于酰胺态和铵态氮肥之间。硝态氮同样也会对植物的生长产生不利影响,在还原过程中,硝态氮会消耗较多的能量。另外,在弱光条件下,植物对硝态氮的吸收也有可能会受到抑制,从而导致氮素供应不足。相比铵态氮肥和硝态氮肥,含氮量较高的酰胺态氮肥为土壤补充了充足的养分[16],更能满足植物的生长需求。由于氮素形态和氮素水平的设置还与牧草栽培方式、施氮时间和气候条件等因素相关,后期还应针对以上干扰因素设置控制试验,进行深入研究。
3.2 氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草营养品质的影响
在高寒地区,老龄人工草地牧草的营养品质较差是一个普遍现象。究其原因,土壤中营养元素含量较低,导致植物对氮、磷等元素的吸收利用效率较低。研究表明,氮素添加可迅速补充植物中的全氮含量,满足植物对营养元素的需求,进而恢复草地生产力,改善草地群落结构和植物的营养品质[25]。粗蛋白和粗脂肪含量是评价牧草营养价值的重要指标,其含量高则表明牧草营养品质较高,而粗纤维和粗灰分含量越高,则表明牧草可消化养分低,品质下降[26]。宋建超等[27]在高寒区的研究表明,氮添加显著提高了垂穗披碱草(Elymus nutans Griseb.)的粗蛋白和粗脂肪含量,与本研究结论一致。本研究中,所有施氮处理均显著提高了饲草的粗蛋白和粗脂肪含量。此外,我们还发现不同氮素形态和施氮水平对饲草的粗蛋白和粗脂肪含量具有显著影响,施用酰胺态氮肥更有利于粗蛋白和粗脂肪的积累,且高氮水平的促进作用更加明显。该现象一方面说明了高寒区氮限制非常严重,改善牧草的营养品质可能需要投入更多的氮肥;另一方面,由于不同的植物或生育期对氮肥的需求量和氮素形态具有明显差异,所以应根据实际情况选择适宜的氮素形态和施氮量。适宜的氮素形态是提高氮素利用率以及植物蛋白质含量的重要途径之一[28]。本研究中,酰胺态氮对植物粗蛋白和粗脂肪的促进效果明显高于铵态氮和硝态氮,这可能与植物的选择吸收能力以及不同氮肥的供氮能力等因素有关[29]。此外,本研究中的3种氮肥均不同程度地提高了饲草的粗灰分含量,降低了饲草的中性洗涤纤维及酸性洗涤纤维含量,与前人研究结论相似[30]。聚类分析将10个处理分为4大类,通过对比试验数据发现,这4大类可划分饲草生产性能和营养品质的优劣,基本对应了不施氮、低氮、中氮和高氮4种属性,因此,施氮水平对饲草生产性能和营养品质的影响是显而易见的。最后,本研究通过灰色关联度分析得出,选用酰胺态氮肥,施氮量为67.5 kg·hm−2·a−1时,多年生栽培草地饲草的生产性能和营养品质综合表现最优,研究结果可为青藏高原环青海湖地区人工草地生产力及营养品质的提高提供参考。
4. 结论
氮素形态和施氮水平对多年生高寒栽培草地饲草的生产性能和营养品质具有显著影响。选择酰胺态氮肥,施氮量为67.5 kg·hm−2·a−1时,多年生栽培草地饲草的生产性能和营养品质综合表现最优,说明适宜的氮肥管理制度对提高研究区饲草生产性能和营养价值具有促进作用。
-
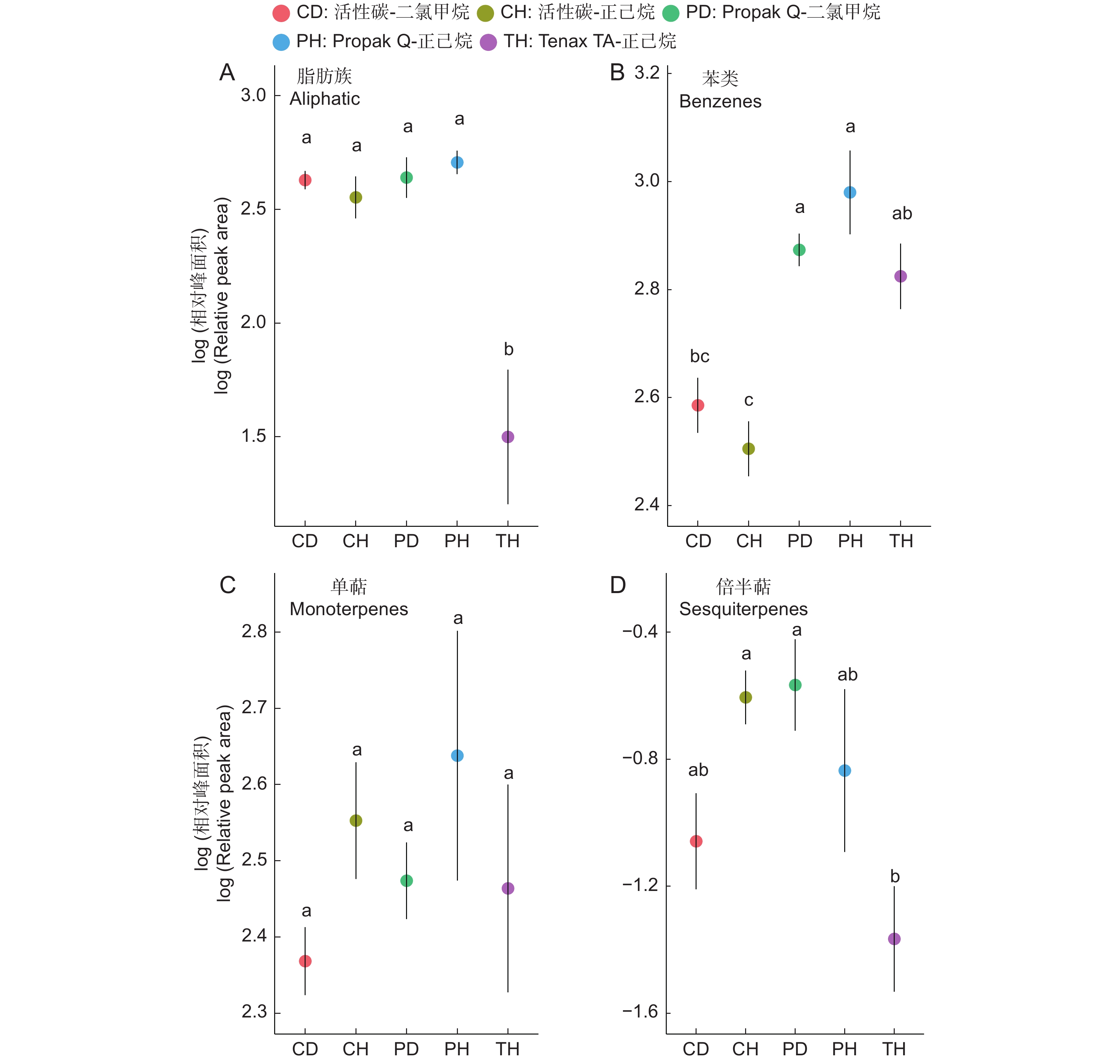
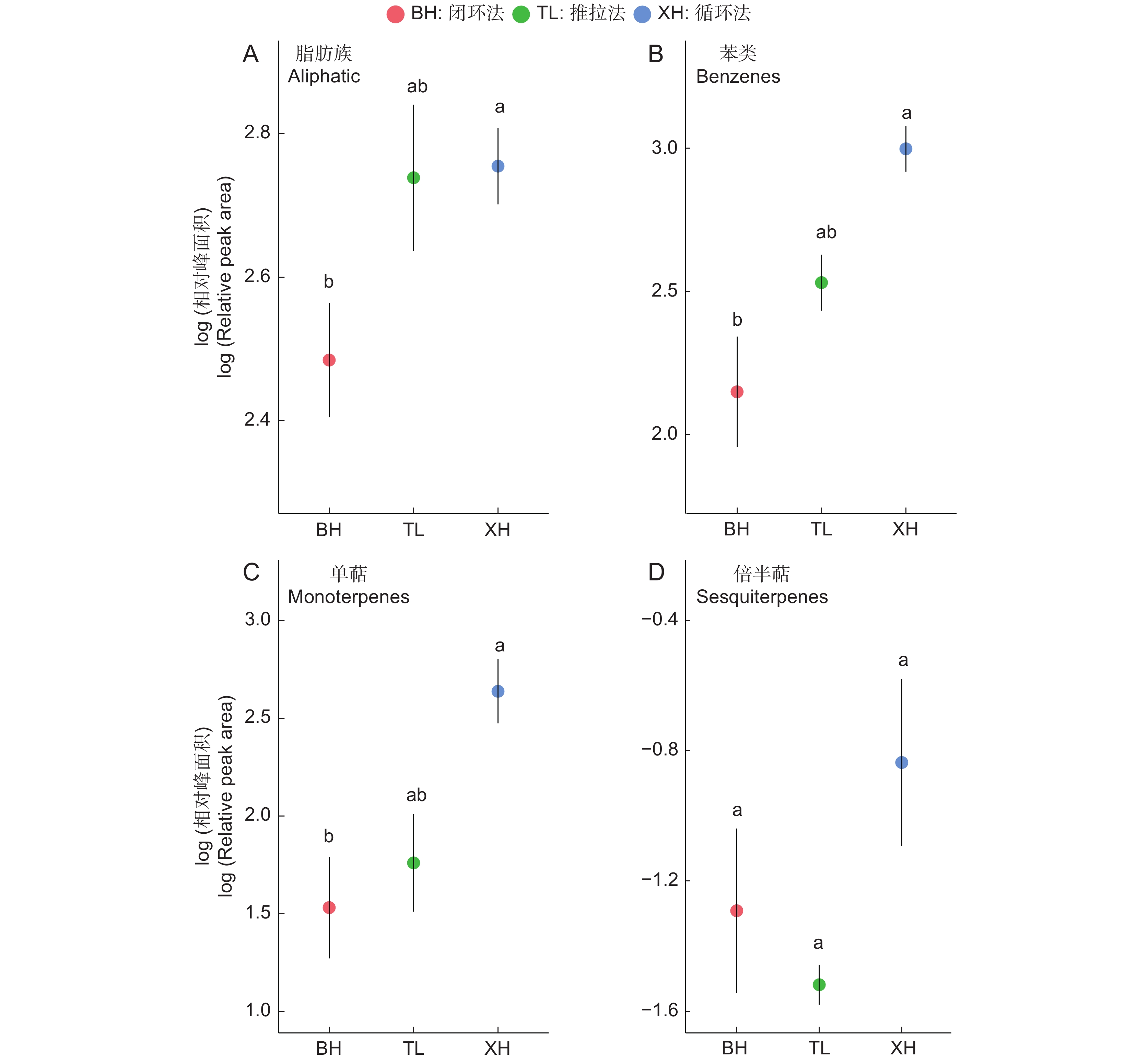
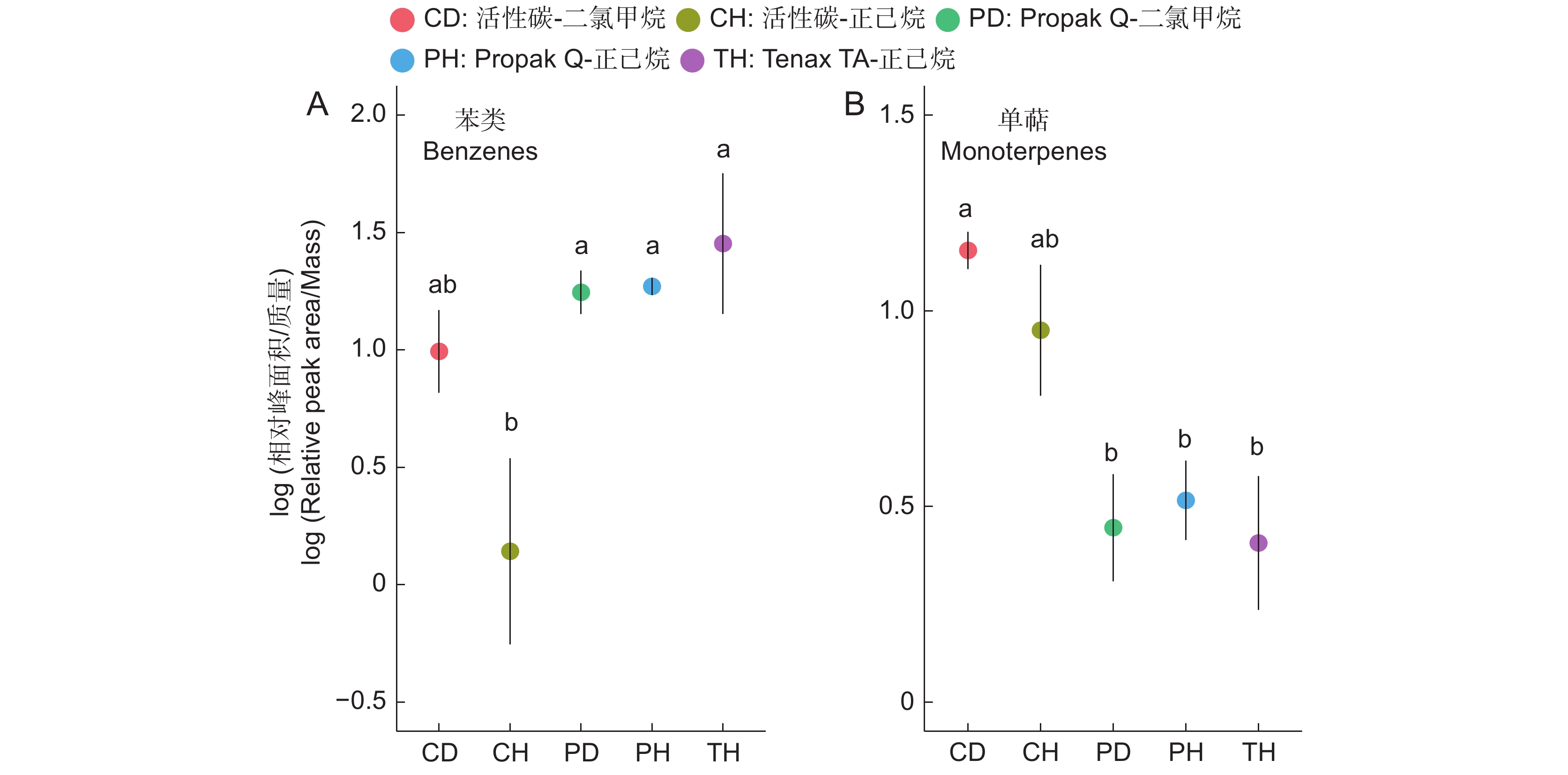
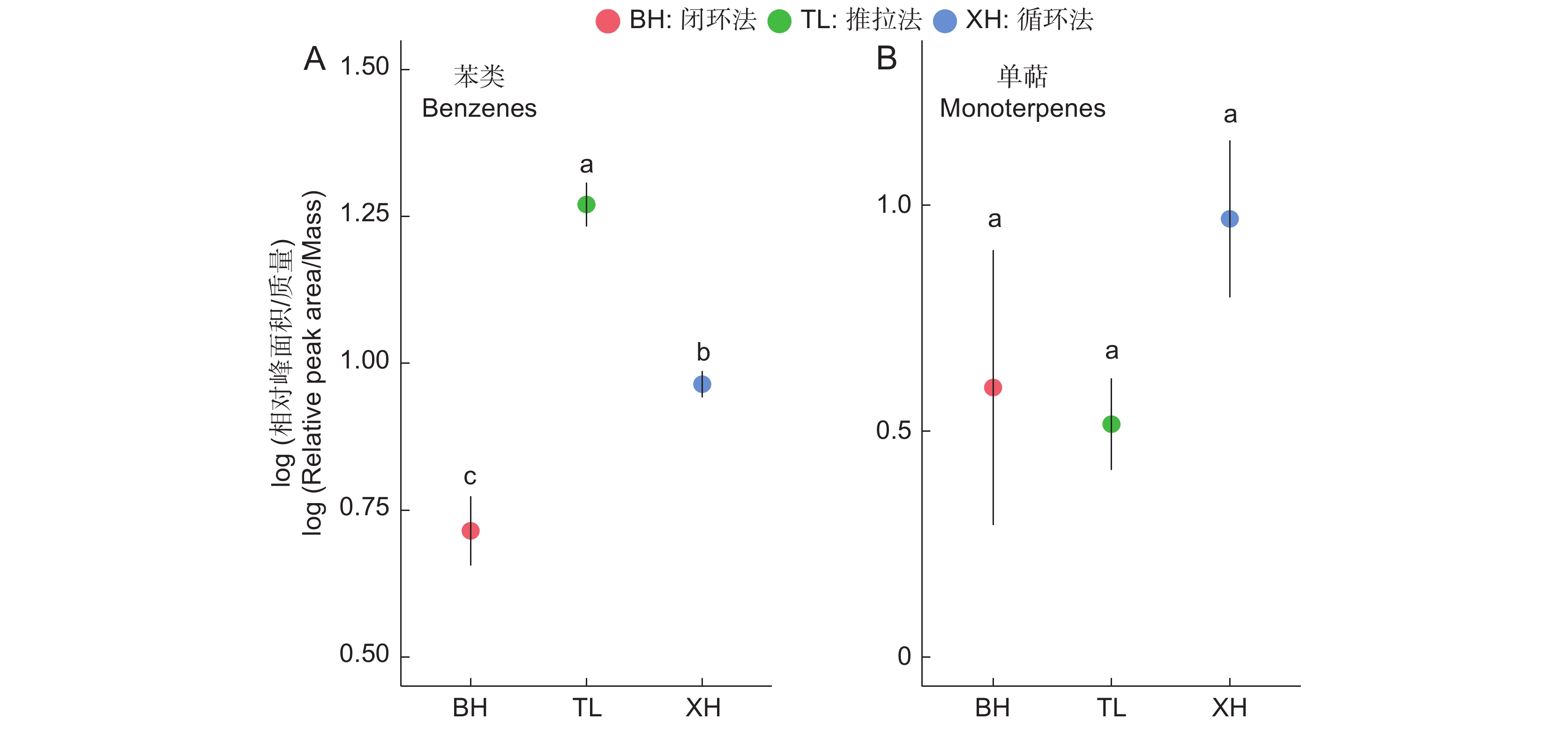
图 2 室内实验中5种吸附剂-洗脱溶液组合在不同物质层面的表现
散点位置代表平均值,线条长度代表标准误。不同字母代表在Tukey HSD成对检验中P<0.05。下同。
Figure 2. Performance of five sorbent trap-elution solvent combinations across different substances in indoor experiments
Dot represents average value and line length represents standard error. Different letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05) in the Tukey HSD pairwise test. Same below.
表 1 使用动态顶空吸附法的花气味研究方案差异示例
Table 1 Examples of differences in floral scent research protocols using dynamic headspace collection
表 2 室内或室外实验中不同实验组的实验方案差异
Table 2 Differences in experimental schemes for different experimental groups in indoor or outdoor experiments
实验
Experiment实验组ID
Group ID吸附剂
Sorbent trap洗脱溶液
Elution solvent连接方式
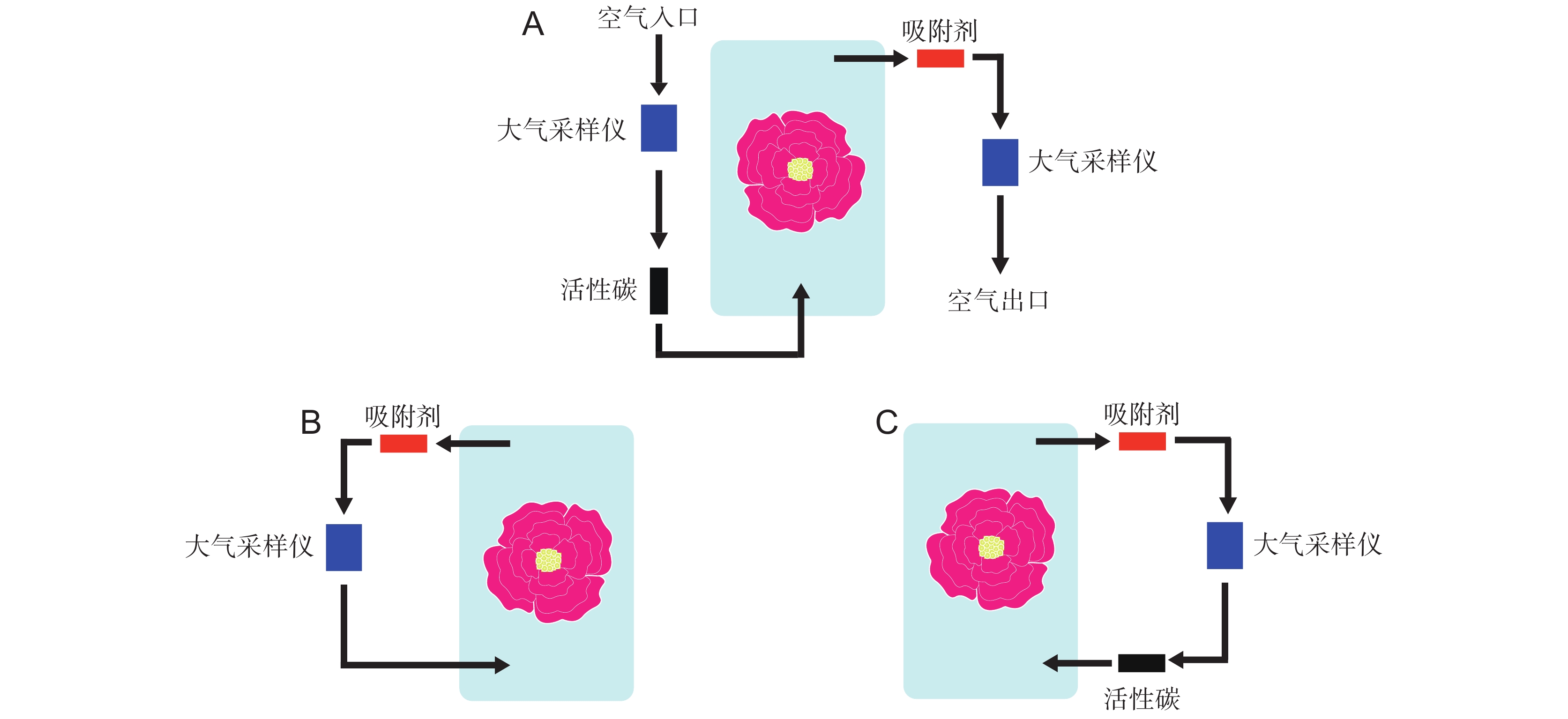
Connection method实验1 1 活性炭 二氯甲烷 循环法 2 活性炭 正己烷 循环法 3 Propak Q 二氯甲烷 循环法 4 Propak Q 正己烷 循环法 5 Tenax TA 正己烷 循环法 实验2 4 Propak Q 正己烷 循环法 6 Propak Q 正己烷 推拉法 7 Propak Q 正己烷 闭环法 实验3 8 Charcoal 二氯甲烷 推拉法 9 Charcoal 正己烷 推拉法 10 Propak Q 二氯甲烷 推拉法 11 Propak Q 正己烷 推拉法 12 Tenax TA 正己烷 推拉法 实验4 13 Propak Q 正己烷 循环法 11 Propak Q 正己烷 推拉法 14 Propak Q 正己烷 闭环法 表 3 不同方法检测大花六道木花气味的实验结果
Table 3 Experimental results of detecting floral scents in Abelia×grandiflora using different methods
实验组
Group物质数字识别号码
CAS number名称
Name参考值
Value标准误
Standard error挥发速率
Emission rate / ng∙g−1∙h−1活性碳-
二氯甲烷100-51-6 苯甲醇 0.61 0.36 116.75 100-52-7 苯甲醛 9.98 6.66 1 913.80 123-35-3 月桂烯 0.06 0.01 12.25 140-11-4 乙酸苄酯 0.16 0.06 31.24 18172-67-3 β-蒎烯 3.03 0.64 580.63 23470-00-0 2-单棕榈酸甘油 0.35 0.35 67.05 3387-41-5 桧烯 0.12 0.04 23.85 5208-59-3 β-波旁烯 0.15 0.05 27.99 60-12-8 苯乙醇 0.74 0.3 141.77 80-56-8 α-蒎烯 11.09 1.86 2 127.34 87-44-5 β-石竹烯 0.39 0.13 74.67 活性碳-
正己烷100-51-6 苯甲醇 0.05 0.03 10.01 100-52-7 苯甲醛 2.23 1.92 428.56 18172-67-3 β-蒎烯 3.08 1.67 591.16 2867-05-2 α-thujene 0.04 0.02 7.08 3387-41-5 桧烯 0.08 0.04 16.24 5208-59-3 β-波旁烯 0.08 0.04 15.04 60-12-8 苯乙醇 0.11 0.09 21.07 72237-36-6 4-己烯-醋酸酯 0.03 0.01 6.57 80-56-8 α-蒎烯 6.94 3.67 1 330.45 Propak Q-
二氯甲烷100-51-6 苯甲醇 0.43 0.2 82.65 100-52-7 苯甲醛 5.69 2.43 1 090.83 119-36-8 水杨酸甲酯 0.06 0.05 10.59 122-78-1 苯乙醛 9.34 3.09 1 791.32 18172-67-3 β-蒎烯 0.92 0.5 177.23 3387-41-5 桧烯 0.02 0.02 4.18 60-12-8 苯乙醇 2.94 1.58 564.48 80-56-8 α-蒎烯 2.15 1.23 411.54 87-44-5 β-石竹烯 0.05 0.03 10.47 Propak Q-
正己烷100-51-6 苯甲醇 0.36 0.09 69.51 100-52-7 苯甲醛 6.07 1.38 1 164.27 119-36-8 水杨酸甲酯 0.05 0.02 9.24 122-78-1 苯乙醛 9.96 2.39 1 909.73 18172-67-3 β-蒎烯 0.81 0.33 155.24 2867-05-2 α-thujene 0.02 0.01 3.46 3387-41-5 桧烯 0.07 0.02 12.58 36653-82-4 十六醇 1.17 1.87 223.88 60-12-8 苯乙醇 2.35 0.97 450.36 80-56-8 α-蒎烯 2.57 1.03 492.12 87-44-5 β-石竹烯 0.07 0.02 13.50 Tenax TA-
正己烷100-51-6 苯甲醇 1.00 0.36 191.97 100-52-7 苯甲醛 16.98 4.82 3 256.74 119-36-8 水杨酸甲酯 0.11 0.02 21.65 122-78-1 苯乙醛 8.40 1.8 1 610.69 18172-67-3 β-蒎烯 1.10 0.28 211.58 2867-05-2 α-thujene 0.02 0.02 3.81 5208-59-3 β-波旁烯 0.19 0.06 37.35 60-12-8 苯乙醇 2.18 0.49 418.78 80-56-8 α-蒎烯 1.82 1.62 348.15 87-44-5 β-石竹烯 0.27 0.15 52.65 闭环法 100-51-6 苯甲醇 0.52 0.14 79.86 100-52-7 苯甲醛 4.18 1.09 641.61 122-78-1 苯乙醛 0.58 0.23 89.67 1686-14-2 α-氧化蒎烯 0.07 0.04 11.33 18172-67-3 β-蒎烯 1.95 2.00 299.25 23470-00-0 2-单棕榈酸甘油 0.58 0.58 89.03 2867-05-2 α-thujene 0.02 0.03 2.90 3779-61-1 反式-β-罗勒烯 0.07 0.07 10.41 4501-58-0 龙脑烯醛 0.09 0.06 13.95 80-56-8 α-蒎烯 3.79 3.63 581.63 循环法 100-51-6 苯甲醇 0.20 0.04 30.68 100-52-7 苯甲醛 7.35 1.08 1 127.83 119-36-8 水杨酸甲酯 0.02 0.01 3.64 122-78-1 苯乙醛 1.55 0.26 237.5 1686-14-2 α-氧化蒎烯 0.03 0.01 4.51 18172-67-3 β-蒎烯 3.15 2.51 482.86 2867-05-2 α-thujene 0.03 0.02 5.00 3387-41-5 桧烯 0.11 0.07 17.01 60-12-8 苯乙醇 0.12 0.05 18.21 80-56-8 α-蒎烯 7.79 5.52 1 195.40 87-44-5 β-石竹烯 0.03 0.01 3.89 注:挥发速率 = (参考值×内参质量) ÷ 采样时间×(进气流速 ÷ 出气流速)。Propak Q-正己烷组合在实验4中代表推拉法。闭环法以及循环法的进气流速及出气流速均为200 mL/min。 Notes: Emission rate = (reference value×internal reference mass) ÷ sampling time×(push rate ÷ pull rate). Propak Q-hexane represents the push-pull method in Experiment 4. Push and pull rates were 200 mL/min in the closed-loop and circulation methods. -
[1] Tholl D,Boland W,Hansel A,Loreto F,Röse USR,Schnitzler JP. Practical approaches to plant volatile analysis[J]. Plant J,2006,45(4):540−560. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02612.x
[2] Pichersky E,Gershenzon J. The formation and function of plant volatiles:perfumes for pollinator attraction and defense[J]. Curr Opin Plant Biol,2002,5(3):237−243. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5266(02)00251-0
[3] Raguso RA. Wake up and smell the roses:the ecology and evolution of floral scent[J]. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst,2008,39:549−569. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.38.091206.095601
[4] Schiestl FP. Ecology and evolution of floral volatile-mediated information transfer in plants[J]. New Phytol,2015,206(2):571−577. doi: 10.1111/nph.13243
[5] Rosenstiel TN,Shortlidge EE,Melnychenko AN,Pankow JF,Eppley SM. Sex-specific volatile compounds influence microarthropod-mediated fertilization of moss[J]. Nature,2012,489(7416):431−433. doi: 10.1038/nature11330
[6] Cardé RT,Willis MA. Navigational strategies used by insects to find distant,wind-borne sources of odor[J]. J Chem Ecol,2008,34(7):854−866. doi: 10.1007/s10886-008-9484-5
[7] Menzel R. Memory dynamics in the honeybee[J]. J Comp Physiol A,1999,185(4):323−340. doi: 10.1007/s003590050392
[8] Kantsa A,Raguso RA,Dyer AG,Sgardelis SP,Olesen JM,Petanidou T. Community-wide integration of floral colour and scent in a Mediterranean scrubland[J]. Nat Ecol Evol,2017,1(10):1502−1510. doi: 10.1038/s41559-017-0298-0
[9] Kantsa A,Raguso RA,Lekkas T,Kalantzi OI,Petanidou T. Floral volatiles and visitors:a meta-network of associations in a natural community[J]. J Ecol,2019,107(6):2574−2586. doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.13197
[10] Larue AAC,Raguso RA,Junker RR. Experimental manipulation of floral scent bouquets restructures flower-visitor interactions in the field[J]. J Anim Ecol,2016,85(2):396−408. doi: 10.1111/1365-2656.12441
[11] Bergström G,Appelgren M,Borg-Karlson AK,Groth I,Strömberg S,Strömberg S. Studies on natural odoriferous compounds. XXⅡ. Techniques for the isolation/enrichment of plant volatiles in the analyses of Ophrys orchids (Orchidaceae)[J]. Chem Scr,1980,16(5):173−180.
[12] Ray HA,Stuhl CJ,Gillett-Kaufman JL. Rapid collection of floral fragrance volatiles using a headspace volatile collection technique for GC-MS thermal desorption sampling[J]. J Vis Exp,2019(154):e58928.
[13] Belliardo F,Bicchi C,Cordero C,Liberto E,Rubiolo P,Sgorbini B. Headspace-solid-phase microextraction in the analysis of the volatile fraction of aromatic and medicinal plants[J]. J Chromatogr Sci,2006,44(7):416−429. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/44.7.416
[14] Raguso RA,Pellmyr O. Dynamic headspace analysis of floral volatiles:a comparison of methods[J]. Oikos,1998,81(2):238−254. doi: 10.2307/3547045
[15] Raguso RA,Levin RA,Foose SE,Holmberg MW,McDade LA. Fragrance chemistry,nocturnal rhythms and pollination "syndromes" in Nicotiana[J]. Phytochemistry,2003,63(3):265−284. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(03)00113-4
[16] Wei JN,Zhu JW,Kang L. Volatiles released from bean plants in response to agromyzid flies[J]. Planta,2006,224(2):279−287. doi: 10.1007/s00425-005-0212-x
[17] Horiuchi JI,Badri DV,Kimball BA,Negre F,Dudareva N,et al. The floral volatile,methyl benzoate,from snapdragon (Antirrhinum majus) triggers phytotoxic effects in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Planta,2007,226(1):1−10. doi: 10.1007/s00425-006-0464-0
[18] Dudareva N,Andersson S,Orlova I,Gatto N,Reichelt M,et al. The nonmevalonate pathway supports both monoterpene and sesquiterpene formation in snapdragon flowers[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2005,102(3):933−938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407360102
[19] Wang H,Zhou WL,Li Z,Niklas KJ,Sun SC. Plant volatiles mediate evolutionary interactions between plants and tephritid flies and are evolutionarily more labile than non-volatile defenses[J]. J Anim Ecol,2021,90(4):846−858. doi: 10.1111/1365-2656.13414
[20] Zhang WB,Jiang YF,Chen SM,Chen FD,Chen F. Concentration-dependent emission of floral scent terpenoids from diverse cultivars of Chrysanthemum morifolium and their wild relatives[J]. Plant Sci,2021,309:110959. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2021.110959
[21] Haynes KF,Zhao JZ,Latif A. Identification of floral compounds from Abelia grandiflora that stimulate upwind flight in cabbage looper moths[J]. J Chem Ecol,1991,17(3):637−646. doi: 10.1007/BF00982132
[22] Chamberlain K,Khan ZR,Pickett JA,Toshova T,Wadhams LJ. Diel periodicity in the production of green leaf volatiles by wild and cultivated host plants of stemborer moths,Chilo partellus and Busseola fusca[J]. J Chem Ecol,2006,32(3):565−577. doi: 10.1007/s10886-005-9016-5
[23] Friberg M,Schwind C,Raguso RA,Thompson JN. Extreme divergence in floral scent among woodland star species (Lithophragma spp.) pollinated by floral parasites[J]. Ann Bot,2013,111(4):539−550. doi: 10.1093/aob/mct007
[24] Zu PJ,Blanckenhorn WU,Schiestl FP. Heritability of floral volatiles and pleiotropic responses to artificial selection in Brassica rapa[J]. New Phytol,2016,209(3):1208−1219. doi: 10.1111/nph.13652
[25] Saunier A,Blande JD. The effect of elevated ozone on floral chemistry of Brassicaceae species[J]. Environ Pollut,2019,255:113257. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113257
[26] Donath J,Boland W. Biosynthesis of acyclic homoterpenes:enzyme selectivity and absolute configuration of the nerolidol precursor[J]. Phytochemistry,1995,39(4):785−790. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(95)00082-I
[27] Koch T,Krumm T,Jung V,Engelberth J,Boland W. Differential induction of plant volatile biosynthesis in the lima bean by early and late intermediates of the octadecanoid-signaling pathway[J]. Plant Physiol,1999,121(1):153−162. doi: 10.1104/pp.121.1.153
[28] Collignon RM,Swift IP,Zou YF,McElfresh JS,Hanks LM,Millar JG. The influence of host plant volatiles on the attraction of longhorn beetles to pheromones[J]. J Chem Ecol,2016,42(3):215−229. doi: 10.1007/s10886-016-0679-x
[29] Tholl D,Chen F,Petri J,Gershenzon J,Pichersky E. Two sesquiterpene synthases are responsible for the complex mixture of sesquiterpenes emitted from Arabidopsis flowers[J]. Plant J,2005,42(5):757−771. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02417.x
[30] 李海东,高岩,金幼菊. 珍珠梅花挥发性物质日动态变化的研究[J]. 内蒙古农业大学学报,2004,25(2):54−59. Li HD,Gao Y,Jin YJ. The daily dymamic variances of the vocs releasing from flower of Siberia kirilowii (regel) maxim[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University,2004,25(2):54−59.
[31] 高群英,高岩,张汝民,杜明利,李刚. 3种菊科植物香气成分的热脱附气质联用分析[J]. 浙江农林大学学报,2011,28(2):326−332. Gao QY,Gao Y,Zhang RM,Du ML,Li G. Aromatic composition in three plant species using TDS-GC/MS[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A& F University,2011,28(2):326−332.
[32] 蔡宙霏,陈雅奇,许馨露,王小东,汪俊宇,等. 4个桂花品种开花进程释放VOCs动态变化分析[J]. 浙江农林大学学报,2017,34(4):608−619. Cai ZF,Chen YQ,Xu XL,Wang XD,Wang JY,et al. Changes of volatile organic compounds released during flowering in four Osmanthus fragrans cultivar groups[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University,2017,34(4):608−619.
[33] 韦赛君,张静,王翔,吕嘉欣,王彬,等. 金钱松林挥发物季节性变化对空气负离子及微生物的影响[J]. 江西农业大学学报,2021,43(6):1316−1326. Wei SJ,Zhang J,Wang X,Lü JX,Wang B,et al. Effects of seasonal variation of volatiles in Pseudolarix amabilis forest on air anion and microorganism[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis,2021,43(6):1316−1326.



 下载:
下载: