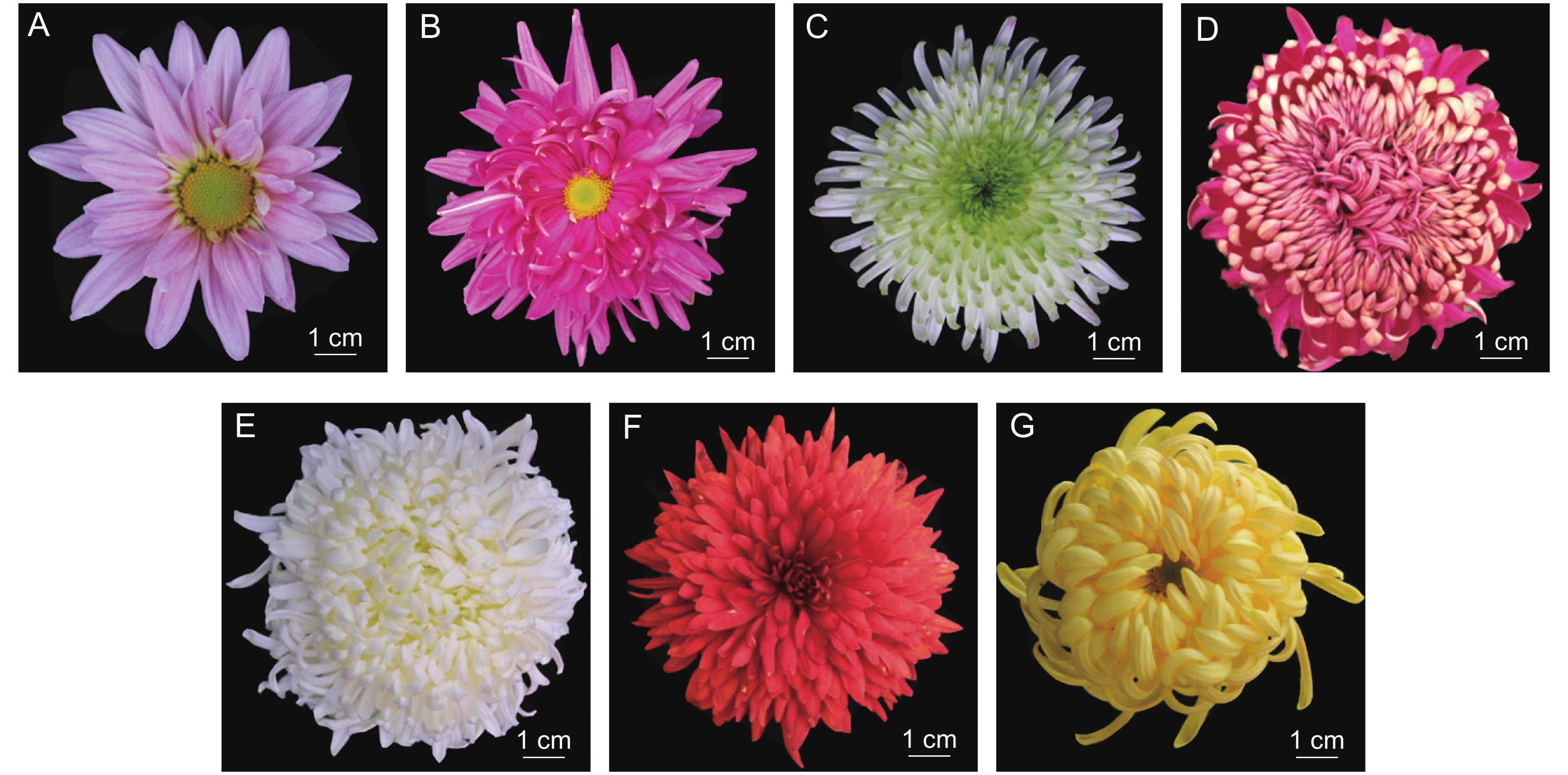
Variation and correlation analysis of florescence and main ornamental traits of Chrysanthemum × morifolium Ramat. varieties
-
摘要:
以菊花(Chrysanthemum × morifolium Ramat.)大菊品种自然群体及7个杂交群体为实验材料,分析比较了不同品种开花期和7个主要观赏性状的变异特点及其相关性,为筛选杂交亲本和选育早花优良品种提供依据。结果显示:大菊自然群体的8个性状中,除开花期外,其余性状变异系数均高于15%;相关性分析结果表明,开花期和封顶叶片数之间呈显著负相关;开花持续期与开花期呈极显著负相关,与舌状花轮数呈极显著正相关。杂交群体的8个性状中,除开花期外,变异系数均高于15%,但各杂交群体的开花期性状变异系数明显高于自然群体;杂交群体Ⅲ和Ⅴ的瓣型与花色更为丰富,且花期也较早。相关性分析结果表明,开花期和瓣型、舌状花轮数、封顶叶片数之间均呈极显著负相关,和花色之间呈显著负相关;开花持续期和舌状花轮数、舌状花数量之间呈极显著正相关,和瓣型之间呈极显著负相关,和花色之间呈显著负相关;开花期和开花持续期之间呈极显著正相关。研究结果表明,通过有性杂交可以获得开花期变异更广泛的子代植株,从而筛选开花期更早的大菊新品种。
Abstract:Using natural and hybrid populations of chrysanthemum as experimental materials, we analyzed the variation characteristics and correlations of florescence and ornamental characters among different varieties, then compared and analyzed the results to provide a basis for screening hybrid parents and breeding good varieties of early-flowering chrysanthemums. Results showed that the coefficients of variation of the eight traits in the natural chrysanthemum population were higher than 15%, except for flowering stage traits. Analysis showed a significant negative correlation between flowering stage and number of stem leaves. There was a highly significant negative correlation between flowering duration and flowering stage, and a highly significant positive correlation between flowering duration and number of ray flower turns. Among the eight traits in the hybrid populations, the coefficients of variation were higher than 15%, except for flowering traits, but the coefficients of variation for florescence traits of each hybrid population were also significantly higher than that of the natural population. Compared with other hybrid populations, the petal types and flower colors of hybrid populations Ⅲ and Ⅴ were more abundant, with earlier flowering stages. Analysis showed a highly significant negative correlation between flowering stage and petal type, number of ray flower turns, and number of stem leaves, and a significant negative correlation between flowering stage and flower color. There was a highly significant positive correlation between flowering duration and number of tubular flower turns and number of tubular flowers, a highly significant negative correlation between flowering duration and petal type, and a significant negative correlation between flowering duration and flower color. There was a highly significant positive correlation between flowering stage and flowering duration. Therefore, progeny plants with wider variation in flowering stage can be obtained through sexual hybridization, with new chrysanthemum varieties showing earlier flowering. Early flowering parents can be selected according to the characteristics of fewer leaves, more ray flower turns, petals close to flat petals, and flower color close to orange and pink lines. Sexual hybridization with varieties exhibiting better flower type and color can be carried out to obtain better early flowering varieties of Chrysanthemum with stable flowering stage from late September to early October.
-
Keywords:
- Chrysanthemum /
- Florescence traits /
- Main ornamental traits /
- Variation /
- Correlation
-
菊花(Chrysanthemum × morifolium Ramat.)作为我国十大传统名花之一,自古以来在观赏植物中就占据重要地位[1, 2]。其品种丰富且具有深厚的历史文化底蕴,代表淡雅、清廉、高洁等君子之德,深受人们的喜爱[3-5]。此外,颜色鲜艳的大菊品种也被称为“寿客”,具有吉祥、长寿的含义,加之作为秋季开放的花卉,在国庆节的花坛、花展应用等方面具有广阔的前景[6, 7]。但目前多数大菊品种开花时间较晚,花期在11 − 12月,要获得国庆节用花产品,就必须将大菊花期提前到9月下旬[8, 9]。而现在普遍采用的遮光等花期调控方式对人力、物力、时间的消耗较大,成本较高[10, 11],因此,培育品质优良的早花品种在大菊育种工作中显得十分重要。
大菊是所有菊花品种中性状变异最为丰富的类群[12, 13],多数品种重瓣性较高,且其瓣型有平瓣类、管瓣类、匙瓣类、畸瓣类等,花型有叠球型、翻卷型、卷散型等,花色有红、白、黄、绿、紫、复色等,因而颇具特色,观赏价值很高[14, 15]。但目前花期在10月初的品种较少,且开花持续期短、重瓣性不高、花型单一,花色也多为黄色、白色,缺少鲜艳色系的品种[16]。而观赏性状更为丰富的大菊,花期则大多在11月下旬至12月上中旬,多数重瓣性高,具有管瓣、匙瓣、复合瓣型等多个瓣型,叠球型、管球型、匙球型、龙爪型、松针型等多种花型,墨色、红色、粉色、黄色、橙色、白色等多个色系[17]。近年来对菊花尤其是大菊的研究主要集中在花型、花色、品种分类研究等方面[18-22],对其开花期相关的研究较少,对早花大菊新品种培育的研究也很缺乏。
相较于花期性状,大菊的花型、花色、叶片数量等性状更为直观,若能找到与花期性状密切相关的花部与叶部性状,将非常有利于杂交育种中的亲本选择、新品种选择及花期遗传规律的分析研究[23, 24]。对大菊品种花期性状和主要观赏性状的相关性进行研究,还可以为获得早花、花期长且观赏价值高的新品种提供依据,对早花良种的选育具有重要意义。
本研究选择了在北京地区栽培性状表现良好的339个大菊品种,在变异分析和相关性分析的基础上进行种资源评价,从中初步筛选出花期较早的品种,参考遗传距离聚类分析的结果,根据父本花粉量大、母本综合性状优良的原则选配7对杂交亲本,通过人工杂交的方法获得共由485株杂交后代组成的7个杂交群体,再对杂交后代进行花期和主要观赏性状的观测及变异分析、相关性分析。通过对自然群体和杂交群体进行花期和主要观赏性状的观测及分析、比较,筛选菊花早花育种的关键性状。本研究结果旨在为通过有性杂交育种培育更多国庆节前开花且观赏性状优良的大菊新品种提供依据,同时对其他观赏植物花期改良的育种工作提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
以北京林业大学菊花种质资源圃保存的339个中国传统大菊品种为材料,于2015 − 2021年对其进行表型数据的观测和计算分析,进行亲本选择与杂交选配,于2017年9月对选配出的7对亲本进行杂交,共获得485株杂交后代,并在2019 − 2021年对杂交后代进行表型数据观测。
每个品种种植3 ~ 5株,于每年4 − 5月进行扦插,插穗选择健壮无病虫害的脚芽,扦插基质选用珍珠岩和蛭石体积比为1∶1的混合基质,扦插于9 × 9的穴盘内;约15 ~ 30 d后,不同品种陆续生根,选择其中健壮、无病虫害的扦插苗进行定植及摘心;7 − 8月的旺盛生长期,需及时补充水分,适时进行叶面喷水,并补充氮肥;7月中旬,每5 d施一次氮磷钾复合肥,直至现蕾;9月中下旬,植株开始现蕾,需摘除侧蕾,保留中间主蕾及1 ~ 2枚备用蕾;植株高度达到25 cm时开始裱扎;各个时期均需做好病虫害防治工作。
1.2 数据测定
观测时间为2015年9月 - 2021年12月。花期性状测定从破膜期开始,每3 d观察一次;花型、叶型性状的测定以盛花期为准,每个品种观测3个样本,取平均值。质量性状主要依据《植物新品种特异性、一致性和稳定性测试指南 — 菊花》(2012)[25]进行赋值,对瓣型和花色进行赋值如下:直平(1)、曲平(2)、畸平(3)、直匙(4)、曲匙(5)、畸匙(6)、直管(7)、曲管(8)、畸管(9);棕色系(1)、橙色系(2)、粉色系(3)、紫色系(4)、红色系(5)、白色系(6)、黄色系(7)、黄绿色系(8)、墨色系(9)。
每个时期均以定植期到达到该时期标准的天数表示;破膜期标准为花蕾表面透明膜破裂,开花期标准为头状花序上最外轮小花初步打开,盛花期标准为头状花序上全部小花完全开放,末花期标准为头状花序开始褪色、花瓣开始凋落。开花持续期用开花期至末花期的天数表示。
1.3 数据处理
采用Excel 2010软件对数据进行初步整理,然后用SPSS 25.0软件分别对花期、花部及叶部等8个性状进行变异分析,使用Person相关系数对花期与主要观赏性状进行相关性分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 自然群体花期和观赏性状的变异及相关性分析
2.1.1 自然群体花期和观赏性状的变异分析
供试大菊品种花期和主要观赏性状的统计、变异系数分析结果见表1。由表1可知,自然群体的花期与7个观赏性状的变异系数均高于15%,且瓣型、舌状花轮数、舌状花数量、花色的变异系数高于36%,达到了高度变异,说明大菊品种间性状差异丰富。但开花期变异系数较小,仅为5.10%。
表 1 大菊自然群体花期和主要观赏性状的变异分析Table 1. Analysis of major variation in chrysanthemum varieties and ornamental characters性状
Trait最小值
Minimum最大值
Maximum标准差
Standard deviation变异系数
Variation coefficient / %花径 / cm 8.00 29.30 3.00 19.00 瓣型 1.00 8.00 1.15 57.33 舌状花轮数 / 轮 0.00 25.00 4.08 51.50 舌状花数量 / 朵 0.00 2531.00 269.01 73.01 封顶叶片数 / 片 10.00 47.00 5.73 25.02 花色 2.00 9.00 1.83 33.50 开花期 / d 145.00 210.00 9.44 5.10 开花持续期 / d 13.00 49.00 6.90 22.30 2.1.2 自然群体花期与观赏性状的相关性分析
对大菊花期、花部与叶部7个主要观赏性状间的相关性进行分析,结果见表2。开花期与封顶叶片数呈显著负相关(P < 0.05);开花持续期与开花期呈极显著负相关(P < 0.01),与舌状花轮数呈极显著正相关(P < 0.01);但两个花期性状和瓣型、舌状花数量之间的相关性均不显著。
表 2 大菊自然群体主要观赏性状和花期性状间的相关系数Table 2. Correlation coefficients between main ornamental and flowering characters of chrysanthemum varieties性状
Trait观赏性状和花期性状间的相关系数 Correlation coefficients between ornamental and flowering characters 花径
Flower diameter瓣型
Petal type舌状花轮数
No. of ray flower rounds舌状花数量
No. of ray flowers封顶叶片数
No. of leaves花色
Color开花期
Flowering period开花持续期
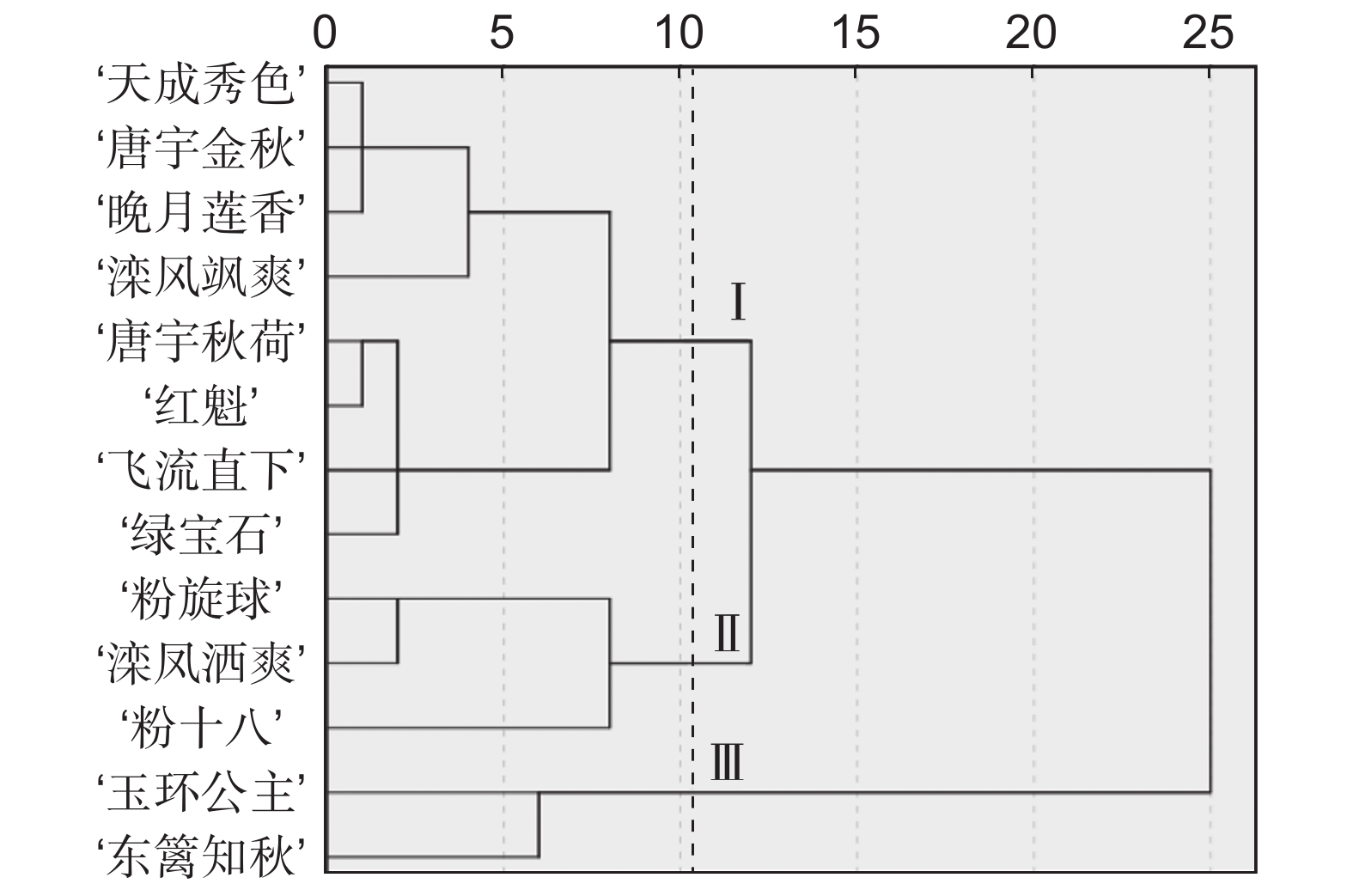
Flowering duration花径 1.00 瓣型 0.11* 1.00 舌状花轮数 −0.08 −0.06 1.00 舌状花数量 −0.04 −0.09 0.12* 1.00 封顶叶片数 −0.01 −0.14* 0.03 −0.01 1.00 花色 0.02 0.03 −0.02 −0.07 −0.02 1.00 开花期 0.06 0.04 −0.07 0.06 −0.12* 0.05 1.00 开花持续期 −0.12 −0.06 0.40** 0.01 0.13 0.04 −0.38** 1.00 注:*、**分别表示在0.05和0.01水平上差异显著。下同。 Note: * and ** indicate significant difference at 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively. Same below. 上述结果表明,封顶叶片数和舌状花轮数对花期影响较大。选择杂交亲本时,应在具有可育性的基础上,优先选择封顶叶片数少、舌状花轮数多的品种,进而再筛选花色鲜艳、多种瓣型且花径较大的品种。据此,在大菊自然群体中筛选出13个花期较早且性状优良的杂交亲本(表3)。以花粉量大的材料作父本,花瓣便于修剪、授粉的作母本,同时基于表型性状对原始数据进行标准化处理,计算欧氏距离[26],进行聚类分析(图1),选配花期相遇、亲缘关系较近的杂交亲本。最终筛选出7对杂交亲本,组配的杂交组合见表4。其中花期较早、开花持续期较短的亲本,舌状花轮数也较少,可用作父本;花期相对较晚、开花持续期较长的亲本,舌状花轮数较多,可用作母本(图2)。其性状表现也符合相关性分析得出的规律。
表 3 初步筛选大菊杂交亲本的性状表现Table 3. Preliminary screening of characters of chrysanthemum hybrid parents杂交亲本
Hybrid parents花径
Flower diameter / cm瓣型
Petal type舌状花轮数
No. of ray flower rounds舌状花数量
No. of ray flowers封顶叶片数
No. of leaves花色
Color开花期
Flowering period / d开花持续期
Flowering duration / d定植日期
Planting date开花日期
Flowering date得分
Score等级
Grade‘东篱知秋’ 15.3 2.0 11.0 434.0 21.0 3.0 152.0 31.0 4月23日 9月22日 86.78 1 ‘唐宇金秋’ 17.4 5.0 12.0 457.0 27.0 7.0 166.0 33.0 4月23日 10月06日 86.37 1 ‘绿宝石’ 16.2 7.0 12.0 459.0 19.0 8.0 161.0 27.0 4月23日 10月01日 86.13 1 ‘滦风飒爽’ 17.6 2.0 25.0 516.0 21.0 6.0 171.0 39.0 4月23日 10月11日 84.80 1 ‘飞流直下’ 16.0 8.0 15.0 480.0 24.0 6.0 166.0 39.0 4月23日 10月06日 84.15 1 ‘红 魁’ 18.2 1.0 25.0 625.0 28.0 5.0 173.0 33.0 4月23日 10月13日 81.18 1 ‘滦凤洒爽’ 15.0 4.0 10.0 420.0 27.0 4.0 172.0 32.0 4月23日 10月12日 80.82 1 ‘唐宇秋荷’ 15.7 1.0 10.0 418.0 33.0 6.0 168.0 40.0 4月23日 10月08日 79.60 1 ‘粉旋球’ 17.8 5.0 8.0 228.0 21.0 6.0 171.0 34.0 4月23日 10月11日 77.14 1 ‘粉十八’ 16.5 7.0 2.0 50.0 17.0 6.0 172.0 36.0 4月23日 10月12日 76.21 1 ‘玉环公主’ 10.9 1.0 2.0 107.0 15.0 3.0 145.0 19.0 4月23日 9月15日 72.31 2 ‘晚月莲香’ 11.5 7.0 11.0 460.0 22.0 6.0 173.0 25.0 4月23日 10月13日 72.30 2 ‘天成秀色’ 16.4 5.0 12.0 458.0 27.0 3.0 165.0 32.0 4月23日 10月05日 72.11 2 表 4 早花大菊杂交组合Table 4. Early flowering chrysanthemum hybrid combinations杂交亲本
Hybrid parents杂交组合编号
Hybrid combination number母本 × 父本 ‘玉环公主’ Ⅰ ‘玉环公主’ × ‘东篱知秋’ ‘东篱知秋’ Ⅱ ‘东篱知秋’ × ‘玉环公主’ ‘绿宝石’ Ⅲ ‘绿宝石’ × ‘玉环公主’ ‘滦风飒爽’ Ⅳ ‘滦风飒爽’ × ‘玉环公主’ ‘滦凤洒爽’ Ⅴ ‘滦凤洒爽’ × ‘玉环公主’ ‘唐宇金秋’ Ⅵ ‘唐宇金秋’ × ‘东篱知秋’ ‘红魁’ Ⅶ ‘红魁’ × ‘东篱知秋’ 2.2 杂交子代群体花期和观赏性状的变异及相关性分析
2.2.1 不同杂交群体间花期和观赏性状的变异分析
对7个杂交群体的花期和主要观赏性状进行变异分析,结果见表5。可以发现,大菊各杂交群体的主要观赏性状和开花持续期性状变异系数普遍高于15%,只有开花期性状变异系数均低于15%,但也明显高于自然群体;且与亲本相比,各性状都产生了超亲现象。说明早花大菊杂交子代株系间性状差异丰富,出现了比自然群体更为广泛的变异。与其他杂交群体相比,杂交群体Ⅲ和Ⅴ的开花期较早,开花持续期较长,且其他性状也较为优良。
表 5 大菊杂交群体花期和主要观赏性状的变异分析Table 5. Variation analysis of flowering period and ornamental characters of chrysanthemum hybrid populations性状
Trait杂交群体
Hybrid combination最小值
Minimum最大值
Maximum标准差
Standard deviation变异系数
Variation coefficient / %花径 / cm Ⅰ 5.20 16.00 2.38 23.00 Ⅱ 8.70 17.70 2.21 18.18 Ⅲ 7.00 17.80 1.95 17.25 Ⅳ 7.00 14.90 1.52 14.09 Ⅴ 6.90 17.20 2.06 18.39 Ⅵ 9.90 18.07 2.54 19.35 Ⅶ 6.00 17.90 2.02 18.50 瓣型 Ⅰ 1.00 5.00 0.53 25.88 Ⅱ 1.00 4.00 0.61 30.87 Ⅲ 1.00 7.00 1.21 67.22 Ⅳ 1.00 5.00 1.07 68.98 Ⅴ 1.00 8.00 1.25 71.05 Ⅵ 1.00 8.00 2.17 74.45 Ⅶ 1.00 5.00 0.78 50.09 舌状花轮数 Ⅰ 1.00 11.00 2.28 55.94 Ⅱ 3.00 24.00 4.58 49.41 Ⅲ 1.00 14.00 3.38 57.41 Ⅳ 1.00 15.00 2.89 48.69 Ⅴ 1.00 12.00 2.25 40.58 Ⅵ 2.00 4.00 3.67 67.29 Ⅶ 1.00 11.00 2.26 44.54 舌状花数量 Ⅰ 32.00 540.00 64.58 73.27 Ⅱ 36.00 664.00 156.56 66.79 Ⅲ 14.00 526.00 117.67 65.66 Ⅳ 29.00 344.00 72.94 54.48 Ⅴ 14.00 399.00 76.49 59.27 Ⅵ 42.00 524.00 128.07 80.55 Ⅶ 29.00 398.00 79.55 66.97 封顶叶片数 Ⅰ 8.00 42.00 5.92 26.93 Ⅱ 16.00 34.00 3.01 13.60 Ⅲ 11.00 33.00 6.63 28.97 Ⅳ 14.00 30.00 4.19 20.46 Ⅴ 12.00 31.00 4.71 23.23 Ⅵ 12.00 35.00 7.02 31.50 Ⅶ 11.00 33.00 4.61 23.69 花色 Ⅰ 2.00 7.00 1.57 39.83 Ⅱ 3.00 7.00 1.44 27.46 Ⅲ 2.00 7.00 1.57 36.52 Ⅳ 2.00 9.00 1.24 31.09 Ⅴ 2.00 8.00 2.04 41.15 Ⅵ 2.00 8.00 1.85 43.27 Ⅶ 2.00 7.00 1.46 36.38 开花期 / d Ⅰ 140.00 192.00 17.12 11.80 Ⅱ 131.00 172.00 16.17 10.70 Ⅲ 131.00 161.00 14.01 10.50 Ⅳ 132.00 168.00 15.00 9.85 Ⅴ 131.00 152.00 12.00 9.10 Ⅵ 140.00 192.00 16.15 11.30 Ⅶ 133.00 190.00 23.15 9.26 开花持续期 / d Ⅰ 14.00 30.00 5.61 25.70 Ⅱ 14.00 45.00 5.72 26.00 Ⅲ 14.00 45.00 6.73 26.10 Ⅳ 15.00 43.00 5.60 22.30 Ⅴ 16.00 45.00 6.32 21.23 Ⅵ 14.00 33.00 6.10 28.33 Ⅶ 15.00 42.00 6.71 35.35 2.2.2 杂交后代花期和主要观赏性状的相关性分析
利用Pearson相关分析研究杂交后代不同性状间的简单相关关系,结果显示,多个性状间的相关性有统计学意义(表6)。其中,开花期和瓣型、舌状花轮数、封顶叶片数之间呈极显著负相关(P < 0.01),和花色之间呈显著负相关(P < 0.05);开花持续期和舌状花轮数、舌状花数量之间呈极显著正相关(P < 0.01),和瓣型之间呈极显著负相关(P < 0.01),和花色之间呈显著负相关(P < 0.05);开花期和开花持续期之间呈极显著正相关(P < 0.01)。花期性状和花径的相关性不显著。
表 6 大菊杂交群体主要观赏性状和花期性状间的相关系数Table 6. Correlation coefficients between main ornamental and flowering period characters of hybrid populations of chrysanthemum性状
Trait主要观赏性状和花期性状间的相关系数 Correlation coefficients between main ornamental and flowering characters 花径
Flower diameter瓣型
Petal
type舌状花轮数
No. of ray flower rounds舌状花数量
No. of ray flowers封顶叶片数
No. of leaves花色
Color开花期
Flowering period开花持续期
Flowering duration花径 1.00 瓣型 0.02 1.00 舌状花轮数 0.17** −0.12** 1.00 舌状花数量 0.16** −0.06 0.79** 1.00 封顶叶片数 0.08 −0.05 0.02 0.09* 1.00 花色 −0.23 0.24 0.28* 0.25 0.09 开花期 0.03 −0.15** −0.15** −0.03 −0.16** −0.35* 1.00 开花持续期 −0.03 −0.44** 0.20** 0.26** −0.07 −0.29* 0.18** 1.00 分析结果表明,早花大菊杂交群体开花期和封顶叶片数之间呈极显著负相关,而花期性状与瓣型、花色、舌状花轮数、舌状花数量之间均存在较强的相关性,开花期和开花持续期之间也存在极显著正相关。但花期性状与花径相关性不显著。
3. 讨论
不同植物及同种植物不同种质资源的花期、花型等性状均存在较大差异[27-29],这些差异的丰富度对于杂交育种中亲本的选育具有重要意义。本研究发现,大菊自然群体与早花杂交群体不同株系的主要观赏性状差异均较大,变异系数均较高,表明在自然群体和杂交群体中均存在丰富的变异,遗传改良潜力较大。一些关键的观赏性状,如瓣型、舌状花轮数、舌状花数量、花色的变幅较大,变异系数较高,甚至超过50%,有利于选育花型优良、变化丰富的菊花品种。
但两类群体中性状的变异程度存在区别,同一性状在两类群体中的变异系数也不相同。其中,花期性状差异最为明显,开花期、开花持续期在杂交群体中的变异系数均高于自然群体,结合性状观测数据,说明通过杂交出现了超亲性状,得到了花期明显提前的株系。而杂交群体中的主要观赏性状如花色、瓣型等的变异系数也较高,说明通过杂交可以在提早花期的基础上获得花色、花型更为丰富的株系,为进一步选育国庆节前开花的早花优良大菊品种奠定基础。
植物各性状间通常存在不同程度的相关性,基于此可通过一个性状预测另一个性状的状况[30],这在数据测定较为困难的花期育种中尤为重要。本研究中,大菊自然群体和杂交群体的开花期性状均与封顶叶片数有较强的相关性,开花持续期均与舌状花轮数有较强的相关性,说明在选育早花优良品种时可以将封顶叶片数和舌状花轮数作为选择亲本的依据。
此外,在早花大菊杂交群体中出现了自然群体中不存在的性状相关性,开花期和开花持续期均与瓣型、花色具有较强的相关性,说明通过杂交获得早花优良品种时,也可根据瓣型和花色进行亲本选择和优良株系的筛选。在此基础上,基于表型性状也可以进行分子标记辅助选择,找到和开花期以及主要观赏性状相关的分子标记,进一步进行遗传分析和良种选育。
在观赏植物优良品种选育过程中,不仅要注重观赏性状,还应当考虑株高、抗逆性等营养性状。对于菊花而言,株高、节间长、抗逆性等是影响其生长发育和观赏品质的重要性状,也是育种者高度关注的性状[31-33]。本研究主要聚焦于花期性状与观赏性状的相关关系,今后还需加强花期性状与营养性状相关性的研究,为选育大菊早花优良品种提供更为全面的理论指导。
4. 结论
基于本研究结果,在未来的早花大菊品种培育工作中,可重点关注杂交群体Ⅲ和Ⅴ,以及自然群体中综合性状优良的品种,根据封顶叶片数少、舌状花轮数多、瓣型接近平瓣、花色接近橙色系和粉色系等特点选择早花亲本,进一步与花色更为鲜艳、花型更为丰富的品种进行有性杂交,获得花期稳定在9月下旬至10月初且变异丰富的杂交子代,再从中选择花型、花色等观赏性状优良的株系,获得国庆节前稳定开花的大菊早花优良品种,应用到实际生产中。
-
表 1 大菊自然群体花期和主要观赏性状的变异分析
Table 1 Analysis of major variation in chrysanthemum varieties and ornamental characters
性状
Trait最小值
Minimum最大值
Maximum标准差
Standard deviation变异系数
Variation coefficient / %花径 / cm 8.00 29.30 3.00 19.00 瓣型 1.00 8.00 1.15 57.33 舌状花轮数 / 轮 0.00 25.00 4.08 51.50 舌状花数量 / 朵 0.00 2531.00 269.01 73.01 封顶叶片数 / 片 10.00 47.00 5.73 25.02 花色 2.00 9.00 1.83 33.50 开花期 / d 145.00 210.00 9.44 5.10 开花持续期 / d 13.00 49.00 6.90 22.30 表 2 大菊自然群体主要观赏性状和花期性状间的相关系数
Table 2 Correlation coefficients between main ornamental and flowering characters of chrysanthemum varieties
性状
Trait观赏性状和花期性状间的相关系数 Correlation coefficients between ornamental and flowering characters 花径
Flower diameter瓣型
Petal type舌状花轮数
No. of ray flower rounds舌状花数量
No. of ray flowers封顶叶片数
No. of leaves花色
Color开花期
Flowering period开花持续期
Flowering duration花径 1.00 瓣型 0.11* 1.00 舌状花轮数 −0.08 −0.06 1.00 舌状花数量 −0.04 −0.09 0.12* 1.00 封顶叶片数 −0.01 −0.14* 0.03 −0.01 1.00 花色 0.02 0.03 −0.02 −0.07 −0.02 1.00 开花期 0.06 0.04 −0.07 0.06 −0.12* 0.05 1.00 开花持续期 −0.12 −0.06 0.40** 0.01 0.13 0.04 −0.38** 1.00 注:*、**分别表示在0.05和0.01水平上差异显著。下同。 Note: * and ** indicate significant difference at 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively. Same below. 表 3 初步筛选大菊杂交亲本的性状表现
Table 3 Preliminary screening of characters of chrysanthemum hybrid parents
杂交亲本
Hybrid parents花径
Flower diameter / cm瓣型
Petal type舌状花轮数
No. of ray flower rounds舌状花数量
No. of ray flowers封顶叶片数
No. of leaves花色
Color开花期
Flowering period / d开花持续期
Flowering duration / d定植日期
Planting date开花日期
Flowering date得分
Score等级
Grade‘东篱知秋’ 15.3 2.0 11.0 434.0 21.0 3.0 152.0 31.0 4月23日 9月22日 86.78 1 ‘唐宇金秋’ 17.4 5.0 12.0 457.0 27.0 7.0 166.0 33.0 4月23日 10月06日 86.37 1 ‘绿宝石’ 16.2 7.0 12.0 459.0 19.0 8.0 161.0 27.0 4月23日 10月01日 86.13 1 ‘滦风飒爽’ 17.6 2.0 25.0 516.0 21.0 6.0 171.0 39.0 4月23日 10月11日 84.80 1 ‘飞流直下’ 16.0 8.0 15.0 480.0 24.0 6.0 166.0 39.0 4月23日 10月06日 84.15 1 ‘红 魁’ 18.2 1.0 25.0 625.0 28.0 5.0 173.0 33.0 4月23日 10月13日 81.18 1 ‘滦凤洒爽’ 15.0 4.0 10.0 420.0 27.0 4.0 172.0 32.0 4月23日 10月12日 80.82 1 ‘唐宇秋荷’ 15.7 1.0 10.0 418.0 33.0 6.0 168.0 40.0 4月23日 10月08日 79.60 1 ‘粉旋球’ 17.8 5.0 8.0 228.0 21.0 6.0 171.0 34.0 4月23日 10月11日 77.14 1 ‘粉十八’ 16.5 7.0 2.0 50.0 17.0 6.0 172.0 36.0 4月23日 10月12日 76.21 1 ‘玉环公主’ 10.9 1.0 2.0 107.0 15.0 3.0 145.0 19.0 4月23日 9月15日 72.31 2 ‘晚月莲香’ 11.5 7.0 11.0 460.0 22.0 6.0 173.0 25.0 4月23日 10月13日 72.30 2 ‘天成秀色’ 16.4 5.0 12.0 458.0 27.0 3.0 165.0 32.0 4月23日 10月05日 72.11 2 表 4 早花大菊杂交组合
Table 4 Early flowering chrysanthemum hybrid combinations
杂交亲本
Hybrid parents杂交组合编号
Hybrid combination number母本 × 父本 ‘玉环公主’ Ⅰ ‘玉环公主’ × ‘东篱知秋’ ‘东篱知秋’ Ⅱ ‘东篱知秋’ × ‘玉环公主’ ‘绿宝石’ Ⅲ ‘绿宝石’ × ‘玉环公主’ ‘滦风飒爽’ Ⅳ ‘滦风飒爽’ × ‘玉环公主’ ‘滦凤洒爽’ Ⅴ ‘滦凤洒爽’ × ‘玉环公主’ ‘唐宇金秋’ Ⅵ ‘唐宇金秋’ × ‘东篱知秋’ ‘红魁’ Ⅶ ‘红魁’ × ‘东篱知秋’ 表 5 大菊杂交群体花期和主要观赏性状的变异分析
Table 5 Variation analysis of flowering period and ornamental characters of chrysanthemum hybrid populations
性状
Trait杂交群体
Hybrid combination最小值
Minimum最大值
Maximum标准差
Standard deviation变异系数
Variation coefficient / %花径 / cm Ⅰ 5.20 16.00 2.38 23.00 Ⅱ 8.70 17.70 2.21 18.18 Ⅲ 7.00 17.80 1.95 17.25 Ⅳ 7.00 14.90 1.52 14.09 Ⅴ 6.90 17.20 2.06 18.39 Ⅵ 9.90 18.07 2.54 19.35 Ⅶ 6.00 17.90 2.02 18.50 瓣型 Ⅰ 1.00 5.00 0.53 25.88 Ⅱ 1.00 4.00 0.61 30.87 Ⅲ 1.00 7.00 1.21 67.22 Ⅳ 1.00 5.00 1.07 68.98 Ⅴ 1.00 8.00 1.25 71.05 Ⅵ 1.00 8.00 2.17 74.45 Ⅶ 1.00 5.00 0.78 50.09 舌状花轮数 Ⅰ 1.00 11.00 2.28 55.94 Ⅱ 3.00 24.00 4.58 49.41 Ⅲ 1.00 14.00 3.38 57.41 Ⅳ 1.00 15.00 2.89 48.69 Ⅴ 1.00 12.00 2.25 40.58 Ⅵ 2.00 4.00 3.67 67.29 Ⅶ 1.00 11.00 2.26 44.54 舌状花数量 Ⅰ 32.00 540.00 64.58 73.27 Ⅱ 36.00 664.00 156.56 66.79 Ⅲ 14.00 526.00 117.67 65.66 Ⅳ 29.00 344.00 72.94 54.48 Ⅴ 14.00 399.00 76.49 59.27 Ⅵ 42.00 524.00 128.07 80.55 Ⅶ 29.00 398.00 79.55 66.97 封顶叶片数 Ⅰ 8.00 42.00 5.92 26.93 Ⅱ 16.00 34.00 3.01 13.60 Ⅲ 11.00 33.00 6.63 28.97 Ⅳ 14.00 30.00 4.19 20.46 Ⅴ 12.00 31.00 4.71 23.23 Ⅵ 12.00 35.00 7.02 31.50 Ⅶ 11.00 33.00 4.61 23.69 花色 Ⅰ 2.00 7.00 1.57 39.83 Ⅱ 3.00 7.00 1.44 27.46 Ⅲ 2.00 7.00 1.57 36.52 Ⅳ 2.00 9.00 1.24 31.09 Ⅴ 2.00 8.00 2.04 41.15 Ⅵ 2.00 8.00 1.85 43.27 Ⅶ 2.00 7.00 1.46 36.38 开花期 / d Ⅰ 140.00 192.00 17.12 11.80 Ⅱ 131.00 172.00 16.17 10.70 Ⅲ 131.00 161.00 14.01 10.50 Ⅳ 132.00 168.00 15.00 9.85 Ⅴ 131.00 152.00 12.00 9.10 Ⅵ 140.00 192.00 16.15 11.30 Ⅶ 133.00 190.00 23.15 9.26 开花持续期 / d Ⅰ 14.00 30.00 5.61 25.70 Ⅱ 14.00 45.00 5.72 26.00 Ⅲ 14.00 45.00 6.73 26.10 Ⅳ 15.00 43.00 5.60 22.30 Ⅴ 16.00 45.00 6.32 21.23 Ⅵ 14.00 33.00 6.10 28.33 Ⅶ 15.00 42.00 6.71 35.35 表 6 大菊杂交群体主要观赏性状和花期性状间的相关系数
Table 6 Correlation coefficients between main ornamental and flowering period characters of hybrid populations of chrysanthemum
性状
Trait主要观赏性状和花期性状间的相关系数 Correlation coefficients between main ornamental and flowering characters 花径
Flower diameter瓣型
Petal
type舌状花轮数
No. of ray flower rounds舌状花数量
No. of ray flowers封顶叶片数
No. of leaves花色
Color开花期
Flowering period开花持续期
Flowering duration花径 1.00 瓣型 0.02 1.00 舌状花轮数 0.17** −0.12** 1.00 舌状花数量 0.16** −0.06 0.79** 1.00 封顶叶片数 0.08 −0.05 0.02 0.09* 1.00 花色 −0.23 0.24 0.28* 0.25 0.09 开花期 0.03 −0.15** −0.15** −0.03 −0.16** −0.35* 1.00 开花持续期 −0.03 −0.44** 0.20** 0.26** −0.07 −0.29* 0.18** 1.00 -
[1] 陈俊愉. 中国菊花过去和今后对世界的贡献[J]. 中国园林,2005,21(9):73−75. Chen JY. Contributions of Chinese chrysanthemum to the world in the past and future[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture,2005,21 (9):73−75. Chen JY. Contributions of Chinese chrysanthemum to the world in the past and future[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 2005, 21(9): 73-75.
[2] 吴丽娜. 《红楼梦》菊花诗的拟题、分配与意象[J]. 明清小说研究,2021(4):121−135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3330.2021.04.008 [3] 戴思兰,王文奎,黄家平. 菊属系统学及菊花起源的研究进展[J]. 北京林业大学学报,2002,24(5-6):234−238. Dai SL,Wang WK,Huang JP. Advances of researches on phylogeny of Dendranthema and origin of chrysanthemum[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2002,24 (5-6):234−238. Dai SL, Wang WK, Huang JP. Advances of researches on phylogeny of Dendranthema and origin of chrysanthemum[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2002, 24(5-6): 234-238.
[4] 戴思兰. 中国菊花的魅力[J]. 中国园林,2012,28(8):46−48. Dai SL. The fascinations of Chinese chrysanthemum[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture,2012,28 (8):46−48. Dai SL. The fascinations of Chinese chrysanthemum[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 2012, 28(8): 46-48.
[5] 秦忠文. 中国传统菊花栽培起源与花文化发展[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2006: 20−33. [6] 李学松, 季玉山, 戴思兰. 百菊图话[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2013: 10−40. [7] 张树林, 戴思兰. 中国菊花全书[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2013: 120−133. [8] 赵小刚. 日中性小菊新品种选育及小菊开花期遗传分析[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2019: 1−10. [9] 秦贺兰. 夏花型小菊新品[J]. 中国花卉园艺,2006(20):46−49. [10] 宋彬,刘景安. 宿根花卉花期调控的研究进展[J]. 北方园艺,2020(1):122−127. Song B,Liu JA. Research advance of flowering time regulator for perennial flower[J]. Northern Horticulture,2020 (1):122−127. Song B, Liu JA. Research advance of flowering time regulator for perennial flower[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2020(1): 122-127.
[11] 张秋玲,刘海鹏,高康,孔德元,戴思兰. 盆栽菊花反季节开花调控技术研究[J]. 黑龙江农业科学,2021(9):62−67. Zhang QL,Liu HP,Gao K,Kong DY,Dai SL. Research on anti-seasonal flowering control technology of potted chrysanthemum[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences,2021 (9):62−67. Zhang QL, Liu HP, Gao K, Kong DY, Dai SL. Research on anti-seasonal flowering control technology of potted chrysanthemum[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021(9): 62-67.
[12] 张莉俊,戴思兰. 菊花种质资源研究进展[J]. 植物学报,2009,44(5):526−535. Zhang LJ,Dai SL. Research advance on germplasm resources of Chrysanthemum × morifolium[J]. Bulletin of Botany,2009,44 (5):526−535. Zhang LJ, Dai SL. Research advance on germplasm resources of Chrysanthemum × morifolium[J]. Bulletin of Botany, 2009, 44(5): 526-535.
[13] 雒新艳,宋雪彬,戴思兰. 中国传统大菊品种数量性状变异及其概率分级[J]. 北京林业大学学报,2016,38(1):101−111. Luo XY,Song XB,Dai SL. Variation and probability grading of quantitative characters of traditional chrysanthemum cultivars[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2016,38 (1):101−111. Luo XY, Song XB, Dai SL. Variation and probability grading of quantitative characters of traditional chrysanthemum cultivars[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(1): 101-111.
[14] 雒新艳. 大菊品种资源遗传多样性研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2009: 32−42. [15] 牛雅静,张蒙蒙,孟昕. 观赏植物托桂花型的研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学,2021,49(24):29−32. Niu YJ,Zhang MM,Meng X. Research progress on anemone type of ornamental plants[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2021,49 (24):29−32. Niu YJ, Zhang MM, Meng X. Research progress on anemone type of ornamental plants[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(24): 29-32.
[16] 宋雪彬,高康,戴思兰,季玉山,王朔,刘昊. 菊花新品种‘东篱知秋’[J]. 园艺学报,2020,47(S2):3024−3025. Song XB,Gao K,Dai SL,Ji YS,Wang S,Liu H. A new large-flowered chrysanthemum cultivar ‘Dongli Zhiqiu’[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2020,47 (S2):3024−3025. Song XB, Gao K, Dai SL, Ji YS, Wang S, Liu H. A new large-flowered chrysanthemum cultivar ‘Dongli Zhiqiu’[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2020, 47(S2): 3024-3025.
[17] 张玉鸽, 高康, 刘芷兰, 宋雪彬, 戴思兰. 不同开花期大菊品种观赏性状综合分析[C]//中国观赏园艺研究进展2018. 哈尔滨: 中国园艺学会, 2018: 50−58. Zhang YG, Gao K, Liu ZL, Song XB, Dai SL. Analysis of florescence ornamental characters on chrysanthemum cultivars[C]//Advances in Ornamental Horticulture of China 2018. Harbin: Chinese Society for Horticultural Science, 2018: 50-58.
[18] 雒新艳,张俊丽,张二海. 大菊主要数量性状分析及其应用探讨[J]. 江苏农业科学,2015,43(7):161−163. [19] 张蒙蒙, 王青, 戴思兰, 季玉山, 王朔. 盆栽小菊表型性状筛选与品种分类研究[C]//中国观赏园艺研究进展2014. 青岛: 中国园艺学会, 2014: 111−117. Zhang MM, Wang Q, Dai SL, Ji YS, Wang S. The screening of the phenotypic traits and taxonomic study for potted chrysanthemum[C]//Advances in Ornamental Horticulture of China 2014. Qingdao: Chinese Society for Horticultural Science, 2014: 111−117.
[20] 许兰杰,梁慧珍,余永亮,谭政委,杨青,李磊. 菊花种质综合评价体系构建及优异种质筛选[J]. 北方园艺,2022(12):55−63. Xu LJ,Liang HZ,Yu YL,Tan ZW,Yang Q,Li L. Establishment of comprehensive evaluation of chrysanthemum germplasm and selection of elite resource[J]. Northern Horticulture,2022 (12):55−63. Xu LJ, Liang HZ, Yu YL, Tan ZW, Yang Q, Li L. Establishment of comprehensive evaluation of chrysanthemum germplasm and selection of elite resource[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2022(12): 55-63.
[21] 高康, 宋雪彬, 戴思兰, 季玉山, 王朔. 基于AHP法的大菊杂种F1代新品种筛选[C]//中国观赏园艺研究进展2016. 长沙: 中国园艺学会, 2016: 127−133. Gao K, Song XB, Dai SL, Ji YS, Wang S. AHP-based screening of traditional chrysanthemum hybrid F1 for new variety[C]//Research Progress of Ornamental Horticulture in China 2016. Changsha: Chinese Society for Horticultural Science, 2016: 127-133.
[22] 宋雪彬,高康,黄河,刘芷兰,戴思兰,嵇彧. 中国传统大菊叶片形态的数量化定义与分类[J]. 植物学报,2021,56(1):10−24. Song XB,Gao K,Huang H,Liu ZL,Dai SL,Ji Y. Quantitative definition and classification of leaves in large-flowered Chinese chrysanthemum based on the morphological traits[J]. Bulletin of Botany,2021,56 (1):10−24. Song XB, Gao K, Huang H, Liu ZL, Dai SL, Ji Y. Quantitative definition and classification of leaves in large-flowered Chinese chrysanthemum based on the morphological traits[J]. Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(1): 10-24.
[23] 盖钧益, 章元明, 王建康. 植物数量性状遗传体系[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003: 1−20. [24] 冯俊杰,赵文达,张新全,刘英杰,袁帅,等. 引种日本多花黑麦草标准品种DUS性状变异分析及应用[J]. 中国农业科学,2022,55(12):2447−2460. Feng JJ,Zhao WD,Zhang XQ,Liu YJ,Yuan S,et al. DUS traits variation analysis and application of standard varieties of Lolium multiflorum introduced from Japan[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2022,55 (12):2447−2460. Feng JJ, Zhao WD, Zhang XQ, Liu YJ, Yuan S, et al. DUS traits variation analysis and application of standard varieties of Lolium multiflorum introduced from Japan[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(12): 2447-2460.
[25] 中华人民共和国农业农村部. GB/T 19557.19-2018 植物品种特异性、一致性和稳定性测试指南 菊花[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T 19557.19-2018 Guidelines for the conduct of tests for distinctness, uniformity and stability-Chrysanthemum × morifolium Ramat. (Chrysanthemum × grandiflorum Ramat.), Chrysanthemum pacificum Nakai (Ajania pacifica Bremer and Humphries) and hybrids between them[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018.
[26] 杜世坤,赵宝勰,赵振宁,高玉芳,李雨阳,等. 间作用大豆亲本的相关性、主成分及聚类分析[J]. 分子植物育种,2022,20(1):266−275. Du SK,Zhao BX,Zhao ZN,Gao YF,Li YY,et al. Correlation analysis,principal component analysis and cluster analysis in parent selection of intercropping soybean[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding,2022,20 (1):266−275. Du SK, Zhao BX, Zhao ZN, Gao YF, Li YY, et al. Correlation analysis, principal component analysis and cluster analysis in parent selection of intercropping soybean[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2022, 20(1): 266-275.
[27] 杨群力,李思锋. 大丽花三种园艺性状之间相关性的研究[J]. 中国农学通报,2009,25(23):295−302. Yang QL,Li SF. Study on relativity among three gardening characters of dahlia pinnata[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2009,25 (23):295−302. Yang QL, Li SF. Study on relativity among three gardening characters of dahlia pinnata[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2009, 25(23): 295-302.
[28] 徐肇友,肖德卿,沈斌,肖纪军,陈杏林,周志春. 秀丽四照花叶色参数和叶形性状的变异及相关性分析[J]. 植物资源与环境学报,2021,30(1):61−68. Xu ZY,Xiao DQ,Shen B,Xiao JJ,Chen XL,Zhou ZC. Variation and correlation analyses on leaf color parameters and leaf shape traits of Cornus hongkongensis subsp. elegans[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment,2021,30 (1):61−68. Xu ZY, Xiao DQ, Shen B, Xiao JJ, Chen XL, Zhou ZC. Variation and correlation analyses on leaf color parameters and leaf shape traits of Cornus hongkongensis subsp. elegans[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2021, 30(1): 61-68.
[29] 赵芳,魏玮,张晓磊,宋国亮,王晓明,等. 224个谷子品种农艺性状聚类和相关性分析[J]. 种子,2022,41(1):74−83. Zhao F,Wei W,Zhang XL,Song GL,Wang XM,et al. Clustering and correlation analysis of agronomic traits of 224 millet varieties[J]. Seed,2022,41 (1):74−83. Zhao F, Wei W, Zhang XL, Song GL, Wang XM, et al. Clustering and correlation analysis of agronomic traits of 224 millet varieties[J]. Seed, 2022, 41(1): 74-83.
[30] 吴瑞,刘文辉,张永超,秦燕,魏小星,刘敏洁. 青藏高原老芒麦落粒性及农艺性状相关性研究[J]. 草业学报,2021,30(4):130−139. Wu R,Liu WH,Zhang YC,Qin Y,Wei XX,Liu MJ. A study of the correlation between seed shattering and agronomic traits of Elymus sibiricus on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica,2021,30 (4):130−139. Wu R, Liu WH, Zhang YC, Qin Y, Wei XX, Liu MJ. A study of the correlation between seed shattering and agronomic traits of Elymus sibiricus on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(4): 130-139.
[31] 王旭,高致明,张红瑞,张景景,马彦秋,元玉碧. 6个药用菊花栽培类型生长势及抗性综合评价[J]. 河南农业大学学报,2012,46(2):131−135. Wang X,Gao ZM,Zhang HR,Zhang JJ,Ma YQ,Yuan YB. Comprehensive evaluation of the growth potential and resistance in six cultivars of medicinal Chrysanthemum morifolium[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University,2012,46 (2):131−135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2340.2012.02.004 Wang X, Gao ZM, Zhang HR, Zhang JJ, Ma YQ, Yuan YB. Comprehensive evaluation of the growth potential and resistance in six cultivars of medicinal Chrysanthemum morifolium[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 2012, 46(2): 131-135, 151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2340.2012.02.004
[32] 吴盼婷,王江民,沈佳逾,杨友翠,管志勇,等. 不同菊花品种根系、地上部和叶片相关指标分析及抗逆性评价[J]. 植物资源与环境学报,2017,26(2):46−54. Wu PT,Wang JM,Shen JY,Yang YC,Guan ZY,et al. Analyses on related indexes of root,above-ground part and leaf of different cultivars of Chrysanthemum morifolium and stress resistance evaluation[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment,2017,26 (2):46−54. Wu PT, Wang JM, Shen JY, Yang YC, Guan ZY, et al. Analyses on related indexes of root, above-ground part and leaf of different cultivars of Chrysanthemum morifolium and stress resistance evaluation[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2017, 26(2): 46-54.
[33] 马杰,徐婷婷,苏江硕,杨信程,房伟民,等. 菊花F1代舌状花耐寒性遗传变异与QTL定位[J]. 园艺学报,2018,45(4):717−724. Ma J,Xu TT,Su JS,Yang XC,Fang WM,et al. Genetic variation and QTL mapping for cold tolerance of ray florets in an F1 population of Chrysanthemum morifolium[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2018,45 (4):717−724. Ma J, Xu TT, Su JS, Yang XC, Fang WM, et al. Genetic variation and QTL mapping for cold tolerance of ray florets in an F1 population of Chrysanthemum morifolium[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2018, 45(4): 717-724.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 宋想,王钟曼,张秋玲,魏媛媛,赵小刚,刘波,戴思兰. 早花露地小菊杂交后代株系的综合评价与筛选. 中国农业科学. 2024(01): 173-189 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李楠昕,姜毅,袁迎春,胡观兴,龚文芳,袁德义. 油茶种间杂交子代花期与花器官性状的变异分析. 森林与环境学报. 2024(02): 183-189 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: