A review on the research progress of the Phytocyanin (PC) protein family
-
摘要:
质体蓝素(Phytocyanin,PC)是植物特有的一类Ⅰ型小分子蓝铜蛋白,可在植物生长发育及应对逆境胁迫过程中发挥调控作用。但目前对PC蛋白的功能研究较为有限,其分子作用机制尚不清楚。本文综述了PC蛋白的结构特征、分类及其基因的表达模式,并对近年来PC蛋白调控植物生长发育、应对生物及非生物胁迫方面的研究进展进行了总结。此外,对未来研究方向及面临的挑战进行了讨论,旨在为进一步理解PC蛋白的分子作用机制及植物抗逆品种的选育提供参考。
Abstract:Phytocyanins (PCs) are a class of plant-specific typeⅠsmall-molecule blue-copper proteins involved in regulating plant growth, development, and stress responses. Despite their importance, functional analysis of PC proteins remains limited, and their molecular mechanisms are not fully understood. This review examines the structural features, classification, and expression patterns of PC proteins. In addition, it summarizes recent advancements in the study of PC proteins, focusing on their roles in plant growth, development, and responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. Unresolved issues and challenges in PC research are also discussed. This work aims to provide a theoretical reference for understanding the molecular mechanisms of PC proteins and for breeding stress-resistant crop cultivars.
-
Keywords:
- Phytocyanin /
- Gene function /
- Molecular mechanism /
- Stress
-
1 1~2)如需查阅附件内容请登录《植物科学学报》网站(http://www.plantscience.cn)查看本期文章。2 如需查阅附表内容请登录《植物科学学报》网站(http://www.plantscience.cn)查看本期文章。 -
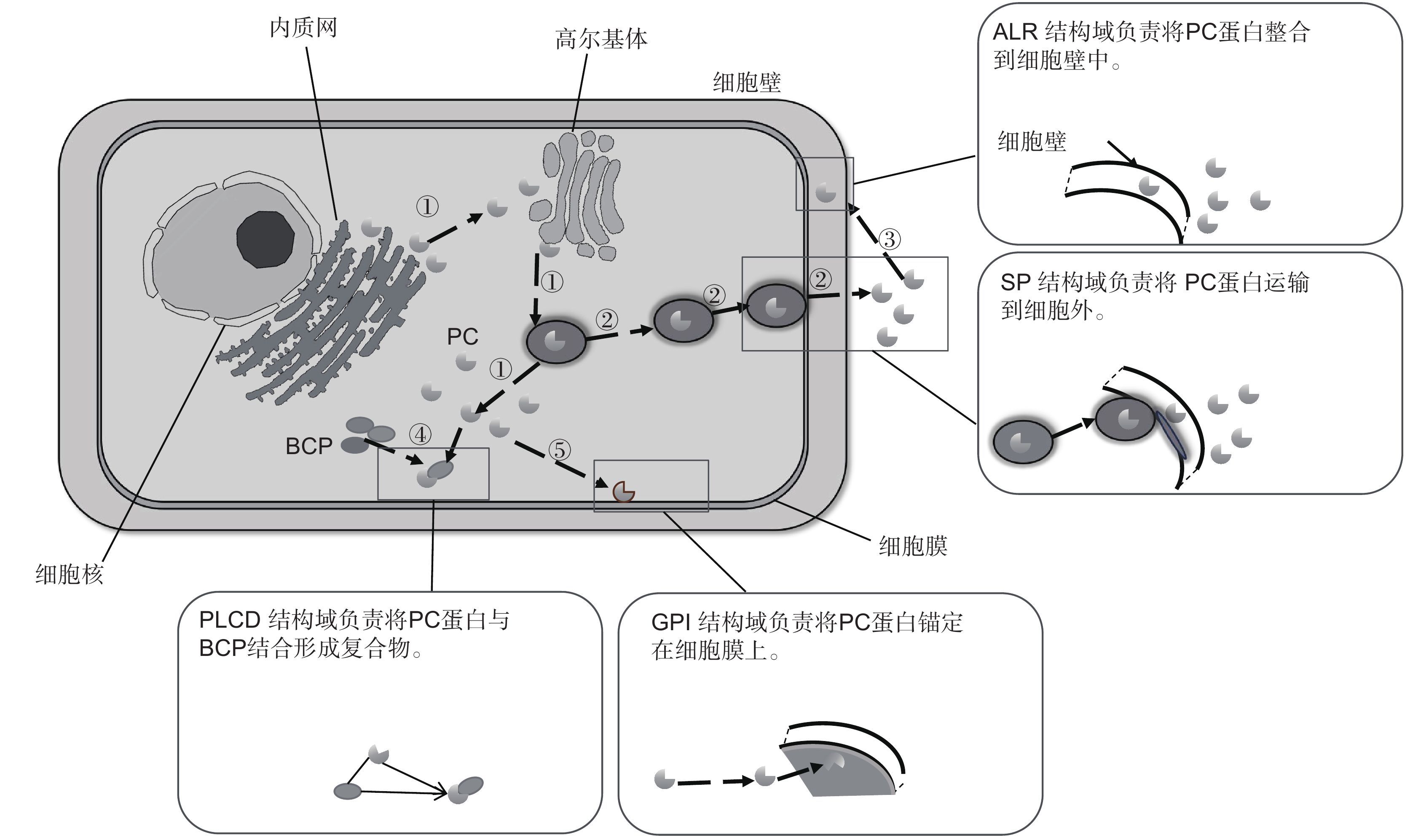
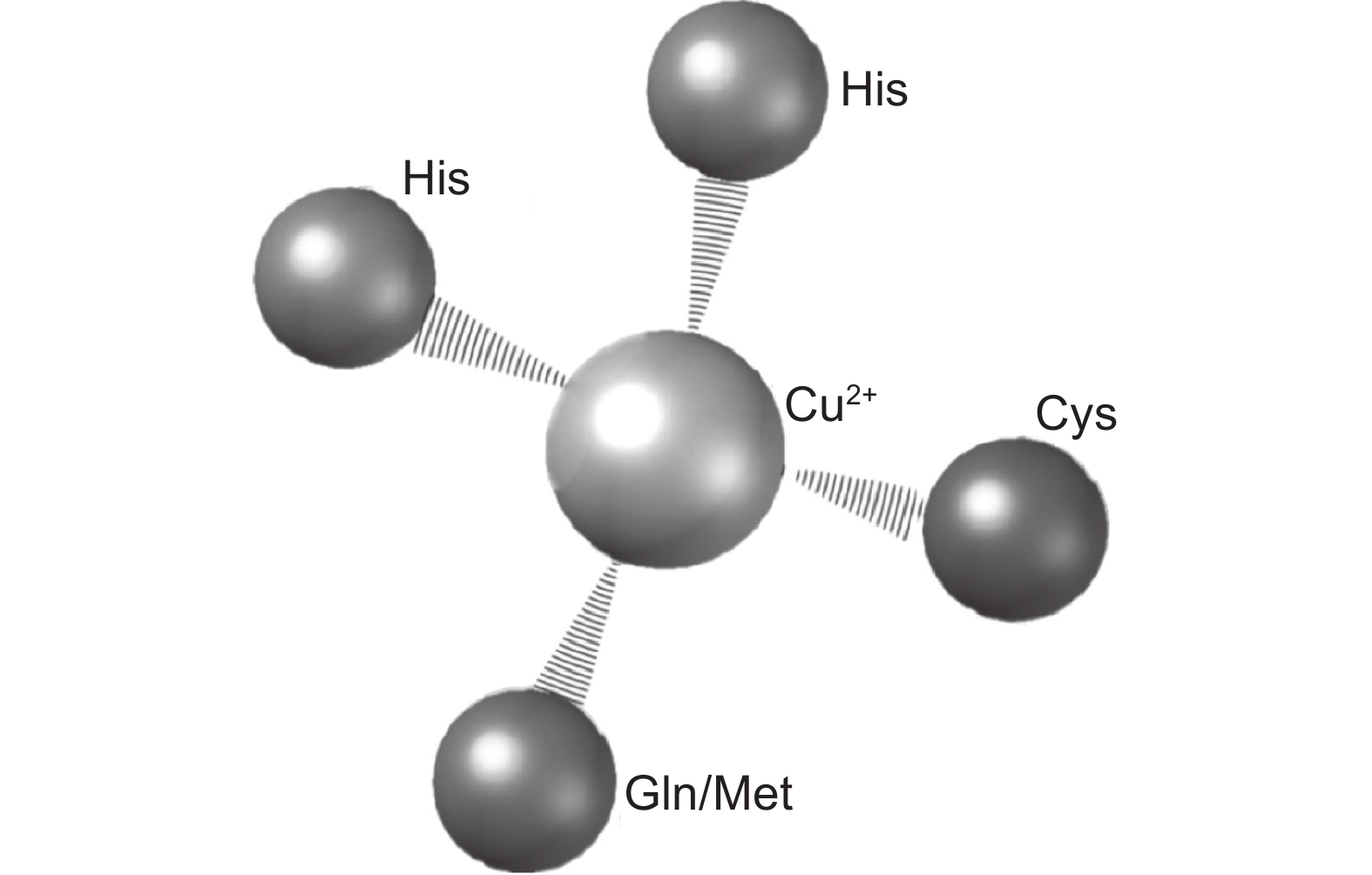
图 3 PC蛋白结构及其功能
① :PC蛋白合成、修饰及释放的过程;② :PC蛋白利用其SP结构域被运输至细胞外;③ :PC蛋白利用ALR结构域被组装到细胞壁中;④ :PC蛋白利用PLCD结构域与BCP互作并组成复合体;⑤ :PC蛋白利用GPI结构域将自己锚定在细胞膜上。
Figure 3. Structures and functions of PC proteins
①: Process of PC protein synthesis, modification, and release; ②: PC protein is transported to the extracellular space using the SP domain; ③: PC protein is assembled into the cell wall using the ALR domain; ④: PC protein utilizes PLCD domain to interact with BCP and form a complex; ⑤: PC protein utilizes the GPI domain to anchor itself on the cell membrane.
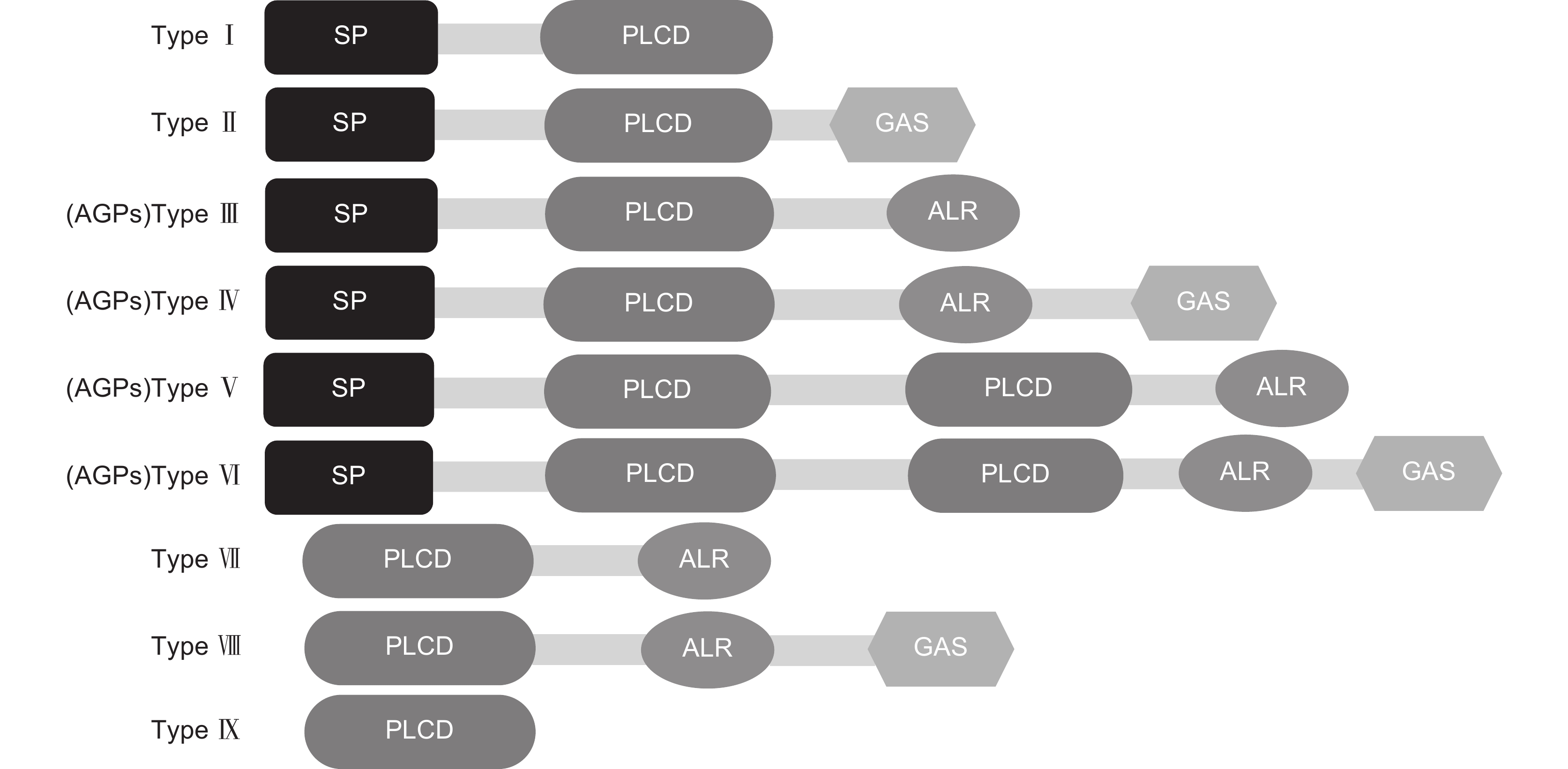
图 4 基于结构域组成的PC蛋白分类(改自孙亚丽[36])
SP:信号肽;PLCD:质体蓝素样结构域/铜结合结构域;ALR:类似阿拉伯半乳糖蛋白区域;GAS:糖基磷脂酰肌醇锚定信号。
Figure 4. Classification of PC proteins based on domain composition (modified from Sun[36])
SP: Signal peptide; PLCD: Plastocyanin like domain/Copper binding domain; ALR: Arabinogalactan protein (AGP)-like region similar to arabinogalactan protein region; GAS: Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor signal.
-
[1] Yruela I. Copper in plants:acquisition,transport and interactions[J]. Funct Plant Biol,2009,36(5):409−430. doi: 10.1071/FP08288
[2] Malkin R,Malmström BG. The state and function of copper in biological systems[M]//Nord FF,ed. Advances in Enzymology and Related Areas of Molecular Biology. Hoboken:John Wiley & Sons,Inc. ,1970:177−244.
[3] Kataoka K,Tsukamoto K,Kitagawa R,Ito T,Sakurai T. Compensatory binding of an asparagine residue to the coordination-unsaturated typeⅠCu center in bilirubin oxidase mutants[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2008,371(3):416−419. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.04.096
[4] Rydén LG,Hunt LT. Evolution of protein complexity:the blue copper-containing oxidases and related proteins[J]. J Mol Evol,1993,36(1):41−66. doi: 10.1007/BF02407305
[5] Shi Y,Xin YY,Wang C,Blankenship RE,Sun F,Xu XL. Cryo-EM structures of the air-oxidized and dithionite-reduced photosynthetic alternative complex Ⅲ from Roseiflexus castenholzii[J]. Sci Adv,2020,6(31):eaba2739. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aba2739
[6] Guzzi R,Sportelli L,Sato K,Cannistraro S,Dennison C. Thermal unfolding studies of a phytocyanin[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta,2008,1784(12):1997−2003. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2008.07.005
[7] Dennison C,Harrison MD,Lawler AT. Alkaline transition of phytocyanins:a comparison of stellacyanin and umecyanin[J]. Biochem J,2003,371(Pt 2):377−383.
[8] Harrison MD,Yanagisawa S,Dennison C. Investigating the cause of the alkaline transition of phytocyanins[J]. Biochemistry,2005,44(8):3056−3064. doi: 10.1021/bi048256v
[9] Battistuzzi G,Bellei M,Dennison C,Di Rocco G,Sato K,et al. Thermodynamics of the alkaline transition in phytocyanins[J]. J Biol Inorg Chem,2007,12(6):895−900. doi: 10.1007/s00775-007-0245-7
[10] Ma HL,Zhao HM,Liu Z,Zhao J. The phytocyanin gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.):genome-wide identification,classification and transcriptional analysis[J]. PLoS One,2011,6(10):e25184. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025184
[11] Nersissian AM,Valentine JS,Immoos C,Hill MG,Hart PJ,et al. Uclacyanins,stellacyanins,and plantacyanins are distinct subfamilies of phytocyanins:plant-specific mononuclear blue copper proteins[J]. Protein Sci,1998,7(9):1915−1929. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560070907
[12] Buitrón S. The role of the small GTPases and the Phytocyanins during secondary cell wall synthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana[D]. Manchester:The University of Manchester,2018:188.
[13] Tello J,Torres-Pérez R,Flutre T,Grimplet J,Ibáñez J. VviUCC1 Nucleotide diversity,linkage disequilibrium and association with rachis architecture traits in grapevine[J]. Genes (Basel),2020,11(6):598. doi: 10.3390/genes11060598
[14] Reyt G,Chao ZF,Flis P,Salas-González I,Castrillo G, et al. Uclacyanin proteins are required for lignified nanodomain formation within casparian strips[J]. Curr Biol,2020,30(20):4103−4111. e6.
[15] Harrison MD,Dennison C. Characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana stellacyanin:a comparison with umecyanin[J]. Proteins,2004,55(2):426−435. doi: 10.1002/prot.20017
[16] Schininà ME,Maritano S,Barra D,Mondovì B,Marchesini A. Mavicyanin,a stellacyanin-like protein from zucchini peelings:primary structure and comparison with other cupredoxins[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta,1996,1297(1):28−32. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(96)00079-9
[17] Hart PJ,Eisenberg D,Nersissian AM,Valentine JS,Herrmann RG,Nalbandyan RM. A missing link in cupredoxins:crystal structure of cucumber stellacyanin at 1.6 Å resolution[J]. Protein Sci,1996,5(11):2175−2183. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560051104
[18] Lan YG,Zhang KM,Wang YM,Wu J,Lin M,et al. Comparative analysis of the stellacyanins (SCs) family and focus on drought resistance of PtSC18 in Populus trichocarpa[J]. Gene,2022,813:146106. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2021.146106
[19] Pan JW,Huang DH,Guo ZL,Kuang Z,Zhang H,et al. Overexpression of microRNA408 enhances photosynthesis,growth,and seed yield in diverse plants[J]. J Integr Plant Biol,2018,60(4):323−340. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12634
[20] Dong J,Kim ST,Lord EM. Plantacyanin plays a role in reproduction in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Physiol,2005,138(2):778−789. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.063388
[21] Hao C,Yang YZ,Du JM,Deng XW,Li L. The PCY-SAG14 phytocyanin module regulated by PIFs and miR408 promotes dark-induced leaf senescence in Arabidopsis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2022,119(3):e2116623119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2116623119
[22] Zhang F,Zhang YC,Zhang JP,Yu Y,Zhou YF,et al. Rice UCL8,a plantacyanin gene targeted by miR408,regulates fertility by controlling pollen tube germination and growth[J]. Rice,2018,11(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12284-018-0253-y
[23] Greene EA,Erard M,Dedieu A,Barker DG. MtENOD16 and 20 are members of a family of phytocyanin-related early nodulins[J]. Plant Mol Biol,1998,36(5):775−783. doi: 10.1023/A:1005916821224
[24] 王玉洁. MtENOD20在蒺藜苜蓿共生固氮过程中的功能研究[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2019:32. [25] Mashiguchi K,Asami T,Suzuki Y. Genome-wide identification,structure and expression studies,and mutant collection of 22 early nodulin-like protein genes in Arabidopsis[J]. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,2009,73(11):2452−2459. doi: 10.1271/bbb.90407
[26] Cao J,Li X,Lv YQ,Ding LN. Comparative analysis of the phytocyanin gene family in 10 plant species:a focus on Zea mays[J]. Front Plant Sci,2015,6:515.
[27] Sun YL,Wu ZF,Wang YJ,Yang JY,Wei GH,Chou MX. Identification of phytocyanin gene family in legume plants and their involvement in nodulation of Medicago truncatula[J]. Plant Cell Physiol,2019,60(4):900−915. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcz007
[28] Li J,Gao GZ,Zhang TY,Wu XM. The putative phytocyanin genes in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L.):genome-wide identification,classification and expression analysis[J]. Mol Genet Genomics,2013,288(1-2):1−20. doi: 10.1007/s00438-012-0726-4
[29] 张帅,林科运,侯纯朴,方玉洁,王幼平. 甘蓝型油菜phytocyanin家族全基因组鉴定和表达分析[J]. 中国油料作物学报,2022,44(1):116−129. Zhang S,Lin KY,Hou CP,Fang YJ,Wang YP. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of phytocyanin family in Brassica napus[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences,2022,44(1):116−129.
[30] Zhang M,Wang XF,Yang J,Wang ZC,Chen B, et al. GhENODL6 isoforms from the phytocyanin gene family regulated verticillium wilt resistance in cotton[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2022,23(6):2913.
[31] Bilal Tufail M,Yasir M,Zuo DY,Cheng HL,Ali M,et al. Identification and characterization of phytocyanin family genes in cotton genomes[J]. Genes,2023,14(3):611. doi: 10.3390/genes14030611
[32] 宋争,李潞滨,梁立雄,王涛. 铁皮石斛phytocyanin基因家族全基因组分析[J]. 林业科学研究,2018,31(2):98−106. Song Z,Li LB,Liang LX,Wang T. Genome-wide analysis of phytocyanin gene family in Dendrobium officinale[J]. Forest Research,2018,31(2):98−106.
[33] Xu L,Wang XJ,Wang T,Li LB. Genome-wide identification,classification,and expression analysis of the phytocyanin gene family in Phalaenopsis equestris[J]. Biol Plant,2017,61(3):445−452. doi: 10.1007/s10535-017-0716-9
[34] Luo SS,Hu WF,Wang Y,Liu B,Yan HW,Xiang Y. Genome-wide identification,classification,and expression of phytocyanins in Populus trichocarpa[J]. Planta,2018,247(5):1133−1148. doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-2849-2
[35] Wang L,Zhang JY,Li HC,Zhang GZ,Hu DD,et al. Genome-wide identification of the phytocyanin gene family and its potential function in salt stress in soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.)[J]. Agronomy,2023,13(10):2484. doi: 10.3390/agronomy13102484
[36] 孙亚丽. 豆科植物Phytocyanin基因家族分析及其在蒺藜苜蓿结瘤过程中的功能研究[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2019:17. [37] Guss JM,Merritt EA,Phizackerley RP,Freeman HC. The structure of a phytocyanin,the basic blue protein from cucumber,refined at 1.8 Å resolution[J]. J Mol Biol,1996,262(5):686−705. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0545
[38] Huang HT,Miao YJ,Zhang YT,Huang L,Cao JS,Lin SE. Comprehensive analysis of arabinogalactan protein-encoding genes reveals the involvement of three BrFLA genes in pollen germination in Brassica rapa[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2021,22(23):13142. doi: 10.3390/ijms222313142
[39] 马浩力,余礼,梁荣洪,赵洁. 高等植物阿拉伯半乳糖蛋白的功能研究[J]. 中国科学:生命科学,2015,45(2):113−123. doi: 10.1360/N052014-00295 Ma HL,Yu L,Liang RH,Zhao J. Functional studies of arabinogalactan proteins in higher plants[J]. Scientia Sinica Vitae,2015,45(2):113−123. doi: 10.1360/N052014-00295
[40] 李莹. 棉花(Gossypium hirsutum)蓝铜蛋白BCP4在纤维细胞伸长中的功能研究[D]. 武汉:华中师范大学,2015:52. [41] Sun MZ,Yang JK,Cai XX,Shen Y,Cui N,et al. The opposite roles of OsmiR408 in cold and drought stress responses in Oryza sativa[J]. Mol Breed,2018,38(10):120. doi: 10.1007/s11032-018-0877-z
[42] Li HJ,Kim YJ,Yang L,Liu Z,Zhang J,et al. Grass-specific EPAD1 is essential for pollen exine patterning in rice[J]. Plant Cell,2020,32(12):3961−3977. doi: 10.1105/tpc.20.00551
[43] Liu C,Shen LP,Xiao Y,Vyshedsky D,Peng C,et al. Pollen PCP-B peptides unlock a stigma peptide-receptor kinase gating mechanism for pollination[J]. Science,2021,372(6538):171−175. doi: 10.1126/science.abc6107
[44] Zhang YC,He RR,Lian JP,Zhou YF,Zhang F,et al. OsmiR528 regulates rice-pollen intine formation by targeting an uclacyanin to influence flavonoid metabolism[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2020,117(1):727−732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1810968117
[45] Zhang JP,Yu Y,Feng YZ,Zhou YF,Zhang F,et al. MiR408 regulates grain yield and photosynthesis via a phytocyanin protein[J]. Plant Physiol,2017,175(3):1175−1185. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.01169
[46] Nakayama T,Shinohara H,Tanaka M,Baba K,Ogawa-Ohnishi M,Matsubayashi Y. A peptide hormone required for Casparian strip diffusion barrier formation in Arabidopsis roots[J]. Science,2017,355(6322):284−286. doi: 10.1126/science.aai9057
[47] 崔亚宁,满奕,宋程威,张曦,钱虹萍,林金星. 植物凯氏带化学成分、生理功能及相关调控机制的研究进展[J]. 中国科学:生命科学,2020,50(2):102−110. doi: 10.1360/SSV-2019-0205 Cui YN,Man Y,Song CW,Zhang X,Qian HP,Lin JX. Chemical components,physiological functions and regulation mechanism of plant Casparian strips[J]. Scientia Sinica Vitae,2020,50(2):102−110. doi: 10.1360/SSV-2019-0205
[48] 翁群清,郑秀娟,解慧芳,孙新立. 植物凯氏带形成分子机制及功能特点的研究进展[J]. 西北植物学报,2017,37(7):1450−1456. Weng QQ,Zheng XJ,Xie HF,Sun XL. Molecular mechanism of formation and functional characteristics of Casparian strip[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2017,37(7):1450−1456.
[49] Li PX,Yu QZ,Gu X,Xu CM,Qi SL, et al. Construction of a functional casparian strip in non-endodermal lineages is orchestrated by two parallel signaling systems in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Curr Biol,2018,28(17):2777−2786. e2.
[50] Zhuang Y,Zuo DQ,Tao YH,Cai HQ,Li L. Laccase3-based extracellular domain provides possible positional information for directing Casparian strip formation in Arabidopsis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2020,117(27):15400−15402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2005429117
[51] Guo YF,Ren GD,Zhang KW,Li ZH,Miao Y,Guo HW. Leaf senescence:progression,regulation,and application[J]. Mol Hortic,2021,1(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s43897-021-00006-9
[52] Ahmad S,Guo YF. Signal transduction in leaf senescence:progress and perspective[J]. Plants (Basel),2019,8(10):405. doi: 10.3390/plants8100405
[53] Kumar V,Kumar Srivastava A,Wani SH,Shriram V,Penna S. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms regulating salt tolerance in plants[J]. Physiol Plant,2021,173(4):1291−1294. doi: 10.1111/ppl.13592
[54] Nahar S,Sahoo L,Tanti B. Screening of drought tolerant rice through morpho-physiological and biochemical approaches[J]. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol,2018,15:150−159. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2018.06.002
[55] Li WM,Wang YJ,Ren H,Guo ZH,Li N,et al. Transcriptomic and physiological analyses identifying Lanzhou lily (Lilium davidii var. unicolor) drought adaptation strategies[J]. Hortic Plant J,2023,9(1):145−157. doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2022.03.003
[56] Saji S,Saji H,Sage-Ono K,Ono M,Nakajima N,Aono M. Phytocyanin-encoding genes confer enhanced ozone tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Sci Rep,2022,12(1):21204. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25706-0
[57] Ezaki B,Gardner RC,Ezaki Y,Matsumoto H. Expression of aluminum-induced genes in transgenic Arabidopsis plants can ameliorate aluminum stress and/or oxidative stress[J]. Plant Physiol,2000,122(3):657−666. doi: 10.1104/pp.122.3.657
[58] Xie KL,Li LL,Zhang HH,Wang R,Tan XX,et al. Abscisic acid negatively modulates plant defence against rice black-streaked dwarf virus infection by suppressing the jasmonate pathway and regulating reactive oxygen species levels in rice[J]. Plant Cell Environ,2018,41(10):2504−2514. doi: 10.1111/pce.13372
[59] Mo HJ,Wang XF,Zhang Y,Zhang GY,Zhang JF,Ma ZY. Cotton polyamine oxidase is required for spermine and camalexin signalling in the defence response to Verticillium dahliae[J]. Plant J,2015,83(6):962−975. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12941
[60] Shaban M,Miao YH,Ullah A,Khan AQ,Menghwar H,et al. Physiological and molecular mechanism of defense in cotton against Verticillium dahliae[J]. Plant Physiol Biochem,2018,125:193−204. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.02.011
-
其他相关附件
-
压缩文件
贾雁茹-附件 点击下载(339KB)
-



 下载:
下载: