Application and prospects of spatial metabolomics technology in plant research
-
摘要:
空间代谢组技术是一种整合了质谱成像和代谢组学的新兴研究技术,该项技术可以获得生物组织中大量已知或未知内源性代谢物分子的结构、含量和空间分布信息,精准定位组织中的代谢物分布,对揭示植物代谢物的合成、积累和调控机理至关重要。本文介绍了空间代谢组技术的研究现状,重点综述了空间代谢组技术在植物组织研究方面的前沿应用,探讨了空间代谢组技术在植物单细胞水平研究领域中的应用与挑战,以期为研究植物生长发育及空间代谢网络的调控提供新的途径,为解决农业生产、植物能源开发等领域的问题提供关键支持。
Abstract:Spatial metabolomics is an emerging research technology that integrates mass spectrometry imaging and metabolomics to analyze the structure, concentration, and spatial distribution of endogenous metabolites within biological tissues. This approach enables the acquisition of both known and unknown metabolite information at high spatial resolution, allowing for precise localization within tissues. It is crucial for elucidating the synthesis, accumulation, and regulation of plant metabolites. This article reviews the current research status of spatial metabolomics technology, with a focus on cutting-edge applications in plant tissue research. Special attention is given to its potential and challenges in the field of single-cell plant studies, aiming to provide new avenues for studying plant growth and development and regulating spatial metabolic networks. Additionally, this technology offers crucial insights for solving problems in agricultural production, plant-based energy development, and other fields.
-
-
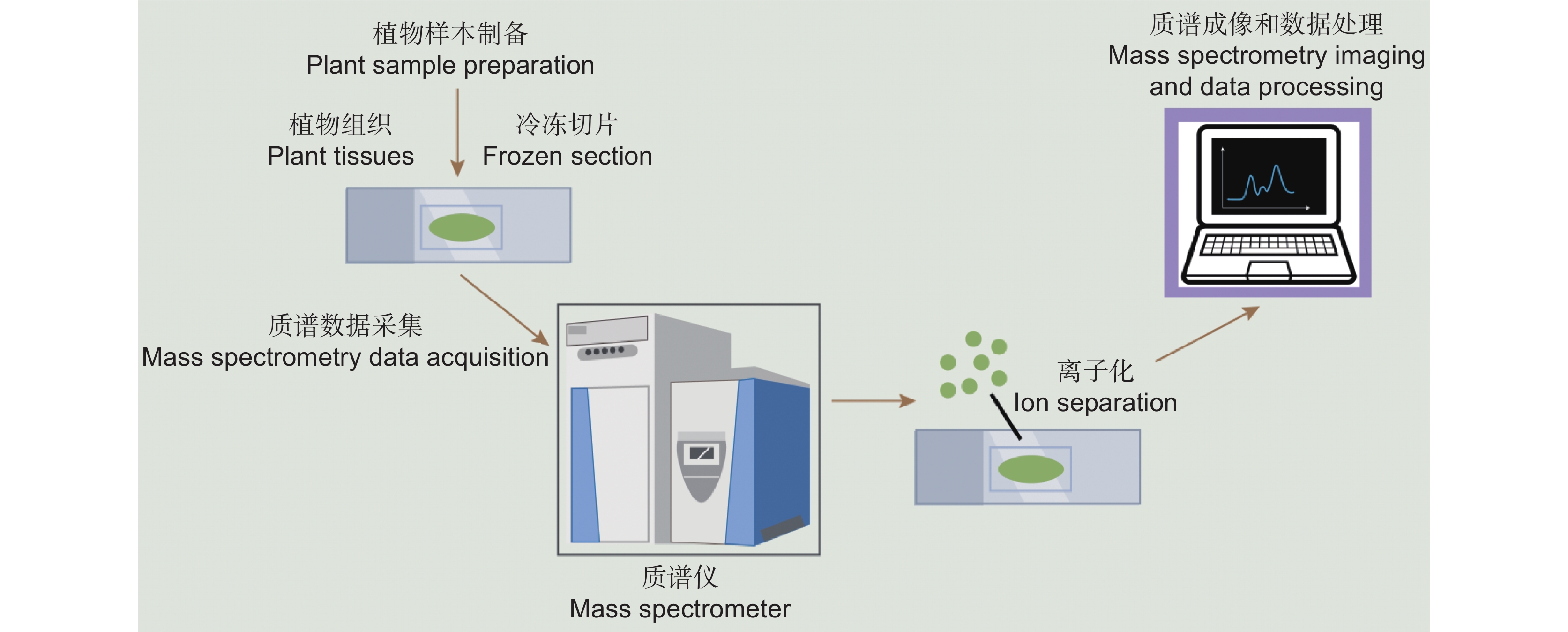
表 1 常见质谱成像技术特点
Table 1 Characteristics of common mass spectrometry imaging techniques
技术类型
Technology type缩写
Abbreviation检测物质
Testing substances空间分辨率
Spatial resolution是否需要基质
Matrix二次离子质谱成像 SIMS 分子量小于1 000 Da的脂质、代谢物 0.05~100 μm 否 解吸电喷雾电离质谱成像 DESI-MSI 代谢物的分子量为0~2 000 Da 50 μm 否 激光溅射-电喷雾电离质谱成像 LA-ESI-MSI 植物细胞的整体分析和较大植物组织的成像分析 30~300 μm 否 基质辅助激光解吸/电离质谱成像 MALDI-MSI 蛋白、多肽、脂质 5 μm 是 表 2 空间代谢组技术在植物研究中的应用汇总
Table 2 Summary of applications of spatially resolved metabolomics in plant research
物种
Plant species代谢组技术
Metabolomics technology组织
Tissues成像代谢物质
Imaging metabolites文献
Reference玉米 Zea mays L. MALDI-MSI 种子 糖类、氨基酸类、脂质类 [22] 水稻 Oryza sativa L. MALDI-MSI、GC-MS 种子 γ-氨基丁酸、氨基酸 [37] 茶 Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze DESI-MSI 叶、根 ECG/CG、EGCG/GCG、没食子酸、EC/C、EGC/GC、assamicain A、L-茶氨酸和缬氨酸 [38] 马铃薯 Solanum tuberosum L. MALDI-MSI 块茎 糖基生物碱 [39] 牡丹Paeonia suffruticosa Andr.、
芍药Paeonia lactiflora Pall.MALDI-MSI、LC-MS 根 单萜、丹皮酚苷类、鞣质类、
黄酮类、糖类和脂类[40] 银杏 Ginkgo biloba L. MALDI/LDI MSI 叶 黄酮、银杏酸、腰果酚、糖类、磷脂和叶绿素 [41] 长春花 Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don MALDI-MSI 花 生物碱 [42] 香蕉 Musa nana Lour. MALDI-TOF、GC-MS 果实 糖类、氨基酸和单胺类 [43] 蓝莓 Vaccinium spp. LA-ESI-MSI 果皮 花青素 [44] 草莓 Fragaria ananassa Duch. MALDI-TOF IMS 果实 柠檬酸、可溶性糖和花青素 [45] 枸杞 Lycium chinense Miller MALDI-MSI 果实 柠檬酸、己糖 [46] 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum L. MALDI-MSI 果实 甾体糖苷类生物碱、花青素和甜菜素 [47] 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh DESI-MSI 叶 茉莉酸、水杨酸、脱落酸和生长素 [49] 板蓝根 Isatis tinctoria L. DESI-MSI 根 3-醛基吲哚、吲哚酚、直铁线莲宁B、
胆碱、L-精氨酸、多巴胺和吡咯素[54] 人参 Panax ginseng C. A. Mey MALDI-MSI 根 皂苷 [56] 雷公藤 Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. MALDI-MSI 根 三萜类化合物、雷公藤红素、
倍半萜吡啶生物碱[57] 丹参Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge DESI-MSI 根、叶 酚酸、丹参酮、琥珀酸和柠檬酸 [58] 光果甘草 Glycyrrhiza glabra L. MALDI-MSI 根茎 三萜皂苷和黄酮 [59] 白芍 Paeonia lactiflora Pall. MALDI-MSI 根 没食子酸鞣质 [60] 灵芝 Ganoderma lucidum (Curtis) P. Karst. LC-MS、DESI-MSI 子实体 灵芝酸 [61] -
[1] Wurtzel ET,Kutchan TM. Plant metabolism,the diverse chemistry set of the future[J]. Science,2016,353(6305):1232−1236. doi: 10.1126/science.aad2062
[2] Etalo DW,de Vos RCH,Joosten MHAJ,Hall RD. Spatially resolved plant metabolomics:some potentials and limitations of laser-ablation electrospray ionization mass spectrometry metabolite imaging[J]. Plant Physiol,2015,169(3):1424−1435. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01176
[3] Petras D,Jarmusch AK,Dorrestein PC. From single cells to our planet-recent advances in using mass spectrometry for spatially resolved metabolomics[J]. Curr Opin Chem Biol,2017,36:24−31. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2016.12.018
[4] DeBerardinis RJ,Keshari KR. Metabolic analysis as a driver for discovery,diagnosis,and therapy[J]. Cell,2022,185(15):2678−2689. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.029
[5] Lee YJ,Perdian DC,Song ZH,Yeung ES,Nikolau BJ. Use of mass spectrometry for imaging metabolites in plants[J]. Plant J,2012,70(1):81−95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.04899.x
[6] Johnson CH,Ivanisevic J,Siuzdak G. Metabolomics:beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,2016,17(7):451−459. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.25
[7] Jun D,Feng YQ. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics for clinical study:recent progresses and applications[J]. TrAC Trends Anal Chem,2023,158:116896. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2022.116896
[8] Beccaria M,Cabooter D. Current developments in LC-MS for pharmaceutical analysis[J]. Analyst,2020,145(4):1129−1157. doi: 10.1039/C9AN02145K
[9] Nagana Gowda GA,Raftery D. NMR-based metabolomics[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol,2021,1280:19−37.
[10] 郭凤丹,王兴军,侯蕾,赵术珍,厉广辉,夏晗. 植物代谢组学研究进展[J]. 山东农业科学,2017,49(12):154−162. Guo FD,Wang XJ,Hou L,Zhao SZ,Li GH,Xia H. Research progress of metabolomics in plants[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences,2017,49(12):154−162.
[11] Ma X,Fernández FM. Advances in mass spectrometry imaging for spatial cancer metabolomics[J]. Mass Spectrom Rev,2024,43(2):235−268. doi: 10.1002/mas.21804
[12] Dyar KA,Eckel-Mahan KL. Circadian metabolomics in time and space[J]. Front Neurosci,2017,11:369. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00369
[13] 王希,汤冬娥,蔡晚霞,尹良红,戴勇. 空间代谢组学研究进展[J]. 临床医学工程,2021,28(S1):36−40. Wang X,Tang DE,Cai WX,Yin LH,Dai Y. Research process in spatially resolved metabolomics[J]. Clinical Medicine & Engineering,2021,28(S1):36−40.
[14] Emwas AH. The strengths and weaknesses of NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry with particular focus on metabolomics research[J]. Methods Mol Biol,2015,1277:161−193.
[15] Markley JL,Brüschweiler R,Edison AS,Eghbalnia HR,Powers R,et al. The future of NMR-based metabolomics[J]. Curr Opin Biotechnol,2017,43:34−40. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2016.08.001
[16] Buchberger AR,DeLaney K,Johnson J,Li LJ. Mass spectrometry imaging:a review of emerging advancements and future insights[J]. Anal Chem,2018,90(1):240−265. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04733
[17] He MJ,Pu WJ,Wang X,Zhang W,Tang D,Dai Y. Comparing DESI-MSI and MALDI-MSI mediated spatial metabolomics and their applications in cancer studies[J]. Front Oncol,2022,12:891018. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.891018
[18] 张琦玥,聂洪港. 质谱成像技术的研究进展[J]. 分析仪器,2018(5):1−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-232x.2018.05.001 Zhang QY,Nie HG. Advances in mass spectrometry imaging technology[J]. Analytical Instrumentation,2018(5):1−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-232x.2018.05.001
[19] Qin L,Zhang YW,Liu YQ,He HX,Han MM,et al. Recent advances in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI) for in situ analysis of endogenous molecules in plants[J]. Phytochem Anal,2018,29(4):351−364. doi: 10.1002/pca.2759
[20] 再帕尔·阿不力孜. 质谱分子成像技术与应用进展[J]. 分析测试学报,2022,41(9):1335−1344 Zeper·Abliz. Progress on mass spectrometry imaging technology and its application[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2022,41(9):1335−1344.
[21] Fujimura Y,Miura D. MALDI mass spectrometry imaging for visualizing in situ metabolism of endogenous metabolites and dietary phytochemicals[J]. Metabolites,2014,4(2):319−346. doi: 10.3390/metabo4020319
[22] Yin ZB,Huang WJ,Fernie AR,Yan SJ. Mass spectrometry imaging techniques:a versatile toolbox for plant metabolomics[J]. Trends Plant Sci,2023,28(2):250−251. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2022.10.009
[23] Tuck M,Grélard F,Blanc L,Desbenoit N. MALDI-MSI towards multimodal imaging:challenges and perspectives[J]. Front Chem,2022,10:904688. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.904688
[24] Anderton CR,Gamble LJ. Secondary ion mass spectrometry imaging of tissues,cells,and microbial systems[J]. Microsc Today,2016,24(2):24−31. doi: 10.1017/S1551929516000018
[25] Marin Carbonne J,Kiss A,Bouvier AS,Meibom A,Baumgartner L,et al. Surface analysis by Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS):principles and applications from Swiss laboratories[J]. Chimia,2022,76(1-2):26−33. doi: 10.2533/chimia.2022.26
[26] Tian H,Six DA,Krucker T,Leeds JA,Winograd N. Subcellular chemical imaging of antibiotics in single bacteria using C60-secondary ion mass spectrometry[J]. Anal Chem,2017,89(9):5050−5057. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b00466
[27] Qi KK,Wu LT,Liu CY,Pan Y. Recent advances of ambient mass spectrometry imaging and its applications in lipid and metabolite analysis[J]. Metabolites,2021,11(11):780. doi: 10.3390/metabo11110780
[28] 殷志斌,黄文洁,伍欣宙,晏石娟. 空间分辨代谢组学进展和挑战[J]. 生物技术通报,2021,37(1):32−51. Yin ZB,Huang WJ,Wu XZ,Yan SJ. Spatially resolved metabolomics:progress and challenges[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin,2021,37(1):32−51.
[29] Coello Y,Jones AD,Gunaratne TC,Dantus M. Atmospheric pressure femtosecond laser imaging mass spectrometry[J]. Anal Chem,2010,82(7):2753−2758. doi: 10.1021/ac9026466
[30] Shrestha B,Patt JM,Vertes A. In situ cell-by-cell imaging and analysis of small cell populations by mass spectrometry[J]. Anal Chem,2011,83(8):2947−2955. doi: 10.1021/ac102958x
[31] Tanaka K,Waki H,Ido Y,Akita S,Yoshida Y,et al. Protein and polymer analyses up to m/z 100 000 by laser ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom,1988,2(8):151−153. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1290020802
[32] Zhu XP,Xu TY,Peng C,Wu SH. Advances in MALDI mass spectrometry imaging single cell and tissues[J]. Front Chem,2022,9:782432. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.782432
[33] He JJ,Luo ZG,Huang L,He JM,Chen Y,et al. Ambient mass spectrometry imaging metabolomics method provides novel insights into the action mechanism of drug candidates[J]. Anal Chem,2015,87(10):5372−5379. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00680
[34] Hieta JP,Kopra J,Räikkönen H,Kauppila TJ,Kostiainen R. Sub-100 μm spatial resolution ambient mass spectrometry imaging of rodent brain with Laser Ablation Atmospheric Pressure Photoionization (LAAPPI) and Laser Ablation Electrospray Ionization (LAESI)[J]. Anal Chem,2020,92(20):13734−13741. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c01597
[35] Huang MZ,Cheng SC,Cho YT,Shiea J. Ambient ionization mass spectrometry:a tutorial[J]. Anal Chim Acta,2011,702(1):1−15. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2011.06.017
[36] Jorge TF,Mata AT,António C. Mass spectrometry as a quantitative tool in plant metabolomics[J]. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci,2016,374(2079):20150370.
[37] Kamjijam B,Suwannaporn P,Bednarz H,Na Jom K,Niehaus K. Elevation of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and essential amino acids in vacuum impregnation mediated germinated rice traced by MALDI imaging[J]. Food Chem,2021,365:130399. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130399
[38] Liao YY,Fu XM,Zhou HY,Rao W,Zeng LT,Yang ZY. Visualized analysis of within-tissue spatial distribution of specialized metabolites in tea (Camellia sinensis) using desorption electrospray ionization imaging mass spectrometry[J]. Food Chem,2019,292:204−210. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.04.055
[39] Deng YM,He MY,Feng F,Feng XS,Zhang Y,Zhang F. The distribution and changes of glycoalkaloids in potato tubers under different storage time based on MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry imaging[J]. Talanta,2021,221:121453. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121453
[40] Li B,Ge JY,Liu W,Hu DJ,Li P. Unveiling spatial metabolome of Paeonia suffruticosa and Paeonia lactiflora roots using MALDI MS imaging[J]. New Phytol,2021,231(2):892−902. doi: 10.1111/nph.17393
[41] Li B,Neumann EK,Ge JY,Gao W,Yang H,et al. Interrogation of spatial metabolome of Ginkgo biloba with high-resolution matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization and laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging[J]. Plant Cell Environ,2018,41(11):2693−2703. doi: 10.1111/pce.13395
[42] Dutkiewicz EP,Su CH,Lee HJ,Hsu CC,Yang YL. Visualizing vinca alkaloids in the petal of Catharanthus roseus using functionalized titanium oxide nanowire substrate for surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry[J]. Plant J,2021,105(4):1123−1133. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15092
[43] Yin ZB,Dong T,Huang WJ,Du MY,Chen D,et al. Spatially resolved metabolomics reveals variety-specific metabolic changes in banana pulp during postharvest senescence[J]. Food Chem X,2022,15:100371. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2022.100371
[44] Berisha A,Dold S,Guenther S,Desbenoit N,Takats Z,et al. A comprehensive high-resolution mass spectrometry approach for characterization of metabolites by combination of ambient ionization,chromatography and imaging methods[J]. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom,2014,28(16):1779−1791. doi: 10.1002/rcm.6960
[45] Wang J,Yang E,Chaurand P,Raghavan V. Visualizing the distribution of strawberry plant metabolites at different maturity stages by MALDI-TOF imaging mass spectrometry[J]. Food Chem,2021,345:128838. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128838
[46] Zhao WH,Zhang YD,Shi YP. Visualizing the spatial distribution of endogenous molecules in wolfberry fruit at different development stages by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging[J]. Talanta,2021,234:122687. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122687
[47] Dong YH,Sonawane P,Cohen H,Polturak G,Feldberg L,et al. High mass resolution,spatial metabolite mapping enhances the current plant gene and pathway discovery toolbox[J]. New Phytol,2020,228(6):1986−2002. doi: 10.1111/nph.16809
[48] 张凤,陈伟. 代谢组学在植物逆境生物学中的研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报,2021,37(8):1−11 Zhang F,Chen W. Research progress of metabolomics in plant stress biology[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin,2021,37(8):1−11.
[49] Zhang C,Žukauskaitė A,Petřík I,Pěnčík A,Hönig M, et al. In situ characterisation of phytohormones from wounded Arabidopsis leaves using desorption electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry imaging[J]. Analyst,2021,146(8):2653−2663.
[50] Dai WD,Hu ZY,Xie DC,Tan JF,Lin Z. A novel spatial-resolution targeted metabolomics method in a single leaf of the tea plant (Camellia sinensis)[J]. Food Chem,2020,311:126007. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.126007
[51] 黄烈岩,聂黎行,董静,杨学欣,贾晓飞,姚令文. 质谱成像技术在中药研究中的应用现状[J]. 药物分析杂志,2022,42(10):1675−1689. Huang LY,Nie LX,Dong J,Yang XX,Jia XF,Yao LW. Recent application of mass spectrometry imaging in traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis,2022,42(10):1675−1689.
[52] Cobice DF,Goodwin RJA,Andren PE,Nilsson A,Mackay CL,Andrew R. Future technology insight:mass spectrometry imaging as a tool in drug research and development[J]. Br J Pharmacol,2015,172(13):3266−3283. doi: 10.1111/bph.13135
[53] 赵杰,冯素香. 空间代谢组学在中药研究中的应用[J]. 中草药,2023,54(20):6569−6579. Zhao J,Feng SX. Application of spatial metabolomics in traditional Chinese medicine research[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2023,54(20):6569−6579.
[54] Nie LX,Dong J,Huang LY,Qian XY,Lian CJ,et al. Microscopic mass spectrometry imaging reveals the distribution of phytochemicals in the dried root of Isatis tinctoria[J]. Front Pharmacol,2021,12:685575. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.685575
[55] Nie LX,Huang LY,Wang XP,Lv LF,Yang XX,et al. Desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging illustrates the quality characters of Isatidis radix[J]. Front Plant Sci,2022,13:897528. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.897528
[56] Bai HR,Wang SJ,Liu JJ,Gao D,Jiang YY,et al. Localization of ginsenosides in Panax ginseng with different age by matrix-assisted laser-desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry imaging[J]. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci,2016,1026:263−271. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.09.024
[57] Lange BM,Fischedick JT,Lange MF,Srividya N,Šamec D,Poirier BC. Integrative approaches for the identification and localization of specialized metabolites in Tripterygium roots[J]. Plant Physiol,2017,173(1):456−469. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01593
[58] Tong Q,Zhang C,Tu Y,Chen JF,Li Q,et al. Biosynthesis-based spatial metabolome of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge by combining metabolomics approaches with mass spectrometry-imaging[J]. Talanta,2022,238:123045. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.123045
[59] Li B,Bhandari DR,Janfelt C,Römpp A,Spengler B. Natural products in Glycyrrhiza glabra (licorice) rhizome imaged at the cellular level by atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization tandem mass spectrometry imaging[J]. Plant J,2014,80(1):161−171. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12608
[60] Li B,Bhandari DR,Römpp A,Spengler B. High-resolution MALDI mass spectrometry imaging of gallotannins and monoterpene glucosides in the root of Paeonia lactiflora[J]. Sci Rep,2016,6:36074. doi: 10.1038/srep36074
[61] Xia J,He XY,Yang W,Song HY,Yang JH,et al. Unveiling the distribution of chemical constituents at different body parts and maturity stages of Ganoderma lingzhi by combining metabolomics with desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging (DESI)[J]. Food Chem,2024,436:137737. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137737
[62] Yu XL,Liu ZX,Sun XW. Single-cell and spatial multi-omics in the plant sciences:technical advances,applications,and perspectives[J]. Plant Commun,2023,4(3):100508. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2022.100508
[63] De Souza LP,Borghi M,Fernie A. Plant single-cell metabolomics-challenges and perspectives[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2020,21(23):8987. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238987
[64] Wei ZW,Xiong XC,Guo CG,Si XY,Zhao YY,et al. Pulsed direct current electrospray:enabling systematic analysis of small volume sample by boosting sample economy[J]. Anal Chem,2015,87(22):11242−11248. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02115
[65] Yamamoto K,Takahashi K,Mizuno H,Anegawa A,Ishizaki K,et al. Cell-specific localization of alkaloids in Catharanthus roseus stem tissue measured with Imaging MS and Single-cell MS[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2016,113(14):3891−3896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1521959113
[66] Huang HJ,Liu HQ,Ma WW,Qin L,Chen LL,et al. High-throughput MALDI-MSI metabolite analysis of plant tissue microarrays[J]. Plant Biotechnol J,2023,21(12):2574−2584. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14154
[67] Qin SJ,Miao DY,Zhang X,Zhang Y,Bai Y. Methods developments of mass spectrometry based single cell metabolomics[J]. TrAC Trends Anal Chem,2023,164:117086. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2023.117086



 下载:
下载:
