Impacts of environmental filtering and dispersal limitation on rare and endangered plant communities of the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China
-
摘要:
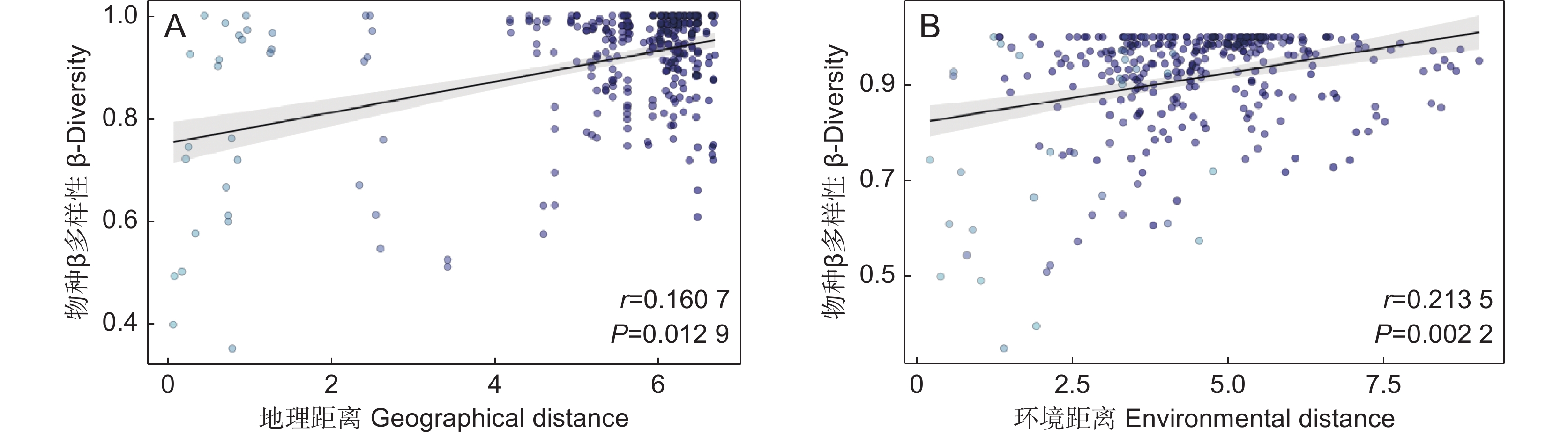
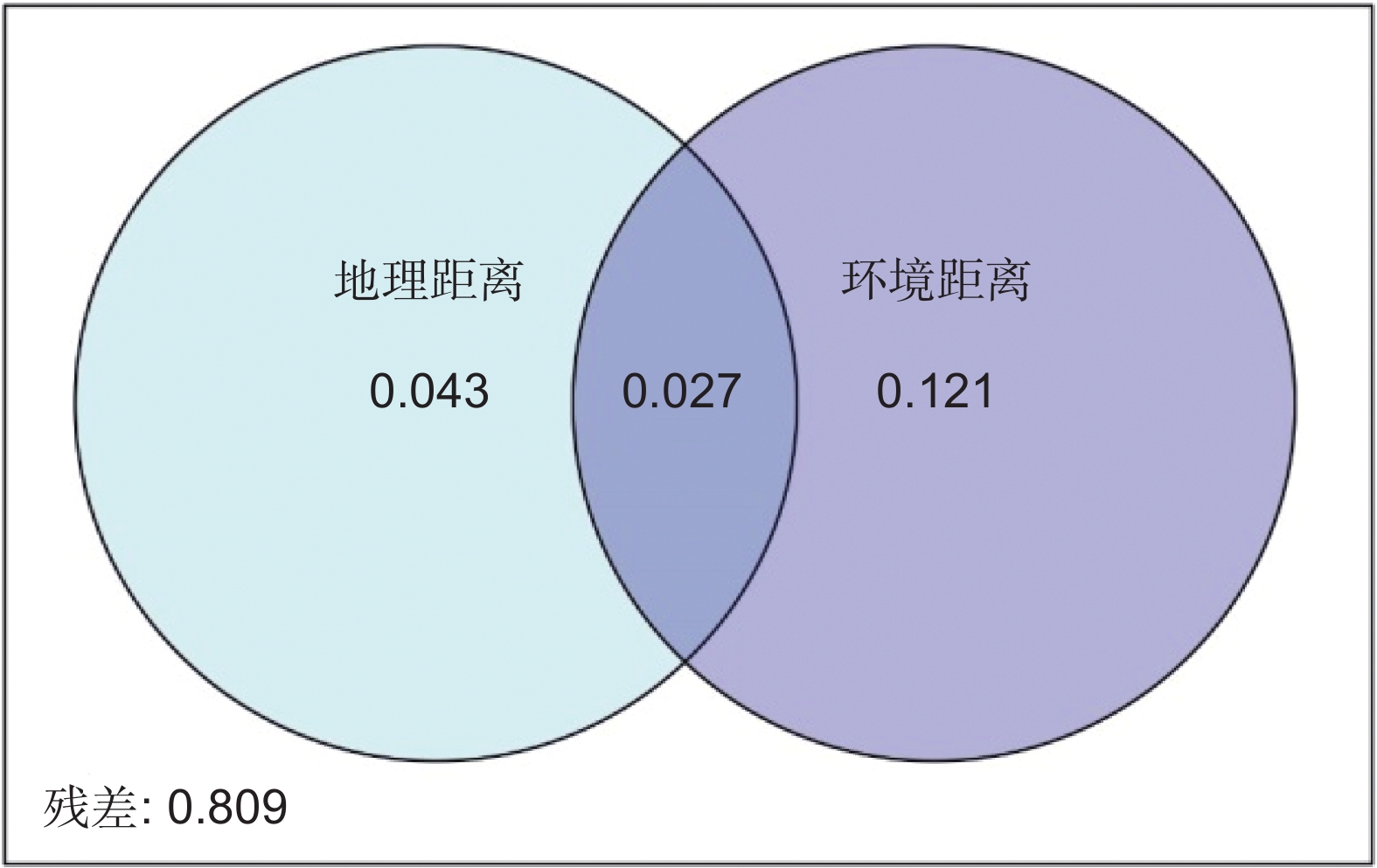
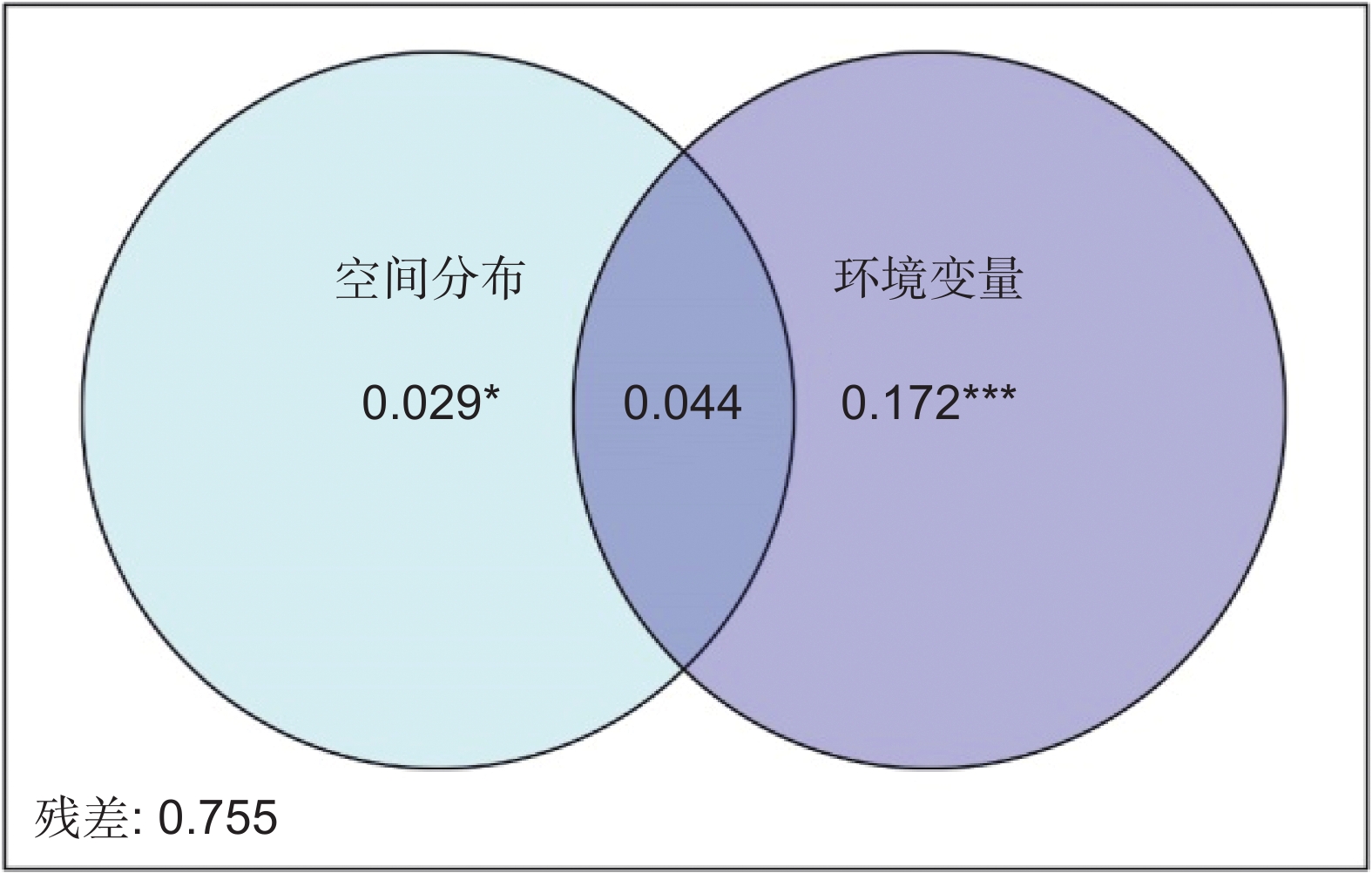
环境过滤和扩散限制是植物群落构建中β多样性形成的重要驱动机制。本研究以我国青藏高原东缘分布的珙桐(Davidia involucrata Baill.)和领春木(Euptelea pleiosperma Hook. f. & Thomson)群落为研究对象,通过分析群落β多样性与地理因素和环境因素的关系,探讨环境过滤和扩散限制在我国青藏高原东缘珍稀濒危植物群落物种周转中的相对作用。结果显示,青藏高原东缘26个珍稀植物群落样方共记录到21种珍稀濒危植物。纬度、海拔、土壤pH值、土壤铵态氮均与群落β多样性呈显著正相关。青藏高原东缘山地珍稀濒危植物群落β多样性与地理距离和环境距离呈显著正相关。基于距离矩阵多元回归(Multiple regressions on distance matrices,MRM)的方差分解结果显示,环境距离和地理距离共同对研究区域珍稀濒危植物群落β多样性做出了19.1%的解释率。基于邻体矩阵主坐标分析(Principal coordinates of neighbor matrices,PCNM)的方差分解结果表明,环境变量和空间距离联合起来对研究区域内珍稀濒危植物群落β多样性提供了24.5%的解释率。总之,环境筛选和扩散限制在塑造青藏高原东缘山地珍稀濒危植物群落方面具有协同作用,其中环境筛选的影响力更为显著。
Abstract:Environmental filtering and dispersal limitation are important drivers of beta-diversity in plant communities. This study investigated the relationships between beta-diversity, geographic distance, and environmental distance in rare and endangered plant communities associated with Davidia involucrata and Euptelea pleiosperma along the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. The aim was to assess the relative contributions of environmental filtering and dispersal limitation on community assembly in these threatened plant assemblages. A total of 21 rare and endangered plant species were recorded across 26 plant communities. Beta-diversity exhibited significant positive correlations with latitude, elevation, soil pH, and soil NH4 concentration. Furthermore, beta-diversity was significantly positively correlated with both geographic and environmental distances. Multiple regression analysis of distance matrices (MRM) indicated that geographic and environmental distances collectively explained 19.1% of the variation in species composition, while principal coordinates of neighbor matrices (PCNM) analysis indicated that these factors explained 24.5% of the variation. Overall, these results suggest that beta-diversity in rare and endangered plant communities along the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is shaped by both environmental filtering and dispersal limitation, with environmental filtering playing a more dominant role in structuring species composition.
-
1 如需查阅附表内容请登录《植物科学学报》网站(http://www.plantscience.cn)查看本期文章。2 如需查阅附表内容请登录《植物科学学报》网站(http://www.plantscience.cn)查看本期文章。 -
表 1 青藏高原东缘领春木和珙桐群落中的珍稀濒危植物名录
Table 1 Rare and endangered species in the plant community associated with Euptelea pleiosperma and Davidia involucrata along the east edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
中文名
Species拉丁名
Latin name科名
FamilyIUCN 红色名录
Red list红皮书
Red data book国家保护植物
National protected大叶柯 Lithocarpus megalophyllus Rehder & E. H. Wilson 壳斗科 近危 是 - - 珙桐 Davidia involucrata Baill. 蓝果树科 - - 是 Ⅰ级 红豆杉 Taxus wallichiana var. chinensis (Pilg.) Florin 红豆杉科 易危 是 - Ⅰ级 胡桃楸 Juglans mandshurica Maxim. 胡桃科 - - 是 - 华榛 Corylus chinensis Franch. 桦木科 - - 是 - 黄杉 Pseudotsuga sinensis Dode 松科 易危 - 是 Ⅱ级 黄檀 Dalbergia hupeana Hance 豆科 近危 是 - - 金钱松 Pseudolarix amabilis (J. Nelson) Rehder 松科 易危 是 是 Ⅱ级 金沙槭 Acer paxii Franch. 无患子科 近危 是 - - 阔叶槭 Acer amplum Rehder 无患子科 近危 是 - - 连香树 Cercidiphyllum japonicum Siebold & Zucc. 连香树科 - - 是 Ⅱ级 领春木 Euptelea pleiosperma Hook. f. & Thomson 领春木科 - - 是 - 楠木 Phoebe zhennan S. K. Lee & F. N. Wei 樟科 易危 是 是 Ⅱ级 润楠 Machilus nanmu (Oliv.) Hemsl. 樟科 濒危 是 - Ⅱ级 山核桃 Carya cathayensis Sarg. 胡桃科 易危 是 - - 山柳 Salix pseudotangii C. Wang & C. Y. Yu 杨柳科 易危 是 - - 山茱萸 Cornus officinalis Siebold & Zucc. 山茱萸科 近危 是 - - 水青树 Tetracentron sinense Oliv. 昆栏树科 - - 是 Ⅱ级 云南旌节花 Stachyurus yunnanensis Franch. 旌节花科 易危 是 - - 长伞梗荚蒾 Viburnum longiradiatum P. S. Hsu & S. W. Fan 五福花科 近危 是 - - 紫果冷杉 Abies recurvata Mast. 松科 易危 是 - - 注:IUCN,世界自然保护联盟(International Union for Conservation of Nature)受威胁物种红色名录(https://www.iucnredlist.org/);红色名录,《中国生物多样性红色名录-高等植物卷》;红皮书,《中国植物红皮书》;国家保护,2021版《国家重点保护野生植物名录》。 Notes: IUCN, Red List of Threatened Species Released by International Union for Conservation of Nature (https://www.iucnredlist.org/); Red list, China’s Red List of Biodiversity-Higher Plants; Red data book, China Red Data Book of Plants; National protected, List of National Key Protected Wild Plants (2021 version). 表 2 环境因子与青藏高原东缘珍稀濒危植物群落β多样性的相关性及其对群落构建的贡献率
Table 2 Correlations between environmental factors and β-diversity index and their contribution rate to rare and endangered plant community assembly along the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
环境因子
Environmental factors相关性
Correlation贡献率
Contribution rater P R2 P 经度 −0.0007 0.9557 0.0144 0.0960 纬度 0.0223 0.0056 0.0471 0.0016 海拔 0.0332 0.0088 0.0274 0.0207 年均温 −0.0079 0.7660 0.0207 0.0541 最冷季均温 −0.0068 0.7766 0.0185 0.0676 最暖季降水 −0.0144 0.1018 0.0077 0.1935 最冷季降水 0.0223 0.0853 0.0345 0.0077 土壤有机质 −0.0036 0.7073 0.0004 0.7866 土壤 0.0230 0.0173 0.0944 0.0001 土壤硝态氮 0.0088 0.3784 0.0609 0.0009 土壤铵态氮 0.0181 0.0086 0.0725 0.0003 土壤有效磷 −0.0029 0.7538 0.0048 0.3326 -
[1] Whittaker RH. Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains,Oregon and California[J]. Ecol Monogr,1960,30(3):279−338. doi: 10.2307/1943563
[2] Soininen J,Lennon JJ,Hillebrand H. A multivariate analysis of beta diversity across organisms and environments[J]. Ecology,2007,88(11):2830−2838. doi: 10.1890/06-1730.1
[3] Qian H,Shimono A. Effects of geographic distance and climatic dissimilarity on species turnover in alpine meadow communities across a broad spatial extent on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Plant Ecol,2012,213(8):1357−1364. doi: 10.1007/s11258-012-0095-4
[4] He JK,Lin HX,Wang RX,Dai C,Yu HY,et al. Joint effects of environmental filtering and dispersal limitation on the species assemblage of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. J Biogeogr,2022,49(4):640−653. doi: 10.1111/jbi.14328
[5] Hubbell SP. The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography[M]. Princeton:Princeton University Press,2001:392.
[6] Gilbert B,Lechowicz MJ. Neutrality,niches,and dispersal in a temperate forest understory[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2004,101(20):7651−7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400814101
[7] 牛克昌,刘怿宁,沈泽昊,何芳良,方精云. 群落构建的中性理论和生态位理论[J]. 生物多样性,2009,17(6):579−593. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09142 Niu KC,Liu YN,Shen ZH,He FL,Fang JY. Community assembly:the relative importance of neutral theory and niche theory[J]. Biodiversity Science,2009,17(6):579−593. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09142
[8] Liu YN,Tang ZY,Fang JY. Contribution of environmental filtering and dispersal limitation to species turnover of temperate deciduous broad-leaved forests in China[J]. Appl Veg Sci,2015,18(1):34−42. doi: 10.1111/avsc.12101
[9] Page NV,Shanker K. Environment and dispersal influence changes in species composition at different scales in woody plants of the Western Ghats,India[J]. J Veg Sci,2018,29(1):74−83. doi: 10.1111/jvs.12586
[10] Condit R,Pitman N,Leigh Jr EG,Chave J,Terborgh J,et al. Beta-diversity in tropical forest trees[J]. Science,2002,295(5555):666−669. doi: 10.1126/science.1066854
[11] Nekola JC,White PS. The distance decay of similarity in biogeography and ecology[J]. J Biogeog,1999,26(4):867−878. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2699.1999.00305.x
[12] Martín-Devasa R,Jiménez-Valverde A,Leprieur F,Baselga A,Gómez-Rodríguez C. Dispersal limitation shapes distance-decay patterns of European spiders at the continental scale[J]. Global Ecol Biogeogr,2024,33(4):e13810. doi: 10.1111/geb.13810
[13] Gravel D,Canham CD,Beaudet M,Messier C. Reconciling niche and neutrality:the continuum hypothesis[J]. Ecol Lett,2006,9(4):399−409. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00884.x
[14] 曲梦君,努尔依拉·阿巴拜克,邹旭阁,赵航,朱威霖,等. 地理距离和环境因子对阿拉善戈壁植物群落β多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性,2022,30(11):22029. doi: 10.17520/biods.2022029 Qu MJ,Nueryila·Ababaike ,Zou XG,Zhao H,Zhu WL,et al. Influence of geographic distance and environmental factors on beta diversity of plants in the Alxa gobi region in northern China[J]. Biodiversity Science,2022,30(11):22029. doi: 10.17520/biods.2022029
[15] 霍兵兵,孙哲明,欧文慧,毛鸿志,胡傲,等. 环境筛选和扩散限制对长江流域湖北段湿地植物群落构建的共同影响[J]. 生态学报,2023,43(5):1804−1811. Huo BB,Sun ZM,Ou WH,Mao HZ,Hu A,et al. Environmental filtering and dispersal limitation jointly affect wetland plant community assembly in Hubei section of the Yangtze River Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2023,43(5):1804−1811.
[16] Kraft NJB,Comita LS,Chase JM,Sanders NJ,Swenson NG,et al. Disentangling the drivers of β diversity along latitudinal and elevational gradients[J]. Science,2011,333(6050):1755−1758. doi: 10.1126/science.1208584
[17] Sun H,Niu Y,Chen YS,Song B,Liu CQ,et al. Survival and reproduction of plant species in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. J Syst Evol,2014,52(3):378−396. doi: 10.1111/jse.12092
[18] 王俊伟,陈永豪,拉琼. 西藏特有种子植物多样性、分布格局及区系特征[J]. 植物科学学报,2023,41(5):594−603. Wang JW,Chen YH,La Q. Diversity,distribution patterns,and floristic characteristics of seed plants endemic to Tibet,China[J]. Plant Science Journal,2023,41(5):594−603.
[19] Wang X,Zhu JL,Peng ST,Zheng TL,Qi ZY,et al. Patterns of grassland community composition and structure along an elevational gradient on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. J Plant Ecol,2022,15(4):808−817. doi: 10.1093/jpe/rtab119
[20] 王健铭,曲梦君,王寅,冯益明,吴波,等. 青藏高原北部戈壁植物群落物种、功能与系统发育β多样性分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性,2022,30(6):21503. doi: 10.17520/biods.2021503 Wang JM,Qu MJ,Wang Y,Feng YM,Wu B,et al. The drivers of plant taxonomic,functional,and phylogenetic β-diversity in the Gobi desert of northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Biodiversity Science,2022,30(6):21503. doi: 10.17520/biods.2021503
[21] 杨胜娴,杨清,李晓东,巢欣,刘惠秋,等. 确定性过程主导高原典型河流浮游植物地理分布格局和群落构建[J]. 生物多样性,2023,31(7):23092. doi: 10.17520/biods.2023092 Yang SX,Yang Q,Li XD,Chao X,Liu HQ,et al. Deterministic processes dominate the geographic distribution pattern and community assembly of phytoplankton in typical plateau rivers[J]. Biodiversity Science,2023,31(7):23092. doi: 10.17520/biods.2023092
[22] Wen L,Zhao KX,Sun HY,Feng G,Sun Q,et al. Drivers of desert plant beta diversity on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Ecol Evol,2024,14(2):e10993. doi: 10.1002/ece3.10993
[23] 赵济. 中国自然地理[M]. 3版. 北京:高等教育出版社,1995:306−321. [24] Xie D,Liu B,Zhao LN,Pandey TR,Liu HY,et al. Diversity of higher plants in China[J]. J Syst Evol,2021,59(5):1111−1123. doi: 10.1111/jse.12758
[25] Abbas S,Nichol JE,Zhang JL,Fischer GA. The accumulation of species and recovery of species composition along a 70 year succession in a tropical secondary forest[J]. Ecol Indic,2019,106:105524. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105524
[26] Borcard D,Legendre P,Drapeau P. Partialling out the spatial component of ecological variation[J]. Ecology,1992,73(3):1045−1055. doi: 10.2307/1940179
[27] Legendre P,Mi XC,Ren HB,Ma KP,Yu MJ,et al. Partitioning beta diversity in a subtropical broad-leaved forest of China[J]. Ecology,2009,90(3):663−674. doi: 10.1890/07-1880.1
[28] 柴永福,岳明. 植物群落构建机制研究进展[J]. 生态学报,2016,36(15):4557−4572. Chai YF,Yue M. Research advances in plant community assembly mechanisms[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2016,36(15):4557−4572.
[29] Saito VS,Perkins DM,Kratina P. A metabolic perspective of stochastic community assembly[J]. Trends Ecol Evol,2021,36(4):280−283. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2021.01.003
[30] 索南邓登,陈卫东,林鹏程. 青藏高原野生濒危药用植物掌裂兰的生境及濒危因素分析[J]. 广西植物,2019,39(9):1166−1179. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201903013 Suonan DD,Chen WD,Lin PC. Habitat and factors of endangerment of wild and endangered medicinal herb Dactylorhiza hatagirea in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Guihaia,2019,39(9):1166−1179. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201903013
[31] Maestre FT. On the importance of patch attributes,environmental factors and past human impacts as determinants of perennial plant species richness and diversity in Mediterranean semiarid steppes[J]. Divers Distrib,2004,10(1):21−29. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-4642.2004.00057.x
[32] 李艳辉,兰天元,王月,于洋,赵常明,等. 神农架植物物种空间周转的驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性,2022,30(4):21377. doi: 10.17520/biods.2021377 Li YH,Lan TY,Wang Y,Yu Y,Zhao CM,et al. Driving factors of spatial turnover of plant species in Shennongjia[J]. Biodiversity Science,2022,30(4):21377. doi: 10.17520/biods.2021377
[33] 李林,魏识广,练据愉,曹洪麟. 亚热带不同纬度植物群落物种多样性分布规律[J]. 生态学报,2020,40(4):1249−1257. Li L,Wei SG,Lian JY,Cao HL. Distributional regularity of species diversity in plant community at different latitudes in subtropics[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2020,40(4):1249−1257.
[34] Gibson N,Prober S,Meissner R,van Leeuwen S. Implications of high species turnover on the south-western Australian sandplains[J]. PLoS One,2017,12(2):e0172977. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172977
[35] 张兴旺,操景景,龚玉霞,张小平. 珍稀植物青檀种子休眠与萌发的研究[J]. 生物学杂志,2007,24(1):28−31. Zhang XW,Cao JJ,Gong YX,Zhang XP. Seed dormancy and germination in rare plant Pterocektis tartarinowii Maxim[J]. Journal of Biology,2007,24(1):28−31.
[36] 杨旭,杨志玲,王洁,檀国印. 濒危植物凹叶厚朴种实特性[J]. 生态学杂志,2012,31(5):1077−1081. Yang X,Yang ZL,Wang J,Tan GY. Fruit and seed traits of endangered species Magnolia officinalis subsp. biloba[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2012,31(5):1077−1081.
[37] 王丹,王孝安,郭华,王世雄,郑维娜,等. 环境和扩散对草地群落构建的影响[J]. 生态学报,2013,33(14):4409−4415. doi: 10.5846/stxb201204180559 Wang D,Wang XA,Guo H,Wang SX,Zheng WN,et al. Effect of species dispersal and environmental factors on species assemblages in grassland communities[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2013,33(14):4409−4415. doi: 10.5846/stxb201204180559
-
其他相关附件
-
DOCX格式
张东附表1~2 点击下载(30KB)
-



 下载:
下载: