Effects of litter extract of Phoebe bournei (Hemsl.) Yang on seed germination, seedling growth, and physiological indices
-
摘要:
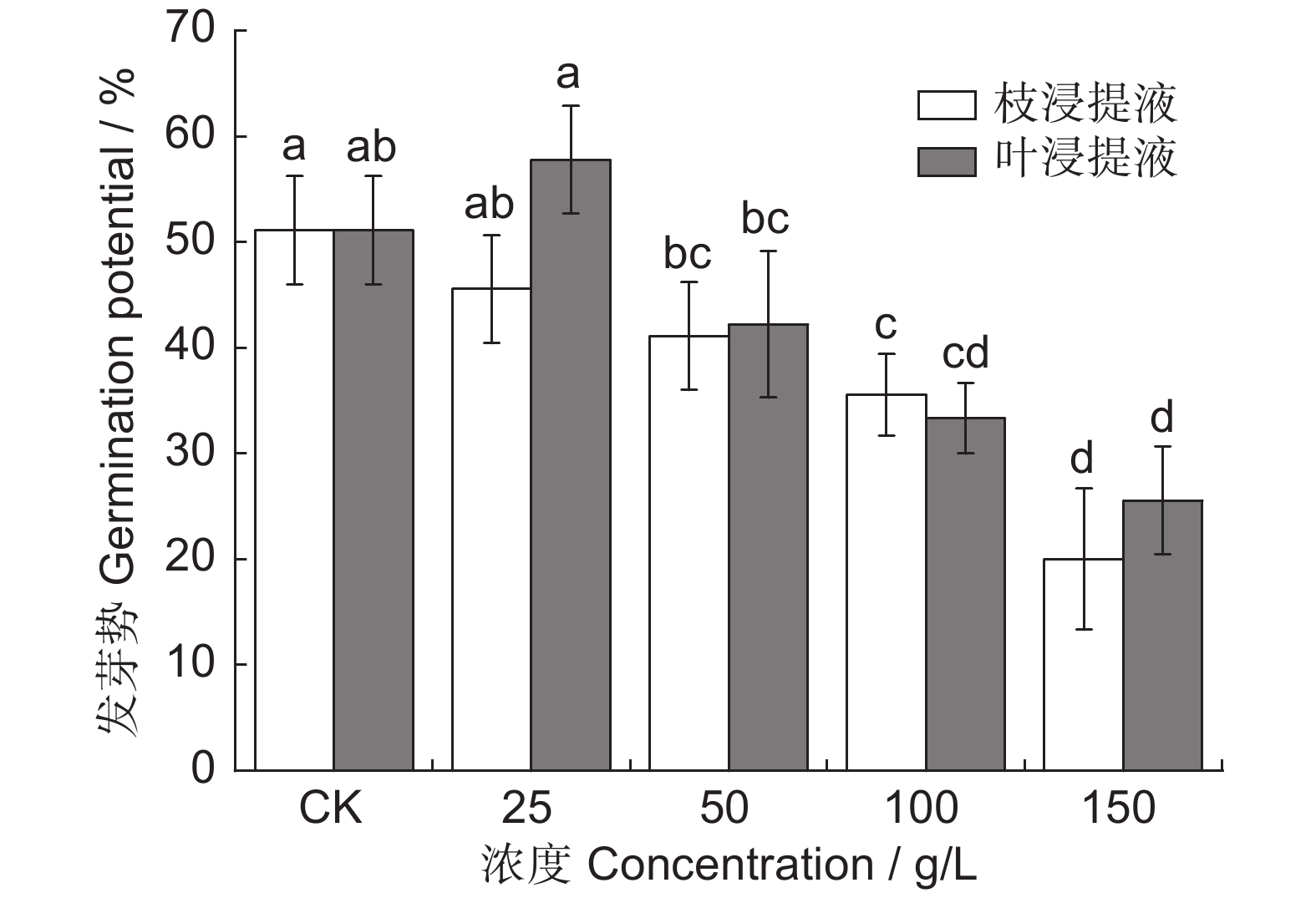
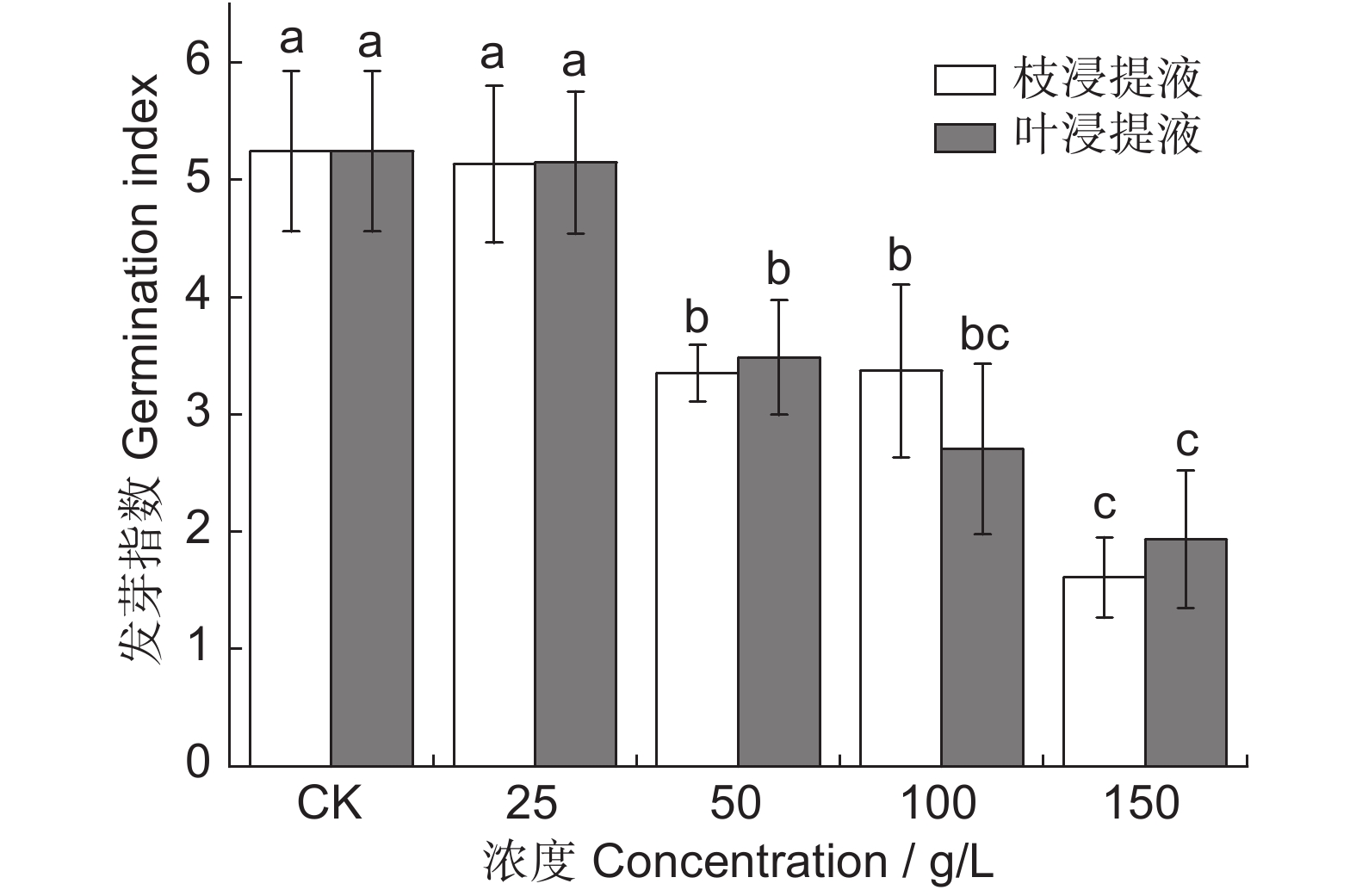
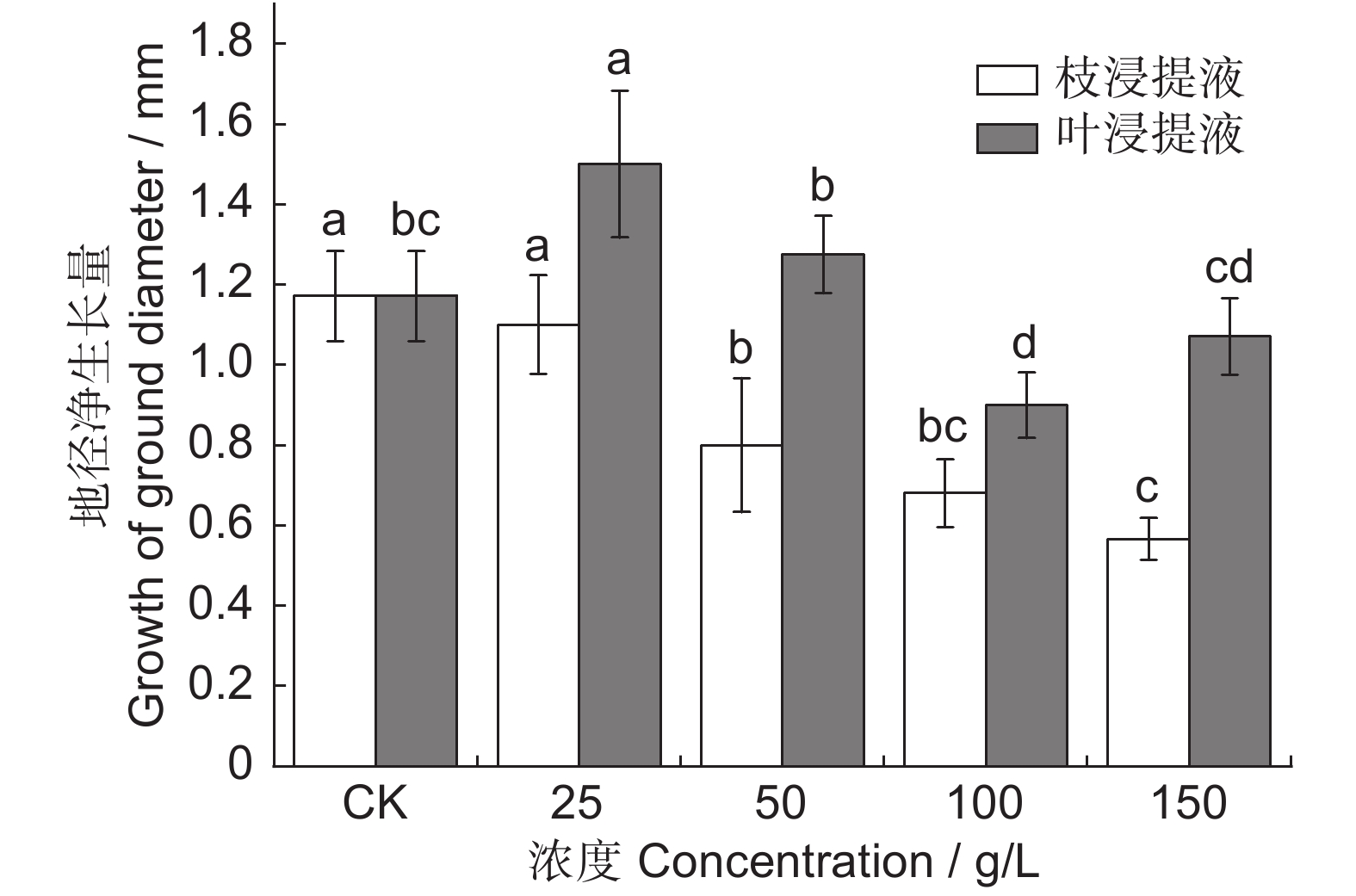
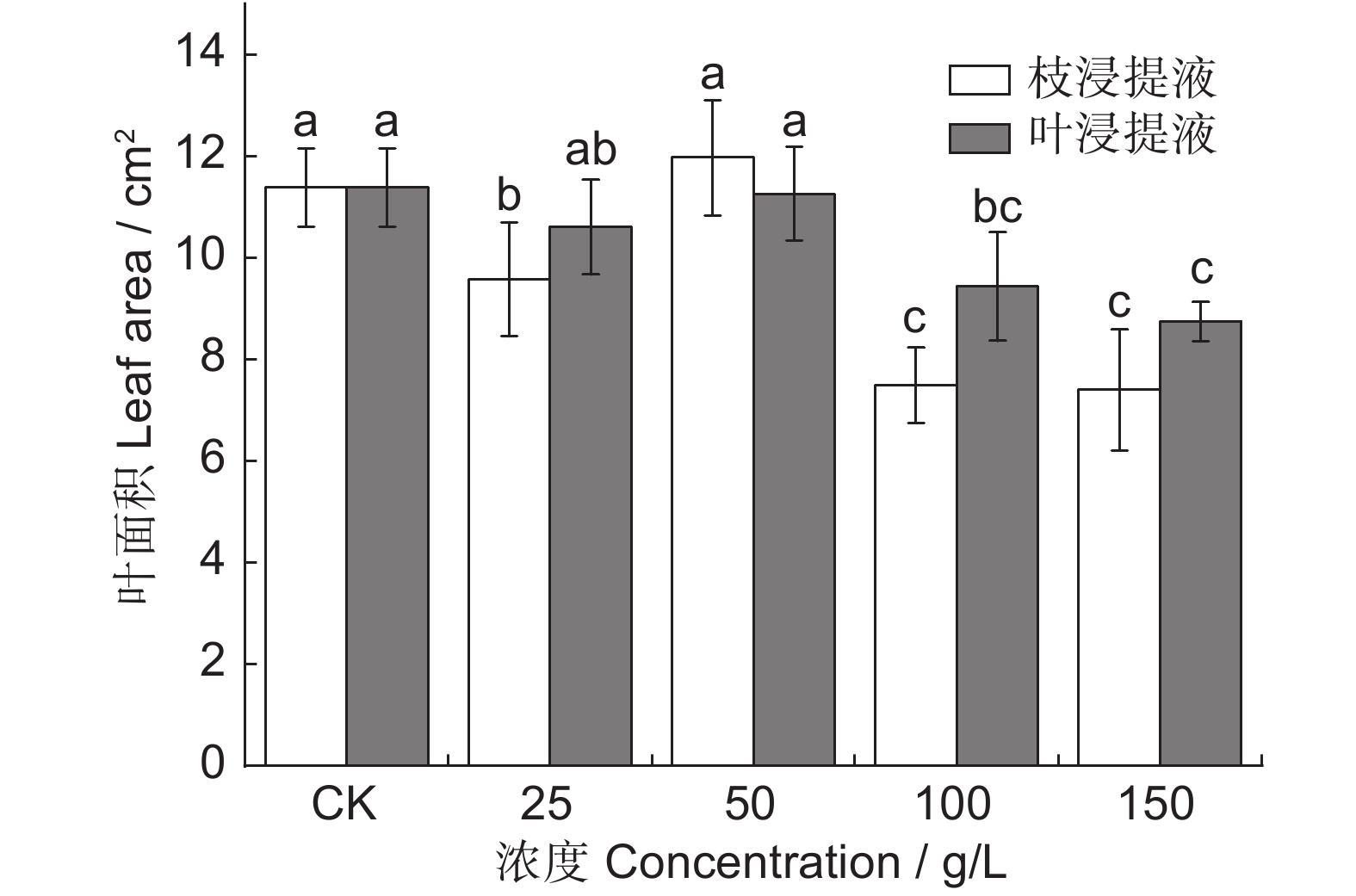
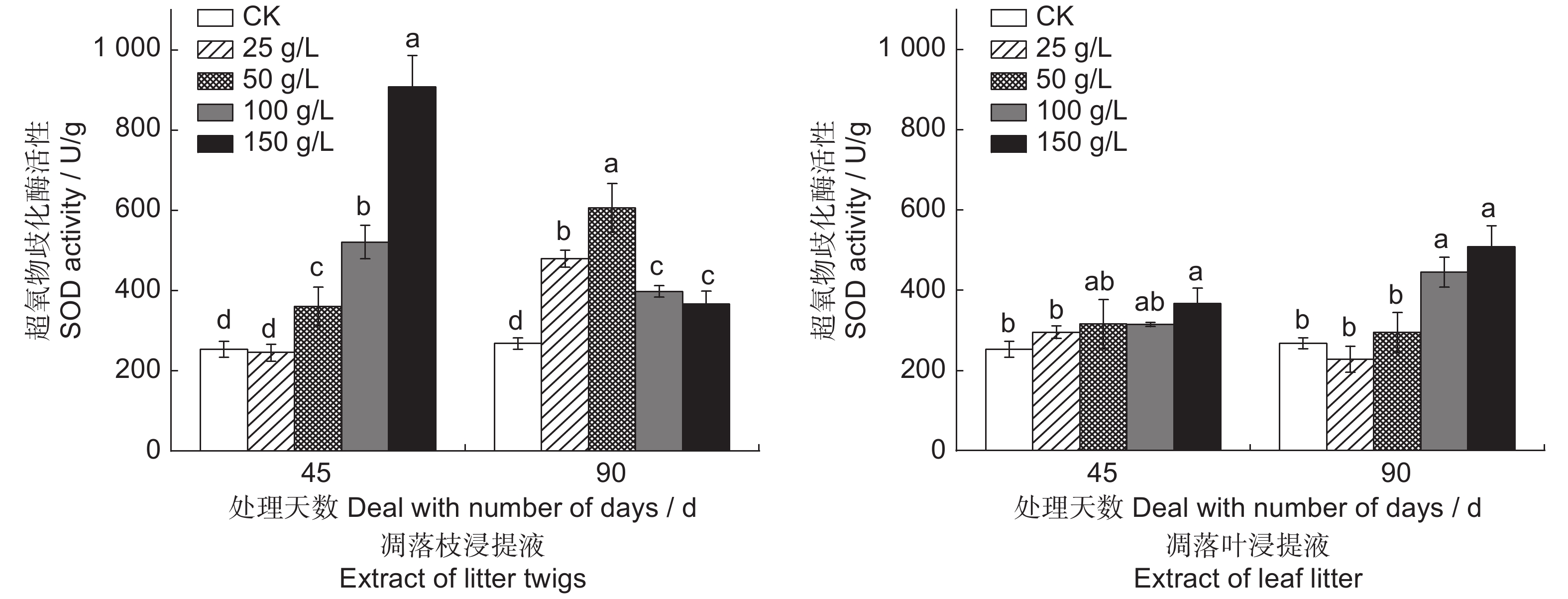
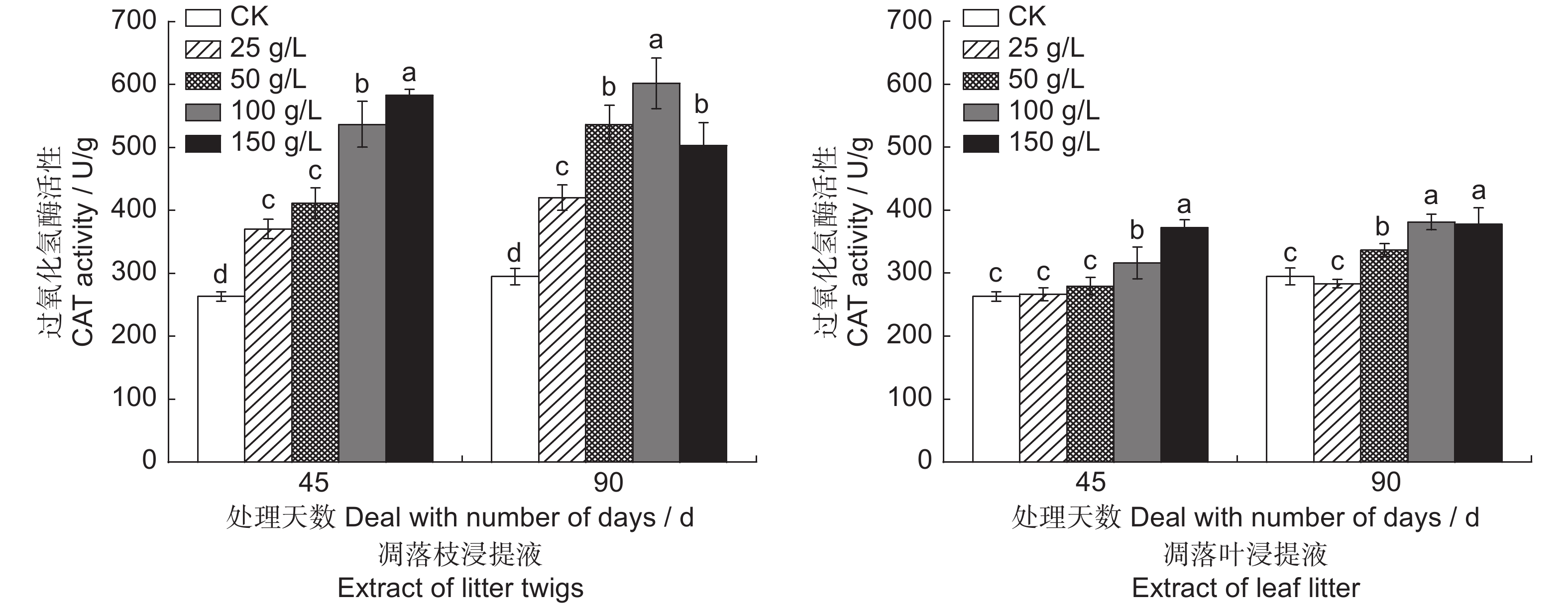
采用不同浓度凋落枝、凋落叶浸提液处理闽楠(Phoebe bournei (Hemsl.) Yang)种子和幼苗,测定其萌发、生长及生理指标。结果显示:(1)整体上,闽楠凋落枝和凋落叶浸提液对自身种子萌发表现为抑制作用,且抑制作用均随两种浸提液浓度升高而增强,且凋落枝抑制作用大于凋落叶。在发芽指标上,抑制强度表现为枝>叶;在根芽长度上,抑制强度表现为叶>枝;综合化感效应表现为枝>叶。(2)凋落枝浸提液对一年生闽楠幼苗生长指标表现为抑制作用,凋落叶浸提液表现为“低促高抑”的效应。高浓度浸提液可严重抑制幼苗生长,并造成大量叶片出现斑点、萎缩和枯黄;(3)闽楠凋落物浸提液对闽楠幼苗生理的影响较为复杂,高浓度浸提液可造成幼苗生理紊乱,导致其抗氧化系统异常,引起丙二醛含量显著增加,叶片细胞膜通透性增大,导致植株处于非正常生长状态,而长期浇灌低浓度浸提液也会使植物处于胁迫状态而引起相关生理指标变化。
Abstract:In this study, different concentrations of Phoebe bournei (Hemsl.) Yang litter branch and leaf extracts were tested to treat P. bournei seeds and seedlings. Seed germination, seedling growth, and physiological indices were measured. Results showed that: (1) Extracts of P. bournei litter branches and leaves inhibited seed germination at all concentrations. Inhibition intensity was enhanced with the increase in the concentration of the two extracts. However, inhibition intensity of the litter branches was greater than that of the litter leaves. Notably, inhibition intensity was branch>leaf regarding the germination index; leaf>branch regarding root bud length; and branch>leaf regarding comprehensive allelopathy. (2) Litter branch extracts inhibited the growth of one-year-old P. bournei seedlings, while litter leaf extracts showed “low promoting and high inhibiting” effects. High concentrations of the extracts seriously inhibited the growth of seedlings, causing many leaves to develop spots, atrophy, and yellow color. (3) The effects of litter extracts on P. bournei seedling physiology were complex. High-concentration extracts disturbed the physiological of seedlings, causing abnormalities in the antioxidant system, significant increases in malondialdehyde (MDA) content, and increases in cell membrane permeability in leaves, resulting in an abnormal growth state. Long-term exposure to low-concentration extracts induced stress in the plants and caused changes in related physiological indices.
-
Keywords:
- Autotoxicity /
- Phoebe bournei /
- Seed germination /
- Seedling growth /
- Litter /
- Allelopathy
-
生物类群的特有现象是生物地理学研究的重要组成部分[1]。随着物种灭绝的速度加快,特有物种在生物多样性保护研究中备受宏观生态学家与保护生物学家的关注[2]。特有种由于其狭域分布的特征,容易变成濒危物种,因此保护特有物种通常能更好地保护珍稀濒危物种[1, 2]。特有物种丰富度(Endemic species richness)是指局限分布于一定区域(行政区、自然保护区、某一山区等)的特有物种的数量。特有种是相对于一个特定的生物地理范围来说的,特有物种丰富度是确定生物多样性优先保护区的重要指标,对生物多样性科学理论研究与保护政策的制定意义重大[3-5]。另外,特有物种的地理空间分布格局也一直是生物学、生态学与保护生物学等众多领域关注的主题[5-8],这些研究的共同结论是,特有物种的空间分布不是随机的,它们在世界各地的分布极不均匀,往往集中在某一特定的区域或生境内。个别物种被发表后就再也没有采集到过其标本,甚至有些物种已濒危,但特有种对生态群落的发展与演化有着独特的作用[4, 6]。因此,评估特有物种空间分布格局对于制定有效的稀有物种保护策略、实施保护行动及界定其保护区范围是必要的。一个地区的特有程度被认为是衡量该地区生态系统独特性的重要指标,因此,特有种丰富度是确定生物多样性保护地点优先次序的最常用标准之一[9, 10]。目前,生物多样性面临急剧丧失的威胁,需要在全球、区域与地方各级中确定优先保护目标,以便将有限的资源集中在最重要的需求对象上[11, 12]。特有物种常常分布稀少,容易灭绝[4]。因此,研究特有物种是迫在眉睫的一项工作,目前为止,国内对某一特定区域特有物种的相关报道很多[13-18],为植物多样性保护与植物区系地理的研究奠定了良好的基础。
西藏高原是一个独特的自然地理单元,有着从热带到寒带所有垂直地带的植被带谱。复杂的地形地貌孕育了西藏丰富的植物区系多样性,特有种数量丰富[19]。但针对西藏特有种子植物层面进行多样性特征、区系性质及分布格局的研究报道还很鲜见。特有物种是一个地区重要的特色生物种质资源,有着极高的科学研究与保护价值,对特有植物的研究更有助于探讨西藏植物区系的发展历史与现状,也有利于特色植物资源的开发与利用。因此,本研究在收集整理西藏特有种子植物名录与物种分布数据的基础上,对科属种组成及其多样性特征、物种生活型多样性、物种垂直海拔分布格局及县域尺度(水平地理)分布格局、属水平植物区系性质等方面进行了分析研究。研究结果旨在回答:(1)目前被描述的西藏特有种子植物有多少种?其多样性组成结构如何及生活型组成比例是多少?(2)植物区系性质如何?(3)特有物种水平地理分布与海拔垂直分布的格局特征如何?研究结果对进一步了解西藏地区的植物多样性,特别是特有植物的基本情况具有重要意义,在一定程度上也可为西藏植被维护与生态修复、植物多样性重点保护红色名录的制定、特色植物种质资源的保护与利用提供基础数据。
1. 数据与方法
1.1 特有种子植物名录的整理
根据物种分布的地理位置信息,将只分布在西藏自治区境内的种子植物称为西藏特有种子植物。基于专著《中国特有种子植物的多样性及其地理分布》[20]初步确定西藏特有种子植物名录数据,通过查阅Flora of China(http://www.efloras.org/) 、西藏植物志(http://db.kib.ac.cn/XZFLORA/SearchEngine.aspx)、泛喜马拉雅植物志(Flora of Pan-Himalayas)等植物志,结合植物在线数据标本库物种2000中国节点 (http://www.sp2000.org.cn/)、The plant list(TPL) (http://www.theplantlist.org/) 、International Plant Name Index(IPNI)(https://www.ipni.org/) 、Plants of the World online(POWO)(https://powo.science.kew.org/)、Tropicos (https://www.tropicos.org/home)、中国苦苣苔科植物保育中心 (http://gccc.gxib.cn/cn/)等植物数据库网站,再根据近两年中国植物新种文献资料整理结果[21, 22]、检索新物种发表信息[23-26]、专科专属分类修订成果[27]、野外数据资料等的整合,对植物名录进行补充、修正与完善,从而得到较为精准的西藏特有种子植物名录数据库。
1.2 物种多样性组成特征与区系分析
按科属种分类群对西藏特有种子植物物种组成和生活型(乔木、灌木、草本植物等)多样性组成结构进行统计,分析包含物种数最多的科属与生活型构成比例。另外,按照吴征镒等[28]及陈灵芝等[29]对植物区系分布类型的划分原理与方法,确定西藏特有种子植物各属级植物区系分布区类型,并进行区系统计分析。
1.3 多样性分布格局的构建
通过查阅Flora of China ( FOC )( http://www.efloras.org/) 、IPNI、全球生物多样性信息网络(GBIF)(http://www.gbif.org/)、中国数字植物标本馆(CVH)(http://www.cvh.org.cn/)、中国植物图像库(PPBC)(http://ppbc.iplant.cn/)、西藏植物志(http://db.kib.ac.cn/XZFLORA/SearchEngine.aspx)、泛喜马拉雅植物志等植物志及植物在线数据标本库,结合多次野外植物学调查数据和新种文献资料,确定西藏特有种子植物县级分布区及海拔分布范围(假定植物志记载的海拔梯度内物种连续分布)。
按照县级行政区域内特有种子植物分布的物种数量,利用ArcGIS 10.4软件的空间地理制图功能来绘制西藏特有种子植物县域尺度的多样性分布格局图。运用Excel 2019软件对海拔梯度区间内的特有物种数量进行录入和整理,并制作图表。统计每一海拔段内特有物种的数量分布,分析特有物种数量的海拔梯度格局变化趋势,并制作变化趋势图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 科属种多样性构成
经统计,西藏特有种子植物有1 079种(不包含种下分类等级,见附表1
1 )),占西藏种子植物(8 008种,包含种下等级)[30]的13.5%;占青藏高原特有种子植物(3 764种)[18]的28.7%,表明西藏种子植物特有现象普遍。根据在线网站植物智(http://www.iplant.cn/)和物种2000中国节点 (http://www.sp2000.org.cn/)的分类结果,1 079种西藏特有种子植物隶属于89科295属。其中被子植物1 075种,裸子植物仅有4种,分别占西藏特有种子植物总种数的99.6%和0.4%。裸子植物仅有4种,分别为察隅冷杉(Abies chayuensis Cheng et L. K. Fu)、贡布红杉(Larix kongboensis R. R. Mill)、诚氏麻黄(Ephedra chengiae Y. Yang & D. K. Ferguson)和通麦柏木(Cupressus rushforthii Maerki & J. Hoch)。根据生活型多样性特征,特有种可分为木本植物与草本植物两大类,具体可分为乔木、灌木、木质藤本、多年生草本、一年生草本、附生草本、寄生草本等13种生活型(表1)。包含物种数最多的前7种生活型类型为多年生草本(716种)、灌木(151种)、乔木(65种)、一年生草本(54种)、附生灌木(30种)、附生草本(18种)、亚灌木(16种),分别占西藏特有种子植物总数的66.4%、14.0%、6.0%、5.0%、2.8%、1.7%与1.5%。由此可知,西藏特有种子植物中生活型类型丰富多样,多年生草本植物占优势。木本植物中,灌木类占54.9%,是主要的生活型,其次是乔木,木质藤本类植物最少。草本植物中,多年生草本是主要生活型,占89.1%,二年生草本、攀援草本、全寄生草本与腐生草本所含物种数均小于10,全寄生类植物与腐生草本植物各有1种,分别为大鳞菟丝子(Cuscuta macrolepis R. C. Fang & S. H. Huang)与米林鸟巢兰(Neottia milinensis J. J. Lei & X. H. Jin),生活型丰富多样。
表 1 西藏特有种子植物的生活型Table 1. Growth forms of seed plants endemic to Tibet, China生活型
Growth form物种数
Number of species百分比
Percentages / %木本
植物乔木 65 6.0 灌木 151 14.0 亚灌木 16 1.5 附生灌木 30 2.8 木质藤本 12 1.1 草本
植物多年生草本 716 66.4 二年生草本 7 0.6 一年生草本 54 5.0 攀援草本 7 0.6 附生草本 18 1.7 全寄生草本 1 0.1 腐生草本 1 0.1 从种的数量上看(表2),物种数大于20的有菊科、毛茛科、豆科、报春花科、罂粟科等19个科 ,共包含843种,占西藏特有种子植物总物种数的78.0%,其中菊科、毛茛科、杜鹃花科、豆科、报春花科、禾本科、小檗科所含特有物种数均 ≥ 40种,毛茛科与菊科的物种数更是超过了100个,分布占总物种数的10.0%与11.7%。
表 2 西藏特有含20种以上科种子植物及其所占比例Table 2. Percentages of families containing more than 20 endemic species in Tibet, China科名
Family物种数
Number of species百分比
Percentage / %报春花科 49 4.5 唇形科 25 2.3 豆科 57 5.3 杜鹃花科 65 6.0 禾本科 41 3.8 虎耳草科 37 3.4 菊科 126 11.7 苦苣苔科 24 2.2 兰科 30 2.8 列当科 38 3.5 龙胆科 24 2.2 毛茛科 107 10.0 蔷薇科 31 2.9 伞形科 25 2.3 石竹科 30 2.8 小檗科 42 3.9 杨柳科 22 2.0 罂粟科 48 4.4 紫草科 22 2.0 其他科 236 22.0 包含物种数在10种以上的属及其所占比例的统计结果见表3,分别有翠雀属(Delphinium)、紫堇属(Corydalis)、杜鹃花属(Rhododendron)等24个属,共计530种,占西藏特有种子植物总物种数的48.9%,优势属的现象也很明显。物种数超过30的有小檗属(Berberis)、马先蒿属(Pedicularis)、报春花属(Primula)、杜鹃花属(Rhododendron)、虎耳草属(Saxifraga)、紫堇属(Corydalis)和翠雀属(Delphinium)。此区域也是一些特征属的现代分布与起源演化中心,如马先蒿属,该属中青藏高原特有种为195种,而其中只在西藏分布的有38种(19.5%);虎耳草属西藏特有种为36种,占该属青藏高原特有种(116种)的31.0%;杜鹃花属中青藏高原特有种为159种,其中只分布在西藏的有37种(23.3%);紫堇属包含126个青藏高原特有种,只分布在西藏的就有39种(31.0%)。
表 3 含10种以上属西藏特有种子植物及其所占比例Table 3. Percentages of genera containing more than 10 endemic species in Tibet, China属名
Genus物种数
Number of species百分比
Percentage / %柳属 Salix 20 1.9 楼梯草属Elatostema 13 1.2 蝇子草属Silene 12 1.2 乌头属Aconitum 29 2.8 翠雀属Delphinium 40 3.8 毛茛属Ranunculus 16 1.5 唐松草属Thalictrum 10 1 紫堇属Corydalis 39 3.7 虎耳草属Saxifraga 35 3.4 黄芪属Astragalus 27 2.5 棘豆属Oxytropis 14 1.3 凤仙花属Impatiens 12 1.2 树萝卜属Agapetes 16 1.5 杜鹃花属Rhododendron 37 3.5 报春花属Primula 35 3.4 龙胆属Gentiana 11 1.1 马先蒿属Pedicularis 32 3 小檗属Berberis 40 3.8 蒿属Artemisia 11 1.1 垂头菊属Cremanthodium 12 1.2 橐吾属Ligularia 11 1.1 风毛菊属Saussurea 29 2.8 秋海棠属Begonia 10 1 其他属 532 51 2.2 属的分布区类型结构
对1 079种西藏特有种子植物进行属的分布区类型划分,结果见表4。1 079种植物隶属于297属,其分布区可划分为15个类型和18个变型,包括了吴征镒等[28]确定的中国植物区系的全部15个类型。具体可分为世界分布的属(23属)、热带亚热带分布的属(81属)、温带性质的属(183属)、中国特有分布的属(10属)等4大类,分别占西藏特有种子植物总属的7.7%、27.3%、61.6%与3.4%。
表 4 西藏特有种子植物属的分布类型Table 4. Distribution types of seed plant genera endemic to Tibet, China分布类型 Area type 属数 Number of genera 百分比 Percentage /% 1. 广布 23 7.7 2. 泛热带分布 18 6.1 2-1. 热带亚洲、大洋洲(至新西兰)和中美洲至南美洲(或墨西哥)间断 2 0.7 2-2. 热带亚洲、非洲和中美洲至南美洲间断Disjuncted 2 0.7 3. 热带亚洲和热带美洲间断分布 6 2.0 4. 旧世界热带分布 8 2.7 4-1. 热带亚洲、非洲(或东非、马达加斯加)和大洋洲间断 2 0.7 5. 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布 15 5.0 6. 热带亚洲和热带非洲分布 3 1.0 6-2. 热带亚洲和东非或马达加斯加间断 2 0.7 7. 热带亚洲分布 18 6.1 7-1.爪哇(或苏门达腊)、喜马拉雅至华南、西南间断或星散 3 1.0 7-2. 热带印度至华南(特别是滇南) 1 0.3 7-4. 越南(或中南半岛)至华南(或西南) 1 0.3 热带成分(2 ~ 7-4)合计 81 27.3 8. 北温带分布 56 19.0 8-2. 北极-高山 6 2.0 8-4. 北温带和南温带间断分布 22 7.4 8-5. 欧亚和温带南美洲间断 3 1.0 9. 东亚和北美间断分布 10 3.4 9-1. 东亚和墨西哥美洲间断 2 0.7 10. 旧世界温带分布 19 6.4 10-1. 地中海、西亚(或中亚)和东亚间断 1 0.3 10-2. 地中海和喜马拉雅间断 2 0.7 10-3. 欧亚和南部非洲(有时还有大洋洲)间断 1 0.3 11. 温带亚洲分布 6 2.0 12. 地中海、西至中亚分布 1 0.3 13. 中亚分布 4 1.3 13-1. 中亚东部(或中部亚洲)分布 1 0.3 13-2. 中亚至喜马拉雅和华西南 9 3.0 14. 东亚分布 7 2.4 14SH. 中国-喜马拉雅 32 10.8 14SJ. 中国-日本 1 0.3 温带成分(8 ~ 14SJ)合计 183 61.6 15. 中国特有分布 10 3.4 总计 297 100.0 世界分布类型的属中包含毛茛属(Ranunculus)、碎米荠属(Cardamine)、悬钩子属(Rubus)、远志属(Polygala)、鼠尾草属(Salvia)、飞蓬属(Erigeron)、千里光属(Senecio)等大属。
温带性质的属中分布类型及变型丰富多样,尤其以北温带分布类型的属为优势,如柏木属(Cupressus)、冷杉属(Abies)、蔷薇属(Rosa)、百合属(Lilium)与披碱草属(Elymus)等共56属,占西藏特有种子植物总属数的19.0%;其次是中国-喜马拉雅分布变型,包括铁破锣属(Beesia)、丛菔属(Solms-laubachia)、独花报春属(Omphalogramma)、玉山竹属(Yushania)与镰序竹属(Drepanostachyum)等32属,占西藏特有种子植物总属数的10.8%。
热带亚热带性质的属同样丰富多样,以热带亚洲分布类型和泛热带分布类型的属占优,均有18属,占西藏特有种子总属数的6.1%,其次是热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布的属,为15属,占西藏特有种子总属数的5.0%。泛热带分布类型的有胡椒属(Piper)、花椒属(Zanthoxylum)、榕属(Ficus)、秋海棠属(Begonia)、薯蓣属(Dioscorea)、石豆兰属(Bulbophyllum)与山壳骨属(Pseuderanthemum)等。热带亚洲分布类型有润楠属(Machilus)、坡垒属(Hopea)、线柱苣苔属(Rhynchotechum)、芒毛苣苔属(Aeschynanthus)、树萝卜属(Agapetes)、新小竹属(Neomicrocalamus)、兜兰属(Paphiopedilum)和蛇根草属(Ophiorrhiza)等。热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布的属有姜属(Zingiber)、蝴蝶兰属(Phalaenopsis)、崖爬藤属(Tetrastigma)、盆距兰属(Gastrochilus)、兰属(Cymbidium)、豆蔻属(Amomum)、小囊兰属(Micropera)、苞舌兰属(Spathoglottis)等。
此外,中国特有分布的属有翅果蓼属(Parapteropyrum)、辐花属(Lomatogoniopsis)、丝苞菊属(Bolocephalus)、秦岭藤属(Biondia)、合头菊属(Syncalathium)、君范菊属(Sinoleontopodium)等,以及2022年才描述发表的单种属十字花科雪古拉荠属(Pulvinatusia)。
2.3 植物多样性分布格局
2.3.1 植物多样性水平地理分布格局
从图1可以看出,西藏特有种子植物总体上呈从东南向西北递减的变化趋势,集中分布在气候温暖湿润的东南部与南部的喜马拉雅几条大沟谷中。物种丰富度呈东南部>南部>中部>东部>西南部>西部>北部的水平多样性地理分布格局,喜马拉雅东南麓是西藏特有种子植物丰富度最高的区域。从县级分布来看,西藏特有种子植物集中分布在东南部的墨脱县、巴宜区、波密县、米林县、察隅县、隆子县、错那县,中部的城关区,以及南部的吉隆县、聂拉木县、亚东县等地区,其中墨脱县特有种数量最多(271种)。特有种数量超过100的有墨脱县、巴宜区、波密县、米林县、察隅县等5个县级行政区。西藏北部和西北部的那曲高原和羌塘高原地区特有种数量较少,物种组成也较为单一,县级分布物种数均不超过10种。西藏地区县级特有种数量之间差异明显,特有种县级分布数量与该区域的植物标本采集强度关系密切。西藏中部的拉萨区域特有种数量明显较高,比周边面积更大、地理环境复杂的县域数量多的多,南部一些县的数量也较少,显然与这些地区的植物标本采集强度及研究程度有着必然的联系。
2.3.2 植物多样性垂直分布格局
西藏特有种子植物的海拔分布范围极广,跨度从152 m到6400 m。根据海拔梯度,每500 m划分1个区间,从0~500 m至6000~6500 m的物种多样性海拔分布格局如图2所示。结果表明,西藏特有种子植物主要分布在3000~4500 m的中高海拔区间,特有物种丰富度呈单峰分布格局。海拔低于500 m分布的物种只有14种,包括西藏胡椒(Piper arunachalensis Gajurel)、西藏坡垒(Hopea shingkeng (Dunn) Bor)、管花马蓝(Strobilanthes tubiflos (C. B. Clarke) J. R. I. Wood)、粉萼短筒苣苔(Boeica arunachalensis D.Borah, R. Kr. Singh, Taram & A. P. Das)、奥云氏秋海棠(Begonia oyuniae Taram & N. Krishna)等。海拔5 500 m以上分布的有7种,分别是西藏繁缕(Stellaria tibetica Kurz)、仲巴翠雀花(Delphinium chungbaense W. T. Wang)、黑果毛茛(Ranunculus melanogynus W. T. Wang)、金球黄堇(Corydalis chrysosphaera C. Marquand et Airy Shaw)、珠峰鳞蕊芥(Lepidostemon everestianus Al-Shehbaz)、圆叶黄芪(Astragalus orbicularifolius P. C. Li et Ni)、珠峰齿缘草(Eritrichium qofengense Lian et J. Q. Wang)。总体上,随着海拔的升高西藏特有种子植物物种丰富度呈先增加后降低的趋势,即特有物种丰富度的海拔垂直分布格局呈驼峰状模式,符合生物多样性地理分布格局中的法则-中域效应假说[31]。
3. 讨论
本研究表明,西藏特有种子植物多样性丰富,依据目前被描述的植物物种,西藏特有种子植物共有1 079种(不包含种下分类等级),占西藏种子植物的13.5%,占青藏高原特有种子植物(3 764种)的28.7%,特有率非常高。物种数最多的前3科为菊科、毛茛科、杜鹃花科;物种数最多的前3属为翠雀属、小檗属、紫堇属。植物生活型多样性分析结果表明,西藏特有种子植物生活型类型丰富多样,有乔木、灌木、木质藤本、多年生草本、一年生草本、附生草本、寄生草本等13种生活型。植物生活型是植物长期对环境适应的表现,是适应各种生态位的结果,这与西藏地区有着丰富的生态环境类型相对应。多年生草本植物占据主要优势,占西藏特有种子植物总物种的66.4%。特有种以多年生草本植物占优势,与其他地区特有种的研究结果相一致[13-16, 32, 33]。西藏特有种子植物的属级地理成分特征为区系类型多样丰富,包含中国种子植物区系的全部15种类型,与各植物区系成分间联系广泛,以温带性质的属为主,其中又以北温带分布性质的属与中国-喜马拉雅成分的属最为密切。另外,在植物区系的发展与起源演化过程中,与热带亚热带性质的属也有紧密的联系和历史渊源,已有研究证明热带性质的属对西藏植物区系的形成与发展有着不容低估的作用[34]。这在一定程度上也反映了西藏植物区系的整体情况。在西藏高原地区独特的地理环境及地质历史事件、一系列山脉隆升等的共同影响下,也孕育出了不少中国特有属的区系成分。
确定物种地理分布格局是生物地理学研究的一个重要出发点[35]。本研究结果表明,西藏特有种子植物的水平地理空间分布(县域尺度)格局极不均匀,特有种沿喜马拉雅山脉集中分布,东南麓是其特有种集中分布的区域,如墨脱县境内分布有271种西藏特有种子植物,其次是巴宜、波密、米林与察隅等县,其特有种丰富度也较高。这些地区独特的新物种很多,且保存有完好的自然生态环境,是探索自然生物资源、生物多样性的宝地。从特有种子植物多样性分布格局研究结果来看,藏东南(墨脱、察隅、波密、米林等地)也是青藏高原特有种丰富度最高的热点区域[18]。西藏特有种子植物的空间地理分布格局与总的种子植物物种丰富度分布格局相一致[36]。从垂直海拔分布格局来看,西藏特有种子植物丰富度随着海拔的升高呈先增后减的变化趋势,特有物种集中分布在3000~4500 m的中高海拔区间。Tiwari 等[37]对尼泊尔喜马拉雅山脉特有植物的分布格局进行了研究,发现这些植物在海拔3800~4200 m之间物种丰富度最高;Werff 和Consiglio[38]对秘鲁分布的特有植物进行了海拔分布格局研究,也发现了类似结果,即特有种的密度在中高海拔出现峰值,与本文的研究结果相一致。在物种海拔垂直分布格局上,相比总的物种丰富度峰值,特有物种的丰富度峰值通常位于更高的海拔区间,这与高海拔地区与世隔绝的加剧形成孤岛效应、土壤表面积的减少、短距离内气候和土壤条件的急剧变化有关,这些因素导致物种种群较小且零散,形成种群隔离,从而有利于狭域特有物种的形成[37, 39, 40]。另外,长期以来,低海拔地区的植物区系和植被受到人类活动的强烈影响,与大范围广布的非特有种相比,特有种可能已受不同程度的影响而灭绝,导致特有物种丰富度在高于总物种丰富度的海拔梯度上出现峰值[5]。
有些特有种的分布范围较广,有些则分布较狭窄,只有1~2个分布点。县域行政区特有种的分布与研究的深入程度及植物标本的采集强度等着有极为密切的关系。西藏中部地区的拉萨比周边几个面积更大、生境类型更复杂的县域高许多,表现出特有种极高的现象,可能与这一原因有关。此地区交通相对便利,自然条件没有那么恶劣,因而是青藏高原植物标本采集活动较为集中的重点地区。这从一定程度上也反映出西藏地区植物标本资源采集的薄弱,甚至还有很多空白地区,但本研究结果在很大程度上也反映了西藏特有种分布格局的整体情况。
本研究基于县域尺度的植物多样性分布格局识别出3个西藏特有种子植物多样性集中丰富的热点地区。Lu等[41]通过重建我国被子植物时间系统发育树,整合物种分布数据、特有类群、濒危性等角度,最后基于综合丰富度指数、综合系统发生指数和受威胁物种分布,识别出42个生物多样性优先保护区,其中西藏有3个,即西藏东南部的雅鲁藏布江-南迦巴瓦峰地区、西藏南部的珠穆朗玛地区与西藏中部的甘巴拉山地区,该结果与本研究相一致。高原面上连续的山脉和峡谷为植物物种迁移与扩散提供了条件,使这些区域的物种丰富度高度集中且多样[42],本研究通过种子植物特有种丰富度识别出的优先保护区域也基本上沿山脉(喜马拉雅山)和峡谷(雅鲁藏布江)分布。
山地热带亚热带潮湿气候的藏东南和藏南地区包含了大量的西藏特有种子植物。未来在资源条件有限的情况下,可针对性地对这些优先区域进行植物多样性调查与保护生物学的研究,同时进一步对每种西藏特有种子植物野外居群的分布范围、种群数量、种群动态特征、生存状况及大尺度地理分布范围、生境异质性等进行全方位实地野外调查,评价特有种的稀有度、濒危等级及保护地位,为制定西藏自治区重点保护植物红色名录的工作提供基础数据,并为国家重点保护野生植物名录的制定提供数据支撑。同时,特有物种是一个地区重要的生物种质资源,建议加大对特有种的实地种群调查和特有珍稀物种的收集保护工作力度,并加强对西藏特有种子植物各个层次的科学研究力度。
-
表 1 闽楠凋落物水浸提液对闽楠种子根茎生长的影响
Table 1 Effects of water extract from Phoebe bournei litter on seed rhizome growth
处理
Treatment浓度
Concentration /
g/L根长
Root length /
cm茎长
Shoot
length / cm叶长
Leaf length /
cm根鲜重
Root fresh
weight / mg根干重
Root dry
weight / mg茎鲜重
Shoot fresh
weight / mg茎干重
Shoot dry
weight / mg枝 CK 5.82±0.83a 5.13±0.61a 1.61±0.13a 80.97±1.08a 22.35±0.48a 102.00±0.95a 29.73±0.52a 25 6.47±0.57a 5.64±0.39a 1.42±0.17ab 76.94±5.17a 19.31±1.99b 89.89±3.29b 25.29±1.55b 50 5.25±0.98ab 5.13±0.44a 1.18±0.21b 65.89±2.98b 16.74±1.44c 81.51±1.36c 21.91±0.76c 100 4.24±0.42b 4.23±0.35b 0.88±0.52c 58.30±2.54c 13.83±0.24d 82.06±1.90c 22.70±0.36c 150 4.21±0.34b 4.07±0.44b 0.84±0.98c 57.88±2.42c 13.34±1.02d 62.92±2.44d 17.81±0.23d 叶 CK 5.82±0.83b 5.13±0.61ab 1.61±0.13a 80.97±1.08b 22.35±0.48ab 102.00±0.95b 29.73±0.51a 25 7.57±0.94a 5.51±0.67a 1.23±0.09b 94.71±0.84a 23.53±0.44a 109.66±2.94a 31.45±1.54a 50 5.23±1.16bc 5.29±0.81ab 1.17±0.08bc 80.57±2.99b 21.19±0.99b 107.77±1.85ab 31.20±1.30a 100 3.79±0.39cd 4.20±0.22bc 1.02±0.07cd 68.29±3.30c 17.93±1.61c 91.13±1.81c 24.10±1.43b 150 2.97±0.69d 3.33±0.56c 0.88±0.05d 63.08±2.95d 15.02±0.67d 68.72±7.36d 20.12±3.37c 注:不同小写字母代表同种浸提液在P<0.05水平上差异显著。下同。 Note: Different lowercase letters indicate that the same extract is significant at P<0.05 level. Same below. 表 2 闽楠凋落物水浸提液对闽楠种子的综合化感效应
Table 2 Allelopathic effects of water extract from Phoebe bournei litter on seeds
化感效应指数RI 化感综合
效应指数
SE处理
Treatment浓度
Concentration / g/L发芽率
Germination rate发芽势
Germination potential发芽指数
Germination index根长
Root
length茎长
Shoot
length叶长
Leaf
length根干重
Root dry
weight茎干重
Shoot dry
weight枝 CK 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 25 −0.25 −0.11 −0.02 −0.11 0.10 −0.12 −0.14 −0.15 −0.07 50 −0.28 −0.20 −0.36 −0.10 0.00 −0.27 −0.25 −0.26 −0.29 100 −0.31 −0.30 −0.36 −0.27 −0.18 −0.45 −0.38 −0.24 −0.31 150 −0.59 −0.61 −0.69 −0.28 −0.21 −0.48 −0.40 −0.40 −0.46 叶 CK 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 25 0.03 0.13 −0.02 0.30 0.07 −0.24 0.05 0.06 0.05 50 −0.16 −0.17 −0.33 −0.10 0.03 −0.27 −0.05 0.05 −0.13 100 −0.28 −0.35 −0.48 −0.35 −0.18 −0.37 −0.20 −0.19 −0.30 150 −0.49 −0.50 −0.63 −0.49 −0.35 −0.45 −0.33 −0.32 −0.45 -
[1] 韩豪. 闽楠天然林种群特征及其天然更新研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2020: 6-7. [2] 葛永金. 闽楠栽培生理生态基础研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2014: 1-4. [3] 唐星林,刘光正,姜姜,刘斌,张运兴,狄岚. 遮阴对闽楠一年生和三年生幼树叶绿素荧光特性及能量分配的影响[J]. 生态学杂志,2020,39(10):3247−3254. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202010.013 Tang XL,Liu GZ,Jiang J,Liu B,Zhang YX,Di L. Effects of shading on the chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics and light energy partitioning of one- and three-year-old Phoebe bournei seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2020,39(10):3247−3254. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202010.013
[4] 黄玉茜,韩立思,杨劲峰,王月,韩晓日. 花生植株和土壤水浸液自毒作用研究及土壤中自毒物质检测[J]. 生态学报,2012,32(19):6023−6032. doi: 10.5846/stxb201109131337 Huang YQ,Han LS,Yang JF,Wang Y,Han XR. Autotoxicity of aqueous extracts from plant,soil of peanut and identification of autotoxic substances in rhizospheric soil[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2012,32(19):6023−6032. doi: 10.5846/stxb201109131337
[5] 张晓玲,潘振刚,周晓锋,倪吾钟. 自毒作用与连作障碍[J]. 土壤通报,2007,38(4):781−784. doi: 10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2007.04.033 Zhang XL,Pan ZG,Zhou XF,Ni WZ. Autotoxicity and continuous cropping obstacles:a review[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2007,38(4):781−784. doi: 10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2007.04.033
[6] 林思祖,杜玲,曹光球. 化感作用在林业中的研究进展及应用前景[J]. 福建林学院学报,2002,22(2):184−188. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-389X.2002.02.023 Lin SZ,Du L,Cao GQ. Advance and application prospects on allelopathy research in forestry[J]. Journal of Fujian College of Forestry,2002,22(2):184−188. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-389X.2002.02.023
[7] 高子勤,张淑香. 连作障碍与根际微生态研究Ⅰ. 根系分泌物及其生态效应[J]. 应用生态学报,1998,9(5):549−554. Gao ZQ,Zhang SX. Continuous cropping obstacle and rhizospheric microecology Ⅰ. Root exudates and their ecological effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,1998,9(5):549−554.
[8] 周凯,郭维明,徐迎春. 菊科植物化感作用研究进展[J]. 生态学报,2004,24(8):1780−1788. Zhou K,Guo WM,Xu YC. Advances of research on allelopathic potential in compositae[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2004,24(8):1780−1788.
[9] 沈文涛,曾敏,黄雪梅,马永红. 凋落物浸提液对连香树种子萌发的化感作用[J]. 林业科技,2019,44(6):5−8. doi: 10.19750/j.cnki.1001-9499.2019.06.002 Shen WT,Zeng M,Huang XM,Ma YH. Allelopathic effect of litter aqueous extracts on cercidiphyllum japonicum seed germination[J]. Forestry Science & Technology,2019,44(6):5−8. doi: 10.19750/j.cnki.1001-9499.2019.06.002
[10] 庄正,李艳娟,刘青青,杨振,刘博,刘爱琴. 凋落物浸提液对杉木种子萌发及幼苗的影响[J]. 森林与环境学报,2017,37(1):29−33. Zhuang Z,Li YJ,Liu QQ,Yang Z,Liu B,Liu AQ. Effects of Chinese fir litter extracts on the seed germination and seedlings[J]. Journal of Forest and Environment,2017,37(1):29−33.
[11] 王哲,蓝亦琦,何中声,刘金福,邢聪,等. 凋落物浸提液对格氏栲种子萌发及胚根生长的影响[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版),2020,49(1):51−58. Wang Z,Lan YQ,He ZS,Liu JF,Xing C,et al. Effects of Castanopsis kawakamii forest litter extract on its seed germination and radicle growth[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition)
,2020,49(1):51−58. [12] 热娜古丽·热西提,刘生智,刘同金,陈炳舟,王家硕. 植物叶面积测量方法综述[J]. 安徽农学通报,2020,26(5):22−23. doi: 10.16377/j.cnki.issn1007-7731.2020.05.009 Renaguli · Rexiti,Liu SZ,Liu TJ,Chen BZ,Wang JS. Survey of plant leaf area measurement methods[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin,2020,26(5):22−23. doi: 10.16377/j.cnki.issn1007-7731.2020.05.009
[13] 徐新娟,李勇超. 2种植物相对电导率测定方法比较[J]. 江苏农业科学,2014,42(7):311−312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1302.2014.07.108 [14] 杨伟宗,刘明. 硫代巴比妥酸测定脂质过氧化物方法的改进[J]. 九江医学,1995,10(1):25−27. Yang WZ,Liu M. Impkovement of measurement of lipid peroxide by thiobarbituric[J]. Jiujiang Medical Journal,1995,10(1):25−27.
[15] 沈文飚,徐朗莱,叶茂炳,张荣铣. 氮蓝四唑光化还原法测定超氧化物歧化酶活性的适宜条件[J]. 南京农业大学学报,1996,19(2):101−102. Shen WB,Xu LL,Ye MB,Zhang RX. The suitable conditions for determining sod activity by nitro blue tetrazolium(NBT) photoreduction method[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University,1996,19(2):101−102.
[16] 杨兰芳,庞静,彭小兰,闫静静. 紫外分光光度法测定植物过氧化氢酶活性[J]. 现代农业科技,2009(20):364−366. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2009.20.247 Yang LF,Pang J,Peng XL,Yan JJ. Measurement of catalase activity in plants by ultraviolet spectrophotometry[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2009(20):364−366. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2009.20.247
[17] 于东立,郭韶鑫,冯志培,范贝贝,杨喜田. 短尾铁线莲不同部位水浸提液对刺槐幼苗根系生长及生理特性的化感作用[J]. 河南农业大学学报,2022,56(2):228−235,280. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2340.2022.2.hennannydxxb202202007 Yu DL,Guo SX,Feng ZP,Fan BB,Yang XT. Allelopathic effects of water extracts from different parts of Clematis brevicaudata on root growth and physiological characteristics of Robinia pseudoacacia seedlings[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University,2022,56(2):228−235,280. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2340.2022.2.hennannydxxb202202007
[18] Oyun MB. Allelopathic potentialities of Gliricidia sepium and Acacia auriculiformis on the germination and seedling vigour of maize (Zea mays L. )[J]. Am J Agric Biol Sci,2006,1(3):44−47. doi: 10.3844/ajabssp.2006.44.47
[19] Mahdavikia F,Saharkhiz MJ,Karami A. Defensive response of radish seedlings to the oxidative stress arising from phenolic compounds in the extract of peppermint (Mentha × piperita L. )[J]. Sci Hortic,2017,214:133−140. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2016.11.029
[20] Lin CC,Kao CH. Effect of NaCl stress on H2O2 metabolism in rice leaves[J]. Plant Growth Regul,2000,30(2):151−155. doi: 10.1023/A:1006345126589
[21] 刘姚姚,张瑞,沈晓飞,王曙光,李伟成. 毛竹林不同浸提液对浙江楠幼苗生长的影响研究[J]. 西部林业科学,2020,49(3):99−108. doi: 10.16473/j.cnki.xblykx1972.2020.03.016 Liu YY,Zhang R,Shen XF,Wang SG,Li WC. Study on the effects of different extracts from phyllostachys edulis forest on the growth of phoebe chekiangensis seedlings[J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science,2020,49(3):99−108. doi: 10.16473/j.cnki.xblykx1972.2020.03.016
[22] 马冬雪,刘仁林. 天然群落枯枝落叶浸提液与其它处理对伯乐树种子发芽的比较研究[J]. 林业科学研究,2012,25(5):632−637. doi: 10.13275/j.cnki.lykxyj.2012.05.017 Ma DX,Liu RL. Comparative study on germination of Bretschneidara sinensis seeds treated with solution extracted from forest litter and other methods[J]. Forest Research,2012,25(5):632−637. doi: 10.13275/j.cnki.lykxyj.2012.05.017
[23] 冯剑,刘强,王瑾,罗炘武,阮长林,张晓楠. 木麻黄浸提液对榄仁树幼苗生长及生理生化的影响[J]. 广西植物,2016,36(3):308−314. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201404037 Feng J,Liu Q,Wang J,Luo XW,Ruan CL,Zhang XN. Effects of leachates from Casuarina equisetifolia on growth and physiological and biochemical characteristics of Terminalia catappa seedlings[J]. Guihaia,2016,36(3):308−314. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201404037
[24] 林静雯, 李莹, 罗洁文, 周垂帆, 刘爱琴. 草甘膦对杉木种子萌发及幼苗生长的毒性效应[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2015, 37(5): 843-848, 858.843-848, 858. Lin JW, Li Y, Luo JW, Zhou CF, Liu AQ. Toxic effect of glyphosate on seed germination and seedling growth of Chinese fir[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2015, 37(5):
[25] 王轶夫,孙玉军,郭孝玉. 基于BP神经网络的马尾松立木生物量模型研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报,2013,35(2):17−21. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.2013.02.018 Wang YF,Sun YJ,Guo XY. Single-tree biomass modeling of Pinus massoniana based on BP neural network[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2013,35(2):17−21. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.2013.02.018
[26] 王安可,毕毓芳,温星,王玉魁,李伟成. 植物化感物质的研究现状[J]. 分子植物育种,2019,17(17):5829−5835. doi: 10.13271/j.mpb.017.005829 Wang AK,Bi YF,Wen X,Wang YK,Li WC. Research advances of plant allelochemicals[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding,2019,17(17):5829−5835. doi: 10.13271/j.mpb.017.005829
[27] 谢星光,陈晏,卜元卿,戴传超. 酚酸类物质的化感作用研究进展[J]. 生态学报,2014,34(22):6417−6428. Xie XG,Chen Y,Bu YQ,Dai CC. A review of allelopathic researches on phenolic acids[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2014,34(22):6417−6428.



 下载:
下载: