Genetic diversity and genetic structure analysis of wild Chinese Rosa roxburghii Tratt. germplasm resources
-
摘要:
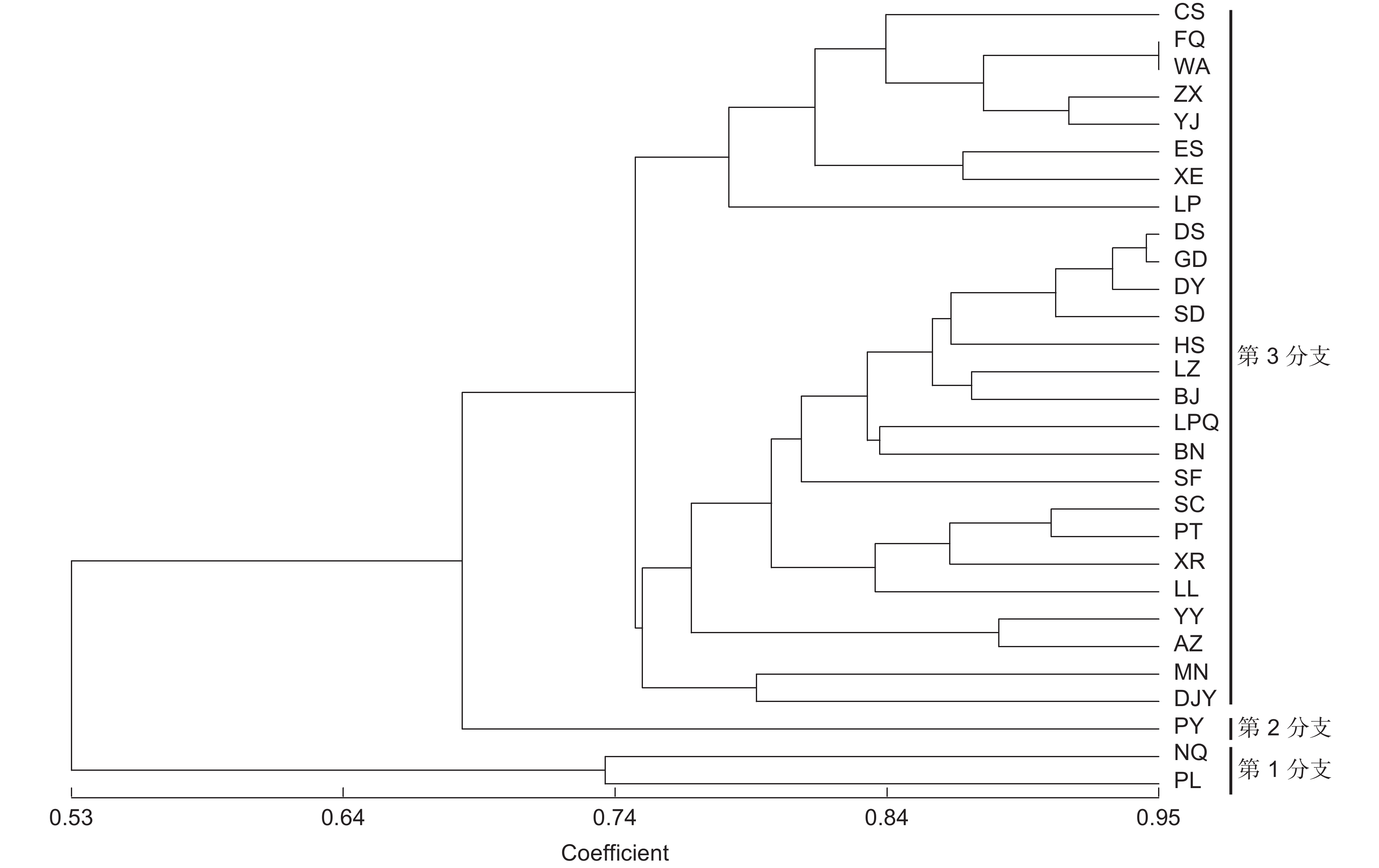
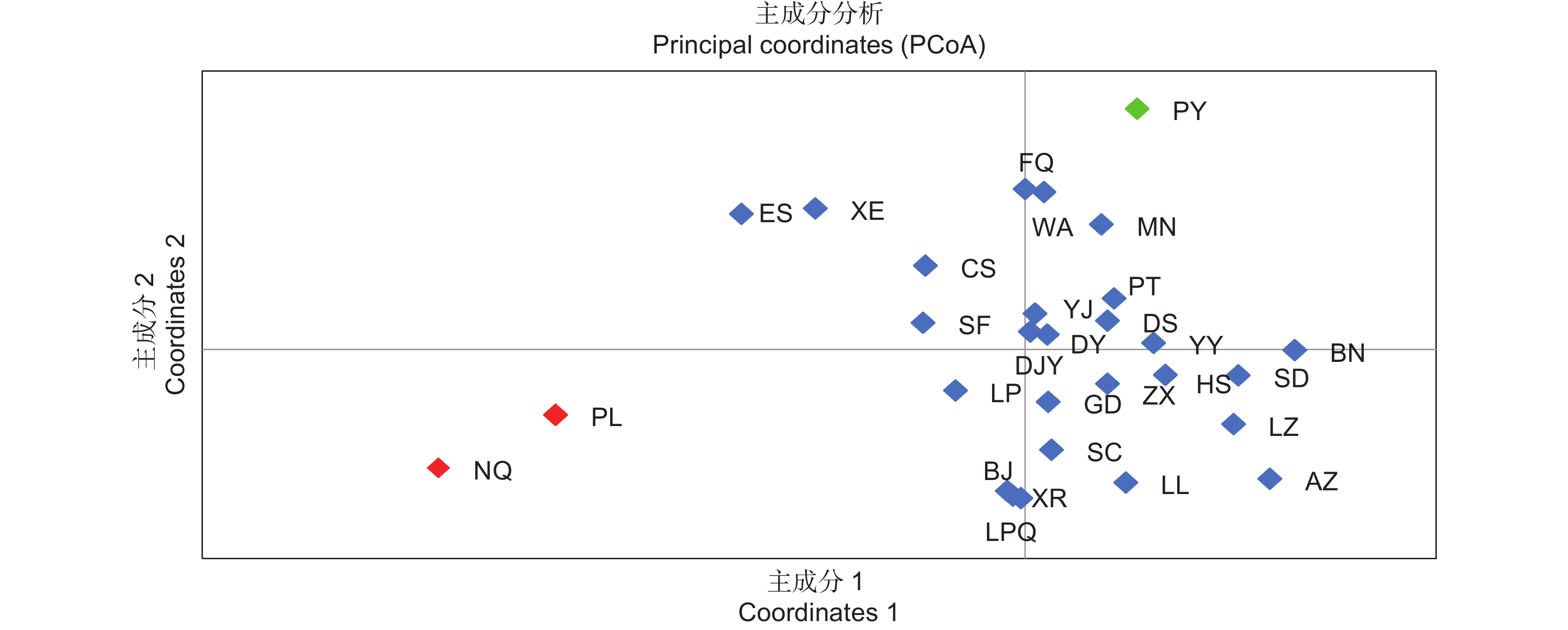
基于10对EST-SSR引物,对中国8个省29个居群的261份野生刺梨(Rosa roxburghii Tratt.)进行毛细管电泳检测,探究其遗传多样性,并进行聚类分析。结果显示,共扩增出了95个等位基因,位点多态性信息含量(PIC)平均值为0.568;群体水平上,平均等位基因数(NA)和有效等位基因数(NE)分别为3.131和2.331,平均观测杂合度(HO)和预期杂合度(HE)分别为0.508和0.488,平均Shannon’s信息指数(I)为0.858,表明野生刺梨种质具有较高的遗传多样性水平。群体遗传分化分析结果显示,平均遗传分化系数(FST)为0.067,基因流(Nm)为4.511,说明刺梨群体间基因流动较频繁。分子方差分析(AMOVA)结果表明刺梨的遗传变异主要来源于居群内(93.64%)。各居群间的Nei氏标准遗传距离范围为0.054~1.269,平均值为0.657,与地理距离表现为显著相关(r=0.467,P<0.000 1)。聚类分析和PCA结果均将29个居群分为3个分支。研究结果说明中国野生刺梨资源核心分布区在我国西南地区。
Abstract:This study explored the genetic diversity and structure of 261 wild Rosa roxburghii Tratt. samples from 29 populations across eight provinces in China, utilizing 10 pairs of polymorphic EST-SSR primers and capillary electrophoresis, providing a clear genetic background for the collection and breeding of R. roxburghii germplasm resources. Results identified 95 alleles among the 261 germplasm materials. The average polymorphism information content of the loci was 0.568. At the population level, the average number of alleles and effective number of alleles were 3.131 and 2.331, respectively, with observed heterozygosity and expected heterozygosity averaging 0.508 and 0.488. The average Shannon’s information index was 0.858, indicating substantial genetic diversity, likely due to the extensive range of sampling sites. Analysis of population genetic differentiation revealed an average genetic differentiation coefficient of 0.067 and gene flow of 4.511, suggesting considerable inter-population gene flow. Analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) indicated that most genetic variation in R. roxburghii came from within populations (r=0.467, P<0.000 1). Nei’s standard genetic distance among populations ranged from 0.054 to 1.269, with an average of 0.657, and was significantly related to geographical distance. Clustering analysis grouped the 29 populations into three main clusters, which was related to geographical location. These results highlight southwestern China as a core distribution area for wild R. roxburghii resources, providing theoretical guidance for the formulation of R. roxburghii conservation strategies.
-
Keywords:
- Rosa roxburghii /
- SSR primers /
- Genetic diversity /
- Genetic structure
-
湿地与森林、海洋并称为地球三大生态系统,其在调节生物多样性和保护自然环境等方面具有不可替代的功能与效益。西藏作为地球上独特的环境地域单元,孕育了非常独特的高寒生态环境,有着丰富的湿地资源。根据全国湿地资源第二次调查结果,西藏现有河流、湖泊、沼泽等各类湿地6.53 × 104 km2,湿地率(即湿地面积占国土面积的比率)达5.31%,高居全国第二位[1]。西藏独特的自然地理环境条件,也孕育了丰富的湿地生物多样性。近几十年来,西藏高原湿地的生物多样性受气候变化和人为活动等因素的威胁越来越严重,其生态状况也引起了世界范围的高度关注[2]。
植物是湿地生态系统的重要组成部分,也是其主要的初级生产者,对维持生态系统结构和功能的稳定有重要作用[3]。植物多样性是评价湿地生态服务价值和生态系统稳定性的重要指标,与土壤、海拔、气候等环境因子密切相关。一方面,环境因子可以影响植物的生长与群落分布,如有研究表明土壤养分含量直接制约植被的生长发育[4]。海拔也被认为是决定植被群落分布的重要因素之一[5],二者的关系目前主要有两种理论。第一种是“中间高度膨胀理论”[6, 7],即植物多样性在中海拔位置达到峰值,而在高海拔和低海拔地区相对较低。第二种是“负相关理论”[8],即植物多样性随着海拔的增加而降低。另一方面,越来越多的研究表明植物的凋落物和根系分泌物可显著改变土壤质地和肥力,进而可能影响植物的多样性[9, 10]。有研究发现,西藏地区水生植物物种丰富度和系统发育多样性随海拔的增加而显著降低[11]。也有研究表明,西藏高寒沼泽湿地植物多样性的变异受到多种环境因子相互作用的影响[12]。目前对西藏湿地植物的研究大多集中在植物物种调查[13, 14]和保护[15]上,而对湿地植物与高寒环境之间关系的探究相对较少[16, 17],因此,探讨西藏湿地植物多样性与环境因子之间关系具有重要意义。
土壤微生物作为湿地生态系统的分解者,在能量流动、物质循环、生态系统演替以及生物多样性维持等方面发挥重要的生态功能。细菌是最常见和最丰富的土壤微生物类群,驱动着绝大多数生物地球化学循环过程,如土壤有机物矿化、硝化、反硝化等[2, 18]。土壤细菌多样性与生态系统稳定性及土壤肥力有关,且能在一定程度上指示土壤养分状况和土壤质量。研究表明,土壤性质[19]、气候因素[20, 21]、地理距离[22]、植物多样性[23]等因子能显著影响土壤细菌多样性。如在高山草地和森林土壤中,pH是土壤细菌多样性形成和维持的主要驱动因子[24, 25];而在石灰质沙漠土壤中,土壤营养盐含量显著改变细菌群落的组成和结构[26]。李明家等[27]对西藏横断山区怒江和澜沧江两个流域进行了研究,发现气候和环境因子是影响细菌多样性的重要因素。甄莉等[28]探究了西藏热泉沉积物中硫氧化细菌的多样性,发现溶解有机碳含量显著影响硫氧化菌群的多样性。此外,植被特征差异也能不同程度地解释土壤微生物的多样性。如在旱地生态系统中,植物丰富度、盖度以及叶片面积等功能性状可以解释土壤细菌多样性的变异[29]。近年来,土壤微生物多样性的相关研究已经引起了国内外的广泛关注,但目前对西藏高寒环境下湿地土壤细菌多样性的研究还较少。
基于此,本研究选取26个具有代表性的西藏高原湿地为对象,探讨湿地植物和土壤细菌多样性,明确影响植物多样性与土壤细菌多样性的关键因子,试图回答“高寒环境下,哪些环境因子能够解释湿地植物和土壤细菌多样性的空间变化?”这一科学问题。研究结果旨在为了解高寒湿地生态系统的植物、微生物和土壤的相互关系,保护湿地生态系统生物多样性提供理论支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 研究地点
于2020年8月在西藏选取26个相互隔离的典型湿地(28.87° ~ 33.44°N,79.77° ~ 91.88°E)开展植被调查与土壤采样工作(图1)。所选湿地的海拔范围为3974 ~ 5206 m,年平均气温(Mean annual temperature, MAT)为−2.72℃ ~ 6.25℃,年平均降水量(Mean annual precipitation, MAP)为41 ~ 429 mm。所选湿地8月的平均降水量(Average precipitation)为67 mm,平均气温(Average temperature)为10.2℃。
依据典型性原则,在每个湿地内选择能够代表整个植被和土壤等特征的地段设置1个样地。记录样地位置(经度、纬度、海拔)及周围环境特点(放牧干扰程度、水源补给方式等)等信息。在样地内随机布设5 ~ 15个样方,样方面积为1 m2(1 m × 1 m),记录样方内的植物种类、个体数(株 / 丛数)和盖度。随机选取其中1个样方,样方内出现的所有植物各取10个叶片用信封保存,当天测定生物量鲜重和叶面积,并带回实验室测干重、碳氮磷含量等植物功能性状。在该样方内取10 g表层根际土放入冻存管中,带回实验室测定细菌多样性,另取150 g根际土放入自封袋中,带回实验室检测土壤理化性质。
1.2 植物多样性与功能性状测定
根据样方调查数据,计算植物的物种丰富度(Richness)、香农指数(Shannon index)等多样性参数。采样结束后,将植物地上部分与地下部分分开,吸干表面水分后测生物量鲜重。叶片在叶面积板上展开并拍照,使用Image J软件测叶面积(Leaf area, LA)。植物样品带回实验室放置于烘箱中,105℃杀青15 min后,立即降低烘箱温度至80℃,48 h后称量生物量干重,并计算干物质含量(Leaf dry matter content, LDMC)和比叶面积(Specific leaf area, SLA)。烘干后的植物样品用球磨仪粉碎,使用元素分析仪(Elementar Analysensysteme, Vario MACRO cube, 美国)测定叶片总碳(TC)和总氮(TN)含量,使用等离子体原子发射光谱仪(Perkin Elmer, Optima 8000 DV, 美国)测定叶片总磷(TP)含量。根据样方内各物种的相对多度(个体数),计算群落水平上各功能性状的群落加权平均数(Community weighted mean, CWM)。
1.3 土壤细菌多样性的测定
基于16S rRNA基因,采用扩增子高通量测序技术测定土壤的细菌多样性。DNA提取步骤如下:称取0.5 g土壤样品,分别加入PB(pH值 8.0)溶液和TNS(pH值 8.0)溶液,在样品破碎仪(Fastprep-24, 美国)下进行破碎,并离心得到上清液,然后分别用试剂PCI(苯酚∶氯仿∶异戊醇 = 25∶24∶1)、CI(氯仿∶异戊醇 = 24∶1)进行提取,离心得到的沉淀加入TE(pH值 8.0)溶液进行溶解,即DNA溶液。DNA溶液提纯后送至上海派森诺公司进行高通量测序。细菌群落DNA片段的双端(Paired-end)测序在Illumina MiSeq 300PE平台进行,对获得的序列使用DADA2方法进行去引物、质量过滤、去噪、拼接和去嵌合体等操作[30],获得的序列即为操作分类单元(Operational taxonomic units, OTUs)代表序列。使用QIIME 2软件中的“qiime feature-table rarefy”功能,抽平深度设为最低样本序列量的97%,获得抽平OTUs表。通过QIIME 2软件计算土壤细菌的Chao1和香农等多样性指数[31, 32]。
1.4 土壤理化性质的测定
新鲜土壤样品使用烘干法测量含水率(Moisture)。土样经自然风干、碾碎、去除细根等预处理后,分别过10目和100目筛备用。过10目筛的土样采用5%的H2O2去除有机质,然后使用激光粒度粒形仪(Mastersizer 3000, 英国)分析土壤黏粒含量(Clay)。过100目筛的土样用哈纳水质分析仪(HANNA HI98194, 意大利)测定pH值和电导率(Electrical conductivity, EC)。土样(过100目筛)经稀HCl酸化后,用元素分析仪测定有机碳含量(TOC)。使用元素分析仪测定土样(过100目筛)TC和TN含量。土样(过100目筛)经微波消解仪消解后采用等离子体原子发射光谱仪测定TP含量。
1.5 气候数据获取
采用WorldClim v2中的Average temperature(℃)、Precipitation(mm)和Bioclimatic variables(分辨率均为30″)栅格数据集,将其导入到ArcGIS 10.6软件中,使用Spatial Analyst Tools工具箱中的Extract Multi Values To Points工具,提取26个采样位点的月平均温度(Average temperature)、月降水量(Average precipitation),并计算年平均温度(MAT)和年降水量(MAP)等两个气候参数。
1.6 统计分析
实验数据使用R 3.6.2软件进行分析。用Shapiro-Wilk法检测数据的正态性和方差齐性,对不符合正态分布的数据进行对数转换或者平方根转换。采用Mantel分析植物功能性状与细菌多样性的关系,采用相关性分析探讨环境因子与植物多样性、细菌多样性的关系。利用多元回归分析寻找植物多样性和细菌多样性的关键影响因子,并通过变差分解得到各因子的解释率。使用基于距离的冗余分析(Distance-based redundancy analysis, db-RDA)对细菌群落的组成情况进行可视化分析,并通过与排序轴的多元回归置换检验得出影响细菌群落组成的关键环境因子和植物因子。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 植物与土壤细菌的多样性
本研究对26个样地的调查结果表明,植物丰富度为1 ~ 6,平均值为3.04;植物香农指数在0 ~ 1.80,平均为1.06(表1)。土壤细菌的Chao1指数在3654 ~ 6509,平均值为4859;土壤细菌的香农指数最小值为8.72,最大值为11.30。
表 1 植物与土壤细菌多样性Table 1. Plant and soil bacterial diversity指标
Index最小值
Minimum最大值
Maximum平均值
Mean植物丰富度 Plant Richness 1 6 3.04 植物香农指数 Plant Shannon 0 1.80 1.06 细菌Chao1指数 Bacteria Chao1 3654 6509 4859 细菌香农指数 Bacteria Shannon 8.72 11.30 10.41 2.2 环境因子与植物多样性的关系
相关性分析结果表明(图2),植物丰富度仅与土壤电导率显著相关,而与其他环境因子没有明显的相关性;植物香农指数与所有环境因子的相关性均不显著。回归分析结果显示(表2),海拔、年平均温度和土壤电导率仅能解释植物丰富度26.71%的变异,但能解释植物香农指数31.92%的变异,其中,土壤电导率是解释植物丰富度和香农指数变异的首要因子,解释量分别为18.41%和16.79%。
表 2 土壤细菌多样性、植物多样性与环境因子的回归分析解释率Table 2. Multiple linear regression analysis of plant and soil bacterial diversity and environmental factors指标
Index细菌Chao1指数
Bacterial Chao1 / %细菌香农指数
Bacterial Shannon / %植物丰富度指数
Plant Richness / %植物香农指数
Plant Shannon / %纬度 Latitude 8.50 6.00 − − 海拔 Altitude 8.57 21.69 8.30 6.82 年降水 MAP 16.30 − − − pH 值 22.57 16.52 − − 年均温 MAT − − − 8.31 电导率 EC − − 18.41 16.79 总解释率 R2 56.25 44.21 26.71 31.92 2.3 环境因子、植物与土壤细菌多样性的关系
相关性分析结果表明(图2),土壤细菌Chao1指数与土壤电导率呈负相关,土壤细菌Chao1、香农指数均与海拔及年降水量呈正相关,而与土壤pH呈负相关。同时,土壤细菌香农指数还与年均温、土壤总有机碳含量显著相关。进一步进行回归分析,结果显示,纬度、海拔、年降水量和土壤pH值能够解释土壤细菌Chao1指数56.25%的变异;同时,纬度、海拔和土壤pH能够解释土壤细菌香农指数44.21%的变异(表2)。
Mantel分析结果表明,土壤细菌Chao1多样性指数与群落水平的植物叶片总氮含量(CWM.TN)呈显著正相关关系(图3)。回归分析表明,植物叶片干物质含量(CWM.LDMC)与植物丰富度是解释土壤细菌Chao1指数变化的主要因子,分别贡献了18.21%和12.14%的解释度,且细菌Chao1指数随CWM.LDMC与植物丰富度的增加而增加。植物叶片总碳含量(CWM.TC)是影响土壤细菌香农指数变异的关键因子,贡献了14.01%的解释度(表3),且CWM.TC与土壤细菌香农指数呈正相关。
表 3 植物多样性、功能性状和土壤细菌多样性的回归分析解释率Table 3. Regression analysis of plant diversity, functional traits, and soil bacterial diversity指标
Index细菌Chao1指数
Bacterial Chao1 / %细菌香农指数
Bacterial Shannon / %群落加权平均叶干物质含量 CWM.LDMC 18.21 − 植物丰富度指数Richness 12.14 − 群落加权平均叶总碳含量CWM.TC − 14.01 总解释率 R2 30.35 14.01 冗余分析结果显示(图4:A),群落水平的植物功能性状(叶片总氮含量CWM.TN和总碳含量CWM.TC)和土壤理化性质(总碳和pH值)对细菌群落组成影响最大,共解释了12.48%的变异,其中前两轴分别解释了5.58%和2.90%。土壤总碳和pH值与第1轴呈正相关,而叶片总氮和总碳含量与第1轴呈负相关。韦恩图分析结果表明(图4:B),叶片总氮和总碳、土壤总碳和pH值分别解释了细菌群落3.15%、1.73%、2.11%和7.12%的差异,而它们的共同解释率很低,仅为0.08%。此外,与植物因子相比,环境因子对细菌群落组成的影响更大(图4:B)。
3. 讨论
植物多样性的变化受多种环境因素的影响,包括气候、海拔和土壤理化性质等。本研究结果表明,西藏高原湿地土壤电导率与植物丰富度呈显著负相关,且是植物多样性变异的首要驱动因子。土壤电导率直接反映土壤的盐度,过高的土壤电导率会改变植物根区的渗透压,影响植物的代谢路径,进而影响其生长速率[33]。崔乔等[34]对盐沼湿地的研究表明,植物群落组成的模式取决于土壤电导率。气候因子(年平均温度和年降水量)也是影响植物多样性的关键因素,一方面可直接制约植物的生长、分布和繁衍,另一方面决定了土壤的水热条件,从而间接影响植物的多样性[35, 36]。本研究结果表明,年平均温度是影响植物多样性的重要因子之一,而年降水量与植物多样性并没有显著的相关性,这可能是因为青藏高原高寒湿地的植物多样性更易受温度的影响[37]。Hong等[38]在河岸带湿地的研究也发现温度而非降水是影响植物物种多样性的关键因子。海拔的变化通常伴随着气候条件的改变(如温度随海拔上升而下降),进而影响植物的多样性。在西藏高原湿地中,我们发现海拔也是影响植物多样性的一个重要因子,随海拔的升高植物多样性显著降低。
细菌多样性的变化往往与环境因子密切相关。本研究发现,环境因子能够解释土壤细菌Chao1指数56.25%的变异和香农指数44.21%的变异,是影响西藏高原湿地土壤细菌多样性变化的关键因素。此外,土壤pH是湿地细菌多样性变化的关键驱动因子,细菌多样性随土壤pH值的增加而显著降低,这与Kang等[39]的研究结果一致。土壤pH会通过影响土壤基质组成、化学性质和养分利用效率来改变细菌群落的活性和多样性[40]。同时,海拔和纬度也是细菌多样性变化的关键驱动因子,细菌的Chao1指数和香农指数均随海拔的增加而显著增加。Wang等[41]对不同海拔梯度细菌群落的生物多样性模式进行了研究,结果发现细菌多样性与海拔呈显著正相关。虽然纬度也是影响细菌多样性变化的关键因子,但本研究发现二者之间不存在显著相关。这可能是因为纬度的变化主要是通过影响气候条件和土壤理化性质,进而改变细菌的多样性。细菌Chao1指数还与年均降水量呈显著正相关,与杨阳等[42]的研究结果一致。
西藏高原湿地植物的功能性状和物种丰富度也是驱动土壤细菌多样性变化的关键因子。很多研究发现土壤细菌多样性随植物多样性的增加而增加[43, 44],但也有研究指出两者并无显著相关性[45]。植物多样性很可能是通过增加凋落物和根系分泌物等的营养资源,从而促进了土壤细菌多样性的增加[46 - 48]。此外,植物多样性的变化也会引起土壤理化特征的改变(如电导率、有机碳含量等),进而影响土壤细菌多样性。Cao等[49]研究发现植物可以通过影响土壤有机碳、总氮等理化因子间接影响土壤细菌多样性。本研究结果表明,与环境因子相比,植物因子对土壤细菌多样性变化的贡献较小,这也说明西藏高原湿地土壤的细菌多样性主要由环境因子(气候、土壤理化性质)决定。
-
表 1 野生刺梨采样数量情况
Table 1 Number of wild Rosa roxburghii samples
编号
Code居群
Population数量
Number编号
Code居群
Population数量
NumberDS 贵州省独山县 12 PL 陕西省平利县 3 DY 贵州省都匀市 8 PY 江西省鄱阳县 5 FQ 贵州省福泉市 6 BJ 湖南省保靖县 5 GD 贵州省贵定县 36 ES 湖北省恩施市 8 HS 贵州省惠水县 3 XE 湖北省宣恩县 10 LL 贵州省龙里县 3 DJY 四川省都江堰 3 PT 贵州省平塘县 4 MN 四川省冕宁县 12 SD 贵州省三都县 15 AZ 四川省安州区 5 WA 贵州省瓮安县 20 YY 重庆市酉阳县 13 XR 贵州省兴仁市 4 BN 重庆市巴南区 16 LZ 贵州省六枝特区 5 LPQ 重庆市梁平区 4 SC 贵州省水城区 6 ZX 云南省镇雄市 10 CS 贵州省长顺县 6 YJ 云南省盐津县 17 LP 贵州省黎平县 4 SF 云南省水富市 6 NQ 陕西省宁强县 12 表 2 刺梨多态性引物
Table 2 Polymorphic primers of Rosa roxburghii
引物
Primer引物序列(5′→3′)
Primer sequence(5′→3′)来源
Source重复基元
Repeated motif产物大小
Product size / bpRox1 F: AATATACACGAACAACAACCATCG
R: GGAACATGACCCCTTTTCTTATT刺梨
R. roxburghii(CTACA)4 147 Rox2 F: GAGTCATGTTGAATGATATTGGC
R: TTTCCTCTTTTCTTCTTTTTCCC刺梨 (TGGA)13 131 Rox3 F: TGAGAACCAAAAGAAACGACTACA
R: GTCACAAATTCACGAGCCATATT刺梨 (AT)8 146 Rox4 F: GAGAGAGTAGCCTTTGATGAGGA
R: GAATGTCGTCAGGGAGCAGTAG刺梨 (CTC)7 146 Sam1 F: ATGCCCTTTTGATGTGCTGGTAGAG
R: TCGGATCTTCTTGTGCTGTTTCTCC月季
R. chinensis(AG)5 233 Sam2 F: TGGTGGCAAACAGGAGAAGATATGG
R: GCAACATCTGCACAACTGGAAGC月季 (GA)5 211 Sam3 F: GCAACAACAGCAACAACTTCCTTTG
R: GTTGGAGTGGCAGTTGATGCTTATG月季 (CAA)5 245 Sam4 F: GTTGCTCCACAGATGCCTCAGTC
R: TGGTTGAAATTGCTGCTGTTGTTGG月季 (CAG)5 258 Sam5 F: GAACCAAGTCCTTCCGCAAA
R: CCAACATAGCGGTTGCTTGA月季 (CTT)5 223 Sam6 F: GTGTACTATCGAGCCGATCCAGGAG
R: AACCACGCTTCAATGGCTCATCC月季 (CT)5 200 表 3 10对SSR引物在261份刺梨种质中的遗传信息
Table 3 Genetic information of 10 SSR primers in 261 Rosa roxburghii germplasms
引物Primer 等位基因数 Number of alleles 有效等位基因数 Effective number of alleles Shannon’s指数Shannon information index 观测杂合度Observed heterozygosity 期望杂合度Effective heterozygosity 多态信息含量Polymorphism information content Sam1 7 1.305 0.307 0.073 0.180 0.227 Sam2 13 1.640 0.476 0.060 0.288 0.503 Sam3 9 1.832 0.661 0.394 0.401 0.456 Sam4 8 2.365 0.986 0.731 0.551 0.548 Sam5 11 2.284 0.913 0.708 0.550 0.576 Sam6 13 2.078 0.813 0.538 0.481 0.521 Rox1 14 2.688 0.997 0.457 0.550 0.750 Rox2 5 2.410 0.903 0.714 0.554 0.599 Rox3 11 3.597 1.323 0.758 0.690 0.782 Rox4 11 3.115 1.200 0.649 0.634 0.718 平均值 10.2 2.311 0.858 0.508 0.488 0.568 表 4 不同居群平均多样性指数
Table 4 Average diversity index of different populations
群体
Population等位基因数
Number of
alleles有效等位基因数
Effective number
of allelesShannon’s指数
Shannon information
index观测杂合度
Observed
heterozygosity期望杂合度
Observed
heterozygosity固定指数
Fixation index多态性位点比率
Polymorphic
site rate / %CS 3.300 2.170 0.868 0.322 0.479 0.346 90.00 DS 3.700 2.780 1.035 0.656 0.572 −0.075 100.00 DY 3.400 2.452 0.941 0.489 0.530 0.064 100.00 FQ 2.900 2.320 0.852 0.463 0.504 0.080 100.00 GD 5.400 2.433 1.013 0.545 0.523 −0.013 100.00 HS 2.000 1.678 0.584 0.450 0.376 −0.192 80.00 LP 2.600 2.078 0.786 0.300 0.482 0.390 100.00 LL 2.600 2.161 0.763 0.517 0.449 −0.186 80.00 PT 2.300 1.877 0.672 0.417 0.426 0.002 90.00 SD 3.500 2.563 0.959 0.661 0.537 −0.165 100.00 WA 3.900 2.536 0.987 0.587 0.535 0.035 100.00 XR 2.300 2.032 0.666 0.600 0.419 −0.472 80.00 LZ 2.400 2.117 0.731 0.675 0.435 −0.561 70.00 SC 2.500 2.008 0.666 0.583 0.391 −0.503 70.00 ES 3.500 2.585 1.033 0.419 0.588 0.307 100.00 XE 3.700 2.533 0.997 0.401 0.540 0.272 100.00 BJ 3.500 2.952 1.062 0.647 0.588 −0.076 90.00 PY 2.500 2.121 0.705 0.340 0.412 0.138 70.00 NQ 4.600 3.223 1.233 0.731 0.645 −0.118 100.00 PL 1.800 1.530 0.476 0.433 0.306 −0.363 70.00 DJY 1.600 1.500 0.381 0.300 0.238 −0.300 40.00 MN 3.500 2.494 0.953 0.553 0.522 0.003 90.00 AZ 3.100 2.489 0.898 0.360 0.503 0.254 90.00 SF 3.000 2.154 0.848 0.440 0.495 0.101 90.00 YJ 4.000 2.877 1.076 0.490 0.562 0.182 100.00 ZX 3.000 2.382 0.894 0.411 0.522 0.286 100.00 LPQ 2.500 2.160 0.699 0.592 0.418 −0.446 80.00 YY 3.700 2.769 1.059 0.680 0.587 −0.185 100.00 BN 4.000 2.631 1.044 0.673 0.565 −0.067 100.00 平均值 3.131 2.331 0.858 0.508 0.488 −0.019 88.97 表 5 各SSR位点F-statistics及基因流
Table 5 F-statistics and gene flow for each SSR microsatellite locus
位点Locus 居群内分化系数
Within-population differentiation coefficient总近交系数
Total inbreeding coefficient基因流Gene flow Sam1 0.142 0.819 1.516 Sam2 0.116 0.918 1.899 Sam3 0.041 0.110 5.828 Sam4 0.039 −0.306 6.084 Sam5 0.091 −0.170 2.503 Sam6 0.044 0.242 5.400 Rox1 0.084 0.623 2.716 Rox2 0.040 0.268 6.008 Rox3 0.038 0.195 6.352 Rox4 0.035 0.065 6.805 平均 值 0.067 0.276 4.511 表 6 刺梨29个居群分子方差分析
Table 6 Analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA)of 29 Rosa roxburghii populations
变异来源
Variance source自由度
df离均差平方和
SS均方
MS估计方差
Estimated variance变异百分比
Percentage variation / %群体间 28 213.437 7.623 0.211 6.36 群体内 493 1 509.647 6.218 3.109 93.64 总计 521 1 723.084 3.320 100 -
[1] 陈明,陈继平. 刺梨授粉结实习性研究[J]. 绵阳农专学报,1993,10(3-4):69−70. Chen M,Chen JP. A study of habit of pollination and fruitage on Roxburgh rose[J]. Journal of Mianyang Agricultural College,1993,10(3-4):69−70.
[2] 胡红菊. 我国野生刺梨资源开发利用探讨[J]. 中国果树,2009(3):71−72. [3] 徐东旭,姜翠棉,宗绪晓. 蚕豆种质资源形态标记遗传多样性分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报,2010,11(4):399−406. Xu DX,Jiang CM,Zong XX. Phenotypic diversity of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) germplasm resources[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2010,11(4):399−406.
[4] Petit RJ,El Mousadik A,Pons O. Identifying populations for conservation on the basis of genetic markers[J]. Conser Biol,1998,12(4):844−855.
[5] Powell W,Morgante M,Andre C,Hanafey M,Vogel J,et al. The comparison of RFLP,RAPD,AFLP and SSR (microsatellite) markers for germplasm analysis[J]. Mol Breed,1996,2(3):225−238.
[6] Tang WJ,Wu TT,Ye J,Sun J,Jiang Y,et al. Erratum to:SNP-based analysis of genetic diversity reveals important alleles associated with seed size in rice[J]. BMC Plant Biol,2016,16(1):128.
[7] Tautz D. Hypervariability of simple sequences as a general source for polymorphic DNA markers[J]. Nucleic Acids Res,1989,17(16):6463−6471.
[8] Powell W,Machray GC,Provan J. Polymorphism revealed by simple sequence repeats[J]. Trends Plant Sci,1996,1(7):215−222.
[9] Liu G,Xie YJ,Zhang DQ,Chen HP. Analysis of SSR loci and development of SSR primers in Eucalyptus[J]. J Forest Res,2018,29(2):273−282.
[10] Singh AK,Chaurasia S,Kumar S,Singh R,Kumari J,et al. Identification,analysis and development of salt responsive candidate gene based SSR markers in wheat[J]. BMC Plant Biol,2018,18(1):249.
[11] Kaur S,Pembleton LW,Cogan NO,Savin KW,Leonforte T,et al. Transcriptome sequencing of field pea and faba bean for discovery and validation of SSR genetic markers[J]. BMC Genomics,2012,13(1):104.
[12] 孙浩男,李蓉,李明阳,郑妍,刘志杰,等. 栽培金鸡菊EST-SSR分子标记开发与亲缘关系分析[J]. 草地学报,2022,30(6):1430−1440. Sun HN,Li R,Li MY,Zheng Y,Liu ZJ,et al. Development of EST-SSR markers based on transcriptome and analysis of genetic relationship of cultivated coreopsis[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica,2022,30(6):1430−1440.
[13] Porebski S,Bailey LG,Baum BR. Modification of a CTAB DNA extraction protocol for plants containing high polysaccharide and polyphenol components[J]. Plant Mol Biol Rep,1997,15(1):8−15.
[14] 张怀山,鄢秀芹,鲁敏,王道平,安华明. 基于EST-SSR标记的贵州野生刺梨居群遗传多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科学,2017,50(6):1098−1108. Zhang HS,Yan XQ,Lu M,Wang DP,An HM. Analysis of the genetic diversity of wild Rosa roxburghii populations in Guizhou province based on EST-SSR marker[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2017,50(6):1098−1108.
[15] 鄢秀芹. 刺梨果实转录组分析及EST-SSR开发与应用[D]. 贵阳:贵州大学,2015:13−29. [16] Lu M,An HM,Li LL. Genome survey sequencing for the characterization of the genetic background of Rosa roxburghii Tratt and leaf ascorbate metabolism genes[J]. PLoS One,2016,11(2):e0147530.
[17] 潘凤. 刺梨的遗传多样性及谱系地理学研究[D]. 贵阳:贵州大学,2022:12−13. [18] 伊贤贵,陈洁,尤禄祥,从睿,王华辰,等. 山樱花群体遗传多样性的SSR分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2018,42(5):25−31. Yi XG,Chen J,You LX,Cong R,Wang HC,et al. Genetic diversity of Cerasus serrulata populations assessed by SSR markers[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition),2018,42(5):25−31.
[19] Peng JY,Shi C,Wang DW,Li SZ,Zhao XL,et al. Genetic diversity and population structure of the medicinal plant Docynia delavayi (Franch.) Schneid revealed by transcriptome based SSR markers[J]. J Appl Res Med Aroma Plants,2021,21:100294.
[20] 从睿. 康定樱桃居群遗传多样性的SSR分析[D]. 南京:南京林业大学,2018:19−28. [21] 吴高琼. 基于SSR分子标记的中国古老月季野生亲本分析[D]. 昆明:云南大学,2019:25−27. [22] 刁霞. 黄毛草莓(Fragarian nilgerrensis Schldl)EST-SSR引物开发及遗传多样性研究[D]. 昆明:云南大学,2019:25−31. [23] 李楠玉,张怀山,安华明,鲁敏. 基于ITS序列对刺梨遗传多样性的分析[J/OL]. 分子植物育种,2021:1-23[2021-09-01]. https://kns. cnki. net/kcms/detail/46.1068. s. 20210827.1325. 005. html. Li NY,Zhang HS,An HM,Lu M. Analysis of genetic diversity of Rosa roxburghii Tratt. based on ITS sequence[J/OL]. Molecular Plant Breeding,2021:1-23[2021-09-01]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.s.20210827.1325.005.html.
[24] 孟艺宏,徐刚标,卢孟柱,姜小龙,郭飞龙. 长柄双花木种群遗传结构及种群历史[J]. 林业科学,2020,56(7):55−62. Meng YH,Xu GB,Lu MZ,Jiang XL,Guo FL. Population genetic structure and demographic history of Disanthus cercidifolius var. longipes[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae,2020,56(7):55−62.
[25] 闫丽君. 基于SSR标记的伯乐树遗传多样性分析[D]. 长沙:中南林业科技大学,2015:19−28. [26] Li LX,Ou WL,Wang YC,Peng JY,Wang DW,Xu S. Comparison of genetic diversity between ancient and common populations of Docynia delavayi (Franch.) Schneid[J]. Gene,2022,829:146498.
[27] 吴敏,吴诗琪,潘凤,石甜,赵财. 中国野生半夏的遗传多样性和遗传结构研究[J/OL]. 广西植物,2023:1-13[2023-07-25]. https://kns. cnki. net/kcms2/detail/45.1134. q. 20230724.1642. 004. html. Wu M,Wu SQ,Pan F,Shi T,Zhao C. Genetic diversity and genetic structure of wild Pinellia ternate(Araceae) in China[J]. Guihaia,2023:1-13[2023-07-25]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/detail/45.1134.q.20230724.1642.004.html.
[28] 张怀山. 基于SSR标记及ITS、cpDNA序列的刺梨遗传多样性分析[D]. 贵阳:贵州大学,2017:23−60. [29] 刘慎谔. 刘慎谔文集[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1985:23−100. [30] 吴诗琪,潘凤,赵财. 西南地区野生刺梨的遗传多样性和遗传结构研究[J]. 广西植物,2023,43(11):2065−2077. Wu SQ,Pan F,Zhao C. Genetic diversity and structure of wild Rosa roxburghii in Southwest China[J]. Guihaia,2023,43(11):2065−2077.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 张曼华,谢元贵,田秀,张蓝月,廖小锋,王军才. 土壤微生物对4种森林类型植物多样性形成的影响. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2025(01): 26-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)




 下载:
下载: