Identification and expression analysis of the TIFY transcription factor family of Cinnamomum camphora (L.) Presl.
-
摘要:
TIFY转录因子对植物生长发育与次生代谢有重要调控作用。本研究利用生物信息学技术鉴定了樟树(Cinnamomum camphora(L.) Presl.)基因组中的21个CcTIFYs基因,并基于转录组数据分析了其表达特性。结果显示,21个成员分属于TIFY、JAZ、PPD与 ZML等4个亚家族,且JAZ亚家族又进一步形成了6个进化分枝。染色体定位与共线性分析显示,CcTIFYs不均匀地分布于9条染色体上,存在14对CcTIFY共线性基因对。种间共线性分析结果表明樟树TIFY家族与毛果杨(Populus trichocarpaTorr. & Gray.)TIFY家族亲缘关系更近。此外,表达分析表明14个成员具有组织表达特异性,CcJAZ11、CcTIFY1与CcJAZ4/5等分别在花、根与籽中优势表达;在不同化学型的叶组织中,5个成员发生了差异表达,其中,CcJAZ10与CcPPD1在柠檬醛型中优势表达,CcJAZ9在甲基丁香酚型中优势表达。研究结果为分析樟树组织发育和次生代谢调控机理提供了参考。
-
关键词:
- 樟树 /
- TIFY转录因子家族 /
- 系统发育 /
- 共线性 /
- 表达分析
Abstract:TIFY transcription factors are crucial for regulating plant growth, development, and secondary metabolism. In this study, 21 TIFY transcription factors were identified in theCinnamomum camphora(L.) Presl. genome using bioinformatics analysis, and their expression patterns were evaluated based on transcriptome data. Conserved domain annotation and phylogenetic analysis revealed thatCcTIFYswere classified into four major subgroups, JAZ, ZML, TIFY, and PPD, with the JAZ group further clustered into six clades (JAZ Ⅰ to JAZ Ⅵ). The 21CcTIFYswere unevenly distributed across nine chromosomes, and intraspecific collinearity analysis detected 14 syntenic gene pairs but no tandemly duplicated gene pairs, indicating that segmental duplication events played a vital role in the expansion of theTIFYgenes in the camphor tree. Interspecific collinearity analysis suggested that CcTIFYs were most closely related to TIFYs in poplar. In addition, expression analysis indicated that two-thirds of the members exhibited tissue-specific expression. NotablyCcJAZ11,CcTIFY1, andCcJAZ4/5showed higher expression in flowers, roots, and developing seeds, respectively. Among the different chemotypes, five members were differentially expressed in leaf tissue, including four up-regulated genes in the citral type and one up-regulated gene in the methyl eugenol type. This study provides insights into the molecular mechanisms of tissue development and secondary metabolite production in the camphor tree.
-
Keywords:
- Cinnamomum camphora /
- TIFY gene /
- Phylogenetic evolution /
- Collinearity /
- Expression analysis
-
TIFY家族是一类植物专一性的转录因子,其所有成员均具有特征性的TIFY保守结构域(核心基序为TIF[F/Y]XG,其中X为任意氨基酸残基,下同)[1]。结合其他保守结构域组成,该家族可被分为TIFY、JAZ、PPD 和ZML等4大亚家族,其中,JAZ亚家族成员序列C端含有额外的Jas保守结构域(基序为SLX2FX2KRX2RX5PY),PPD亚家族成员序列N端含有独特的PPD结构域,且C端含有变形的Jas保守结构域,ZML亚家族成员在C端含有C2C2-GATA(基序为C-X2-C-X20-C-X2-C)和CCT结构域[2]。系统发育分析结果显示,TIFY、PPD和ZML亚家族成员分别形成1枝独立的进化枝,而JAZ亚家族成员则形成了6枝进化分枝[2]。至2023年初,已从近30种植物中鉴定到了TIFY家族成员,包括拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh)[1]、水稻(Oryza sativa L.)[3]与毛果杨(Populus trichocarpa Torr. & Gray.)[4]等,在油菜(Brassica napus L.)[5]中发现了多达77个成员,而在丹参(Salvia militiorrhiza Bunge)[6]和西瓜(Citrullus lanatus (Thunb.) Matsum.&Nakai)[7]中均只发现了15个成员。
TIFY转录因子在植物生长发育、次生代谢、响应激素信号及环境胁迫等过程中均具有重要调控作用。譬如,在器官发育调控方面,过量表达拟南芥AtTIFY1基因可引起花序、叶柄和下胚轴延长[8, 9];AtTIFY8可与REV互作,调控下游与叶片衰老密切相关的AtWRKY53的转录水平,过量表达或突变AtTIFY8可加快或延迟叶片衰老[10];突变AtTIFY4a(PPD1)和AtTIFY4b(PPD2)则造成叶片弯曲及叶面积增大[11],二者还可通过KIX-PPD-MYC-GIF1 通路参与调控种子大小[12]。在水稻中,过量表达OsJAZ10基因也可增加谷粒大小、谷粒宽度和重量,相对野生型谷粒大小提高了约14%,谷粒宽度和重量都增加了约30%[13]。在木材形成方面,毛白杨(P. tomentosa Carr.)PtoJAZ5基因在发育中的木质部优势表达,过量表达该基因可抑制次生壁的加厚及下调次生壁相关合成基因的表达[14]。在响应环境胁迫方面,抑制OsJAZ9基因的表达可以降低水稻耐盐性[15],OsJAZ1基因则可通过JA与ABA信号通路减弱植株的耐旱性[16]。在调控次生代谢方面,来自拟南芥的研究提供了TIFY转录因子参与调控花青素累积的证据[17-20];在栽培苹果(Malus domestica Borkh.)中,目前已知MdJAZ1、MdJAZ2与MdJAZ18等均负调控花青素和原花青素的合成[21-23];在丹参中,多个JAZs参与萜类化合物丹参酮的合成调控,其中SmJAZ3/4/8起抑制作用,而SmJAZ1/2/5/6/9则起促进作用[24, 25]。
樟树(Cinnamomum camphora (L.) Presl)是我国南方常见高大乔木,集材用、药用、香料及生态用途于一身。其枝叶富含精油,是我国生产木本天然香料的主要植物资源之一。根据叶精油的主成分含量,可将之划分为芳樟醇型、桉叶油素型、柠檬醛型、樟脑型、天然龙脑型及异橙花叔醇等不同的化学类型[26, 27]。樟树茎杆材质细腻,质地坚硬且耐腐蚀虫蛀,为江南四大名木之一。樟树籽富含中碳链脂肪酸,是具有巨大开发潜力的木本油料资源。然而,目前关于樟树次生代谢物合成、木材形成及种子发育等机理还知之甚少。基于近期公布的樟基因组和转录组数据[27],本研究在樟中开展了TIFY基因家族的鉴定与表达分析,研究结果旨在为后续解析樟优良性状的形成机制提供基因资源。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 数据来源
樟树染色体水平基因组、全长转录组、6种不同组织(花、树皮、小枝、根、叶与籽)和8种化学型(左旋芳樟醇型、樟脑型、天然龙脑型、1,8-桉叶油素型、柠檬醛型、异橙花叔醇型、甲基丁香酚型与甲基异丁香酚型)的二代转录组数据均由本课题组前期测序获得(部分数据尚未公布)[27]。模式植物拟南芥、水稻与毛果杨的基因组数据从NCBI数据库(https://www.ncbi.nlm. nih.gov/genome )下载获得,对应的TIFY家族序列来源于PlantTFDB(http://planttfdb.gao-lab.org/index.php)数据库。
1.2 樟树TIFY基因家族成员鉴定及序列特征分析
基于樟树基因组预测蛋白集数据,使用hmmer2.3.2软件(http://hmmer.org/),调用pfam文件注释CcTIFY保守结构域(pfam06200),并获得各候选成员基因ID;从基因组预测CDS集中获得对应的CDS序列,随后通过本地blastn软件[28]与樟树全长转录组序列比对及手工矫正,获得全长编码序列;利用ExPASy在线工具(https://web.expasy.org/protparam)预测各成员编码蛋白的大小及等电点等基本情况;利用MEME 工具(http://memesuite.org/tools/meme)对蛋白序列进行保守基序分析;利用GSDS软件(http://gsds.gao-lab.org/)分析CcTIFY家族各成员基因结构;利用在线软件TargetP-2.0(https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/services/TargetP-2.0)、Softberry(http://www.softberry.com)及WoLF PSORT(https://www.genscript.com/wolf-psort.html)等预测CcTIFY家族各成员的亚细胞定位情况。
1.3 构建樟树TIFY基因家族的系统发育树
首先,利用MEGA11.0软件[29]中的Clustal W程序对4个物种TIFY家族成员进行氨基酸序列多重比对,并借助trimAL软件对保守区域进行裁剪;随后基于最大似然法(Maximum likelihood,ML)构建无根树,结果以newick文件保存;最后,通过EvolView软件(https://evolgenius.info//evolview-v2)对进化树进行可视化修饰。
1.4 樟树TIFY家族成员染色体定位和共线性分析
根据樟树基因组gff3注释文件提取各TIFY家族成员的染色体坐标信息;利用TBtools软件[30]中的MCSanX程序分析各成员在基因组中的复制类型和种内共线性情况。本研究中,基因串联复制设置为两个条件[31-33]:(1)两个同源基因比对区域覆盖度大于70%(较短基因相对于较长的基因),且序列相似性大于70%;(2)两个基因在染色体上的距离小于100 kb。利用TBtools软件中Advanced Circles程序可视化各成员染色体定位情况及种内共线性关系,使用Multiple Synteny Plot程序分析TIFY家族成员在拟南芥、樟树与毛果杨的种间共线性情况,并筛选种间共线性基因对。最后,借助TBtools软件中的Simple Ka/Ks Calculator程序计算复制基因对和共线性基因对的非同义替换率(Ka)和同义替换率(Ks)。
1.5 樟树TIFY家族各成员的表达分析
基于本课题组前期测序完成的8种化学型叶组织和6种不同组织部位的二代转录组数据,分析樟树TIFY家族各成员的基因表达情况。8种化学型叶组织中,有5种其精油主成分为单萜类化合物(左旋芳樟醇、1,8-桉叶油素、樟脑、龙脑和柠檬醛),1种为倍半萜类化合物(橙花叔醇),2种为苯丙烯类(甲基丁香酚和甲基异丁香酚)。6种组织部位分别为成熟花、成熟叶、小枝、树皮、主根及不同发育阶段的樟籽(包含果肉和种子)。樟籽样本具体包括体积快速膨大S1、S2和S3期(分别取自7月初、8月初和9月初),成熟S4期(取自10月初,籽体积恒定,且果皮颜色开始加深)和成熟后S5期(取自11月初,果皮颜色紫化)。
表达情况分析方法为:获取各成员对应转录本的FPKM值,归一化与对数 (log 2) 化处理后构建数据矩阵;差异表达基因筛选标准为 P值<0.01及log2 (表达量倍数)≥1.0;最后利用TBtools软件绘制樟树CcTIFY家族基因的表达图谱,并进行聚类分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 樟树TIFY基因家族成员鉴定与理化性质分析
通过保守结构域注释和CDS序列人工矫正,本研究从樟树基因组中共获得21个完整的TIFY编码基因,其中19个成员的氨基酸序列包含典型的TIFY保守结构域,2个成员具有变形的TIFY结构域。基因编码116~583个氨基酸残基,分子量为12.98~63.35 kDa,等电点为5.05~9.89。结合Jas、C2C2-GATA锌指结构、CCT和PPD等结构域的注释结果,21个CcTIFY家族成员进一步被细分为TIFY、JAZ、ZML和PPD等4个亚家族,分别被命名为CcTIFY1-2、CcJAZ1-11、CcZML1-7和CcPPD1。亚细胞定位信号预测结果显示,CcTIFY7/10/11、CcZML1/7等5个成员定位于叶绿体,CcJAZ4、CcZML2/4等3个成员定位于细胞质,其余家族成员则定位于细胞核中(表1)。
表 1 樟树TIFY家族基因基本信息Table 1. Characteristics of predicted TIFY family in Cinnamomum camphora genome基因名称
Gene基因登录号
Accession No.蛋白大小
Protein length / aaTify结构域
Tify motif亚细胞定位
Subcellular localizationCcJAZ1 Cca.gene26099 261 TIFYSG 细胞核 CcJAZ2 Cca.gene31020 392 TIFYGG 细胞核 CcJAZ3 Cca.gene31955 116 TIFYNG 细胞核 CcJAZ4 Cca.gene16854 219 TIFYNG 细胞质 CcJAZ5 Cca.gene32166 264 TIFYGG 细胞核 CcJAZ6 Cca.gene32297 391 TVFYAG 细胞核 CcJAZ7 Cca.gene21329 124 TIFYNG 叶绿体 CcJAZ8 Cca.gene3287 336 TIFYGG 细胞核 CcJAZ9 Cca.gene3121 258 TIFYGG 细胞核 CcJAZ10 Cca.gene3036 165 TIFYSG 叶绿体 CcJAZ11 Cca.gene36159 123 TIFYNG 叶绿体 CcZML1 Cca.gene34662 333 TVNLQG 叶绿体 CcZML2 Cca.gene37247 330 TLSFQG 细胞质 CcZML3 Cca.gene13670 583 TLSFNG 细胞核 CcZML4 Cca.gene35327 355 TLSFQG 细胞质 CcZML5 Cca.gene38719 572 TLSFNG 细胞核 CcZML6 Cca.gene353 334 TLSFQD 细胞核 CcZML7 Cca.gene15532 355 TLSFQG 叶绿体 CcTIFY1 Cca.gene13838 412 TIFYDG 细胞核 CcTIFY2 Cca.gene33234 407 TIFYAG 细胞核 CcPPD1 Cca.gene18919 355 TIFYDG 细胞核 2.2 樟树TIFYs转录因子的保守Motif鉴定
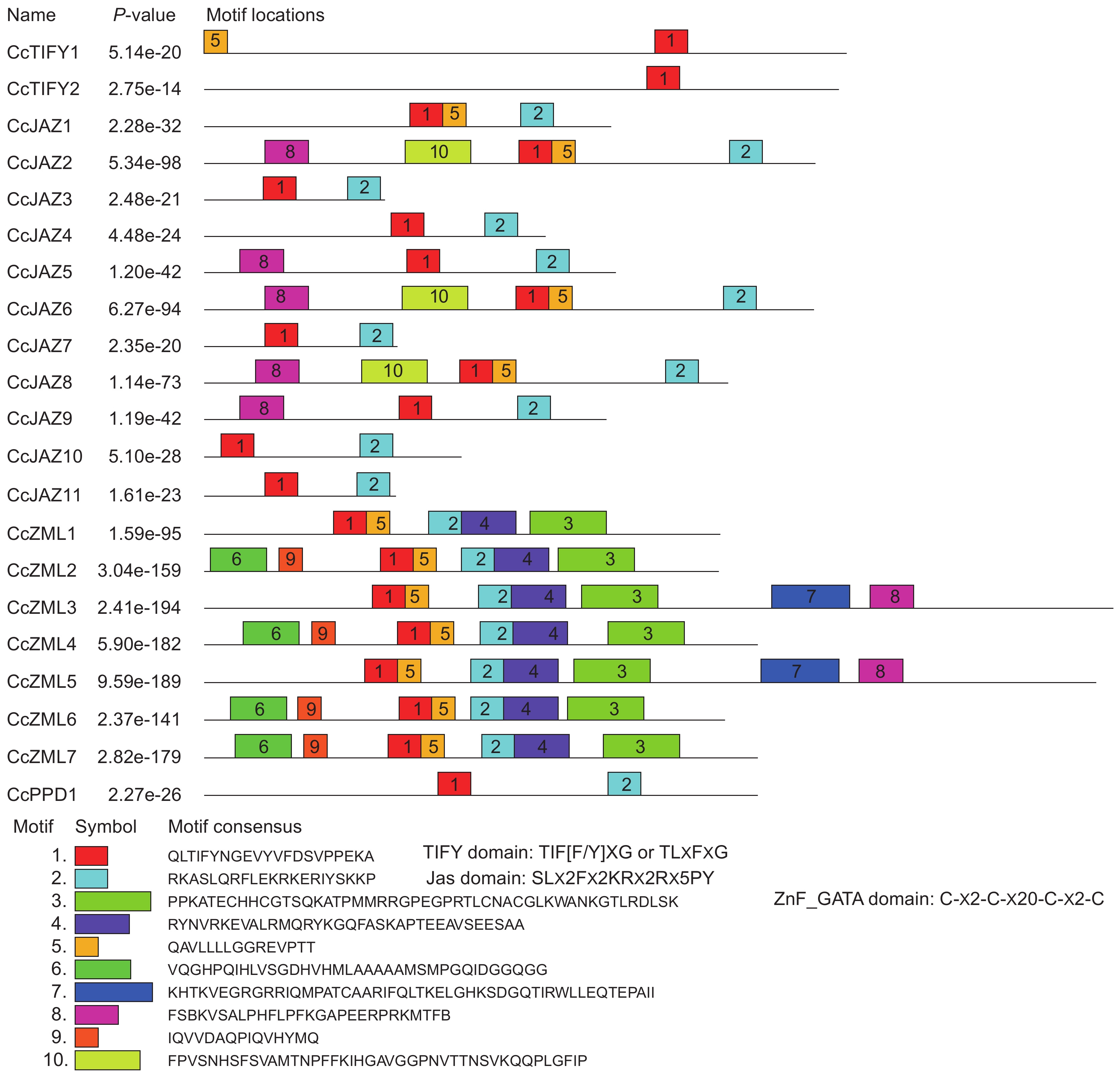
CcTIFY转录因子家族含有10个保守Motif,分别命名为Motif 1~10(图1)。Motif 1存在于所有成员中,包含典型的TIFY核心基序TIFYNG。Motif 2为CcJAZ、CcZML和CcPPD亚家族成员所共有,对应JAS (又称CCT2)和CCT结构域。Motif 3/4/6/7/9为CcZML亚家族成员所独有,其中对应ZnF_GATA结构域的Motif 3/4见于所有CcZML亚家族成员,Motif 6/7/9的分布则具有随机性。Motif 5/8存在于部分CcJAZ和CcZML亚家族成员中,而Motif 10则出现于部分CcJAZ成员中。
2.3 樟树TIFYs基因结构分析
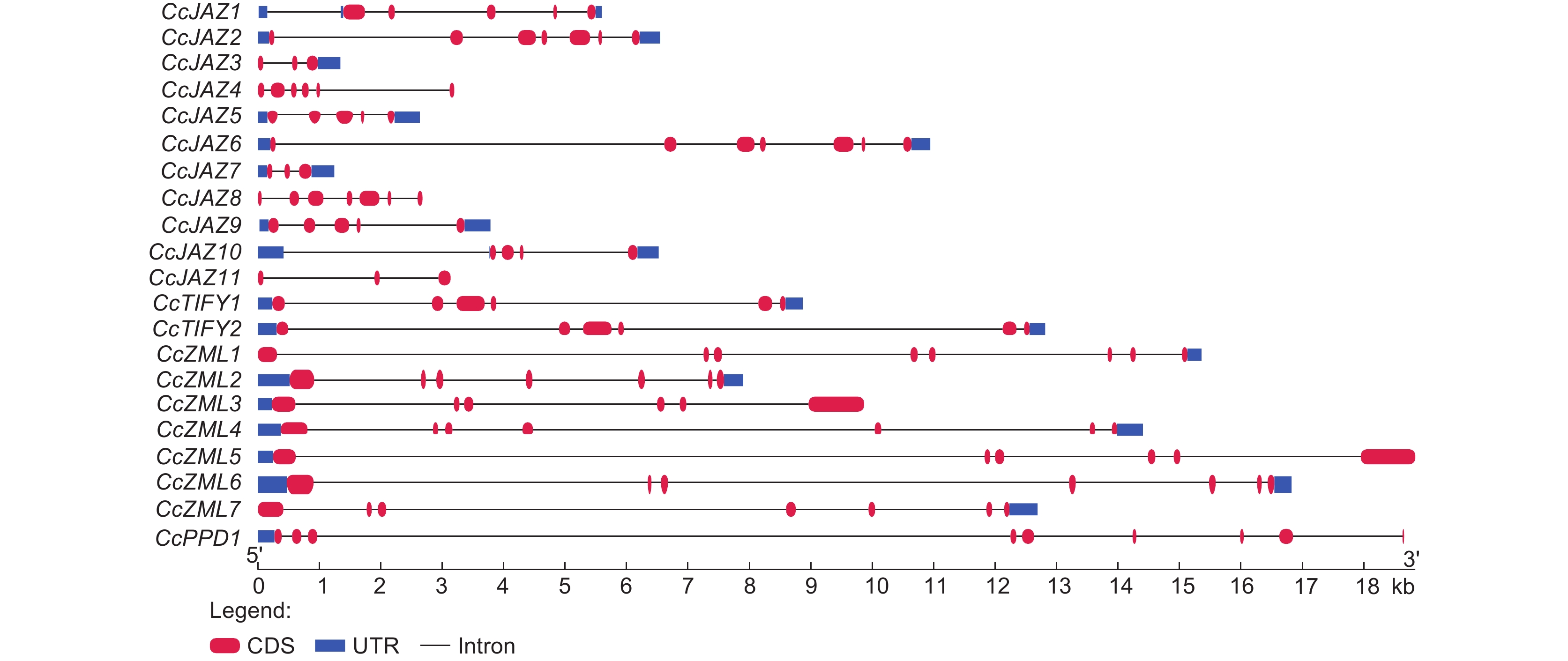
本研究通过比对基因组序列和全长转录组序列,分析了樟树TIFYs外显子-内含子的个数及长度比例(图2)。结果显示CcTIFY亚家族的2个基因皆包含6个外显子和5个内含子,外显子和内含子的长度较一致;CcJAZ亚家族的11个基因外显子-内含子数目及序列长度均呈多样性,其中CcJAZ2/6/8 等3个基因外显子最多,为8个,而CcJAZ3/7/11等3个基因外显子最少,为3个;CcZML亚家族的7个基因外显子-内含子数目及序列长度差异显著,其中CcZML1有8个外显子,CcZML3/5有6个外显子,各基因内含子长度也差异显著;CcPPD1基因包含9个外显子。
2.4 樟树TIFY家族系统进化分析
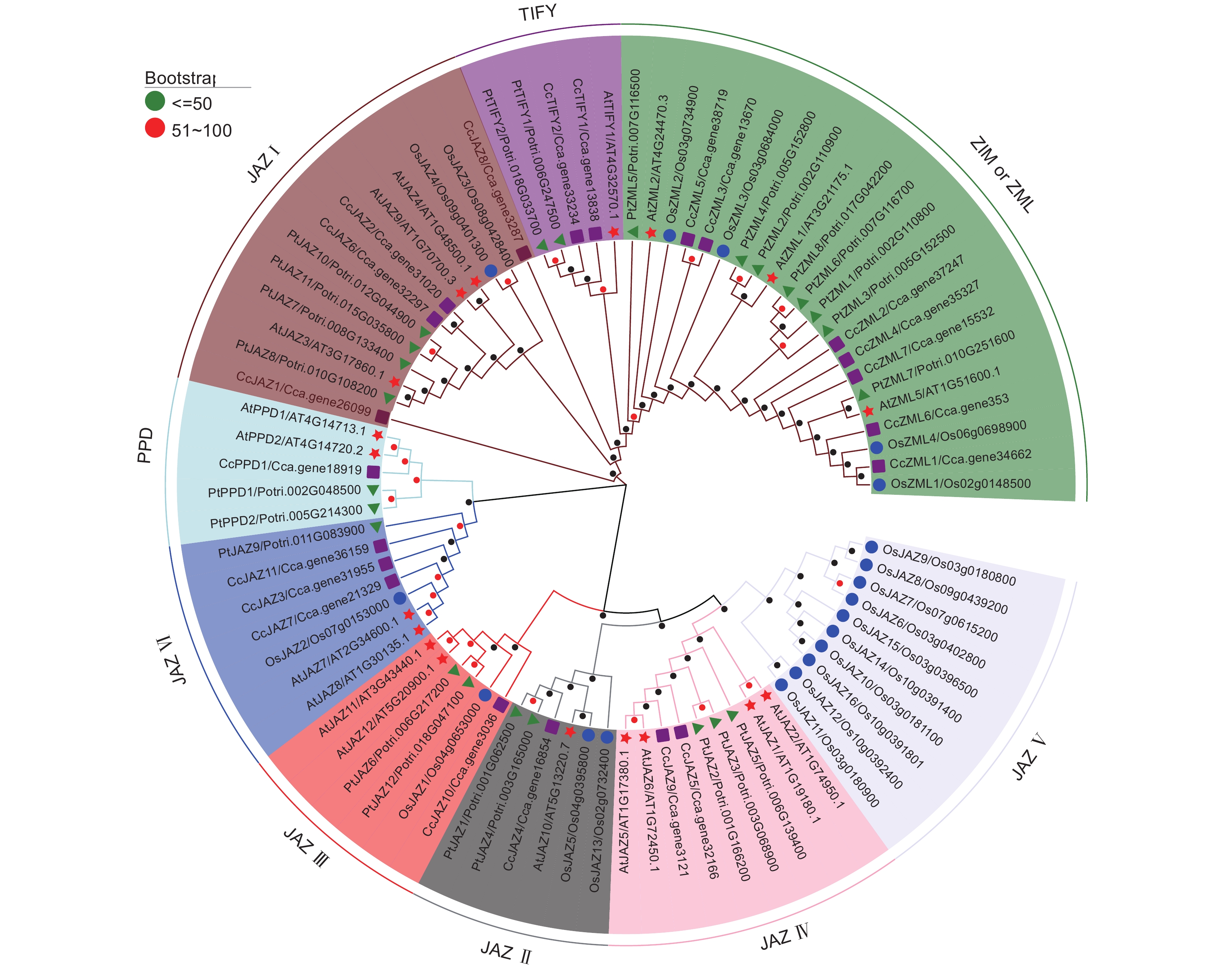
为深入了解被子植物TIFY家族的系统发生关系,本研究构建了拟南芥、毛果杨(代表真核双子叶植物)、水稻(代表单子叶植物)和樟树(代表基被双子叶植物)的TIFY家族成员进化树,总计83个TIFY成员形成了9个进化分枝。樟树TIFY家族成员除了JAZ Ⅴ分枝之外,在其他进化分枝都有分布。TIFY分枝和PPD分枝均由5个成员组成,分别来自拟南芥、毛果杨和樟树,两个分枝不包含水稻的家族成员,可能在单子叶植物进化过程中发生了丢失。JAZ亚家族的51个成员进一步形成了6个分枝(JAZⅠⅥ),其中JAZ Ⅴ分枝仅由来自水稻的家族成员组成,且发生了显著性扩张;而JAZ Ⅳ分枝成员全部来自拟南芥、毛果杨和樟树,两大分枝的共同祖先在双子叶与单子叶植物形成后发生了独立复制事件(图3)。ZML亚家族成员在进化树上组成了ZIM 或ZML进化分枝,单子叶植物和双子叶植物成员未形成独立的分枝,表明该亚家族成员在陆生植物进化早期便发生了分化和显著性突变。
2.5 樟树TIFYs的染色体定位和共线性分析
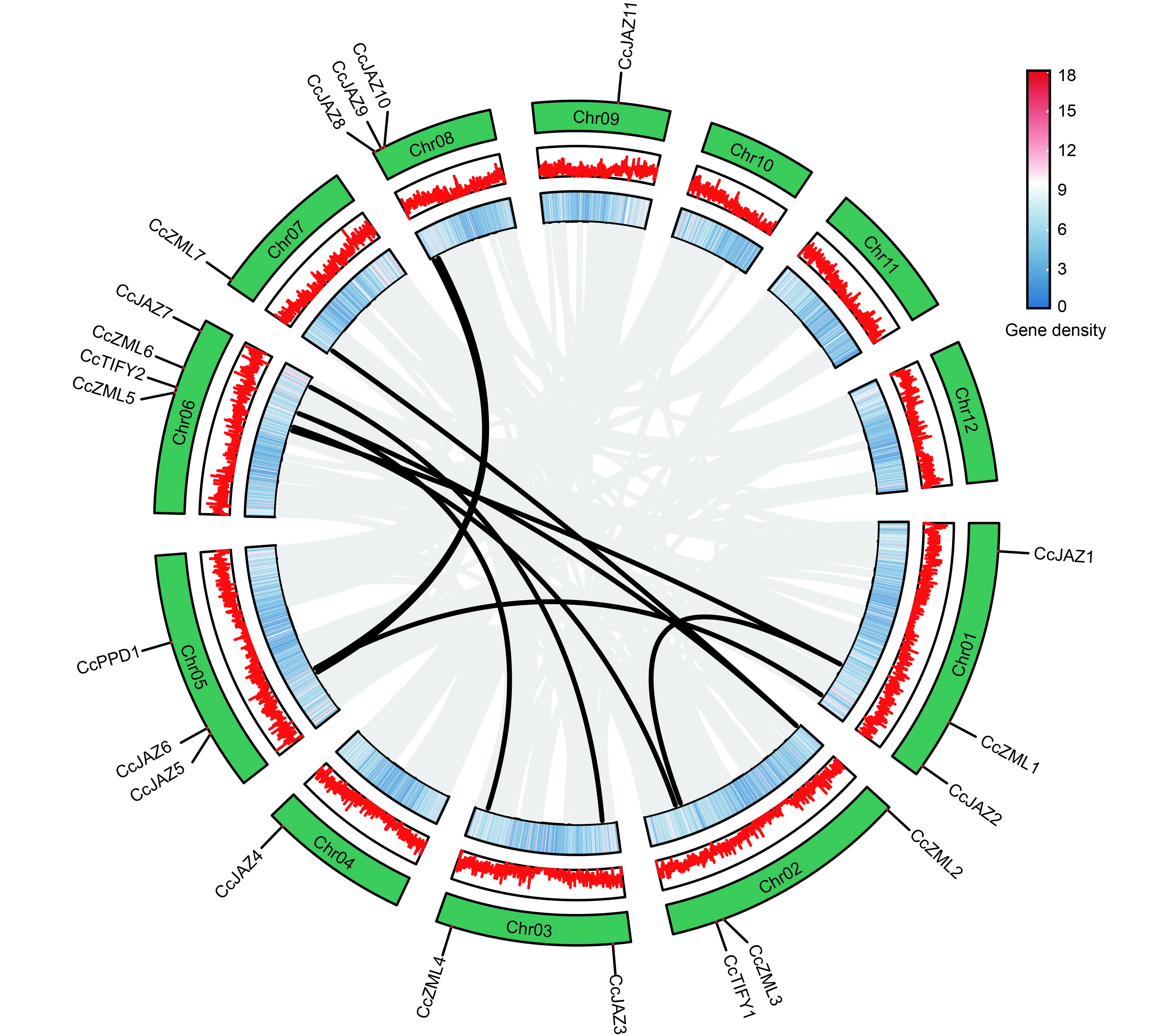
染色体定位分析显示,21个CcTIFY基因非均匀地分布于9条染色体上,其中Chr06上有4个,Chr01、Chr02、Chr05和Chr08各有3个,Chr03有两个,Chr04、Chr07和Chr09各有1个(图4)。种内染色体共线性分析发现,共有14个CcTIFY共线性基因对,未发现基因串联复制簇。基于系统进化和种内共线性分析结果,在樟树TIFY家族发现了2对旁系同源基因对,即CcJAZ2与CcJAZ6、CcZML3与CcZML5。进一步计算共线性基因对的Ka和Ks,发现2对共线性基因对的Ka/Ks 均小于1,表明樟树TIFY家族在进化过程受到了纯化选择。
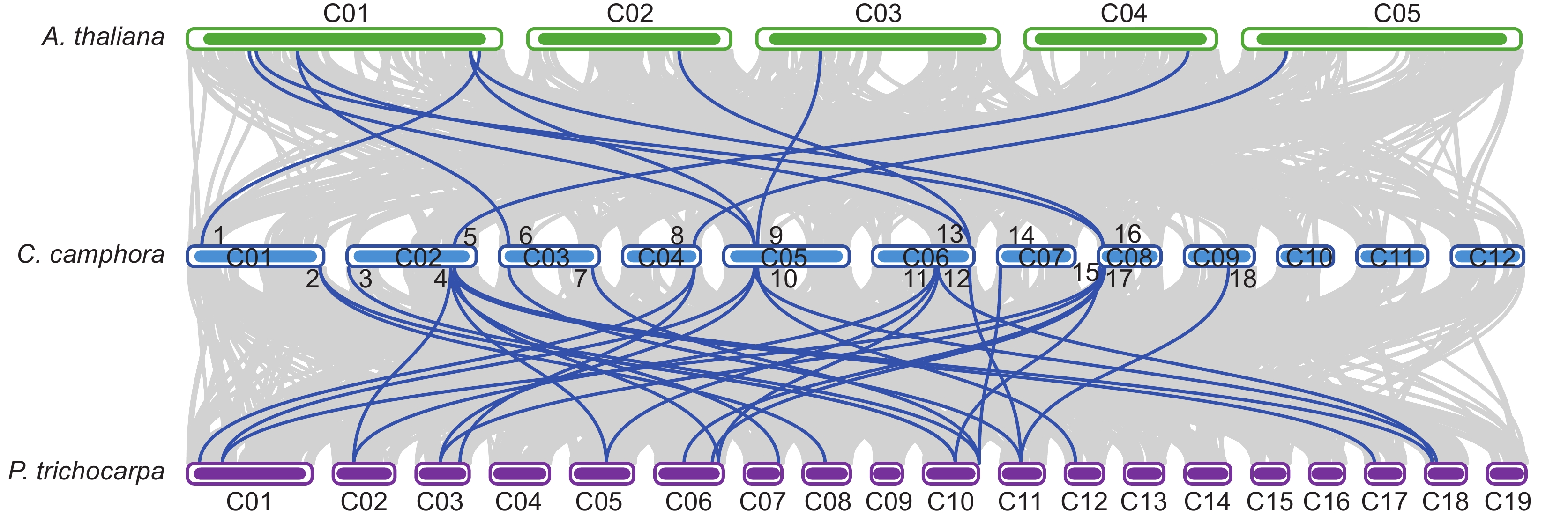
物种间共线性分析结果显示(图5),樟树TIFY家族中有8个成员与拟南芥TIFY成员具有共线性关系,分别为TIFY亚家族的CcTIFY1,和JAZ亚家族的CcJAZ1/3/4/5/6/7/9;此外,17个CcTIFY家族成员与毛果杨TIFY成员存在共线性关系,暗示樟树与毛果杨的TIFY家族可能具有更近的亲缘关系和更相似的进化历程。
![]() 图 5 TIFY基因家族在毛果杨、拟南芥和樟树中的染色体共线性分析Figure 5. Collinearity analysis of TIFY gene families among Populus trichocarpa, Arabidopsis thaliana, and Cinnamomum camphora1:CcJAZ1; 2:CcJAZ2;3:CcZML2;4:CcZML3;5:CcTIFY1;6:CcJAZ3;7:CcZML4;8:CcJAZ9;9:CcJAZ5;10:CcJAZ6;11:CcZML5;12:CcTIFY2;13:CcJAZ7;14:CcZML7;15:CcJAZ8;16:CcJAZ9;17:CcJAZ10;18:CcJAZ11。
图 5 TIFY基因家族在毛果杨、拟南芥和樟树中的染色体共线性分析Figure 5. Collinearity analysis of TIFY gene families among Populus trichocarpa, Arabidopsis thaliana, and Cinnamomum camphora1:CcJAZ1; 2:CcJAZ2;3:CcZML2;4:CcZML3;5:CcTIFY1;6:CcJAZ3;7:CcZML4;8:CcJAZ9;9:CcJAZ5;10:CcJAZ6;11:CcZML5;12:CcTIFY2;13:CcJAZ7;14:CcZML7;15:CcJAZ8;16:CcJAZ9;17:CcJAZ10;18:CcJAZ11。2.6 樟树TIFY家族基因组织表达模式分析
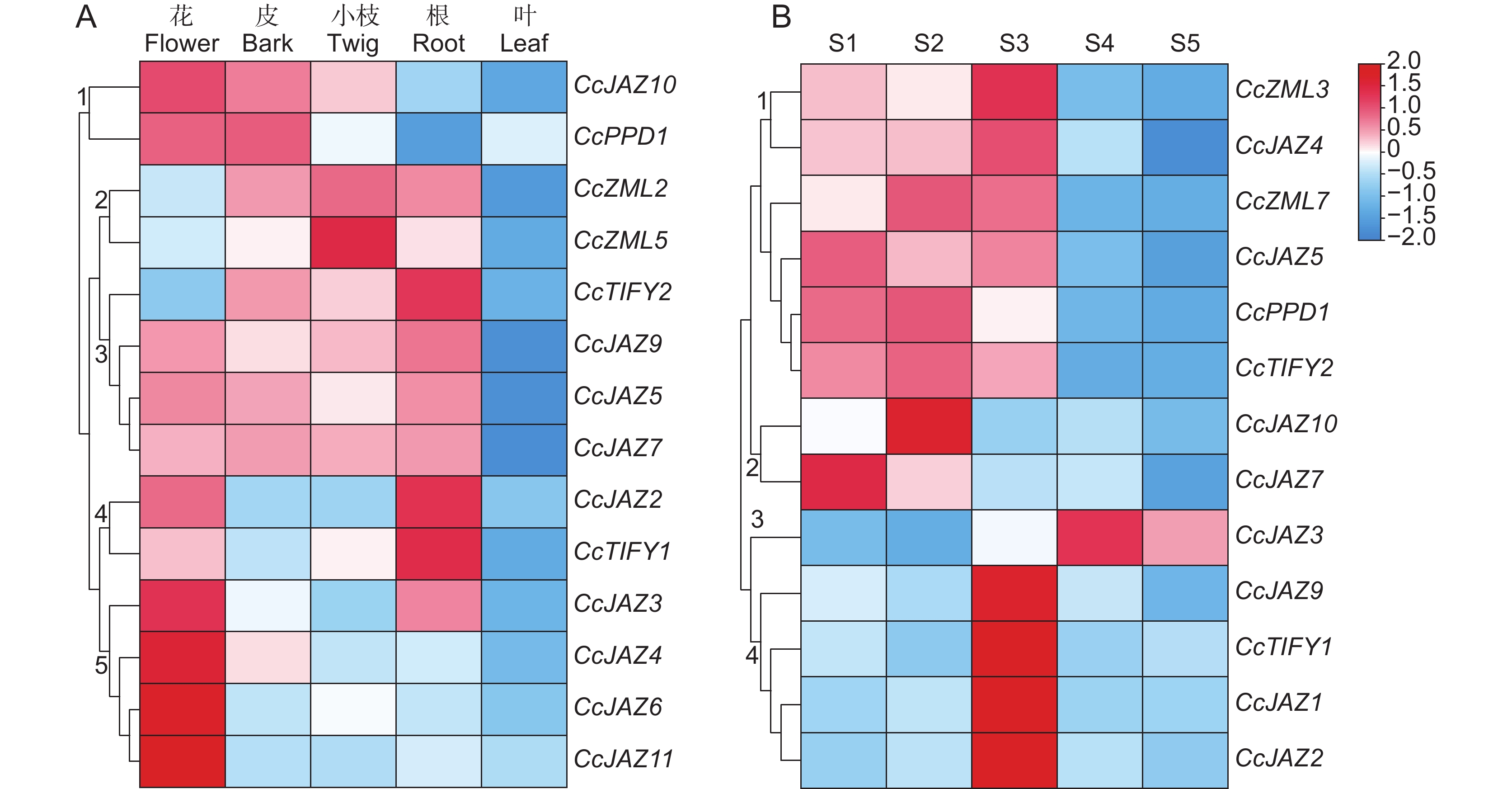
基于花、树皮、小枝、根、叶与不同发育期樟籽等6种组织的转录组数据,分析了TIFY家族各成员的组织表达模式。结果显示,CcJAZ1/8在花、皮、小枝、根与叶等5种组织中皆不表达,而CcZML1/3/4/6/7等5个成员则为组成型表达。其余14个成员具有5种不同的表达模式(图6:A)。第1种模式包括CcJAZ10和CcPPD1,主要在花与皮中优势表达;第2种模式主要在小枝、根和皮中优势表达(CcZML2/5);第3种模式包括CcTIFY2和CcJAZ5/7/9等4个成员,其在叶中的表达显著低于其他组织;第4种模式包括CcTIFY1和CcJAZ2,在根部优势表达;第5种模式包括CcJAZ3/4/6/11等4个成员,皆在花中显著上调或特异性表达。
不同时期樟籽转录组数据显示,CcZML1/6和CcJAZ8/11等4个成员在5个生长时期的表达水平皆极低,CcZML2/4/5/6等4个成员的表达水平均较高,但无显著差异。其他13个成员则具有4种不同模式(图6:B)。第1种包括CcZML3/7、CcJAZ4/5、CcPPD1和CcTIFY2等6个成员,主要在樟籽体积增长的S1~S3期优势表达;第2种包括CcJAZ7/10,主要在S2或S1期优势表达;CcJAZ3为第3种模式,主要在S4期优势表达;CcJAZ1/2/9和CcTIFY1等组成了第4种模式,其表达量在S3期发生了显著上调。
2.7 樟树TIFY家族基因在不同化学型叶组织中的表达
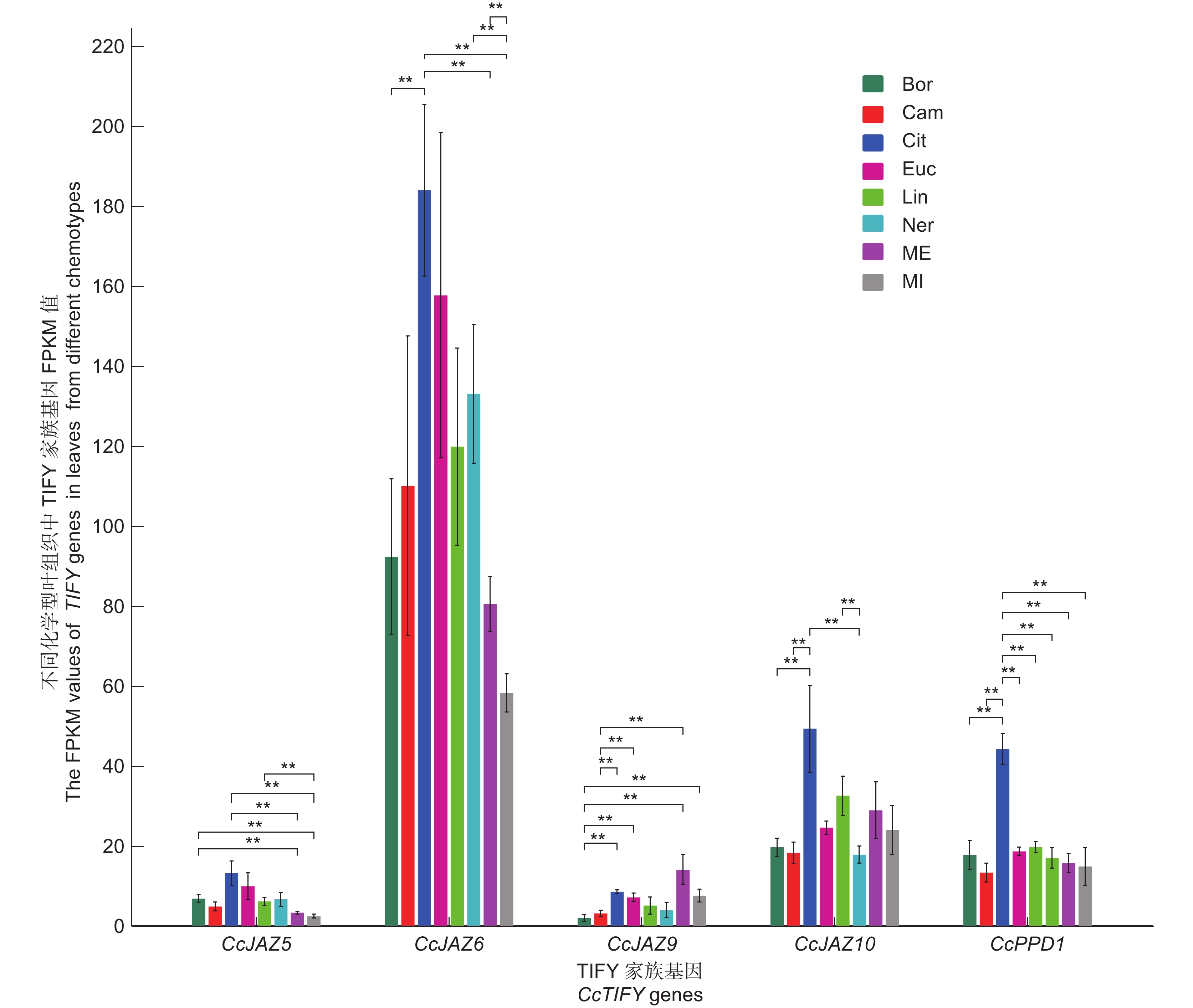
基于8种化学型的叶组织转录组数据,比较了CcTIFY基因家族各成员的表达水平。结果显示,CcJAZ3/7/8/11等4个基因在所有化学型的叶组织中几乎均不表达;CcTIFY1/2、CcJAZ1/4与CcZML1等5个基因在所有叶组织中的表达水平极低(FPKM值<5);而CcZML2/34/5/6/7和CcJAZ2等基因为组成型表达,在化学型间的差异不显著。CcJAZ9在不同化学型间的表达具有差异,相对于龙脑型、樟脑型、芳樟醇型和橙花叔醇型等,其在甲基丁香酚型中的表达量显著升高(图7)。其余4个基因在柠檬醛型中优势表达,且相对于其他部分化学型,其表达量差异达到了显著水平(图7)。
![]() 图 7 樟树不同化学型叶组织中TIFY家族成员表达分析Bor:龙脑型;Cam:樟脑型;Cit:柠檬醛型;Ecu:桉叶油素型;Lin:芳樟醇型;Ner:异橙花叔醇型;Me:甲基丁香酚型;Mi:甲基异丁香酚型。**:P<0.01。Figure 7. Expression analysis of TIFY genes in leaves from different Cinnamomum camphora chemotypesBor: Borneol type; Cam: Camphor type; Cit: Citral type; Ecu: Eucalyptol type; Lin: Linalool type; Me: Methyl eugenol type; Mi: Methyl isoeugenol type. **: P<0.01.
图 7 樟树不同化学型叶组织中TIFY家族成员表达分析Bor:龙脑型;Cam:樟脑型;Cit:柠檬醛型;Ecu:桉叶油素型;Lin:芳樟醇型;Ner:异橙花叔醇型;Me:甲基丁香酚型;Mi:甲基异丁香酚型。**:P<0.01。Figure 7. Expression analysis of TIFY genes in leaves from different Cinnamomum camphora chemotypesBor: Borneol type; Cam: Camphor type; Cit: Citral type; Ecu: Eucalyptol type; Lin: Linalool type; Me: Methyl eugenol type; Mi: Methyl isoeugenol type. **: P<0.01.3. 讨论
目前已在约30种植物中进行了TIFY家族的鉴定,大部分为真核双子叶和单子叶植物,极少数为裸子植物和苔藓植物,但木兰类植物(基被双子叶植物)还未见报道。本研究通过生物信息学方法从樟树基因组鉴定了21个TIFY转录因子,并将其划分为4个亚家族,首次分析了基被双子叶植物的TIFY家族序列特征、组成、共线性及系统发育等信息,可为研究植物TIFY家族的进化提供参考。
樟树的TIFY家族成员数量与中华猕猴桃(Actinidia chinensis Planch.)相当[34],家族结构类似于绝大部分双子叶植物,且与拟南芥和毛果杨具有相似的进化拓扑结构,表明樟树TIFY家族在进化上更接近真核双子叶植物。种内共线性分析结果显示,樟树TIFY家族存在14个基因结构相似的共线性对,且未发现串联复制簇,暗示该家族成员的扩张主要来源于部分染色体的大片段复制,与毛果杨TIFY家族类似[4]。种间共线性分析结果表明,与拟南芥相比,樟树TIFY家族与毛果杨之间的种间共线性对更多,可能与二者同为木本乔木有关。
基因表达分析结果表明,樟树大部分JAZ亚家族成员的表达具有组织特异性,可能在器官发育过程中具有重要调控作用。CcJAZ3/11、CcJAZ4和CcJAZ6在花中优势表达或特异表达,推测可能参与花器官的发育调控。在进化分枝上,CcJAZ6和AtJAZ4/9都来自JAZⅠ进化分枝,AtJAZ4/9发生突变后开花延迟[35, 36];而CcJAZ3/11与AtJAZ7/8同处于JAZ Ⅵ分枝,已有研究表明AtJAZ7/8参与调控雄蕊和花序的发育[37, 38]。CcTIFY1在根中优势表达,目前研究显示,植物TIFY主要参与叶片弯曲、叶面积及种子大小的调控[11, 12],对根的调控还未见报道。在樟籽发育过程中,CcJAZ4/5/7/9在S1~S3期优势表达,推测可能参与了籽体积的发育调控;CcJAZ1/2/9在S3期的樟籽中优势表达,暗示其在该时期发挥特殊生物学功能,可能与此时樟籽油的大量合成有关。此外,CcJAZ3在种子发育后期上调表达,可能参与花青素等物质的合成调控。拟南芥中已发现多个JAZ亚家族成员具有调控器官发育的功能,包括调控侧根、根毛、雄蕊与叶片衰老等诸多过程[8-13]。不同JAZ亚家族成员的生物学功能具有冗余性和拮抗性[39],显示了JAZ亚家族调控植物器官发育的复杂性。
TIFY家族对萜类化合物的合成调控主要是通过与其他转录因子互作间接发挥作用,且多受外源激素信号的诱导[24, 25]。TIFY家族可以通过调控次生代谢物的分泌来影响腺毛的发育或分布密度等,从而间接影响萜类化合物的合成[40, 41]。在樟树不同化学型之间,只有5个家族成员发生了差异表达,其中4个在柠檬醛型中优势表达,可能因为柠檬醛型的腺体较其他化学型发达。柠檬醛型樟树在自然界的分布极少,有专家认为其是樟树与其他富含柠檬醛型精油的樟属植物如猴樟(Camphora bodinieri (H. Lév.) Y. Yang, Bing Liu & Zhi Yang )的杂交种,腺体较一般樟树发达。在苯丙素类化合物的合成过程中,JAZ亚家族成员可与MYB类转录因子互作,间接调控通路相关基因[42]。CcJAZ9在甲基丁香酚型樟树中优势表达,可能间接参与了甲基丁香酚合成通路中某个功能基因的调控。
-
图 5 TIFY基因家族在毛果杨、拟南芥和樟树中的染色体共线性分析
Figure 5. Collinearity analysis of TIFY gene families among Populus trichocarpa, Arabidopsis thaliana, and Cinnamomum camphora
1:CcJAZ1; 2:CcJAZ2;3:CcZML2;4:CcZML3;5:CcTIFY1;6:CcJAZ3;7:CcZML4;8:CcJAZ9;9:CcJAZ5;10:CcJAZ6;11:CcZML5;12:CcTIFY2;13:CcJAZ7;14:CcZML7;15:CcJAZ8;16:CcJAZ9;17:CcJAZ10;18:CcJAZ11。
图 7 樟树不同化学型叶组织中TIFY家族成员表达分析
Bor:龙脑型;Cam:樟脑型;Cit:柠檬醛型;Ecu:桉叶油素型;Lin:芳樟醇型;Ner:异橙花叔醇型;Me:甲基丁香酚型;Mi:甲基异丁香酚型。**:P<0.01。
Figure 7. Expression analysis of TIFY genes in leaves from different Cinnamomum camphora chemotypes
Bor: Borneol type; Cam: Camphor type; Cit: Citral type; Ecu: Eucalyptol type; Lin: Linalool type; Me: Methyl eugenol type; Mi: Methyl isoeugenol type. **: P<0.01.
表 1 樟树TIFY家族基因基本信息
Table 1 Characteristics of predicted TIFY family in Cinnamomum camphora genome
基因名称
Gene基因登录号
Accession No.蛋白大小
Protein length / aaTify结构域
Tify motif亚细胞定位
Subcellular localizationCcJAZ1 Cca.gene26099 261 TIFYSG 细胞核 CcJAZ2 Cca.gene31020 392 TIFYGG 细胞核 CcJAZ3 Cca.gene31955 116 TIFYNG 细胞核 CcJAZ4 Cca.gene16854 219 TIFYNG 细胞质 CcJAZ5 Cca.gene32166 264 TIFYGG 细胞核 CcJAZ6 Cca.gene32297 391 TVFYAG 细胞核 CcJAZ7 Cca.gene21329 124 TIFYNG 叶绿体 CcJAZ8 Cca.gene3287 336 TIFYGG 细胞核 CcJAZ9 Cca.gene3121 258 TIFYGG 细胞核 CcJAZ10 Cca.gene3036 165 TIFYSG 叶绿体 CcJAZ11 Cca.gene36159 123 TIFYNG 叶绿体 CcZML1 Cca.gene34662 333 TVNLQG 叶绿体 CcZML2 Cca.gene37247 330 TLSFQG 细胞质 CcZML3 Cca.gene13670 583 TLSFNG 细胞核 CcZML4 Cca.gene35327 355 TLSFQG 细胞质 CcZML5 Cca.gene38719 572 TLSFNG 细胞核 CcZML6 Cca.gene353 334 TLSFQD 细胞核 CcZML7 Cca.gene15532 355 TLSFQG 叶绿体 CcTIFY1 Cca.gene13838 412 TIFYDG 细胞核 CcTIFY2 Cca.gene33234 407 TIFYAG 细胞核 CcPPD1 Cca.gene18919 355 TIFYDG 细胞核 -
[1] Vanholme B,Grunewald W,Bateman A,Kohchi T,Gheysen G. The tify family previously known as ZIM.[J]. Trends Plant Sci,2007,12(6):239−244. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2007.04.004
[2] Bai YH,Meng YJ,Huang DL,Qi YH,Chen M. Origin and evolutionary analysis of the plant-specific TIFY transcription factor family[J]. Genomics,2011,98(2):128−136. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2011.05.002
[3] Ye HY,Du H,Tang N,Li XH,Xiong LZ. Identification and expression profiling analysis of TIFY family genes involved in stress and phytohormone responses in rice[J]. Plant Mol Biol,2009,71(3):291−305. doi: 10.1007/s11103-009-9524-8
[4] Wang Y,Pan F,Chen DM,Chu WY,Liu HL,Xiang Y. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the Populus trichocarpa TIFY gene family[J]. Plant Physiol Biochem,2017,115:360−371. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.04.015
[5] He X,Kang Y,Li WQ,Liu W,Xie P,et al. Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of the TIFY gene family in the response to multiple stresses in Brassica napus L.[J]. BMC Genomics,2020,21(1):736. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07128-2
[6] Li L,Liu YC,Huang Y,Li B,Ma W,et al. Genome-wide identification of the TIFY family in Salvia miltiorrhiza reveals that SmJAZ3 interacts with SmWD40-170,a relevant protein that modulates secondary metabolism and development[J]. Front Plant Sci,2021,12:630424. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.630424
[7] Yang YX,Ahammed GJ,Wan CP,Liu HJ,Chen RR,Zhou Y. Comprehensive analysis of TIFY transcription factors and their expression profiles under jasmonic acid and abiotic stresses in watermelon[J]. Int J Genomics,2019,2019:6813086.
[8] Nishii A,Takemura M,Fujita H,Shikata M,Yokota A,Kohchi T. Characterization of a novel gene encoding a putative single zinc-finger protein,ZIM,expressed during the reproductive phase in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,2000,64(7):1402−1409. doi: 10.1271/bbb.64.1402
[9] Shikata M,Matsuda Y,Ando K,Nishii A,Takemura M,et al. Characterization of Arabidopsis ZIM,a member of a novel plant-specific GATA factor gene family[J]. J Exp Bot,2004,55(397):631−639. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erh078
[10] Andrade Galan AG,Doll J,Saile SC,Wünsch M,Roepenack-Lahaye EV,et al. The non-JAZ TIFY protein TIFY8 of Arabidopsis thaliana interacts with the HD-ZIP Ⅲ transcription factor REVOLUTA and regulates leaf senescence[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2023,24(4):3079. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043079
[11] White DWR. PEAPOD regulates lamina size and curvature in Arabidopsis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2006,103(35):13238−13243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604349103
[12] Liu ZP,Li N,Zhang YY,Li YH. Transcriptional repression of GIF1 by the KIX-PPD-MYC repressor complex controls seed size in Arabidopsis[J]. Nat Commun,2020,11(1):1846. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15603-3
[13] Mehra P,Pandey BK,Verma L,Prusty A,Singh AP, et al. OsJAZ11 regulates spikelet and seed development in rice[J]. Plant Direct,2022,6(5):e401.
[14] Zhao X,Jiang XM,Li ZY,Song Q,Xu CZ,Luo KM. Jasmonic acid regulates lignin deposition in poplar through JAZ5-MYB/NAC interaction[J]. Front Plant Sci,2023,14:1232880. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1232880
[15] Wu H,Ye HY,Yao RF,Zhang T,Xiong LZ. OsJAZ9 acts as a transcriptional regulator in jasmonate signaling and modulates salt stress tolerance in rice[J]. Plant Sci,2015,232:1−12. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.12.010
[16] Fu J,Wu H,Ma SQ,Xiang DH,Liu RY,Xiong LZ. OsJAZ1 attenuates drought resistance by regulating JA and ABA signaling in rice[J]. Front Plant Sci,2017,8:2108. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.02108
[17] Li CJ,Shi L,Li X,Wang YN,Bi YJ,et al. ECAP is a key negative regulator mediating different pathways to modulate salt stress-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis[J]. New Phytol,2022,233(5):2216−2231. doi: 10.1111/nph.17937
[18] Xie Y,Tan HJ,Ma ZX,Huang JR. DELLA proteins promote anthocyanin biosynthesis via sequestering MYBL2 and JAZ suppressors of the MYB/bHLH/WD40 complex in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Mol Plant,2016,9(5):711−721. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2016.01.014
[19] Li CJ,Shi L,Wang YN,Li W,Chen BQ, et al. Arabidopsis ECAP is a new adaptor protein that connects JAZ repressors with the TPR2 co-repressor to suppress Jasmonate-responsive anthocyanin accumulation[J]. Mol Plant,2020,13(2):246−265.
[20] Qi TC,Song SS,Ren QC,Wu DW,Huang H,et al. The Jasmonate-ZIM-domain proteins interact with the WD-Repeat/bHLH/MYB complexes to regulate Jasmonate-mediated anthocyanin accumulation and trichome initiation in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Plant Cell,2011,23(5):1795−1814. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.083261
[21] An JP,Xu RR,Liu X,Zhang JC,Wang XF,et al. Jasmonate induces biosynthesis of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin in apple by mediating the JAZ1-TRB1-MYB9 complex[J]. Plant J,2021,106(5):1414−1430. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15245
[22] An XH,Tian Y,Chen KQ,Liu XJ,Liu DD,et al. MdMYB9 and MdMYB11 are involved in the regulation of the JA-induced biosynthesis of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin in apples[J]. Plant Cell Physiol,2015,56(4):650−662. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcu205
[23] Liu XJ,An XH,Liu X,Hu DG,Wang XF,et al. MdSnRK1.1 interacts with MdJAZ18 to regulate sucrose-induced anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin accumulation in apple[J]. J Exp Bot,2017,68(11):2977−2990. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx150
[24] Pei TL,Ma PD,Ding K,Liu SJ,Jia YY,et al. SmJAZ8 acts as a core repressor regulating JA-induced biosynthesis of salvianolic acids and tanshinones in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots[J]. J Exp Bot,2018,69(7):1663−1678. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx484
[25] Ma PD,Pei TL,Lv BB,Wang M,Dong JAN,Liang ZS. Functional pleiotropism,diversity,and redundancy of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge JAZ family proteins in jasmonate-induced tanshinone and phenolic acid biosynthesis[J]. Hortic Res,2022,9:uhac166. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhac166
[26] 张峰,毕良武,赵振东. 樟树植物资源分布及化学成分研究进展[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2017,29(3):517−531. Zhang F,Bi LW,Zhao ZD. Review on plant resources and chemical composition of camphor tree[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2017,29(3):517−531.
[27] Wang XD,Xu CY,Zheng YJ,Wu YF,Zhang YT,et al. Chromosome-level genome assembly and resequencing of camphor tree (Cinnamomum camphora) provides insight into phylogeny and diversification of terpenoid and triglyceride biosynthesis of Cinnamomum[J]. Hortic Res,2022,9:uhac216. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhac216
[28] Zhang Z,Schwartz S,Wagner L,Miller W. A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences[J]. J Comput Biol,2000,7(1-2):203−214. doi: 10.1089/10665270050081478
[29] Tamura K,Stecher G,Kumar S. MEGA11:molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11[J]. Mol Biol Evol,2021,38(7):3022−3027. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab120
[30] Chen CJ,Chen H,Zhang Y,Thomas HR,Frank MH,et al. TBtools:an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data[J]. Mol Plant,2020,13(8):1194−1202. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
[31] Gu ZL,Cavalcanti A,Chen FC,Bouman P,Li WH. Extent of gene duplication in the genomes of Drosophila,Nematode,and yeast[J]. Mol Biol Evol,2002,19(3):256−262. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a004079
[32] Yang SH,Zhang XH,Yue JX,Tian DC,Chen JQ. Recent duplications dominate NBS-encoding gene expansion in two woody species[J]. Mol Genet genomics,2008,280(3):187−198. doi: 10.1007/s00438-008-0355-0
[33] Zhao P,Wang DD,Wang RQ,Kong NN,Zhang C,et al. Genome-wide analysis of the potato Hsp20 gene family:identification,genomic organization and expression profiles in response to heat stress[J]. BMC Genomics,2018,19(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4443-1
[34] Tao JJ,Jia HM,Wu MT,Zhong WQ,Jia DF,et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the TIFY gene family in kiwifruit[J]. BMC Genomics,2022,23(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08398-8
[35] Oblessuc PR,Obulareddy N,DeMott L,Matiolli CC,Thompson BK,Melotto M. JAZ4 is involved in plant defense,growth,and development in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant J,2020,101(2):371−383. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14548
[36] Yang DL,Yao J,Mei CS,Tong XH,Zeng LJ,et al. Plant hormone jasmonate prioritizes defense over growth by interfering with gibberellin signaling cascade[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2012,109(19):E1192−E1200.
[37] Song SS,Qi TC,Huang H,Ren QC,Wu DW,et al. The Jasmonate-ZIM domain proteins interact with the R2R3-MYB transcription factors MYB21 and MYB24 to affect jasmonate-regulated stamen development in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Cell,2011,23(3):1000−1013. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.083089
[38] Yan HZ,Yoo MJ,Koh J,Liu LH,Chen Y,et al. Molecular reprogramming of Arabidopsis in response to perturbation of jasmonate signaling[J]. J Proteome Res,2014,13(12):5751−5766. doi: 10.1021/pr500739v
[39] Liu B,Seong K,Pang SH,Song JQ,Gao H,et al. Functional specificity,diversity,and redundancy of Arabidopsis JAZ family repressors in jasmonate and COI1-regulated growth,development,and defense[J]. New Phytol,2021,231(4):1525−1545. doi: 10.1111/nph.17477
[40] Yan XX,Cui LP,Liu XY,Cui YC,Wang ZJ,et al. NbJAZ3 is required for jasmonate-meditated glandular trichome development in Nicotiana benthamiana[J]. Physiol Plant,2022,174(2):e13666. doi: 10.1111/ppl.13666
[41] Xie LH,Yan TX,Li L,Chen MH,Hassani D,et al. An HD-ZIP-MYB complex regulates glandular secretory trichome initiation in Artemisia annua[J]. New Phytol,2021,231(5):2050−2064. doi: 10.1111/nph.17514
[42] Zhou ML,Sun ZM,Ding MQ,Logacheva MD,Kreft I,et al. FtSAD2 and FtJAZ1 regulate activity of the FtMYB11 transcription repressor of the phenylpropanoid pathway in Fagopyrum tataricum[J]. New Phytol,2017,216(3):814−828. doi: 10.1111/nph.14692



 下载:
下载: