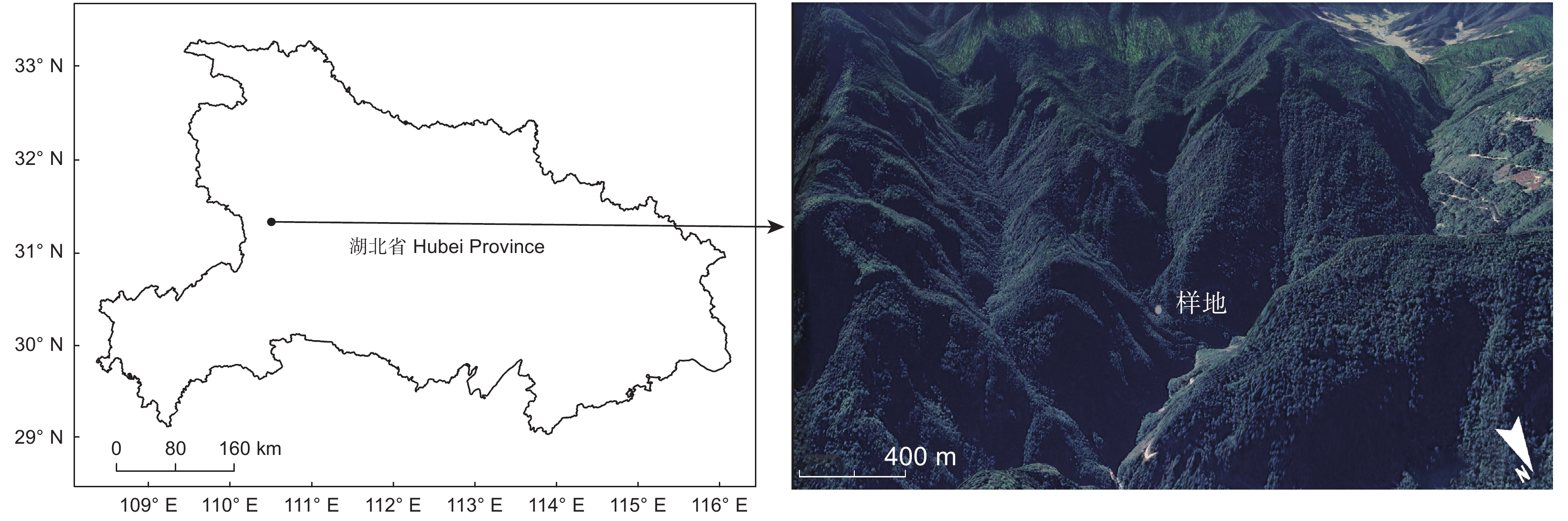
Species composition and community structure of broad-leaved evergreen forests of Cyclobalanopsis myrsinifolia Blume+Cyclobalanopsis oxyodon Miq. on the southern slopes of Shennongjia
-
摘要:
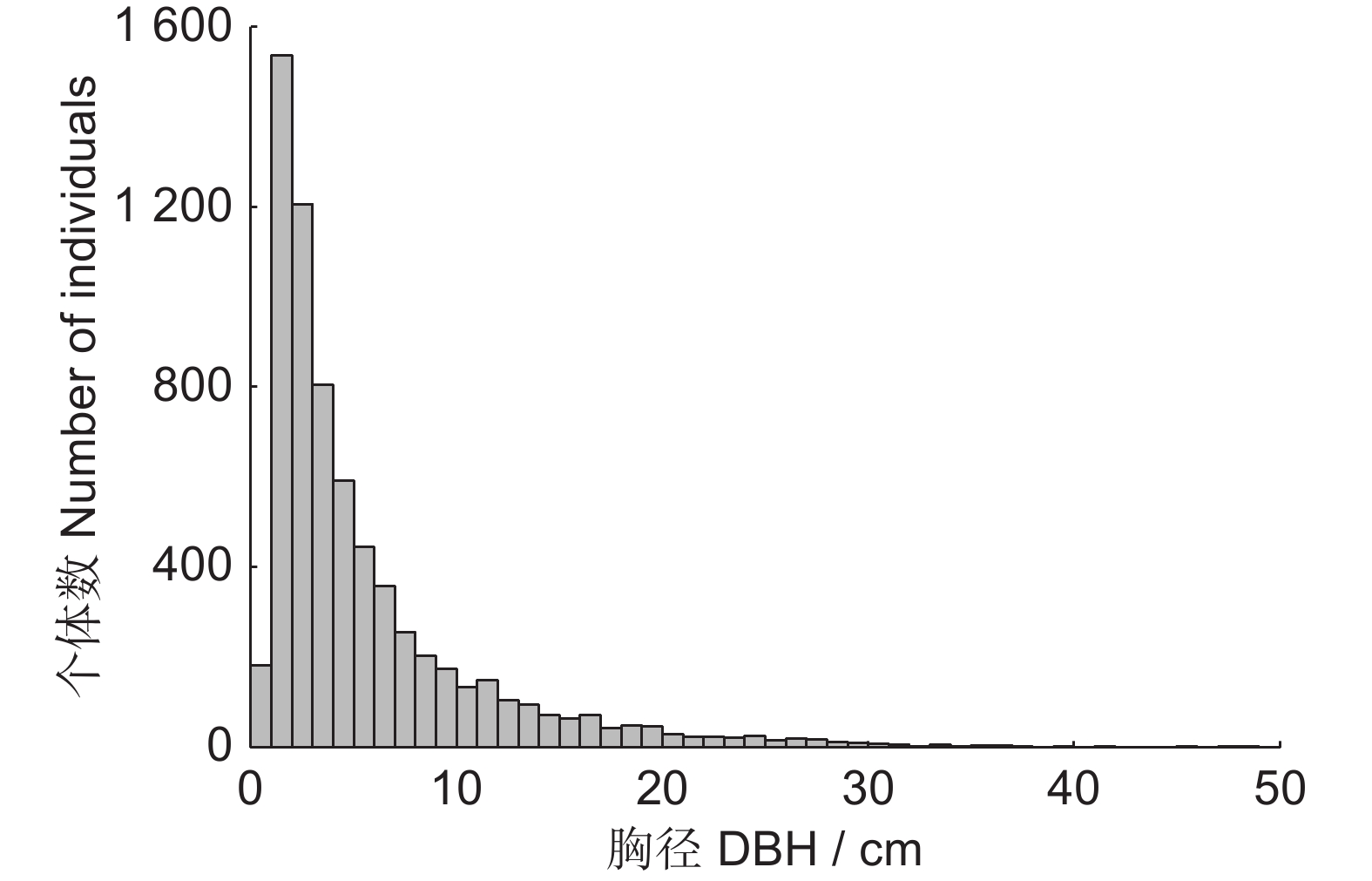
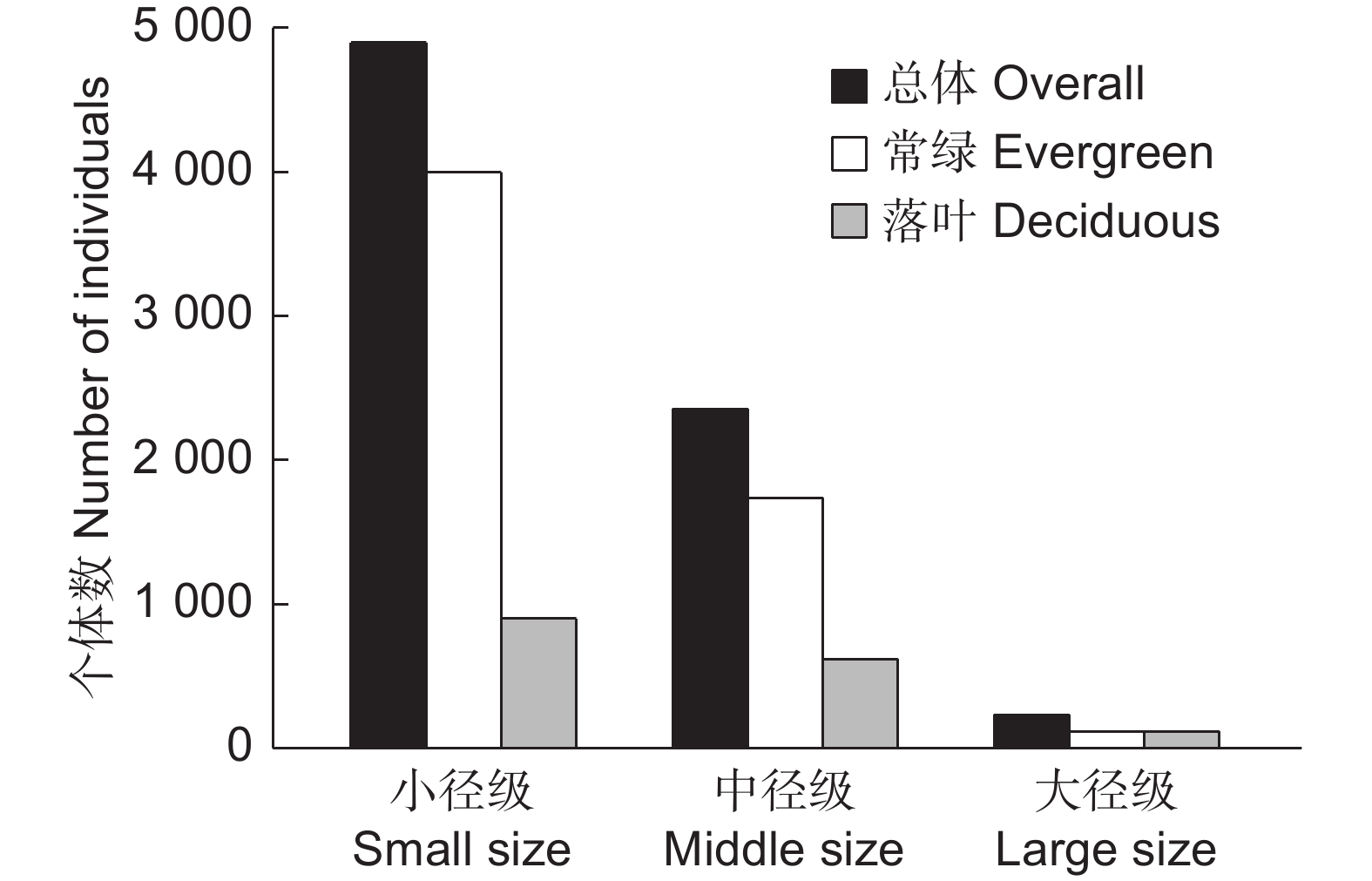
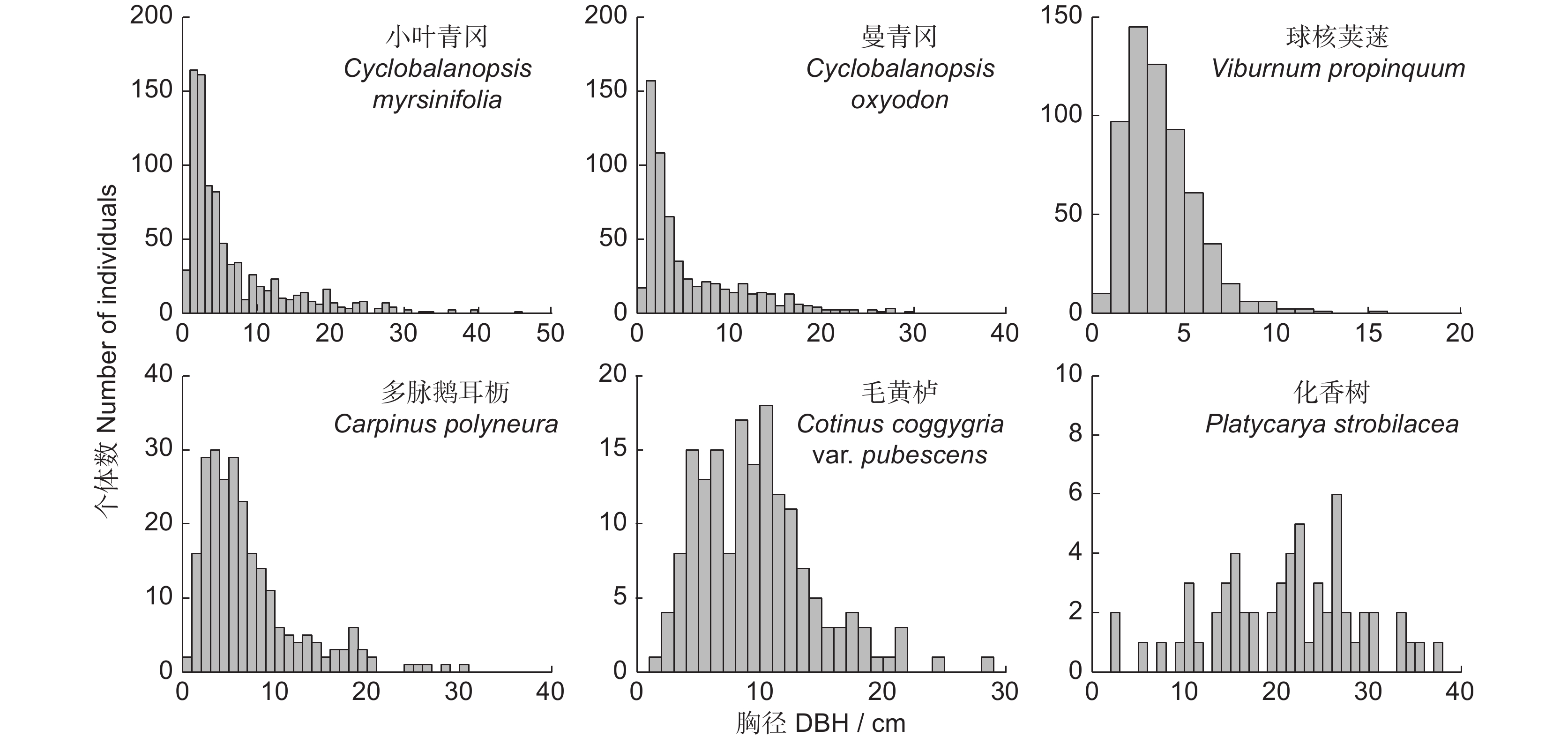
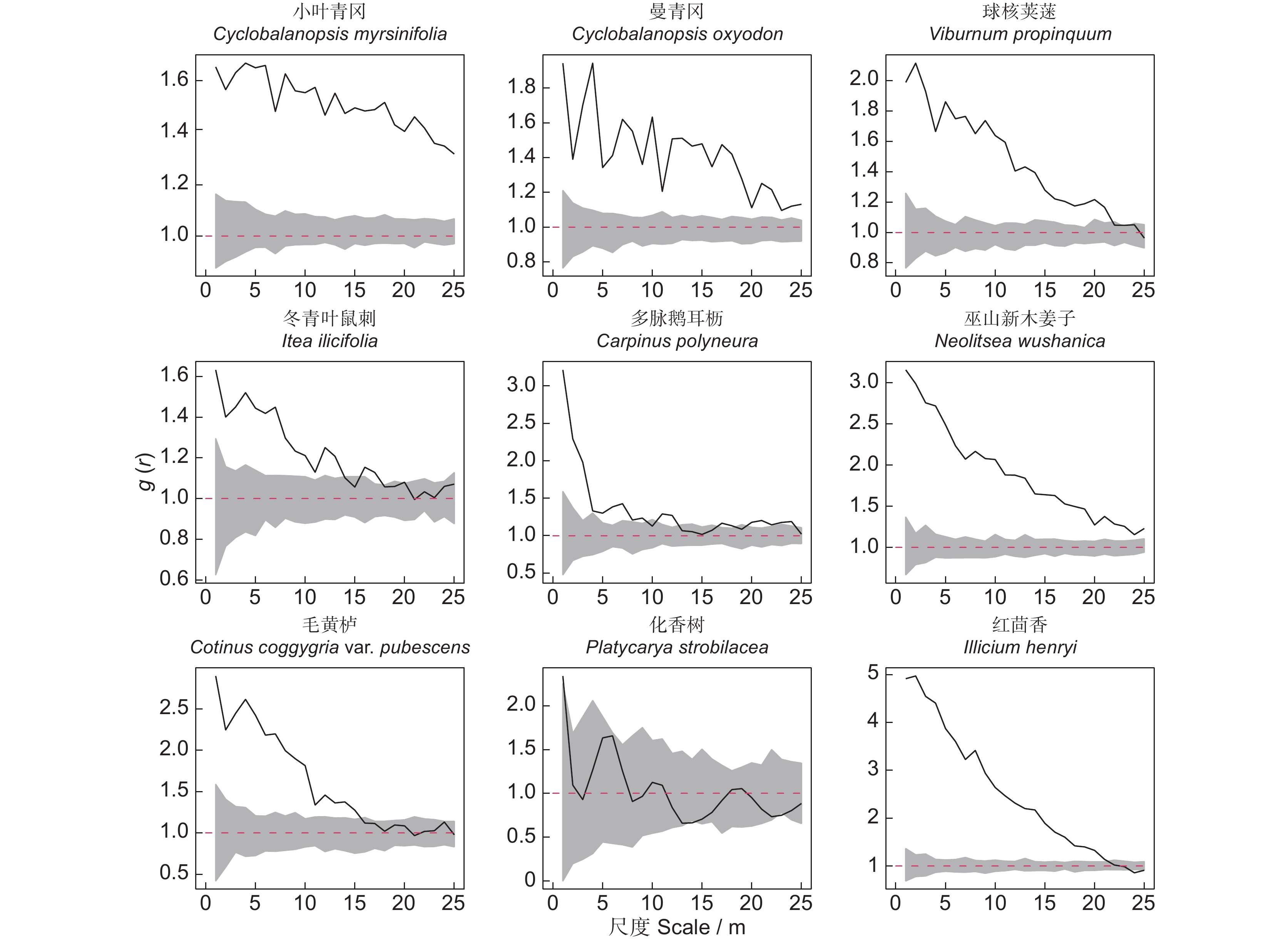
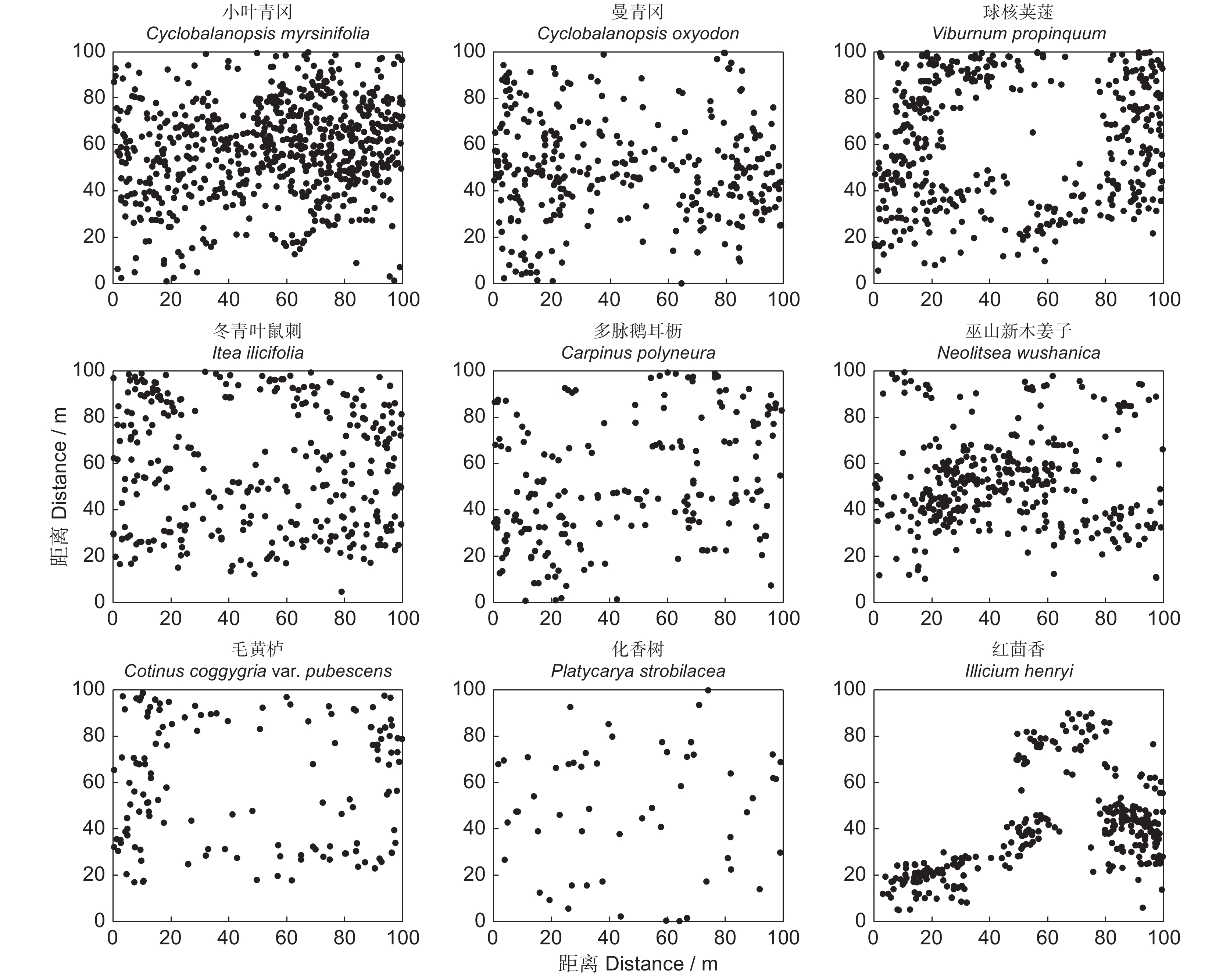
本研究在神农架南坡建立1 hm2的常绿阔叶林动态监测固定样地,分析了该群落的物种组成、区系特征、垂直结构、径级结构和空间分布格局。结果显示,群落物种丰富,共调查到维管植物216种,隶属78科154属,其中胸径≥1 cm的木本植物38科69属107种。区系成分中,热带分布的科、属分别占总科、属数的50.00%和40.58%;温带分布的科、属分别占总科、属数的34.21%和53.63%。常绿树种占比55.14%(59种),落叶树种占比44.86%(48种),其中常绿树种的多度、胸高断面积和重要值占比分别为82.23%、64.79%和73.03%。偶见种占比33.64%(36种),稀有种占比8.41%(9种)。群落垂直结构明显,可分为乔木层、灌木层和草本层,各个层次物种丰富。径级结构呈倒“J”型,属于增长型群落。优势种的空间分布呈现出不同程度的聚集分布。研究表明,该群落的常绿树种重要值明显高于落叶树种,属于小叶青冈(Cyclobalanopsis myrsinifolia Blume)+曼青冈(Cyclobalanopsis oxyodon Miq.)群系,是该区域代表性的常绿阔叶林。区系成分体现出神农架作为中亚热带和北亚热带分界线的特征。群落有着较好的更新能力,呈现向常绿阔叶林顶极群落演替的趋势。
Abstract:This study established a 1-hm2 fixed plot for dynamic monitoring of broad-leaved evergreen forest on the southern slopes of Shennongjia to examine the species composition, floristic characteristics, vertical structure, diameter class structure, and spatial distribution pattern of this community. Results revealed high species richness, with a total of 216 vascular plant species identified, belonging to 78 families and 154 genera. Of these, 107 species were woody plants with a diameter at breast height (DBH)≥1 cm, distributed across 38 families and 69 genera. In terms of floristic composition, families and genera with tropical distribution accounted for 50.00% and 40.58% of the total, respectively, while those with temperate distribution accounted for 34.21% and 53.63%, respectively. Evergreen tree species accounted for 55.14% (59 species), while deciduous tree species accounted for 44.86% (48 species), with the dominance, basal area, and importance values of evergreen tree species being 82.23%, 64.79%, and 73.03%, respectively. Occasional species accounted for 33.64% (36 species) and rare species accounted for 8.41% (nine species). The vertical structure of the community was well-defined, with distinct tree, shrub, and herb layers, each exhibiting high species richness. The diameter class structure exhibited a reverse "J" shape, indicative of a growth-type community. Spatially, dominant species showed varying degrees of clustered distribution. This study indicated that the importance value of evergreen tree species in the community was significantly higher than that of deciduous tree species, belonging to the Cyclobalanopsis myrsinifolia Blume+Cyclobalanopsis oxyodon Miq. community, representing a typical evergreen broad-leaved forest in the region. The floristic composition reflects the characteristics of Shennongjia as the boundary between the subtropical and north subtropical zones. The community demonstrates robust regenerative capability, indicating a successional trajectory toward climax evergreen broad-leaved forests.
-
当今世界煤炭、石油、天然气等不可再生资源的过度消耗,使我们面临着能源短缺问题,另一方面,石油、天然气等资源消耗过程中产生的CO2等气体,又造成了环境污染和温室效应等问题[1]。人类社会的可持续性发展,必须寻求可再生的清洁能源,开发能源作物是解决能源问题和环境问题的有效途径之一。第一代能源作物是以玉米(Zea mays L.)、高粱(Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench)、甘蔗(Saccharum officinarum L.)、大豆(Glycine max (L.) Merr.)、油菜(Brassica campestris L.)等为代表的粮食作物或经济作物,目前成熟的工业化利用主要是生产生物燃料。然而,这些作物大多为一年生,需要年年耕种,投入成本高且挤占了本已有限的耕地,带来了与人争粮,与粮食争地的负面效应。因此,第一代能源作物用于工业化生产受到极大限制。鉴于此,以芒属(Miscanthus)、柳枝稷(Panicum virgatum L.)、杨(Populus)、柳(Salix babylonica L.)等为代表的第二代能源作物应运而生[2, 3]。其中,芒属植物(俗称芒草)具有生物量高,生态适应性强,多年生等优点,可用于与煤混合燃烧发电、发酵制造乙醇和环境修复等,在生物能源领域受到广泛关注[4-6]。自20世纪70年代起,芒属资源开始作为能源作物出现在人们视野,其中芒(M. sinensis Anderss.)与荻(M. sacchariflorus (Maxim.) Hack.)的不育杂种奇岗(M. × giganteus)成为欧美国家主推的能源作物[6, 7]。
芒属作为能源植物具有以下一些优良的特性。首先,芒草是C4植物,生物量大,具有很强的光捕获能力和转化效率[8]。据报道,奇岗的高度可达7 m,在欧洲干物质年产量可达44 t/hm2[9]。在我国,芒和南荻(M. lutarioriparius L. Liou ex S. L. Chen & Renvoize)的干物质年产量也可分别达到15.1 t/hm2和22.8 t/hm2 [10]。其次,芒草为多年生草本,一次种植可持续收获至少20年,大大减少了播种所带来的人力物力消耗。与其他能源植物相比,在土地使用、种植、灌溉、施肥以及杂草和病虫害管理上成本较低[6, 7]。再者,芒草有耐寒、耐旱、耐贫瘠、耐盐碱和耐污染的优良品质。例如,奇岗在低温下光合效率比玉米高80%[11],对铝、铬和锌等重金属有极强的耐受力[12, 13]。此外,芒草比一般的植物能更多地吸收CO2放出O2,具有降低温室效应的作用[14],其发达的根系能够截流雨水、涵养水源、防止表土流失和滑坡,具有很高的水土保持价值[15]。简言之,芒草既可用于生物能源、造纸等产业,也是园林观赏、生态恢复的优质原材料,具有重要的开发利用前景[6, 14, 16]。
中国是芒属植物的多样性中心,该属约14个种,其中7个分布在中国,包括生物量最高的中国特有种—南荻,为我们研究开发芒属植物提供了丰富的天然种质资源[17]。考虑到中国有约1亿hm2的边际土地,大约769.37 × 104 hm2适合芒属植物生长,如果在这些边际土地上种植芒草,以干物质产量18.1 ~ 44.2 t/hm2计算,总产量为每年13 521.7 × 104 t,其发电量为每年183.9 TW,减少CO2排放量为21 242.4 × 104 t[14,18]。因此,中国具有开发利用芒属植物资源的有利条件和广阔前景。
尽管如此,迄今对芒属植物资源的利用仍十分不充分,欧美广泛耕种的奇岗为不育杂种,基因型单一、抗逆性差,大规模推广存在一定风险;其两个亲本(芒和荻)丰富的野生资源并未得到充分开发利用;而芒属其他野生种资源更未得到有效的发掘和利用[19]。虽然其基本生物学特性、野生资源调查和收集以及人工栽培和管理等已开展了不少研究,取得了一定的成绩[10, 11, 16, 17, 20],但迄今人们对芒草基本的生物学特性、物种分类及种间关系、群体遗传学特点和适应性机制仍缺乏清楚的认识,这些无疑阻碍了芒草资源的充分利用和为打造能源作物而开展的分子辅助育种工作。本文介绍了芒草的分类学现状、遗传多样性和群体遗传结构特点、资源研究和开发等方面的基本情况,总结了前人取得的研究成果以及存在的问题,以期对未来芒属植物的研究及资源的开发利用有所裨益。
1. 芒属植物的分类和地理分布
芒属隶属于禾本科黍亚科须芒草族甘蔗亚族,由Andersson[21]于1855年建立,含5种,主要区别特征是花序上小花两性,小穗成对着生,且具小穗柄。随着类群研究的不断深入,芒属类群的数目也不断增加,但同时不同的分类学观点也导致芒属的界定及其范围以及物种数目出现争议、甚至混乱。Pilger[22]将芒属非洲分布的4个种处理为属下的一个组sect. Miscanthidium,而Clayton[23]和Hartley[24]则分别支持它们应独立成属Miscanthidium或属下的组。孙必兴和王松[25]描述了红山茅属(Rubimons),认为该属花序紧缩呈圆锥花序,无基盘毛,同芒属植物有别。但是Chen和Renvoize[26]以及Sun等[27]却将该属放在芒属中,包括2种。刘亮[28]将喜马拉雅和我国西南山区分布、仅具2个花药的10个种独立为双药芒属(Diandranthus(Keng)L. Liu)。但随后的细胞和分子系统学研究表明双药芒属染色体基数为10,和黄金茅属(Eulalia)与高粱属(Sorghum)的关系更近,如Hodkinson等[29]认为,喜马拉雅南部地区的特有种M. fuscus(Roxb.)Benth.(=Sclerostachya fusca(Roxb.)A. Camus)与非洲分布的芒属物种和甘蔗属(Saccharum)的部分物种有较近的亲缘关系。由此可见,早期定义的芒属是禾本科中一个类群间性状多有交叉、比较庞杂的属,即广义芒属(Miscanthus s.l.),依不同学者的观点包含约13 ~ 24个种,分布于亚洲、太平洋群岛及热带非洲[23, 30]。芒属主要的分类系统见表1。
表 1 芒属主要分类系统Table 1. Main classifications proposed for the genus Miscanthus刘亮[28]
Liu[28]Chen 和 Renvoize[26]
Chen and Renvoize[26]Sun等[27]
Sun et al.[27]荻属
Triarrhena2种8变种8变型 荻组
Sect. Triarrhena2种 芒亚属
Subgenus
Miscanthus荻组
Sect. Triarrhena1种 2亚种 芒属
Miscanthus6种 芒组
Sect. Miscanthus2种 芒组
Sect. Miscanthus2种 2变种 双药芒属
Diandranthus10种 朝日芒组
Sect. Kariyasua3种 平截颖亚属
Subgenus Diandranthus3种2变种 双药芒组
Sect. Diandra5种 Hodkinson等[29]利用2个叶绿体片段与核基因ITS对芒属、甘蔗属及近缘属进行系统发生分析,认为东亚和东南亚分布的芒属类群形成一单系分支,染色体基数均为x=19,是相对自然的类群,并将其定义为狭义芒属(Miscanthus s.s.)。随着分类学研究的不断深入,尤其是分子证据的广泛应用,大量证据表明广义芒属并未构成单系群,而是包括了Hodkinson等[29]定义的狭义芒属、双药芒属、红山茅属、Sclerostachya、Miscanthidium等不同属的物种,而且这些属的界定和关系也存在很多争议[7, 31]。
根据Hodkinson等[7]的总结,狭义芒属大致包括11 ~ 12个种,主要分布在亚洲和部分太平洋岛国。尽管狭义芒属的范畴基本清楚,但也存在物种界定不明确的问题。例如,刘亮[28]曾发表了金县芒 M. jinxianensis L. Liu,而Sun等[27]不承认该种。Andersson[21]从芒中分出紫芒M. purpurascens Andersson,并得到刘亮[28]的认可,但Nakai[32]和Flora of China [26]分别将其处理为芒的变型和异名。Honda[33]发表M. flavidus Honda,但在Flora of China中该种被处理为芒的异名[26]。尽管Sun等[27]将南荻处理为荻的亚种,但刘亮[28]却在南荻种下建立了8变种8变型。
造成芒属分类上有如此诸多争议的主要原因在于:(1)形态分类划分标准的不统一;(2)对自然杂交和多倍体类群研究不足;(3)缺乏利用可靠分子标记进行的系统发生研究;(4)缺乏基于群体水平变异式样的深入研究,存在较多的同物异名(Synonymy)。因此,针对表型性状群体变异式样的研究有助于清楚地界定芒草类群,而在全面取样的基础上,利用更高分辨率的分子标记重建芒属植物的系统发生关系是解决上述问题的关键。为此,马洪峥[31]选取广义芒属及近缘类群16个物种,利用14个叶绿体片段重建了该类植物的系统发育关系,认为广义芒属可以划分为3大支系,建议将双药芒支系和红山茅支系移出芒属,分别恢复为独立的属,其余东亚和东南亚分布为主的类群构成狭义芒属的成员。随后,Li等[17]选用24个SSR标记,对采自覆盖中国全境100个居群的芒属植物开展了较为全面的群体遗传学和进化历史研究。这些最新的研究进展表明以东亚和东南亚分布为主的芒属植物构成一个单系,包括中国有分布的4个种:芒、五节芒(M. floridulus (Labil.) Warb. ex K. Schum. & Lauterb.)、荻和南荻;另3种为特有种,仅分布于日本(少序芒M. oligostachyus Stapf.、短毛荻M. tinctorius (Steud.) Hack.)和韩国(M. longiberbis Nakai)。这些结果与Hodkinson等[29]对狭义芒属的界定一致。因此,笔者支持Hodkinson等[29]的界定,中国含2组4种:芒组(Sect. Miscanthus)含芒和五节芒,荻组(Sect. Trarrihena)含荻和南荻。下文涉及芒属的相关论述均按狭义芒属的范畴展开。
芒属物种分布于亚洲的东部、东南亚地区和太平洋群岛,其中芒、五节芒和荻分布较为广泛。芒主要分布于中国除青藏地区、西北地区西部以外的所有地区、朝鲜半岛和日本、印度尼西亚和太平洋群岛等东南亚地区,在海拔2 500 m以下的山地、丘陵和荒坡原野常形成优势群落;五节芒分布于中国南部和东南部以及东南亚,主要生长在海拔2 400 m以下的山坡上;荻分布在长江流域以北地区以及朝鲜半岛、日本和俄罗斯远东,主要生长于海拔4 100 m以下的山坡和路边、草地、平原和河岸湿地[27]。南荻是中国的特有种,常见于洞庭湖为中心的湖南、湖北一带,多生长在海拔50 m以下的岸边湿地[34]。其他几个物种是否成立以及种间关系还不是很清楚或存在争议,包括少序芒、短毛荻和中间型芒(M. intermedius (Honda)),均为日本特有种;M. changii是朝鲜半岛特有种[7, 31]。
2. 开花物候和交配系统
芒属植物花期变异较大,同一物种的开花时间也会由于纬度和气候条件而存在差异[35-38]。例如,在日本本州岛北纬32° ~ 40°分布的芒其抽穗期差异有3个月之多[35]。荻在江汉平原9月中旬至10月中旬已经开花结实[36],但在山东微山9月才开始抽穗[37]。安徽合肥地区五节芒抽穗期为每年的5-6月,开花时间为6月下旬[38]。自然条件下芒属植物的花期差异在同质园中仍旧能够体现。Jenson等[39]将在中国东北部、韩国和日本采集的芒、荻和M. × giganteus在英国阿伯里斯特威斯附近进行同地栽培试验,连续3年的统计结果显示芒的开花时间从6月中旬一直延续到11月下旬,荻的开花时间比芒晚1个月左右。将整个中国范围内采集的芒、荻和南荻群体分别种植在湖北江夏和甘肃庆阳,结果表明纬度更低的湖北江夏种植区内芒的花期为6-11月,荻比芒开花时间晚半月,南荻花期较短,为9月中旬到10月中旬;而纬度更高的甘肃庆阳种植区内,芒、荻和南荻的花期比湖北江夏晚1~2个月[40]。由于以上各项研究实验地点的气候土壤条件不同,且开花时间的判定标准不统一,所以很难得出具体统一的结果。但是现有观测和大田试验结果表明,五节芒的花期最早,一般在5-6月;芒由于地理分布范围最广,因此花期跨度最大,为6-11月;荻比芒晚了半月到1个月;南荻花期很短,大约在8月中旬-10月(表2)。自然条件和同质园实验中芒属植物表现出相似的花期差异,说明这种花期差异具有一定的遗传基础。由于花期隔离会限制物种间的基因交流,推测花期隔离有可能是芒属种间生殖隔离的重要方式。
表 2 芒属物种的开花时间Table 2. Flowering time of Miscanthus species物种
Species野外观测点或取样点
Observation or sampling
station in the wild同质园观测点
Observation station in
common garden花期
Flowering time荻 M. sacchariflorus 中国江汉平原 9月中旬-10月中旬花果期[36] 荻 山东微山县 9月抽穗[37] 五节芒 M. floridulus 安徽合肥 5-6月抽穗,6月下旬开花[38] 芒 M. sinensis 中国东北部、韩国、日本 英国阿伯里斯特威斯 6月中旬-11月下旬抽穗[39] 荻 中国东北部、韩国、日本 英国阿伯里斯特威斯 7月中旬-11月下旬抽穗[39] 芒 中国 湖北江夏 6月初-9月初抽穗[40] 荻 中国 湖北江夏 6月下旬-9月初抽穗[40] 南荻 M. lutarioriparius 中国 湖北江夏 8月中旬-9月初抽穗[40] 芒 中国 甘肃庆阳 7月中旬-10月下旬抽穗[40] 荻 中国 甘肃庆阳 7月中旬-10月下旬抽穗[40] 南荻 中国 甘肃庆阳 9月下旬-10月上旬抽穗[40] 芒属植物自交率极低,自交不亲和。Hirayoshi等[41]最早对日本的芒M. sinensis var. condensatus 和M. tinctorius进行了自交实验,发现自交的植株结实率很低(0 ~ 6.2%),而异交的植株结实率较高(18.25% ~ 61.82%)。对欧洲地区芒13个个体、荻1个个体、M. × giganteus 2个个体进行套袋自交实验,3个种的自交结实率分别为0、0.01和0,而异交结实率为42.2% ~ 57.5%,该研究同时对10个芒个体进行自交和杂交实验,套袋的自交植株中,花期早的植株结实率为0.07%,花期处在中间的植株结实率为0.03%,花期晚的植株结实率为0.08%;配对的异交植株中,3种时期的植株结实率分别为42.2%、45.1%和45.8%;而自由交配的植株中分别为57.5%、50.0%和52.1%[42]。可见芒属植物的自交不亲和不是绝对的,一些基因型在特殊的条件下自交可以产生极少的种子,自由交配比配对杂交的植株结实率高。Jiang等[43]再次证实芒的自交不亲和性,并发现大多数自花花粉的花粉管较短,只能到达雌蕊的柱头表面,仅有少部分能进入花粉管通道。而雌蕊的发育阶段会影响花粉和雌蕊的相互作用,雌蕊越不成熟,花粉管越能接近胚珠。
3. 细胞学、多倍化和杂交
芒属植物细胞学研究开展较早,五节芒、奇岗、中间型芒、少序芒、荻、芒和短毛荻的染色体基数为19[7]。有研究推测,芒属x=19的染色体基数起源于x=10和x=9的亲本,近年来图谱的研究发现芒属基因组与高粱属的基因组高度相似,且经历过基因组重复事件[44, 45]。Tang等[46]利用PI和DAPI组合(CPD)染色和45S rDNA探针荧光原位杂交对芒、五节芒、荻和南荻的中期染色体进行了分析,结果显示4个种核型皆为2n= 2x=38=34m(2SAT) + 4sm。流式细胞仪被广泛用于基因组大小的测定,不同研究中芒属类群DNA的含量略有差异,但基本趋势是芒DNA含量最大,为(5.27 ± 0.2) pg/2C,其次是五节芒(5.17 ± 0.3) pg/2C、南荻(4.26 ± 0.6) pg/2C、荻(3.96 ± 0.2) pg/2C[47, 48]。
芒属中多倍化现象很普遍,存在二倍体至六倍体等多种倍性(表3)。目前荻和芒中都有多个同源多倍体和异源多倍体被鉴定。例如,同源三倍体M. sinensis ‘Goliath’、M. sinensis var. condensatus、M. sinensis ‘Autumn Light’;同源四倍体M. sacchariflorus;异源三倍体中最具代表性的是M. × giganteus;此外还有M. sacchariflorus var. brevibarbis、M. sacchariflorus var. glaber等[7]。Adati和Shiotani[49]用核型分析显示四倍体的荻是异源多倍体起源,由两套不同染色体组成,一套是具随体的染色体,而另外一套是不具随体的染色体,两套和芒同源,另两套部分同源。五倍体M. sacchariflorus var. latifolius是由荻和芒构成的异源多倍体,而中间型芒M. intermedius是由少序芒M. oligostachyus和短毛荻M. tinctorius构成的异源多倍体[49]。整个芒属染色体倍性很复杂,非整倍体现象也常被报道[7, 42]。我们可以通过选择父母本倍性、育性恢复和打破自交不亲和体系等方法,人工对芒属物种进行多倍化,从而选育出优良性状[50-52]。另外,可以通过构建不育基因型来降低芒草广泛种植后产生的入侵风险[53]。
表 3 芒属物种的倍性和染色体数目Table 3. Ploidy and chromosome number of Miscanthus species物种
Species倍性和染色体数目
Ploidy and chromosome number荻
M. sacchariflorus2n=2x=38[7]
2n =3x =57
2n =4x =76
2n =5x=95[35]南荻
M. lutarioriparius2n=4x=76 [7] 芒
M. sinensis2n =2x=38、36、50、42
2n =3x=57[42]五节芒
M. floridulus2n =2x=38[7]
2n =3x=57[42]少序芒
M. oligostachyus2n =2x=38[7] 中间型芒
M. intermedius2n =4x=76[42]
2n =6x=114[7]短毛荻
M. tinctorius2n=2x=38
2n=4x=76
2n=6x=114[7]芒属植物天然杂交现象很普遍,目前广泛推广的M. × giganteus本身就是一个天然的三倍体杂交种,多项研究鉴定出芒和荻的天然杂交株系[54, 55],以及芒和五节芒种间自然杂交株系[56]。利用芒属植物花期调控技术和远缘杂交技术,现已成功在五节芒和荻[57, 58]、南荻与芒[59]、荻与南荻[60]之间完成人工杂交,并在子一代杂交群体中鉴定出了大量明显的分离性状和超亲现象。
4. 群体遗传变异和适应性分化
早期针对芒属开展的一些群体遗传学研究,多偏重于资源利用和开发,且多局限在某个国家或局部地区,所用分子标记都是传统的Isoenzyme、AFLP、SSR及其叶绿体片段序列等[61-64]。近年来群体遗传学研究的取样范围逐渐扩大,涵盖整个中国、日本和韩国等地区,随着测序技术和基因组学的飞速发展,简化基因组(RAD-seq)等组学手段被广泛采用(表4)[64-84],人们对芒属植物种间关系、遗传多样性和群体遗传结构以及谱系地理等方面的认识逐步加深[17, 65, 66]。Clark等[65]用RAD-seq和SSR标记对中国、韩国和日本的773份芒样品进行了研究,所有样品被分为6个组,其中4组分布于亚洲大陆(中国北部、东南部、中部的秦岭-长江一带和四川盆地以及韩国),另外两组分布在日本北部和南部。该研究还显示中国东南部是温带亚洲芒的起源中心,分几条路径迁移到北方和亚洲东部[65]。基于采自中国100个芒属物种居群的SSR检测,Li等[17]发现4个芒属物种(芒、五节芒、荻和南荻)均具有高水平的遗传多样性,既体现在物种水平上(He =0.559 ~ 0.708),也体现在种内群体水平上(He=0.468 ~ 0.599),意味着这些天然芒草群体蕴含着丰富的、可被利用的遗传资源。该研究进一步推断从末次冰期到现在,中国的芒和五节芒经历了群体扩张,相比之下荻和南荻则经历了一定的群体收缩;而且,五节芒很可能起源于中国东南地区的芒,并经历了生态物种形成过程。Zhang等[67]通过PacBio测序和Hi-C图谱对五节芒基因组进行测序和组装,与甘蔗亚族基因组之间的比较分析发现,芒属和甘蔗属在4.6-4.3 Ma分化开来,之后芒属的祖先经历同源多倍化事件,并在此过程中发生染色体融合和基因丢失。该研究对分布在中国的芒、五节芒、荻、南荻的74份材料进行了重测序,分析结果表明荻和南荻关系密切,而五节芒与这两个物种的距离较远。五节芒与其他物种相比遗传多样性更高,而荻和南荻相对较低。
表 4 芒属物种群体遗传学研究概况Table 4. Summary of studies on population genetics of Miscanthus species编号No. 类群
Species分子标记
Marker取样范围
Sampling area群体和个体数目
Amount of populations and accessions1 芒[64] cpDNA 日本全境 30群体,636个体 2 芒[76] SSR 中国西南地区 26群体,389个体 3 芒[61] SSR 中国全境 459个体 4 芒[77] ISSR 中国浙江省、广东省 12群体,93个体 5 芒[78] SRAP 中国西南地区 26群体,260个体 6 芒[65] RAD-seq,SSR 中、日、韩 737个体 7 荻、芒[79] SSR 韩国全境 69个体 8 芒[80] cpDNA 中国西南地区 14群体,75个体 9 荻和芒[81] RAD-seq,SSR 日本全境 745个体 10 南荻[82] SSR 中国长江中下游地区 25群体,644个体 11 芒[83] SSR 美国东部 228个体 12 荻[66] RAD-seq 中、日、韩、俄 764个体 13 芒、五节芒、荻、南荻[17] SSR 中国全境 100群体,1 960个体 14 南荻[84] SCoT 中国长江中下游地区 9群体,153个体 迄今,很多田间试验和实验室控制实验研究了芒属植物不同基因型之间农艺性状的差异,并取得了明显的进展,涉及产量、耐旱、耐寒、开花时间、化学成分和种子萌发等[7, 68, 69]。通过多个地点的同质园实验来探讨不同基因型之间的适应性差异也逐步开展起来。例如,Clifton-Brown 和 Lewandowski[70]将M. × giganteus、荻、芒的不同基因型分别种植在位于不同温度梯度上的瑞典、丹麦、英国和德国的试验田中,发现不同基因型在过冬能力上存在明显区别。Yan等[40]将在中国广泛收集的芒属93个基因型种植于3种自然环境中(冬季寒冷的温带草地、半干旱的黄土高原、温暖湿润的中国中部地区),检测到高水平的生长性状差异,以及呈显著水平的Site × Population交互作用。Dong等[71]在3个不同地点对M. × giganteus基因型进行了3年的田间试验,观测过冬率、产量、抽穗期、株高等表型,分析不同地点试验田中植株的过冬率和产量差异,找到了比“1993-1780”(现在大规模推广的基因型)具有更高过冬率和产量的基因型。这些研究表明,芒属植物中存在大量的表型差异,这些表型差异为后续利用关联分析、QTL定位等技术进行分子标记辅助育种提供了群体的表型数据[72-75]。
在群体遗传学研究中应用转录组数据不但可以得到该物种遗传和表达上的差异,而且可以了解物种遗传和表达对环境条件响应的信息。Xu等[85, 86]和Zhu等[87]对湖北江夏(原生境)和甘肃庆阳(胁迫生境)两个试验地的南荻进行转录组分析,发现低表达基因对环境变化相对更敏感,遗传多样性低的基因在胁迫环境下更易发生变异,而且lncRNA比蛋白质编码mRNA对环境变化更敏感,揭示了lncRNA对环境变化的响应特征。60%的基因在庆阳比在江夏核苷酸多样性降低,说明大多数基因在胁迫环境下受到了选择作用,一些非生物胁迫反应基因和光合作用相关基因响应胁迫环境。Song等[88]将南荻的天然群体种在山东东营的高盐性实验样地上,对比盐胁迫条件下和原生境条件下群体的转录组数据,找到59个响应高盐环境的基因,功能主要涉及植物防御、光合作用、细胞新陈代谢、信号转导和解毒作用,不同基因的表达趋势体现了典型的表达调和性,即与生长相关的基因表达量下调,伴随与抗性相关基因的表达量上升。Xing等[89]探讨南荻在驯化过程中基因的表达差异,分别找到共变异表达模式(Co-variation expression pattern,CE)基因和高表达变异(Top rank of expression fold change,TE)基因,CE基因多与水的利用效率有关,而TE基因多与生物或非生物胁迫相关,CE和TE基因的表达差异反映了南荻驯化过程中适应新环境的能力。Yan等[90]对南荻群体进行转录组测序,发现南荻群体间不同基因表达水平的差异较高,例如光合作用相关基因和对温度和活性氧刺激相关基因的表达水平在某些群体中显著高于其他群体,群体内部核苷酸多样性与表达多样性呈显著负相关,群体间则呈正相关,说明遗传和表达差异在物种适应性和种群持续性上扮演不同角色。Hu等[91]对南荻5个组织(叶、茎、根、侧芽和根茎芽)进行de novo转录组测序,寻找到很多和根茎发育相关的候选基因。目前,转录组相关研究多集中于南荻中,而其他几个重要的近缘物种,如芒、五节芒、荻的相关研究较少,另外,目前研究多停留在差异表达基因分析和功能注释上,我们可以通过寻找表达差异基因与QTL关联基因相一致的基因,从而进一步缩小候选基因的范围,提高候选基因的可靠性。
5. 资源利用和遗传改良
芒属植物既是重要的能源植物,又可用于园林观赏、造纸、生态恢复以及建筑材料[4, 16, 92, 93]。芒属植物对太阳能的转化效率以及对水分的利用效率均远远高于一般农作物[94, 95]。目前,欧美国家对芒草的开发已进入产业化应用阶段,如丹麦已经利用芒草与煤混合发电,英国的Elean公司是世界上最大的生物质发电厂,其燃料来自Anglian Straw公司大规模种植的芒草,美国农业部曾启动“能源植物援助计划”(Biomass Crop Assistance Program,BCAP),大力发展芒草等能源植物的种植,并开展了一系列纤维素乙醇商业化项目[96]。初步估计,若将美国9.7%的耕地用于种植芒草,则可生产133 × 109 L乙醇,相当于美国1/5的汽油消耗[94];而将欧盟35%的闲置土地种植芒草,将解决欧盟12%的能源需求[97]。
现在欧美国家广泛推广的三倍体杂种M. × giganteus平均干物质年产量为30 t/hm2 [11]。由于M. × giganteus基因型单一,在抗逆性等方面存在局限性,其亲本芒、荻以及另外两个近缘种五节芒和南荻也已作为能源作物被开发并利用。其中南荻和五节芒在生物质产量方面表现出优良特性,可以与M. × giganteus相媲美。五节芒在我国华东地区的干物质年产量可达31.9 t/hm2,我国的特有种南荻年产量约22.8 t/hm2 [14]。研究表明,芒和五节芒表现出较强的耐热性和耐旱性[38, 98-100];荻抗寒能力优于芒、五节芒和南荻[40, 101];而芒、五节芒、荻和南荻均能耐受中度盐碱环境,尤其是南荻的耐盐能力高于其他3个物种[10, 102]。芒属植物还表现出对多种重金属的耐性,可用于矿山废弃地植被恢复[103]。
要实现芒属植物大规模栽培生产,离不开对芒属资源的研究和利用。欧美国家虽然不是芒属植物的天然分布区,但十分重视扩大其种质资源的遗传基础,多个欧洲国家联合启动了“欧洲芒改良计划”,构建芒属核心种质和育种体系,利用生物技术手段开展新品种培育[104]。美国伊利诺伊州大学专注于产量、稳定性、开花时间、越冬能力、低温光合作用、叶片延展、耐寒性等性状[7]。
中国早在20世纪50年代就开始了对芒属植物的遗传改良,但早期的研究主要集中在将南荻作为造纸原料或将五节芒作为牧草的利用上[96],用系统选育法培育出了‘突节荻’和‘胖节荻’新品种,其产量和纤维含量明显优于以往的栽培品种,提高了造纸经济效益[105]。湖南农业大学在芒属植物的育种工作中取得突出成果,曾先后建立了芒属植物人工快繁和远缘杂交技术体系,并培育出‘湘杂芒1号’、‘2号’和‘3号’等第一批芒属能源植物新品种[96],分别培育出适合发酵产沼气型、适合直燃型和适合发酵产乙醇型的杂交株系[59]。利用植物细胞工程技术选育出了同源四倍体新品种‘芙蓉南荻’,利用转基因技术培育出南荻的抗虫品种,这是国际上第一例转基因芒属植物。此外,荻与南荻杂交F1代也表现出明显的杂种优势[60]。
为了实现芒草资源的高效利用,需要对其产量、抗逆性、化学组成成分等性状进行优化,精确的遗传图谱和准确的QTL定位是了解性状遗传机制的前提,有助于制定切实可行的遗传改良方案。由于芒属物种的基因组大而且杂合度高,其遗传图谱的研究进展比较缓慢。早期研究主要利用RAPD、SSR等分子标记构建遗传图谱,随着二代测序技术的发展,芒属物种高分辨率的遗传图谱陆续产生,其标记间距可以达到0.3 cM,已经有涉及生物量、开花时间、叶片条纹、抗逆性等性状的大量QTL被定位(表5)。
表 5 芒属植物遗传图谱和QTL研究汇总Table 5. Summary of studies on genetic map and QTLs of Miscanthus species编号
No.物种
Species标记
Marker图谱长度
Length / cM分辨率
Average interval / cMQTL 相关性状
Characters1 芒[106-110] RAPD 1075 4.2 45 花期、产量、株高、茎秆直径、矿物组成等 2 芒[44, 111] RNA-seq SSR 1782 2.7 72 株高、分蘖直径、分蘖数目等 3 芒[112] GBS 2396 0.6 4 荻、芒[113] SSR 1999 9.0 2238 8.0 5 芒[114] RAD-seq 1599 0.8 6 叶片斑马状条纹的有无和密度 1612 0.9 6 五节芒、荻[115] SSR 2053 3.3 66 株高、抽穗时间、开花时间等 1685 3.5 7 荻和芒[45, 72] RAD-seq 2223 0.3 112 腋芽数、茎秆密度、茎秆节数等 8 芒[116] GBS 2396 0.6 5 开花时间 近年来,全基因组关联分析(Genome-wide association studies,GWAS)技术被广泛应用于芒草属资源的研究和发掘,大量与抽穗期、植株高度、茎叶长度、木质素含量、产量、抗性等性状相关的位点被定位和解析[61, 73]。Nie等[117]用SRAP、ISAP和SSR标记对中国西南地区的芒进行关联分析,发现一个与产量相关的标记,以及11个与其他性状关联的标记。Clark等[75]发现了27个与产量相关的SNP,并在不同种植点和不同年份间找到298个与其他性状相关的SNP,在单个种植点和多个种植点得到的基因组预测的准确性相似。Dong等[74]针对芒的耐寒性进行关联分析,共发现73个关联位点,该作者前期另一项研究对芒的耐寒性进行QTL分析,有一个QTL区段包含了此研究中的5个关联位点和一个响应寒冷的基因,其他的QTL区段中包含2个关联位点和3个响应寒冷的基因。目前芒草的基因定位仍存在定位区间大、区间内包含基因多的问题。将不同基因定位技术相结合,发掘区间的重叠区域,例如可以将BSA(Bulked segregation analysis)与遗传图谱相结合,或者将GWAS分析与遗传图谱分析相结合,将有助于缩小区间,筛选出更加可靠的候选基因。另外,目前的研究得到了众多的候选基因,但缺乏后续的基因验证,未来可以通过Southern blot、Northern bolt、qRT-PCR、RNA干扰、基因敲除等技术来对候选基因进行功能验证。
6. 展望
迄今,在芒属野生资源的调查评估、分类学、分子系统学、群体遗传学以及遗传改良等方面已取得了很大进展,但其中很多问题仍未解决或存在争议,有待进一步的深入研究。首先,科学的分类和明确的种间关系对人们认识、保护和合理利用生物多样性资源至关重要,而芒属的界定、芒属与近缘属的系统发生关系以及属下各个类群的分类仍存在诸多问题。造成这些问题的原因不仅和类群本身复杂的生物学特性有关(如大多自交不亲和,个别情况下存在种间天然杂交现象以及多倍化现象),同时也和研究策略不合理、研究不够深入有关(取样范围不全面,缺乏足够的群体水平研究以及对重要性状研究不够深入),对这些问题的进一步探讨是下一步工作的重点之一。
其次,针对芒属植物群体遗传结构和进化历史的研究仍然十分薄弱,有很多基本的群体遗传学和进化历史问题亟待解决,包括:(1)芒属野生种质资源调查和搜集还不全面,有些物种(如分布在中国和东亚地区的荻和南荻)研究比较全面,而对于分布在东南亚国家的芒属植物几乎没有研究报道。(2)群体遗传结构研究不够深入导致物种及种下等级的划分存在很大矛盾,包括属下组的划分和类群间的关系。其原因既有来自以往研究所用分子标记的分辨率不高,也和研究材料没有按照群体策略进行取样有很大关系。因此,选用分辨率更高的分子标记和群体取样策略进行深入研究是亟待开展的工作。(3)芒属很多物种的起源和进化历史尚不清楚,物种形成方式和机制更缺乏研究。例如中国、日本和韩国的特有种是如何起源的,广域分布的芒、五节芒、荻中谁是祖先种,起源中心在哪里,何时起源,经历了怎样的进化路线等问题都尚无定论。了解物种形成方式和机制既是探讨性状进化、生态适应、物种分化等进化生物学重要问题的基础,也是资源利用和遗传改良的基础,应加大研究的力度。
再者,随着测序技术的快速提高以及测序成本的急速下降,组学技术得到了飞速发展,对植物科学研究带来了前所未有的机遇[118, 119]。例如,Mitros等[120]完成了芒的染色体水平基因组组装,Zhang等[67]发布五节芒基因组数据,Miao等[121]构建第一个染色体水平的南荻基因组。荻基因组(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/?term=Miscanthus + sacchariflorus) 也在NCBI发布。芒属基因组数据的发表将大力推动芒属及近缘类群基因组数据库的构建和发展(例如CSGRqtl database、Gramene等)以及相关生物学理论研究,有助于通过GWAS、GS、比较基因组学等方法和技术寻找与驯化相关的基因或QTL,为交叉利用甘蔗乃至整个禾本科植物的图谱数据提供便利,加快芒草资源的开发和改良。
我国有着丰富的芒属植物资源优势,但是资源的有效利用、产业化技术研发和科研成果转化方面却相对滞后,是未来重点关注和加大研究力度的领域。我国有大面积的边际土地,包括黄河滩地和滨海盐土、南方低山丘陵的红壤、西北地区的黄绵土等,要有效利用这些边际土地进行大规模种植,并开发配套的产业化技术,实现科学技术到生产力的转化,需要各级政府部门、科研院所和企业单位联合起来,结合各方的资源、技术和人才优势,这将有利于我国芒属资源的发掘、整合和开发利用。
1 1~2)如需查阅附表内容请登录《植物科学学报》网站(http://www.plantscience.cn)查看本期文章。 -
表 1 神农架南坡常绿阔叶林植物区系类型
Table 1 Floristic composition of plants in the evergreen broad-leaved forest on the southern slopes of Shennongjia
区系类型
Floristic types科Family 属Genera 数量
Number比例
Rate / %数量
Number比例
Rate / %1世界分布 Cosmopolitan 6 15.79 1 1.45 2泛热带分布 Pantropic 11 28.95 9 13.04 3热带亚洲和热带南美洲间断分布
Tropical Asia and South Tropical America disjuncted5 13.16 5 7.25 4旧世界热带分布 Old World Tropic 1 2.63 1 1.45 5热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布
Tropical Asia to Tropical Australasia Oceania1 2.63 3 4.35 6热带亚洲至热带非洲分布
Tropical Asia to Tropical Africa1 2.63 1 1.45 7热带亚洲分布 Tropical Asia − − 9 13.04 8北温带分布 North Temperate 11 28.95 18 26.09 9东亚和北美间断分布
East Asia and North America disjuncted1 2.63 11 15.94 10旧世纪温带分布 Old World Temperate − − 4 5.8 14东亚分布 East Asia 1 2.63 4 5.8 15中国特有分布 Endemic to China − − 3 4.35 合计 Total 38 100 69 100 -
[1] Prăvălie R. Major perturbations in the Earth's forest ecosystems. Possible implications for global warming[J]. Earth-Sci Rev,2018,185:544−571. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.06.010
[2] Kalaba FK. A conceptual framework for understanding forest socio-ecological systems[J]. Biodivers Conserv,2014,23(14):3391−3403. doi: 10.1007/s10531-014-0792-5
[3] O'Connor CD,Falk DA,Lynch AM,Swetnam TW,Wilcox CP. Disturbance and productivity interactions mediate stability of forest composition and structure[J]. Ecol Appl,2017,27(3):900−915. doi: 10.1002/eap.1492
[4] Rudolf VHW,Rasmussen NL. Population structure determines functional differences among species and ecosystem processes[J]. Nat Commun,2013,4:2318. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3318
[5] Bannar-Martin KH,Kremer CT,Ernest SKM,Leibold MA,Auge H,et al. Integrating community assembly and biodiversity to better understand ecosystem function:the Community Assembly and the Functioning of Ecosystems (CAFE) approach[J]. Ecol Lett,2018,21(2):167−180. doi: 10.1111/ele.12895
[6] 吴征镒. 中国植被[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1980:823−836. [7] Wang HB,Jin J,Yu PY,Fu WJ,Morrison L,et al. Converting evergreen broad-leaved forests into tea and moso bamboo plantations affects labile carbon pools and the chemical composition of soil organic carbon[J]. Sci Total Environ,2020,711:135225. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135225
[8] Betts MG,Wolf C,Ripple WJ,Phalan B,Millers KA,et al. Global forest loss disproportionately erodes biodiversity in intact landscapes[J]. Nature,2017,547(7664):441−444. doi: 10.1038/nature23285
[9] 祝燕,赵谷风,张俪文,沈国春,米湘成,等. 古田山中亚热带常绿阔叶林动态监测样地——群落组成与结构[J]. 植物生态学报,2008,32(2):262−273. Zhu Y,Zhao GF,Zhang LW,Shen GC,Mi XC,et al. Community composition and structure of gutianshan forest dynamic plot in a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest,East China[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology,2008,32(2):262−273.
[10] 叶万辉,曹洪麟,黄忠良,练琚愉,王志高,等. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林20公顷样地群落特征研究[J]. 植物生态学报,2008,32(2):274−286. doi: 10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2008.02.005 Ye WH,Cao HL,Huang ZL,Lian JY,Wang ZG,et al. Community structure of a 20hm2 lower subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest plot in Dinghushan,China[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology,2008,32(2):274−286. doi: 10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2008.02.005
[11] 谢宗强,申国珍,周友兵,樊大勇,徐文婷,等. 神农架世界自然遗产地的全球突出普遍价值及其保护[J]. 生物多样性,2017,25(5):490−497. doi: 10.17520/biods.2016268 Xie ZQ,Shen GZ,Zhao YB,Fan DY,Xu WT,et al. The outstanding universal value and conservation of the Shennongjia World Natural Heritage Site[J]. Biodiversity Science,2017,25(5):490−497. doi: 10.17520/biods.2016268
[12] 宋永昌. 中国东部森林植被带划分之我见[J]. 植物学报,1999,41(5):541−552. Song YC. Perspective of the vegetation zonation of forest region in eastern China[J]. Acta Botanica Sinica,1999,41(5):541−552.
[13] 马明哲,申国珍,熊高明,赵常明,徐文婷,等. 神农架自然遗产地植被垂直带谱的特点和代表性[J]. 植物生态学报,2017,41(11):1127−1139. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2017.0092 Ma MZ,Shen GZ,Xiong GM,Zhao CM,Xu WT,et al. Characteristic and representativeness of the vertical vegetation zonation along the altitudinal gradient in Shennongjia Natural Heritage[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2017,41(11):1127−1139. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2017.0092
[14] 刘蕾,申国珍,陈芳清,罗璐,谢宗强,喻杰. 神农架海拔梯度上4种典型森林凋落物现存量及其养分循环动态[J]. 生态学报,2012,32(7):2142−2149. doi: 10.5846/stxb201111291822 Liu L,Shen GZ,Chen FQ,Luo L,Xie ZQ,Yu J. Dynamic characteristics of litterfall and nutrient return of four typical forests along the altitudinal gradients in Mt. Shennongjia,China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2012,32(7):2142−2149. doi: 10.5846/stxb201111291822
[15] 罗璐,申国珍,谢宗强,喻杰. 神农架海拔梯度上4种典型森林的乔木叶片功能性状特征[J]. 生态学报,2011,31(21):6420−6428. Luo L,Shen GZ,Xie ZQ,Yu J. Leaf functional traits of four typical forests along the altitudinal gradients in Mt. Shennongjia[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2011,31(21):6420−6428.
[16] 邓舒雨,董向忠,马明哲,臧振华,徐文婷,等. 基于森林碳库动态评估神农架国家级自然保护区的保护成效[J]. 生物多样性,2018,26(1):27−35. doi: 10.17520/biods.2017240 Deng SY,Dong XZ,Ma MZ,Zang ZH,Xu WT,et al. Evaluating the effectiveness of Shennongjia National Nature Reserve based on the dynamics of forest carbon pools[J]. Biodiversity Science,2018,26(1):27−35. doi: 10.17520/biods.2017240
[17] 吴冬秀,张琳,宋创业,张淑敏. 陆地生态系统生物观测指标与规范[M]. 北京:中国环境出版集团,2019:71−80. [18] 吴征镒,周浙昆,李德铢,彭华,孙航. 世界种子植物科的分布区类型系统[J]. 云南植物研究,2003,25(3):245−257. Wu ZY,Zhou ZK,Li DZ,Peng H,Sun H. The areal-types of the world families of seed plants[J]. Acta Botanica Yunnanica,2003,25(3):245−257.
[19] 吴征镒. 中国种子植物属的分布区类型[J]. 云南植物研究,1991,13(S4):1−139. [20] Hubbell SP,Foster RB. Commonness and rarity in a neotropical forest:implications for tropical tree conservation[M]//Soulé M,ed. Conservation Biology:Science of Scarcity and Diversity. Sunderland:Sinauer,1986:205−231.
[21] Illian J,Penttinen A,Stoyan H,Stoyan D. Statistical Analysis and Modelling of Spatial Point Patterns[M]. Hoboken:John Wiley & Sons,Ltd. ,2008:516−517.
[22] 倪健,陈仲新,董鸣,陈旭东,张新时. 中国生物多样性的生态地理区划[J]. 植物学报,1998,40(4):370−382. Ni J,Chen ZX,Dong M,Chen XD,Zhang XS. An ecogeographical regionalization for biodiversity in China[J]. Acta Botanica Sinica,1998,40(4):370−382.
[23] 于倩,谢宗强,熊高明,陈志刚,杨敬元. 神农架巴山冷杉(Abies fargesii)林群落特征及其优势种群结构[J]. 生态学报,2008,28(5):1931−1941. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.05.006 Yu Q,Xie ZQ,Xiong GM,Chen ZG,Yang JY. Community characteristics and population structure of dominant species of Abies fargesii forests in Shennongjia National Nature Reserve[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2008,28(5):1931−1941. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.05.006
[24] 丁晖,杨云方,徐海根,方炎明,陈晓,等. 武夷山典型常绿阔叶林物种组成与群落结构[J]. 生态学报,2015,35(4):1142−1154. Ding H,Yang YF,Xu HG,Fang YM,Chen X,et al. Species composition and community structure of the typical evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Wuyi Mountains of Southeastern China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2015,35(4):1142−1154.
[25] Bunyavejchewin S,Baker PJ,LaFrankie JV,Ashton PS. Structure,history,and rarity in a seasonal evergreen forest in western Thailand[M]//Losos EC,Leigh EG Jr,eds. Tropical Forest Diversity and Dynamism:Findings From A Large-Scale Plot Network. Chicago:University of Chicago Press,2004:145−158.
[26] 丁晖,方炎明,杨青,陈晓,袁发银,等. 武夷山中亚热带常绿阔叶林样地的群落特征[J]. 生物多样性,2015,23(4):479−492. doi: 10.17520/biods.2015021 Ding H,Fang YM,Yang Q,Chen X,Yuan FY,et al. Community characteristics of a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest plot in the Wuyi Mountains,Fujian Province,southeastern China[J]. Biodiversity Science,2015,23(4):479−492. doi: 10.17520/biods.2015021
[27] 田自强,陈玥,陈伟烈,胡东. 神农架龙门河地区的植被制图及植被现状分析[J]. 植物生态学报,2002,26(S1):30−39. Tian ZQ,Chen Y,Chen WL,Hu D. Vegetation mapping and analysis at Longmenhe region,Shennongjia,China[J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica,2002,26(S1):30−39.
[28] Hao ZQ,Zhang J,Song B,Ye J,Li BH. Vertical structure and spatial associations of dominant tree species in an old-growth temperate forest[J]. For Ecol Manage,2007,252(1-3):1−11. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2007.06.026
[29] 陈灵芝. 中国的生物多样性:现状及其保护对策[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1993:114−122. [30] Weiner J,Solbrig OT. The meaning and measurement of size hierarchies in plant populations[J]. Oecologia,1984,61(3):334−336. doi: 10.1007/BF00379630
[31] 何春梅,刘润清,杨治春,尹秋龙,贾仕宏,等. 秦岭皇冠暖温性落叶阔叶林物种组成与群落结构[J]. 应用生态学报,2021,32(8):2737−2744. He CM,Liu RQ,Yang ZC,Yin QL,Jia SH,et al. Species composition and community structure of warm temperate deciduous broadleaved forests in Huangguan of Qinling Mountains,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2021,32(8):2737−2744.
[32] 樊凡,赵联军,马添翼,熊心雨,张远彬,等. 川西王朗亚高山暗针叶林25.2 hm2动态监测样地物种组成与群落结构特征[J]. 植物生态学报,2022,46(9):1005−1017. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2022.0094 Fan F,Zhao LJ,Ma TY,Xiong XY,Zhang YB,et al. Community composition and structure in a 25.2 hm2 subalpine dark coniferous forest dynamics plot in Wanglang,Sichuan,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2022,46(9):1005−1017. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2022.0094
[33] 李立,陈建华,任海保,米湘成,于明坚,杨波. 古田山常绿阔叶林优势树种甜槠和木荷的空间格局分析[J]. 植物生态学报,2010,34(3):241−252. Li L,Chen JH,Ren HB,Mi XC,Yu MJ,Yang B. Spatial patterns of Castanopsis eyrei and Schima superba in mid-subtropical broad-leaved evergreen forest in Gutianshan National Reserve,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2010,34(3):241−252.
[34] Condit R. Research in large,long-term tropical forest plots[J]. Trends Ecol Evol,1995,10(1):18−22. doi: 10.1016/S0169-5347(00)88955-7
[35] 祝燕,白帆,刘海丰,李文超,李亮,等. 北京暖温带次生林种群分布格局与种间空间关联性[J]. 生物多样性,2011,19(2):252−259. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.08024 Zhu Y,Bai F,Liu HF,Li WC,Li L,et al. Population distribution patterns and interspecific spatial associations in warm temperate secondary forests,Beijing[J]. Biodiversity Science,2011,19(2):252−259. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.08024
[36] Shen GC,Yu MJ,Hu XS,Mi XC,Ren HB,et al. Species-area relationships explained by the joint effects of dispersal limitation and habitat heterogeneity[J]. Ecology,2009,90(11):3033−3041. doi: 10.1890/08-1646.1
[37] 张忠华,胡刚,刘立斌,程安云,胡聪,等. 黔中北亚热带喀斯特次生林动态监测样地:物种组成与群落结构[J]. 生态学报,2022,42(2):742−754. Zhang ZH,Hu G,Liu LB,Cheng AY,Hu C,et al. Species composition and community structure of a north subtropical karst secondary forest in central Guizhou Province,China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2022,42(2):742−754.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 何拓,曾岩,殷亚方,张坤,袁良琛,董晖,周志华. 为野生植物保护和可持续贸易奠定科学基础——CITES植物委员会第27次会议评述. 生物多样性. 2024(09): 171-175 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)
-
其他相关附件
-
DOCX格式
刘明伟附表1~2 点击下载(24KB)
-



 下载:
下载: