Species diversity and interspecific association of Rhodoleia championii Hook. f. + Castanopsis fordii Hance community in Nankun Mountain, Longmen, Guangdong Province
-
摘要:
以广东省龙门县南昆山南亚热带典型红花荷(Rhodoleia championii Hook. f.)+南岭栲(Castanopsis fordii Hance)群落为研究对象,通过样方调查和方差比率法、Fisher精确检验等方法,分析群落物种多样性和种间关系。结果显示:(1)该群落物种多样性较高,乔木层的物种分布均匀,灌木层的物种数量多但分布不均,多样性指数低于乔木层;(2)群落总体呈显著正联结,种间形成稳定的搭配关系。乔木层中,存在1对极显著正联结种对,5对显著正联结种对,以及2对显著负联结种对;(3)基于种群聚类、种间联结性及生态习性分析,将14个主要种群划分为4个生态种组,同组树种的生态习性和资源需求相似,多呈正联结,不同组的树种多呈负联结。研究结果为南昆山天然次生林保护提供了理论依据。
-
关键词:
- 南昆山 /
- 种间联结 /
- 方差比率法 /
- 优势种群 /
- Fisher精确检验
Abstract:This study investigated the Rhodoleia championii Hook. f. + Castanopsis fordii Hance community, a representative subtropical forest in Nankun Mountain, Longmen County, Guangdong Province. Quadrat-based surveys, coupled with the variance ratio method (VR) and Fisher’s exact test, were employed to assess species diversity and interspecific associations. Results revealed that: (1) The community exhibited high species diversity, with a relatively even distribution of species in the tree layer, whereas the shrub layer contained a greater number of species but exhibited uneven distribution, leading to a lower diversity index; (2) The overall interspecific associations within the community were significantly positive, suggesting a stable community structure. In the tree layer, one highly significant positive association pair, five significant positive association pairs, and two significant negative association pairs were identified; (3) Based on population clustering, interspecific connectivity, and ecological habits, the 14 dominant populations were classified into four ecological species groups. Species within the same group exhibited similar ecological adaptations and resource requirements, generally displaying positive associations, while species from different groups predominantly exhibited negative associations. These findings provide a theoretical basis for the conservation and management of natural secondary forests in Nankun Mountain.
-
-
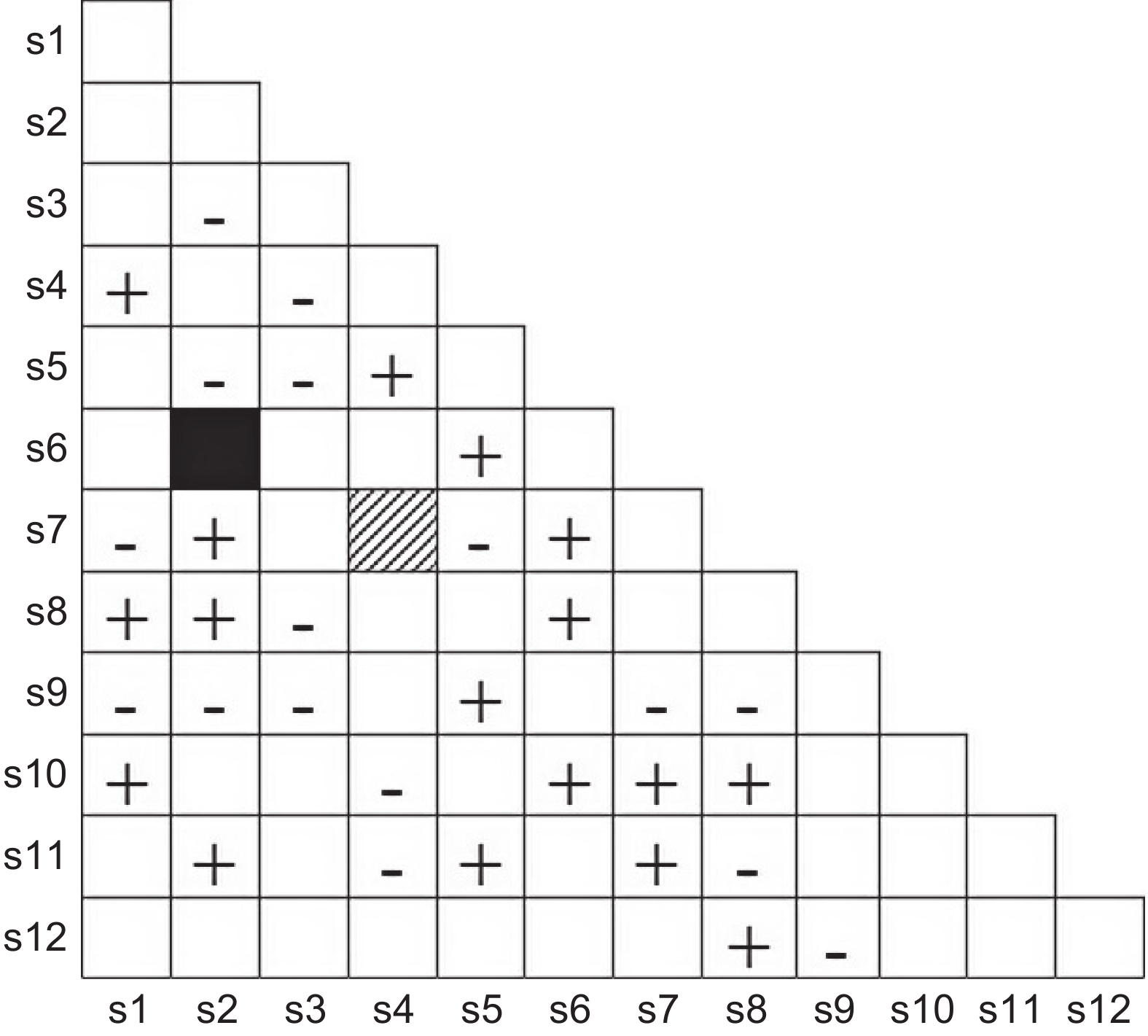
图 1 乔木层优势种种间Fisher精确检验半矩阵
□:无联结;+:正联结。−:负联结;■:极显著正联结;▤:显著正联结;▨:显著负联结;下同。s1:红花荷;s2:南岭栲;s3:杉木;s4:山黄皮;s5:岭南青冈;s6:甜槠;s7:二色波罗蜜;s8:桃叶石楠;s9:香楠;s10:鹿角锥;s11:鼠刺;s12:软荚红豆;s13:阿丁枫;s14:子凌蒲桃;s15:岭南槭;s16:红淡比;s17:小叶青冈;s18:光叶山矾;s19:短序润楠;s20:粘木;s21:密花树;s22:野含笑;s23:铁榄。
Figure 1. Semi-matrix diagram of Fisher’s test of dominant tree species in the arbor layer
□: Non–correlation; +: Positive correlation; −: Negative correlation; ■: Significant positive correlation; ▤: Positive correlation; ▨: Negative correlation; Same below. s1: Rhodoleia championii Hook. f.; s2: Castanopsis fordii Hance; s3: Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) Hook.; s4: Aidia cochinchinensis Lour.; s5: Cyclobalanopsis championii Benth.; s6: Castanopsis eyrei (Champ. ex Benth.) Tutcher; s7: Artocarpus styracifolius Pierre; s8: Photinia prunifolia (Hook. & Arn.) Lindl.; s9: Aidia canthioides (Champ. ex Benth.) Masam.; s10: Castanopsis lamontii Hance; s11: Itea chinensis Hook. & Arn.; s12: Ormosia semicastrata Hance; s13: Altingia chinensis (Champ. ex Benth.) Oliv. ex Hance; s14: Syzygium championii (Benth.) Merr. & L. M. Perry; s15: Acer tutcheri Duthie; s16: Cleyera japonica Thunb.; s17: Cyclobalanopsis myrsinifolia Blume; s18: Symplocos lancifolia Siebold & Zucc.; s19: Machilus breviflora (Benth.) Hemsl.; s20: Ixonanthes reticulata Jack; s21: Myrsine seguinii H. Lév.; s22: Michelia skinneriana Dunn; s23: Sinosideroxylon wightianum (Hook. & Arn.) Aubrév.
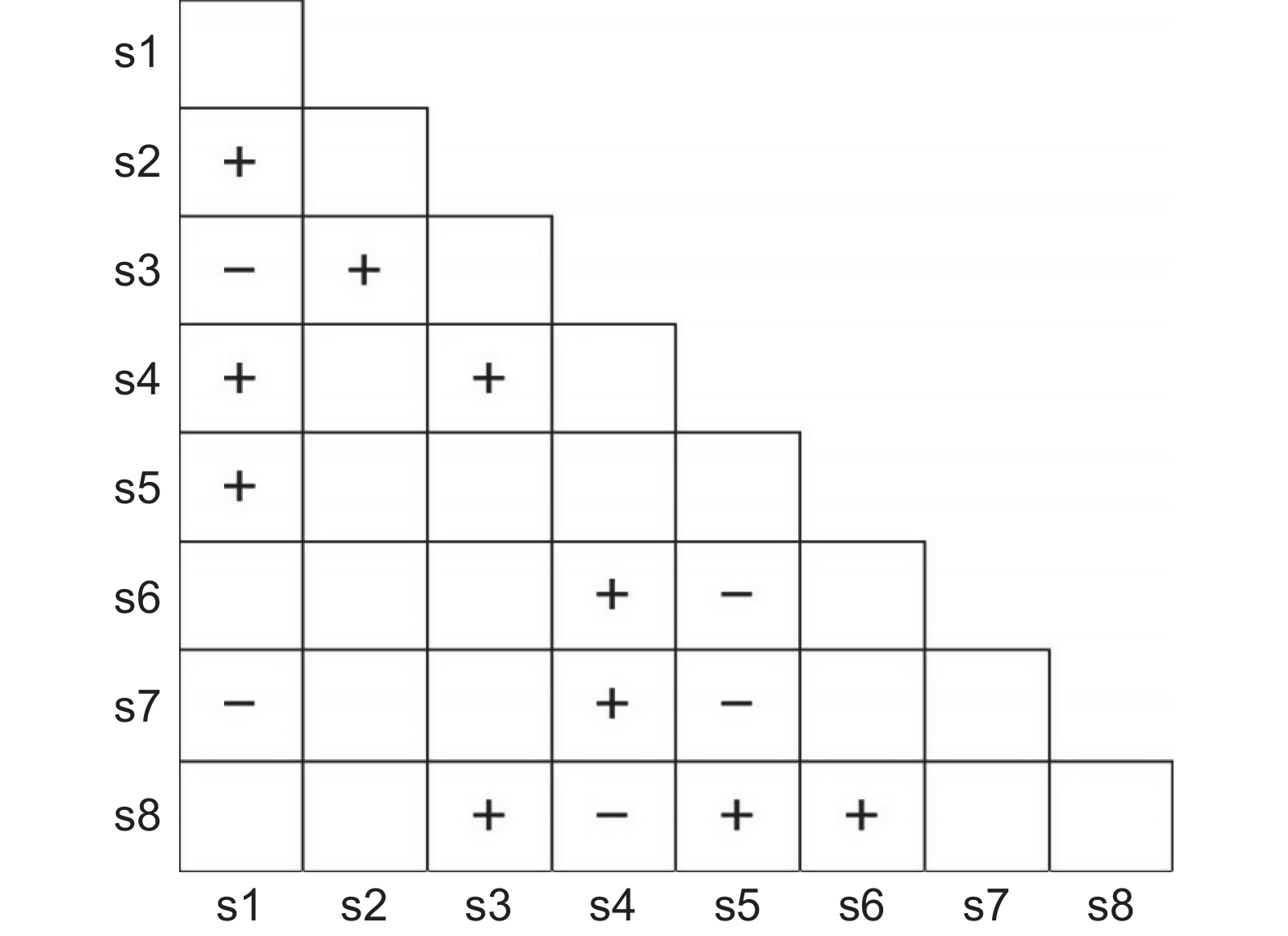
图 2 灌木层优势种种间Fisher精确检验半矩阵
s1:细枝柃;s2:彗竹;s3:苦竹;s4:鼠刺;s5:红花荷;s6:山黄皮;s7:铁榄;s8:枇杷叶紫珠;s9:短序润楠;s10:山乌桕;s11:红淡比;s12:天料木。
Figure 2. Semi-matrix diagram of Fisher’s test of dominant species in the shrub layer
s1: Eurya loquaiana Dunn; s2: Pseudosasa hindsii C. D. Chu & C. S. Chao; s3: Pleioblastus amarus (Keng) P. C. Keng; s4: Itea chinensis Hook. & Arn.; s5: Rhodoleia championii Hook. f.; s6: Aidia cochinchinensis Lour.; s7: Sinosideroxylon wightianum (Hook. & Arn.) Aubrév.; s8: Callicarpa kochiana Makino; s9: Machilus breviflora (Benth.) Hemsl.; s10: Triadica cochinchinensis Lour.; s11: Cleyera japonica Thunb.; s12: Homalium cochinchinense (Lour.) Druce.
图 3 草本层优势种种间Fisher精确检验半矩阵
s1:芒萁;s2:乌毛蕨;s3:金毛狗;s4:中华里白;s5:乌蔹莓;s6:蔓生莠竹;s7:石果珍珠茅;s8:黑莎草。
Figure 3. Semi-matrix diagram of Fisher’s test of dominant species in the herb layer
s1: Dicranopteris pedata (Houtt.) Nakaike; s2: Blechnum orientale (L.) C. Presl; s3: Cibotium barometz (L.) J. sm.; s4: Diplopterygium chinensis (Rosenst.) De Vol; s5: Causonis japonica (Thunb.) Raf. ; s6: Microstegium fasciculatum (L.) Henrard; s7: Scleria lithosperma (L.) sw.; s8: Gahnia tristis Nees.
表 1 群落主要植物的科、属、种数
Table 1 Number of families, genera, and species in the Rhodoleia championii+Castanopsis fordii community
层
Layer科
Families属
Genera种
Species乔木层 27 33 41 灌木层 37 44 58 草本层 20 29 32 总体 53 78 102 表 2 乔木层各物种相对多度、相对频度、相对优势度和重要值
Table 2 Relative abundance, relative frequency, relative dominance, and importance value of species in the arbor layer
序号
Number种名
Species相对多度
RA / %相对优势度
RD / %相对频度
RF / %重要值
IV / %1 红花荷Rhodoleia championii Hook. f. 8.86 7.91 6.67 23.44 2 南岭栲Castanopsis fordii Hance 6.33 9.63 5.71 21.67 3 杉木Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) Hook. 3.80 11.22 2.86 17.87 4 山黄皮Aidia cochinchinensis Lour. 8.23 1.27 6.67 16.16 5 岭南青冈Quercus championii Benth. 4.43 6.91 3.81 15.15 6 甜槠Castanopsis eyrei (Champ. ex Benth.) Tutcher 4.43 5.55 4.76 14.74 7 二色波罗蜜Artocarpus styracifolius Pierre 3.80 7.23 2.86 13.88 8 桃叶石楠Photinia prunifolia (Hook. & Arn.) Lindl. 6.33 2.10 4.76 13.19 9 香楠Aidia canthioides (Champ. ex Benth.) Masam. 5.06 1.73 4.76 11.55 10 鹿角锥Castanopsis lamontii Hance 1.27 7.80 1.90 10.97 其他31个树种 48.73 46.46 57.14 152.34 总计 100 100 100 300 表 3 灌木层各物种相对多度、相对频度、相对优势度和重要值
Table 3 Relative abundance, relative frequency, relative dominance, and importance value of species in the shrub layer
序号
Number种名
Species相对多度
RA / %相对优势度
RD / %相对频度
RF / %重要值
IV / %1 细枝柃Eurya loquaiana Dunn 1.40 45.46 2.44 49.30 2 彗竹Pseudosasa hindsii (Munro) C. D. Chu & C. S. Chao 27.06 7.26 7.32 41.64 3 苦竹Pleioblastus amarus (Keng) P. C. Keng 28.62 4.55 7.32 40.48 4 鼠刺Itea chinensis Hook. & Arn. 5.44 4.66 5.69 15.79 5 红花荷Rhodoleia championii Hook. f. 2.18 2.86 4.07 9.10 6 山黄皮Aidia cochinchinensis Lour. 2.33 1.63 4.88 8.84 7 铁榄Sinosideroxylon wightianum (Hook. & Arn.) Aubrév. 2.80 2.30 2.44 7.53 8 枇杷叶紫珠Callicarpa kochiana Makino 1.56 1.98 3.25 6.79 9 短序润楠Machilus breviflora (Benth.) Hemsl. 0.78 2.28 3.25 6.31 10 山乌桕Triadica cochinchinensis Lour. 2.64 0.38 3.25 6.28 其他48个树种 24.26 22.98 54.47 101.71 总计 100 100 100 300 表 4 草本层各物种相对多度、相对频度、相对优势度和重要值
Table 4 Relative abundance, relative frequency, relative dominance, and importance value of species in the herb layer
序号
Number种名
Species相对多度
RA / %相对优势度
RD / %相对频度
RF / %重要值
IV / %1 芒萁Dicranopteris pedata (Houtt.) Nakaike 47.80 24.15 11.29 83.23 2 乌毛蕨Blechnum orientale (L.) C. Presl 16.51 38.17 14.52 69.19 3 金毛狗蕨Cibotium barometz (L.) J. Sm. 4.72 15.05 8.06 27.83 4 中华里白Diplopterygium chinensis (Rosenst.) De Vol 3.93 8.28 9.68 21.88 5 乌蔹莓Causonis japonica (Thunb.) Raf. 1.26 0.58 6.45 8.29 6 蔓生莠竹Microstegium fasciculatum (L.) Henrard 3.93 0.29 3.23 7.45 7 石果珍珠茅Scleria lithosperma (L.) Sw. 2.04 1.80 3.23 7.07 8 黑莎草Gahnia tristis Nees 1.73 1.80 3.23 6.75 其他23个物种 13.36 4.94 40.32 68.31 总计 100 100 100 300 -
[1] 王伯荪,余世孝,彭少麟,李鸣光. 植物群落学实验手册[M]. 广州:广东高等教育出版社,1996:10−15. [2] Liu ZW,Zhu Y,Wang JJ,Ma W,Meng JH. Species association of the dominant tree species in an old-growth forest and Implications for enrichment planting for the restoration of natural degraded forest in subtropical China[J]. Forests,2019,10(11):957. doi: 10.3390/f10110957
[3] Forbes SA. On the local distribution of certain Illinois fishes:an essay in statistical ecology[J]. Ill Nat Hist Surv,1909,7(1-10):273−303.
[4] Zhang WJ. Calculation and statistic test of partial correlation of general correlation measures[J]. Selforganizology,2015,2(4):65−77.
[5] Ott M,Held L. Bayesian calibration of p-values from fisher's exact test[J]. Int Stat Rev,2019,87(2):285−305. doi: 10.1111/insr.12307
[6] 包和平,白玉峰,包德喜. 四格列联表的独立性Fisher精确检验的近似检验法[J]. 数理医药学杂志,2007,20(3):301−302. [7] Song Q,Wang TM. Effects of shrub encroachment in the Inner Mongolia ecotones between forest and grassland on the species diversity and interspecific associations[J]. Agronomy,2022,12(10):2575. doi: 10.3390/agronomy12102575
[8] 陈章和,李鸣光,吕小红,暨淑仪. 广东南昆山自然保护区森林群落[J]. 生态科学,1983,2(1):18−29. Chen ZH,Li MG,Lü XH,Ji SY. A study on the forest communities in natural reserve of Nankunshan,Guangdong[J]. Ecological Science,1983,2(1):18−29.
[9] 庄雪影,王通,甄荣东,黄坚城. 增城市主要森林群落植物多样性研究[J]. 林业科学研究,2002,15(2):182−189. Zhuang XY,Wang T,Zhen RD,Huang JC. Floristic diversity of major forest communities in Zengcheng City,Guangdong Province[J]. Forest Research,2002,15(2):182−189.
[10] 林媚珍. 广东南昆山与其邻近地区植物区系的比较[J]. 热带地理,1997,17(1):36−40. Lin MZ. Comparison between the flora of the Nankun Mountain and those in its adjacent regions[J]. Tropical Geography,1997,17(1):36−40.
[11] 乔琦,邢福武,陈红锋,钟文超. 广东省南昆山伯乐树群落特征及其保护策略[J]. 西北植物学报,2010,30(2):377−384. Qiao Q,Xing FW,Chen HF,Zhong WC. Characteristics of community and in situ conservation strategy of Bretschneidera sinensis in Nankun Mountain,Guangdong Province[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2010,30(2):377−384.
[12] 杨晓丽,邢福武,陈树钢,曾庆文. 广东省南昆山自然保护区厚叶木莲的群落特征研究[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报,2013,21(4):356−364. Yang XL,Xing FW,Chen SG,Zeng QW. Structure characteristics of Manglietia pachyphylla community in Nankunshan Nature Reserve,Guangdong Province[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany,2013,21(4):356−364.
[13] 钟奇锋,朱婷,朱文辉,钟文超,江良为,等. 广东龙门南昆山珍稀濒危植物调查及保护研究[J]. 广西林业科学,2022,51(5):709−715. Zhong QF,Zhu T,Zhu WH,Zhong WC,Jiang LW,et al. Investigation and protection of rare and endangered plants in Longmen Nankunshan,Longmen,Guangdong[J]. Guangxi Forestry Science,2022,51(5):709−715.
[14] 冯欣欣,刘志贤,古文强,刘健勋,余金昌,等. 金缕梅科红花荷属野生资源及其园林开发潜力评估[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报,2022,30(5):727−734. Feng XX,Liu ZX,Gu WQ,Liu JX,Yu JC,et al. Wild resource of Rhodoleia (Hamamelidaceae) and garden development potential evaluation[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany,2022,30(5):727−734.
[15] 何汉波,朱政财,王海华,林福新,陈小金,朱嘉焕. 增城区白水寨景区红花荷群落特征[J]. 林业与环境科学,2017,33(4):67−71. He HB,Zhu ZC,Wang HH,Lin FX,Chen XJ,Zhu JH. The community characteristics of Rhodoleia championii in Baishuizhai Science Spot of Zengcheng District[J]. Forestry and Environmental Science,2017,33(4):67−71.
[16] 戴建阅,陈林,林瑞芬,张尚坤,邢福武. 广东银屏山森林公园红花荷群落特征与物种多样性研究[J]. 林业资源管理,2011,39(3):52−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6622.2011.03.012 Dai JY,Chen L,Lin RF,Zhang SK,Xing FW. Community characteristics and species diversity of Rhodoleia championii community in Dongguan Yinpingshan Forest Park,Guangdong[J]. Forest Resource Management,2011,39(3):52−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6622.2011.03.012
[17] 钟象景,张粤. 广东象头山国家级自然保护区红花荷植物群落特征分析[J]. 广东林业科技,2006,22(3):26−31. Zhong XJ,Zhang Y. The Analysis of characters of Rhodoleia championii communities in Guangdong Xiangtoushan National Nature Reserve[J]. Guangdong Forestry Science and Technology,2006,22(3):26−31.
[18] 上官铁梁,张峰. 山西绵山植被优势种群的分布格局与种间联结的研究[J]. 武汉植物学研究,1988,6(4):357−364. Shangguan TL,Zhang F. Research on the pattern and associations between dominants of the vegetation in Mian Mountain,Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research,1988,6(4):357−364.
[19] Schluter D. A variance test for detecting species associations,with some example applications[J]. Ecology,1984,65(3):998−1005.
[20] 金山,武帅楷. 太行山南段油松林火烧迹地优势草本生态位及种间关系[J]. 北京林业大学学报,2021,43(4):35−46. Jin S,Wu SK. Niche and interspecific association of dominant species in herb layer of burned Pinus tabuliformis forest in the southern Taihang Mountain of northern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2021,43(4):35−46.
[21] Li YD,Xu H,Chen DX,Luo TS,Mo JH,et al. Division of ecological species groups and functional groups based on interspecific association: a case study of the tree layer in the tropical lowland rainforest of Jianfenling in Hainan Island,China[J]. Front For China,2008,3(4):407−415. doi: 10.1007/s11461-008-0049-0
[22] 任泽楷,杨礼香. 珍稀濒危植物绣球茜(Dunnia sinensis Tutcher)的生境特征和繁殖技术[J]. 生态科学,2020,39(3):25−30. Ren ZK,Yang LX. The habitat and propagation techniques of Dunnia sinensis Tutcher,a critically rare and endangered plant in southern China[J]. Ecological Science,2020,39(3):25−30.
[23] 李化. 十字水度假村对中国本土生态旅游的启示[J]. 中国发展观察,2010(6):60−62. [24] 王重阳,赵联军,孟世勇. 王朗国家级自然保护区滑坡体兰科植物分布格局及其保护策略[J]. 生物多样性,2022,30(2):21313. doi: 10.17520/biods.2021313 Wang CY,Zhao LJ,Meng SY. Spatial distribution pattern and protection strategy for orchids in landslide mass of the Wanglang National Nature Reserve[J]. Biodiversity Science,2022,30(2):21313. doi: 10.17520/biods.2021313
[25] 陈聪琳,赵常明,刘明伟,徐凯,徐文婷,等. 神农架南坡小叶青冈+曼青冈常绿阔叶林主要木本植物生态位与种间联结[J]. 生态学报,2024,44(11):4889−4903. Chen CL,Zhao CM,Liu MW,Xu K,Xu WT,et al. The ecological niche and interspecific association of main woody plants in the evergreen broad-leaved forest of Cyclobalanopsis myrsinifolia+C. oxyodon on the south slope of Shennongjia[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2024,44(11):4889−4903.
[26] 张明霞,王得祥,康冰,张岗岗,刘璞,等. 秦岭华山松天然次生林优势种群的种间联结性[J]. 林业科学,2015,51(1):12−21. Zhang MX,Wang DX,Kang B,Zhang GG,Liu P,et al. Interspecific associations of dominant plant populations in secondary forest of Pinus armandii in Qinling Mountains[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae,2015,51(1):12−21.
[27] 许涵,黄久香,唐光大,张浩,彭逸生,庄雪影. 南昆山观光木所在群落优势树种的种间联结性[J]. 华南农业大学学报,2008,29(1):57−62. doi: 10.7671/j.issn.1001-411X.2008.01.015 Xu H,Huang JX,Tang GD,Zhang H,Peng YS,Zhuang XY. Interspecific associations of dominant trees in the communities with Tsoongiodendron odorum on Nankunshan[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University,2008,29(1):57−62. doi: 10.7671/j.issn.1001-411X.2008.01.015
[28] 涂洪润,李娇凤,杨丽婷,白金莲,卢国琼,等. 桂林岩溶石山青冈群落主要乔木树种的种间关联[J]. 应用生态学报,2019,30(1):67−76. Xu HR,Li JF,Yang LT,Bai JL,Lu GQ,et al. Interspecific associations of the main tree populations of the Cyclobalanopsis glauca community in karst hills of Guilin,Southwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2019,30(1):67−76.
[29] Mehrvarz SS,Naqinezhad A,Ravanbakhsh M,Vasefi N. A survey of plant species diversity and ecological species group from the coastal zone of Boujagh National Park,Guilan,Iran[J]. Ecol Balkanica,2016,8(1):89−99.
[30] 任晴,袁位高,吴初平,王志高,江波,等. 浙江省红楠生境地群落数量分类和环境解析[J]. 生态学报,2020,40(15):5277−5287. Ren Q,Yuan WG,Wu CP,Wang ZG,Jiang B,et al. Community quantitative classification and environmental analysis of the Machilus thunbergii habitat in Zhejiang Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2020,40(15):5277−5287.
[31] 白小军,谷会岩. 大兴安岭次生林区优势种群落叶松种内联结和关联性分析[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报,2023,43(5):108−119. Bai XJ,Gu HY. Intraspecific association and correlation analysis of Larix gmelinii in the secondary forests of the Daxin’an Mountains[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology,2023,43(5):108−119.
[32] 刘美玲. 福建省乐东拟单性木兰林的群落生态学研究[D]. 厦门:厦门大学,2020:32. [33] 张倩媚,陈北光,周国逸. 鼎湖山主要林型优势树种种间联结性的计算方法研究[J]. 华南农业大学学报,2006,27(1):79−83. Zhang QM,Chen BG,Zhou GY. Interspecific association of the dominant species in two typical communities in Dinghushan,South China[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University,2006,27(1):79−83.
[34] 黄世能,李意德,骆土寿,王伯荪. 海南岛尖峰岭次生热带山地雨林树种间的联结动态[J]. 植物生态学报,2000,24(5):569−574. Huang SN,Li YD,Luo TS,Wang BS. Dynamics of associations between tree species in a secondary tropical montane rain forest at Jianfengling on Hainan Island[J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica,2000,24(5):569−574.



 下载:
下载: