Analysis of plant and soil bacterial diversity and their influencing factors in Tibetan Plateau wetlands
-
摘要:
植物和微生物是湿地生态系统的主要组成部分,也是其能量流动和物质循环的重要驱动力。了解湿地植物和土壤微生物的多样性及其关键影响因子,对于维持湿地生态系统的结构和功能有重要意义。本研究对西藏高原26个湿地进行野外调查和实验室分析,以揭示湿地植物与土壤细菌多样性的关系,明确影响植物多样性和土壤细菌多样性的关键因子。结果显示,植物群落特征与土壤细菌多样性显著相关,但驱动土壤细菌多样性变异的主要因素是环境因子而非植物。植物多样性的变异主要受土壤电导率影响,而细菌多样性的变异则与海拔、年降水量、土壤pH值以及植物功能性状(叶片总氮和总碳)相关。
Abstract:Plants and microorganisms are the main components of wetland ecosystems and important drivers of energy flow and material cycling. Understanding the diversity of plants and soil microorganisms and their influencing factors is important for maintaining the structure and function of wetland ecosystems. In this study, we conducted a field investigation and laboratory analysis of 26 Tibetan Plateau wetlands to reveal the relationship between wetland plant diversity and soil bacterial diversity, and to identify key factors affecting both. Results showed that plant diversity was significantly related to soil bacterial diversity, but the main factors driving changes in soil bacterial diversity were environmental factors rather than plants. Plant diversity was mainly affected by soil electrical conductivity, while soil bacterial diversity was influenced by altitude, mean annual precipitation, soil pH, and plant functional traits (leaf carbon content and nitrogen content).
-
Keywords:
- Plateau wetland /
- Plants /
- Microorganisms /
- Biodiversity /
- Electrical conductivity
-
湿地与森林、海洋并称为地球三大生态系统,其在调节生物多样性和保护自然环境等方面具有不可替代的功能与效益。西藏作为地球上独特的环境地域单元,孕育了非常独特的高寒生态环境,有着丰富的湿地资源。根据全国湿地资源第二次调查结果,西藏现有河流、湖泊、沼泽等各类湿地6.53 × 104 km2,湿地率(即湿地面积占国土面积的比率)达5.31%,高居全国第二位[1]。西藏独特的自然地理环境条件,也孕育了丰富的湿地生物多样性。近几十年来,西藏高原湿地的生物多样性受气候变化和人为活动等因素的威胁越来越严重,其生态状况也引起了世界范围的高度关注[2]。
植物是湿地生态系统的重要组成部分,也是其主要的初级生产者,对维持生态系统结构和功能的稳定有重要作用[3]。植物多样性是评价湿地生态服务价值和生态系统稳定性的重要指标,与土壤、海拔、气候等环境因子密切相关。一方面,环境因子可以影响植物的生长与群落分布,如有研究表明土壤养分含量直接制约植被的生长发育[4]。海拔也被认为是决定植被群落分布的重要因素之一[5],二者的关系目前主要有两种理论。第一种是“中间高度膨胀理论”[6, 7],即植物多样性在中海拔位置达到峰值,而在高海拔和低海拔地区相对较低。第二种是“负相关理论”[8],即植物多样性随着海拔的增加而降低。另一方面,越来越多的研究表明植物的凋落物和根系分泌物可显著改变土壤质地和肥力,进而可能影响植物的多样性[9, 10]。有研究发现,西藏地区水生植物物种丰富度和系统发育多样性随海拔的增加而显著降低[11]。也有研究表明,西藏高寒沼泽湿地植物多样性的变异受到多种环境因子相互作用的影响[12]。目前对西藏湿地植物的研究大多集中在植物物种调查[13, 14]和保护[15]上,而对湿地植物与高寒环境之间关系的探究相对较少[16, 17],因此,探讨西藏湿地植物多样性与环境因子之间关系具有重要意义。
土壤微生物作为湿地生态系统的分解者,在能量流动、物质循环、生态系统演替以及生物多样性维持等方面发挥重要的生态功能。细菌是最常见和最丰富的土壤微生物类群,驱动着绝大多数生物地球化学循环过程,如土壤有机物矿化、硝化、反硝化等[2, 18]。土壤细菌多样性与生态系统稳定性及土壤肥力有关,且能在一定程度上指示土壤养分状况和土壤质量。研究表明,土壤性质[19]、气候因素[20, 21]、地理距离[22]、植物多样性[23]等因子能显著影响土壤细菌多样性。如在高山草地和森林土壤中,pH是土壤细菌多样性形成和维持的主要驱动因子[24, 25];而在石灰质沙漠土壤中,土壤营养盐含量显著改变细菌群落的组成和结构[26]。李明家等[27]对西藏横断山区怒江和澜沧江两个流域进行了研究,发现气候和环境因子是影响细菌多样性的重要因素。甄莉等[28]探究了西藏热泉沉积物中硫氧化细菌的多样性,发现溶解有机碳含量显著影响硫氧化菌群的多样性。此外,植被特征差异也能不同程度地解释土壤微生物的多样性。如在旱地生态系统中,植物丰富度、盖度以及叶片面积等功能性状可以解释土壤细菌多样性的变异[29]。近年来,土壤微生物多样性的相关研究已经引起了国内外的广泛关注,但目前对西藏高寒环境下湿地土壤细菌多样性的研究还较少。
基于此,本研究选取26个具有代表性的西藏高原湿地为对象,探讨湿地植物和土壤细菌多样性,明确影响植物多样性与土壤细菌多样性的关键因子,试图回答“高寒环境下,哪些环境因子能够解释湿地植物和土壤细菌多样性的空间变化?”这一科学问题。研究结果旨在为了解高寒湿地生态系统的植物、微生物和土壤的相互关系,保护湿地生态系统生物多样性提供理论支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 研究地点
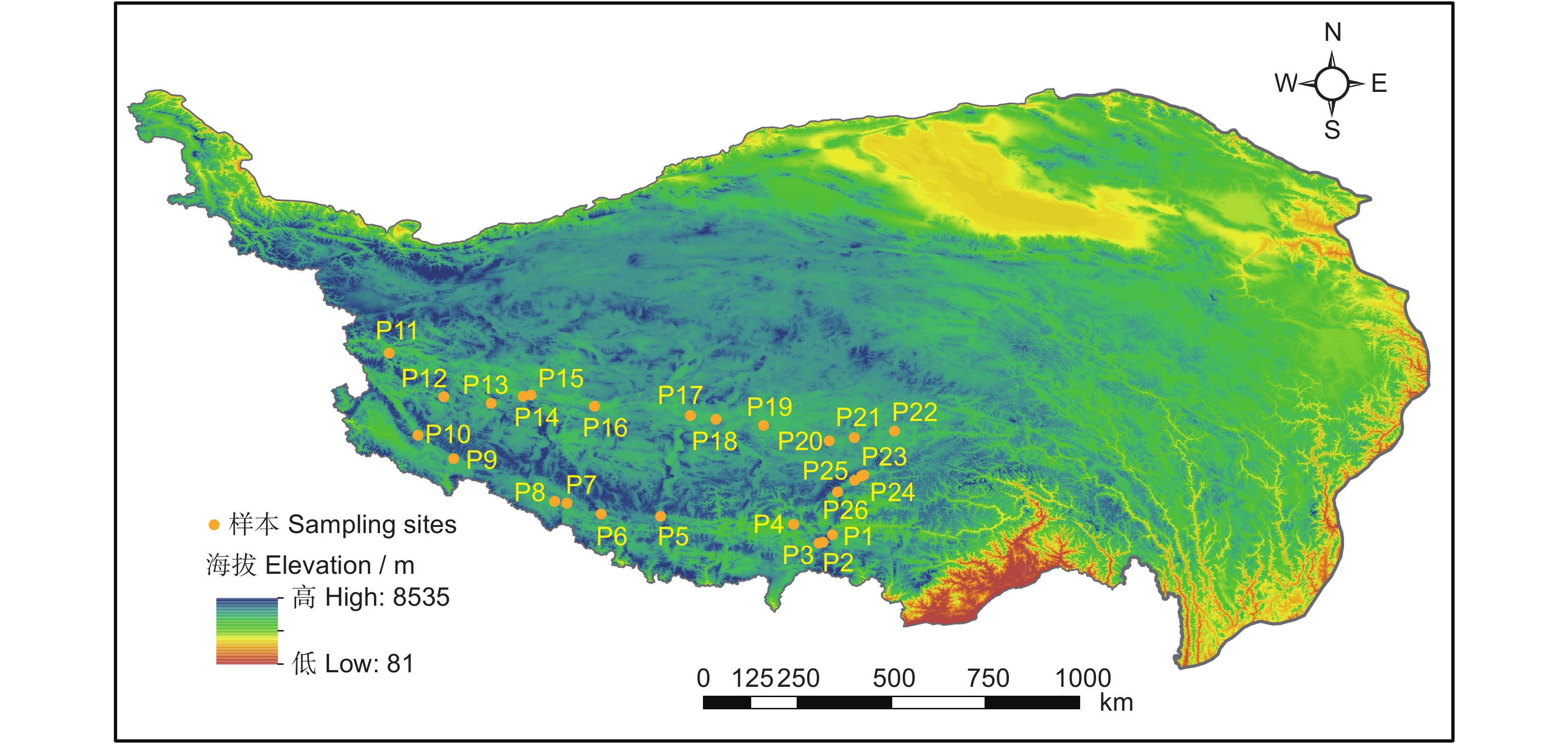
于2020年8月在西藏选取26个相互隔离的典型湿地(28.87° ~ 33.44°N,79.77° ~ 91.88°E)开展植被调查与土壤采样工作(图1)。所选湿地的海拔范围为3974 ~ 5206 m,年平均气温(Mean annual temperature, MAT)为−2.72℃ ~ 6.25℃,年平均降水量(Mean annual precipitation, MAP)为41 ~ 429 mm。所选湿地8月的平均降水量(Average precipitation)为67 mm,平均气温(Average temperature)为10.2℃。
依据典型性原则,在每个湿地内选择能够代表整个植被和土壤等特征的地段设置1个样地。记录样地位置(经度、纬度、海拔)及周围环境特点(放牧干扰程度、水源补给方式等)等信息。在样地内随机布设5 ~ 15个样方,样方面积为1 m2(1 m × 1 m),记录样方内的植物种类、个体数(株 / 丛数)和盖度。随机选取其中1个样方,样方内出现的所有植物各取10个叶片用信封保存,当天测定生物量鲜重和叶面积,并带回实验室测干重、碳氮磷含量等植物功能性状。在该样方内取10 g表层根际土放入冻存管中,带回实验室测定细菌多样性,另取150 g根际土放入自封袋中,带回实验室检测土壤理化性质。
1.2 植物多样性与功能性状测定
根据样方调查数据,计算植物的物种丰富度(Richness)、香农指数(Shannon index)等多样性参数。采样结束后,将植物地上部分与地下部分分开,吸干表面水分后测生物量鲜重。叶片在叶面积板上展开并拍照,使用Image J软件测叶面积(Leaf area, LA)。植物样品带回实验室放置于烘箱中,105℃杀青15 min后,立即降低烘箱温度至80℃,48 h后称量生物量干重,并计算干物质含量(Leaf dry matter content, LDMC)和比叶面积(Specific leaf area, SLA)。烘干后的植物样品用球磨仪粉碎,使用元素分析仪(Elementar Analysensysteme, Vario MACRO cube, 美国)测定叶片总碳(TC)和总氮(TN)含量,使用等离子体原子发射光谱仪(Perkin Elmer, Optima 8000 DV, 美国)测定叶片总磷(TP)含量。根据样方内各物种的相对多度(个体数),计算群落水平上各功能性状的群落加权平均数(Community weighted mean, CWM)。
1.3 土壤细菌多样性的测定
基于16S rRNA基因,采用扩增子高通量测序技术测定土壤的细菌多样性。DNA提取步骤如下:称取0.5 g土壤样品,分别加入PB(pH值 8.0)溶液和TNS(pH值 8.0)溶液,在样品破碎仪(Fastprep-24, 美国)下进行破碎,并离心得到上清液,然后分别用试剂PCI(苯酚∶氯仿∶异戊醇 = 25∶24∶1)、CI(氯仿∶异戊醇 = 24∶1)进行提取,离心得到的沉淀加入TE(pH值 8.0)溶液进行溶解,即DNA溶液。DNA溶液提纯后送至上海派森诺公司进行高通量测序。细菌群落DNA片段的双端(Paired-end)测序在Illumina MiSeq 300PE平台进行,对获得的序列使用DADA2方法进行去引物、质量过滤、去噪、拼接和去嵌合体等操作[30],获得的序列即为操作分类单元(Operational taxonomic units, OTUs)代表序列。使用QIIME 2软件中的“qiime feature-table rarefy”功能,抽平深度设为最低样本序列量的97%,获得抽平OTUs表。通过QIIME 2软件计算土壤细菌的Chao1和香农等多样性指数[31, 32]。
1.4 土壤理化性质的测定
新鲜土壤样品使用烘干法测量含水率(Moisture)。土样经自然风干、碾碎、去除细根等预处理后,分别过10目和100目筛备用。过10目筛的土样采用5%的H2O2去除有机质,然后使用激光粒度粒形仪(Mastersizer 3000, 英国)分析土壤黏粒含量(Clay)。过100目筛的土样用哈纳水质分析仪(HANNA HI98194, 意大利)测定pH值和电导率(Electrical conductivity, EC)。土样(过100目筛)经稀HCl酸化后,用元素分析仪测定有机碳含量(TOC)。使用元素分析仪测定土样(过100目筛)TC和TN含量。土样(过100目筛)经微波消解仪消解后采用等离子体原子发射光谱仪测定TP含量。
1.5 气候数据获取
采用WorldClim v2中的Average temperature(℃)、Precipitation(mm)和Bioclimatic variables(分辨率均为30″)栅格数据集,将其导入到ArcGIS 10.6软件中,使用Spatial Analyst Tools工具箱中的Extract Multi Values To Points工具,提取26个采样位点的月平均温度(Average temperature)、月降水量(Average precipitation),并计算年平均温度(MAT)和年降水量(MAP)等两个气候参数。
1.6 统计分析
实验数据使用R 3.6.2软件进行分析。用Shapiro-Wilk法检测数据的正态性和方差齐性,对不符合正态分布的数据进行对数转换或者平方根转换。采用Mantel分析植物功能性状与细菌多样性的关系,采用相关性分析探讨环境因子与植物多样性、细菌多样性的关系。利用多元回归分析寻找植物多样性和细菌多样性的关键影响因子,并通过变差分解得到各因子的解释率。使用基于距离的冗余分析(Distance-based redundancy analysis, db-RDA)对细菌群落的组成情况进行可视化分析,并通过与排序轴的多元回归置换检验得出影响细菌群落组成的关键环境因子和植物因子。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 植物与土壤细菌的多样性
本研究对26个样地的调查结果表明,植物丰富度为1 ~ 6,平均值为3.04;植物香农指数在0 ~ 1.80,平均为1.06(表1)。土壤细菌的Chao1指数在3654 ~ 6509,平均值为4859;土壤细菌的香农指数最小值为8.72,最大值为11.30。
表 1 植物与土壤细菌多样性Table 1. Plant and soil bacterial diversity指标
Index最小值
Minimum最大值
Maximum平均值
Mean植物丰富度 Plant Richness 1 6 3.04 植物香农指数 Plant Shannon 0 1.80 1.06 细菌Chao1指数 Bacteria Chao1 3654 6509 4859 细菌香农指数 Bacteria Shannon 8.72 11.30 10.41 2.2 环境因子与植物多样性的关系
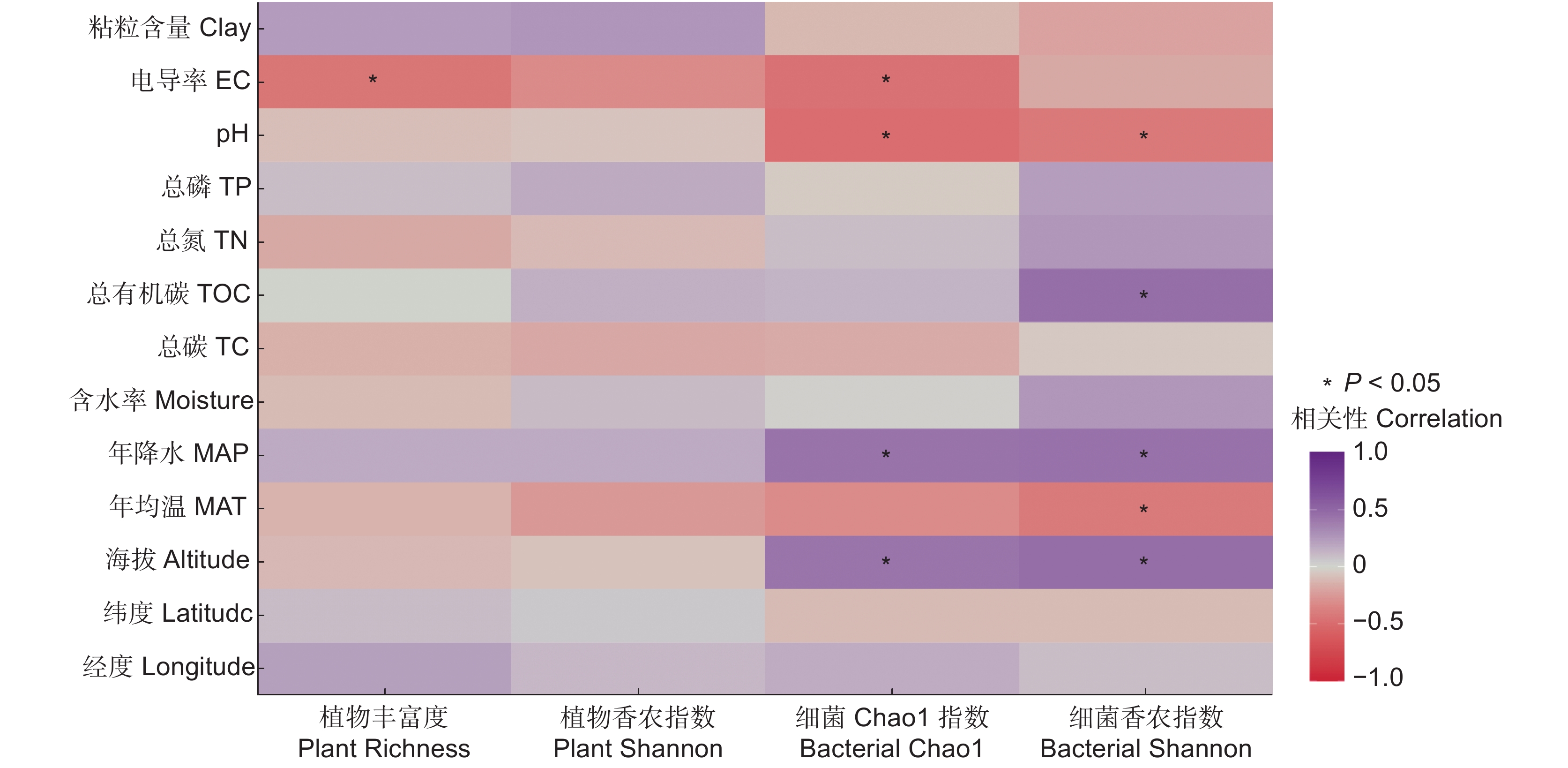
相关性分析结果表明(图2),植物丰富度仅与土壤电导率显著相关,而与其他环境因子没有明显的相关性;植物香农指数与所有环境因子的相关性均不显著。回归分析结果显示(表2),海拔、年平均温度和土壤电导率仅能解释植物丰富度26.71%的变异,但能解释植物香农指数31.92%的变异,其中,土壤电导率是解释植物丰富度和香农指数变异的首要因子,解释量分别为18.41%和16.79%。
表 2 土壤细菌多样性、植物多样性与环境因子的回归分析解释率Table 2. Multiple linear regression analysis of plant and soil bacterial diversity and environmental factors指标
Index细菌Chao1指数
Bacterial Chao1 / %细菌香农指数
Bacterial Shannon / %植物丰富度指数
Plant Richness / %植物香农指数
Plant Shannon / %纬度 Latitude 8.50 6.00 − − 海拔 Altitude 8.57 21.69 8.30 6.82 年降水 MAP 16.30 − − − pH 值 22.57 16.52 − − 年均温 MAT − − − 8.31 电导率 EC − − 18.41 16.79 总解释率 R2 56.25 44.21 26.71 31.92 2.3 环境因子、植物与土壤细菌多样性的关系
相关性分析结果表明(图2),土壤细菌Chao1指数与土壤电导率呈负相关,土壤细菌Chao1、香农指数均与海拔及年降水量呈正相关,而与土壤pH呈负相关。同时,土壤细菌香农指数还与年均温、土壤总有机碳含量显著相关。进一步进行回归分析,结果显示,纬度、海拔、年降水量和土壤pH值能够解释土壤细菌Chao1指数56.25%的变异;同时,纬度、海拔和土壤pH能够解释土壤细菌香农指数44.21%的变异(表2)。
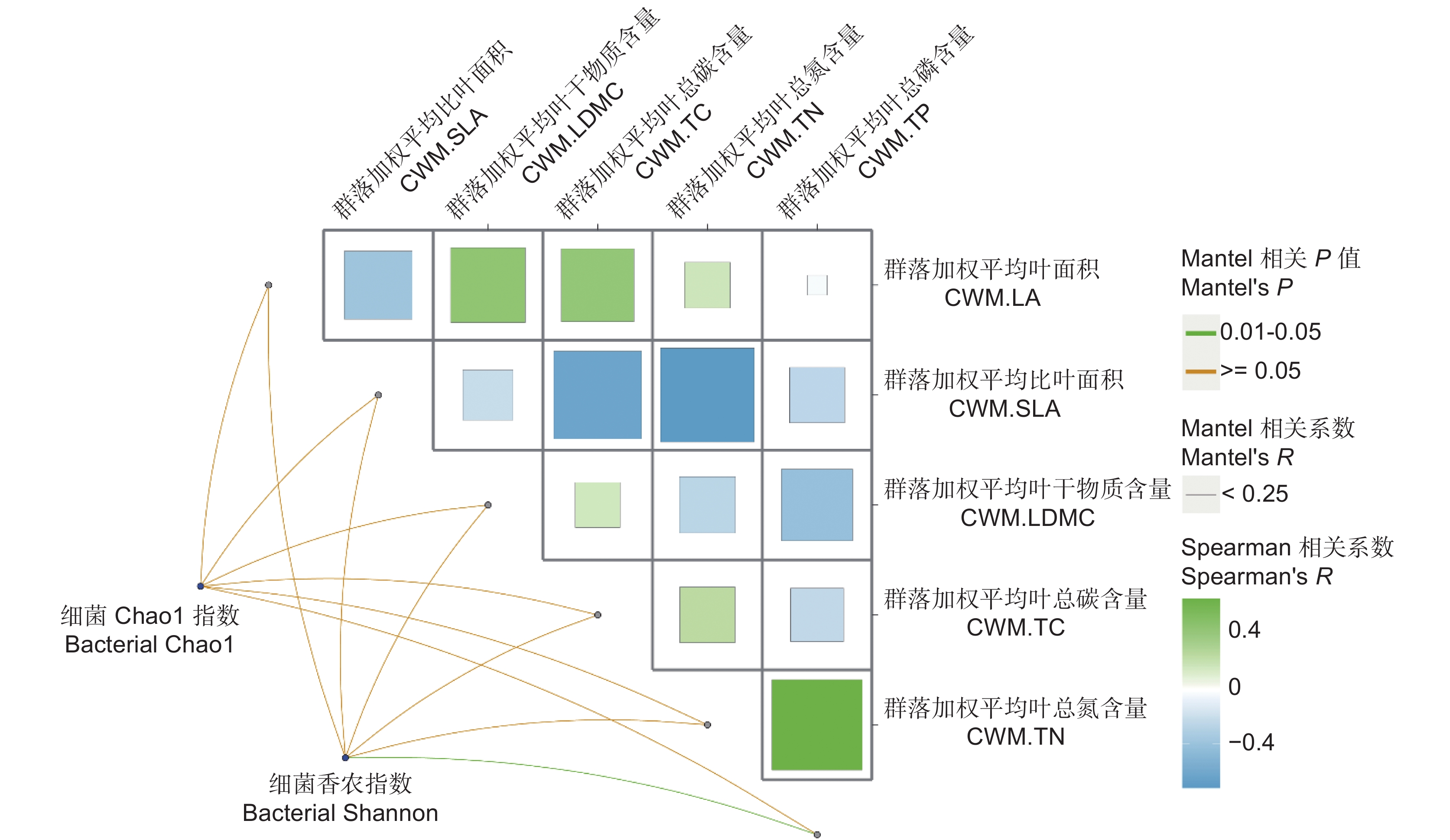
Mantel分析结果表明,土壤细菌Chao1多样性指数与群落水平的植物叶片总氮含量(CWM.TN)呈显著正相关关系(图3)。回归分析表明,植物叶片干物质含量(CWM.LDMC)与植物丰富度是解释土壤细菌Chao1指数变化的主要因子,分别贡献了18.21%和12.14%的解释度,且细菌Chao1指数随CWM.LDMC与植物丰富度的增加而增加。植物叶片总碳含量(CWM.TC)是影响土壤细菌香农指数变异的关键因子,贡献了14.01%的解释度(表3),且CWM.TC与土壤细菌香农指数呈正相关。
表 3 植物多样性、功能性状和土壤细菌多样性的回归分析解释率Table 3. Regression analysis of plant diversity, functional traits, and soil bacterial diversity指标
Index细菌Chao1指数
Bacterial Chao1 / %细菌香农指数
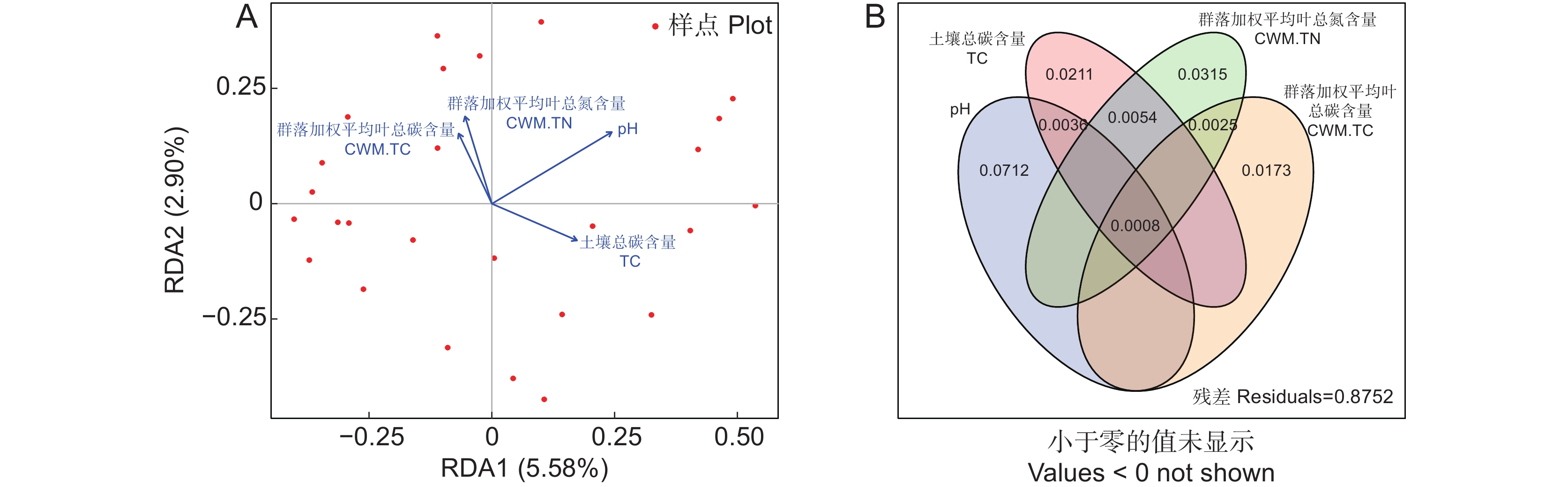
Bacterial Shannon / %群落加权平均叶干物质含量 CWM.LDMC 18.21 − 植物丰富度指数Richness 12.14 − 群落加权平均叶总碳含量CWM.TC − 14.01 总解释率 R2 30.35 14.01 冗余分析结果显示(图4:A),群落水平的植物功能性状(叶片总氮含量CWM.TN和总碳含量CWM.TC)和土壤理化性质(总碳和pH值)对细菌群落组成影响最大,共解释了12.48%的变异,其中前两轴分别解释了5.58%和2.90%。土壤总碳和pH值与第1轴呈正相关,而叶片总氮和总碳含量与第1轴呈负相关。韦恩图分析结果表明(图4:B),叶片总氮和总碳、土壤总碳和pH值分别解释了细菌群落3.15%、1.73%、2.11%和7.12%的差异,而它们的共同解释率很低,仅为0.08%。此外,与植物因子相比,环境因子对细菌群落组成的影响更大(图4:B)。
3. 讨论
植物多样性的变化受多种环境因素的影响,包括气候、海拔和土壤理化性质等。本研究结果表明,西藏高原湿地土壤电导率与植物丰富度呈显著负相关,且是植物多样性变异的首要驱动因子。土壤电导率直接反映土壤的盐度,过高的土壤电导率会改变植物根区的渗透压,影响植物的代谢路径,进而影响其生长速率[33]。崔乔等[34]对盐沼湿地的研究表明,植物群落组成的模式取决于土壤电导率。气候因子(年平均温度和年降水量)也是影响植物多样性的关键因素,一方面可直接制约植物的生长、分布和繁衍,另一方面决定了土壤的水热条件,从而间接影响植物的多样性[35, 36]。本研究结果表明,年平均温度是影响植物多样性的重要因子之一,而年降水量与植物多样性并没有显著的相关性,这可能是因为青藏高原高寒湿地的植物多样性更易受温度的影响[37]。Hong等[38]在河岸带湿地的研究也发现温度而非降水是影响植物物种多样性的关键因子。海拔的变化通常伴随着气候条件的改变(如温度随海拔上升而下降),进而影响植物的多样性。在西藏高原湿地中,我们发现海拔也是影响植物多样性的一个重要因子,随海拔的升高植物多样性显著降低。
细菌多样性的变化往往与环境因子密切相关。本研究发现,环境因子能够解释土壤细菌Chao1指数56.25%的变异和香农指数44.21%的变异,是影响西藏高原湿地土壤细菌多样性变化的关键因素。此外,土壤pH是湿地细菌多样性变化的关键驱动因子,细菌多样性随土壤pH值的增加而显著降低,这与Kang等[39]的研究结果一致。土壤pH会通过影响土壤基质组成、化学性质和养分利用效率来改变细菌群落的活性和多样性[40]。同时,海拔和纬度也是细菌多样性变化的关键驱动因子,细菌的Chao1指数和香农指数均随海拔的增加而显著增加。Wang等[41]对不同海拔梯度细菌群落的生物多样性模式进行了研究,结果发现细菌多样性与海拔呈显著正相关。虽然纬度也是影响细菌多样性变化的关键因子,但本研究发现二者之间不存在显著相关。这可能是因为纬度的变化主要是通过影响气候条件和土壤理化性质,进而改变细菌的多样性。细菌Chao1指数还与年均降水量呈显著正相关,与杨阳等[42]的研究结果一致。
西藏高原湿地植物的功能性状和物种丰富度也是驱动土壤细菌多样性变化的关键因子。很多研究发现土壤细菌多样性随植物多样性的增加而增加[43, 44],但也有研究指出两者并无显著相关性[45]。植物多样性很可能是通过增加凋落物和根系分泌物等的营养资源,从而促进了土壤细菌多样性的增加[46 - 48]。此外,植物多样性的变化也会引起土壤理化特征的改变(如电导率、有机碳含量等),进而影响土壤细菌多样性。Cao等[49]研究发现植物可以通过影响土壤有机碳、总氮等理化因子间接影响土壤细菌多样性。本研究结果表明,与环境因子相比,植物因子对土壤细菌多样性变化的贡献较小,这也说明西藏高原湿地土壤的细菌多样性主要由环境因子(气候、土壤理化性质)决定。
-
表 1 植物与土壤细菌多样性
Table 1 Plant and soil bacterial diversity
指标
Index最小值
Minimum最大值
Maximum平均值
Mean植物丰富度 Plant Richness 1 6 3.04 植物香农指数 Plant Shannon 0 1.80 1.06 细菌Chao1指数 Bacteria Chao1 3654 6509 4859 细菌香农指数 Bacteria Shannon 8.72 11.30 10.41 表 2 土壤细菌多样性、植物多样性与环境因子的回归分析解释率
Table 2 Multiple linear regression analysis of plant and soil bacterial diversity and environmental factors
指标
Index细菌Chao1指数
Bacterial Chao1 / %细菌香农指数
Bacterial Shannon / %植物丰富度指数
Plant Richness / %植物香农指数
Plant Shannon / %纬度 Latitude 8.50 6.00 − − 海拔 Altitude 8.57 21.69 8.30 6.82 年降水 MAP 16.30 − − − pH 值 22.57 16.52 − − 年均温 MAT − − − 8.31 电导率 EC − − 18.41 16.79 总解释率 R2 56.25 44.21 26.71 31.92 表 3 植物多样性、功能性状和土壤细菌多样性的回归分析解释率
Table 3 Regression analysis of plant diversity, functional traits, and soil bacterial diversity
指标
Index细菌Chao1指数
Bacterial Chao1 / %细菌香农指数
Bacterial Shannon / %群落加权平均叶干物质含量 CWM.LDMC 18.21 − 植物丰富度指数Richness 12.14 − 群落加权平均叶总碳含量CWM.TC − 14.01 总解释率 R2 30.35 14.01 -
[1] 刘务林, 朱雪林. 中国西藏高原湿地[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2013: 306−326. [2] Wan WJ,Gadd GM,Yang YY,Yuan WK,Gu JD,et al. Environmental adaptation is stronger for abundant rather than rare microorganisms in wetland soils from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Mol Ecol,2021,30 (10):2390−2403. doi: 10.1111/mec.15882
[3] Maltby E,Acreman MC. Ecosystem services of wetlands:pathfinder for a new paradigm[J]. Hydrol Sci J,2011,56 (8):1341−1359. doi: 10.1080/02626667.2011.631014
[4] Bledsoe RB,Goodwillie C,Peralta AL. Long-term nutrient enrichment of an oligotroph-dominated wetland increases bacterial diversity in bulk soils and plant rhizospheres[J]. mSphere,2020,5 (3):e00035−20.
[5] Sim-Sim M,Lopes T,Ruas S,Stech M. Does altitude shape molecular diversity and richness of bryophytes in Madeira’s natural forest? A case study with four bryophyte species at two altitudinal levels[J]. Plant Ecol Evol,2015,148 (2):171−180. doi: 10.5091/plecevo.2015.1041
[6] Cardelús CL,Colwell RK,Watkins Jr JE. Vascular epiphyte distribution patterns:explaining the mid-elevation richness peak[J]. J Ecol,2006,94 (1):144−156. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2745.2005.01052.x
[7] Rosenzweig ML. Species Diversity in Space and Time[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1995: 460.
[8] 唐志尧,方精云. 植物物种多样性的垂直分布格局[J]. 生物多样性,2004,12(1):20−28. Tang ZY,Fang JY. A review on the elevational patterns of plant species diversity[J]. Biodiversity Science,2004,12 (1):20−28. doi: 10.17520/biods.2004004 Tang ZY, Fang JY. A review on the elevational patterns of plant species diversity[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2004, 12(1): 20-28. doi: 10.17520/biods.2004004
[9] Shang RG,Li SF,Huang XB,Liu WD,Lang XD,Su JR. Effects of soil properties and plant diversity on soil microbial community composition and diversity during secondary succession[J]. Forests,2021,12 (6):805. doi: 10.3390/f12060805
[10] Ping YM,Pan X,Li W,Wang JZ,Cui LJ. The soil bacterial and fungal diversity were determined by the stoichiometric ratios of litter inputs:evidence from a constructed wetland[J]. Sci Rep,2019,9 (1):13813. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50161-9
[11] 周亚东,董洪进,严雪,刘星,王青锋. 西藏地区水生植物多样性及其空间格局初探[J]. 环境生态学,2020,2(11):7−12. Zhou YD,Dong HJ,Yan X,Liu X,Wang QF. Diversity and spatial pattern of aquatic plants in Tibet[J]. Environmental Ecology,2020,2 (11):7−12. Zhou YD, Dong HJ, Yan X, Liu X, Wang QF. Diversity and spatial pattern of aquatic plants in Tibet[J]. Environmental Ecology, 2020, 2(11): 7-12.
[12] 达文彦,李石胜,古桑群宗,温晓迪,何柄枚,等. 乃朗高寒沼泽湿地植物群落特征与环境因子的关系[J]. 西藏科技,2020(8):9−15. [13] 潘成梅,刘洋,安瑞志,黄香,巴桑. 西藏麦地卡湿地的浮游植物—1. 优势种的时空生态位[J]. 湖泊科学,2021,33(6):1805−1819. Pan CM,Liu Y,An RZ,Huang X,Ba S. Phytoplankton in the Mitika Wetland,Tibet,China:1. Spatio-temporal niche of dominant species[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2021,33 (6):1805−1819. doi: 10.18307/2021.0616 Pan CM, Liu Y, An RZ, Huang X, Ba S. Phytoplankton in the Mitika Wetland, Tibet, China: 1. Spatio-temporal niche of dominant species[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2021, 33(6): 1805-1819. doi: 10.18307/2021.0616
[14] 胡樱,贾慧萍,王志鸽,魏晶晶,王慧春. 青海湿地及其植物资源研究现状[J]. 青海草业,2020,29(1):27−30. HU Y,Jia HP,Wang ZG,Wei JJ,Wang HC. The Qinghai wetland and its research present situation of plant resources[J]. Qinghai Prataculture,2020,29 (1):27−30. HU Y, Jia HP, Wang ZG, Wei JJ, Wang HC. The Qinghai wetland and its research present situation of plant resources[J]. Qinghai Prataculture, 2020, 29(1): 27-30.
[15] 宋思梦,陈梁婧,张茂娟,王欣然,梁蔡佳,周旭. 甘孜州湿地自然保护区生态环境现状及保护措施探讨[J]. 现代园艺,2021,44(17):79−82. [16] 褚青帅,刘贵华,邢伟. 青藏高原湿地植物轻金属元素含量特征及其与环境因素的关系研究[J]. 植物科学学报,2021,39(2):121−131. Chu QS,Liu GH,Xing W. Concentrations of light metal elements in wetland plants and relationships with environmental factors in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Plant Science Journal,2021,39 (2):121−131. Chu QS, Liu GH, Xing W. Concentrations of light metal elements in wetland plants and relationships with environmental factors in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Plant Science Journal, 2021, 39(2): 121-131.
[17] 刘泰龙,姬亚丽,刘怡萱,吴玄峰,陈飞飞,刘星. 基于转录组测序探讨西藏麦地卡湿地5种植物对高海拔光照的适应机制[J]. 植物科学学报,2021,39(6):632−642. Liu TL,Ji YL,Liu YX,Wu XF,Chen FF,Liu X. Study on the adaptive mechanisms of five plants to high-altitude light based on transcriptome sequencing in Maidica wetland of Tibet[J]. Plant Science Journal,2021,39 (6):632−642. Liu TL, Ji YL, Liu YX, Wu XF, Chen FF, Liu X. Study on the adaptive mechanisms of five plants to high-altitude light based on transcriptome sequencing in Maidica wetland of Tibet[J]. Plant Science Journal, 2021, 39(6): 632-642.
[18] Jiang XL,Yao L,Guo LD,Liu GH,Liu WZ. Multi-scale factors affecting composition,diversity,and abundance of sediment denitrifying microorganisms in Yangtze lakes[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,2017,101 (21):8015−8027. doi: 10.1007/s00253-017-8537-5
[19] Sui X,Zhang RT,Frey B,Yang LB,Liu YN,et al. Soil physicochemical properties drive the variation in soil microbial communities along a forest successional series in a degraded wetland in northeastern China[J]. Ecol Evol,2021,11 (5):2194−2208. doi: 10.1002/ece3.7184
[20] Delgado-Baquerizo M,Reich PB,Khachane AN,Campbell CD,Thomas N,et al. It is elemental:soil nutrient stoichiometry drives bacterial diversity[J]. Environ Microbiol,2017,19 (3):1176−1188. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13642
[21] Zhou W,Jiang XL,Ouyang J,Lu B,Liu WZ,Liu GH. Environmental factors,more than spatial distance,explain community structure of soil ammonia-oxidizers in wetlands on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Microorganisms,2020,8 (6):933. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8060933
[22] Jiang XL,Liu WZ,Yao LG,Liu GH,Yang YY. The roles of environmental variation and spatial distance in explaining diversity and biogeography of soil denitrifying communities in remote Tibetan wetlands[J]. FEMS Microbiol Ecol,2020,96 (5):fiaa063. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiaa063
[23] Wardle DA,Bardgett RD,Klironomos JN,Setälä H,van der Putten WH,Wall DH. Ecological linkages between aboveground and belowground biota[J]. Science,2004,304 (5677):1629−1633. doi: 10.1126/science.1094875
[24] Yashiro E,Pinto-Figueroa E,Buri A,Spangenberg JE,Adatte T,et al. Local environmental factors drive divergent grassland soil bacterial communities in the western Swiss Alps[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol,2016,82 (21):6303−6316. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01170-16
[25] Ni YY,Yang T,Ma YY,Zhang KP,Soltis PS,et al. Soil pH determines bacterial distribution and assembly processes in natural mountain forests of eastern China[J]. Glob Ecol Biogeogr,2021,30 (11):2164−2177. doi: 10.1111/geb.13373
[26] Guo JX,Zhou YX,Guo HJ,Min W. Saline and alkaline stresses alter soil properties and composition and structure of gene-based nitrifier and denitrifier communities in a calcareous desert soil[J]. BMC Microbiol,2021,21 (1):246. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02313-z
[27] 李明家,吴凯媛,孟凡凡,沈吉,刘勇勤,等. 西藏横断山区溪流细菌beta多样性组分对气候和水体环境的响应[J]. 生物多样性,2020,28(12):1570−1580. Li MJ,Wu KY,Meng FF,Shen J,Liu YQ,et al. Beta diversity of stream bacteria in Hengduan Mountains:the effects of climatic and environmental variables[J]. Biodiversity Science,2020,28 (12):1570−1580. doi: 10.17520/biods.2019390 Li MJ, Wu KY, Meng FF, Shen J, Liu YQ, et al. Beta diversity of stream bacteria in Hengduan Mountains: The effects of climatic and environmental variables[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2020, 28(12): 1570-1580. doi: 10.17520/biods.2019390
[28] 甄莉,吴耿,杨渐,蒋宏忱. 西藏热泉沉积物的硫氧化细菌多样性及其影响因素[J]. 微生物学报,2019,59(6):1089−1104. Zhen L,Wu G,Yang J,Jiang HC. Distribution and diversity of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria in the surface sediments of Tibetan hot springs[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica,2019,59 (6):1089−1104. Zhen L, Wu G, Yang J, Jiang HC. Distribution and diversity of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria in the surface sediments of Tibetan hot springs[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2019, 59(6): 1089-1104.
[29] Delgado-Baquerizo M,Fry EL,Eldridge DJ,de Vries FT,Manning P,et al. Plant attributes explain the distribution of soil microbial communities in two contrasting regions of the globe[J]. New Phytol,2018,219 (2):574−587. doi: 10.1111/nph.15161
[30] Callahan BJ,McMurdie PJ,Rosen MJ,Han AW,Johnson AJA,Holmes SP. DADA2:High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data[J]. Nat Methods,2016,13 (7):581−583. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3869
[31] Chao A. Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population[J]. Scand J Statist,1984,11 (4):265−270.
[32] Shannon CE. A mathematical theory of communication[J]. Bell Syst Tech J,1948,27 (3):379−423.
[33] Rahman MM,Mostofa MG,Keya SS,Siddiqui MN,Ansary MMU,et al. Adaptive mechanisms of halophytes and their potential in improving salinity tolerance in plants[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2021,22 (19):10733. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910733
[34] 崔乔,何彤慧,全晓塞,陈向全,何玉实. 鄂尔多斯盐沼湿地土壤盐分特征对植物群落的影响[J]. 盐湖研究,2022,30(1):25−32. Cui Q,He TH,Quan XS,Chen XQ,He YS. Effects of soil salinity characteristics on plant community in ordos salt marsh wetland[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research,2022,30 (1):25−32. Cui Q, He TH, Quan XS, Chen XQ, He YS. Effects of soil salinity characteristics on plant community in ordos salt marsh wetland[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2022, 30(1): 25-32.
[35] Harrison S,Spasojevic MJ,Li DJ. Climate and plant community diversity in space and time[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2020,117 (9):4464−4470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1921724117
[36] 何远政,黄文达,赵昕,吕朋,王怀海. 气候变化对植物多样性的影响研究综述[J]. 中国沙漠,2021,41(1):59−66. He YZ,Huang WD,Zhao X,Lü P,Wang HH. Review on the impact of climate change on plant diversity[J]. Journal of Desert Research,2021,41 (1):59−66. He YZ, Huang WD, Zhao X, Lv P, Wang HH. Review on the impact of climate change on plant diversity[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 59-66.
[37] Nottingham AT,Fierer N,Turner BL,Whitaker J,Ostle NJ,et al. Microbes follow Humboldt:temperature drives plant and soil microbial diversity patterns from the Amazon to the Andes[J]. Ecology,2018,99 (11):2455−2466. doi: 10.1002/ecy.2482
[38] Hong ZD,Ding SY,Zhao QH,Qiu PW,Chang JL,et al. Plant trait-environment trends and their conservation implications for riparian wetlands in the Yellow River[J]. Sci Total Environ,2021,767:144867. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144867
[39] Kang EZ,Li Y,Zhang XD,Yan ZQ,Wu HD,et al. Soil pH and nutrients shape the vertical distribution of microbial communities in an alpine wetland[J]. Sci Total Environ,2021,774:145780. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145780
[40] Neina D. The role of soil pH in plant nutrition and soil remediation[J]. Appl Environ Soil Sci,2019,2019:5794869.
[41] Wang JJ,Soininen J,He JZ,Shen J. Phylogenetic clustering increases with elevation for microbes[J]. Environ Microbiol Rep,2012,4 (2):217−226. doi: 10.1111/j.1758-2229.2011.00324.x
[42] 杨阳,章妮,蒋莉莉,陈克龙. 青海湖高寒草地土壤理化性质及微生物群落特征对模拟降水的响应[J]. 草地学报,2021,29(5):1043−1052. Yang Y,Zhang N,Jiang LL,Chen KL. Effects of simulated precipitation on soil edaphic physicochemical factors and microbial community characteristics in bird island of Qinghai Lake on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica,2021,29 (5):1043−1052. Yang Y, Zhang N, Jiang LL, Chen KL. Effects of simulated precipitation on soil edaphic physicochemical factors and microbial community characteristics in bird island of Qinghai Lake on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(5): 1043-1052.
[43] Fu WG,Wang YX,Wei W,Li PP. Species diversity and functional prediction of soil bacterial communities in constructed wetlands with different plant conditions[J]. Curr Microbiol,2019,76 (3):338−345. doi: 10.1007/s00284-019-01634-7
[44] Bahram M,Netherway T,Hildebrand F,Pritsch K,Drenkhan R,et al. Plant nutrient-acquisition strategies drive topsoil microbiome structure and function[J]. New Phytol,2020,227 (4):1189−1199. doi: 10.1111/nph.16598
[45] Delgado-Baquerizo M,Bardgett RD,Vitousek PM,Maestre FT,Williams MA,et al. Changes in belowground biodiversity during ecosystem development[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2019,116 (14):6891−6896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1818400116
[46] Lange M,Eisenhauer N,Sierra CA,Bessler H,Engels C,et al. Plant diversity increases soil microbial activity and soil carbon storage[J]. Nat Commun,2015,6:6707. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7707
[47] Yuan X,Knelman JE,Gasarch E,Wang DL,Nemergut DR,Seastedt TR. Plant community and soil chemistry responses to long-term nitrogen inputs drive changes in alpine bacterial communities[J]. Ecology,2016,97 (6):1543−1554. doi: 10.1890/15-1160.1
[48] Chen SP,Wang WT,Xu WT,Wang Y,Wan HW,et al. Plant diversity enhances productivity and soil carbon storage[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2018,115 (16):4027−4032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1700298114
[49] Cao QQ,Zhang HJ,Ma W,Wang RQ,Liu J. Composition characteristics of organic Matter and bacterial communities under the Alternanthera philoxeroide invasion in wetlands[J]. Appl Sci,2020,10 (16):5571. doi: 10.3390/app10165571
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 张曼华,谢元贵,田秀,张蓝月,廖小锋,王军才. 土壤微生物对4种森林类型植物多样性形成的影响. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2025(01): 26-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)



 下载:
下载: