Study on population structure and seedling regeneration of Hopea hainanensis Merr. & Chun under ex situ conservation in Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden
-
摘要:
本研究在中国科学院西双版纳植物园设置的500 m2样地中对迁地栽培植物坡垒(Hopea hainanensis Merr. & Chun)种群进行调查,采用径级结构代替龄级结构分析坡垒种群的结构特征,同时编制了静态生命表,分析种群的存活率、死亡率及消失率。结果显示,迁地栽培的坡垒种群更新的苗木尚无大径级的个体;但栽培的坡垒大部分个体能开花结果及自然更新,且幼苗数量较多,幼苗密度为19550 株/hm2,, 占种群个体数的86.00%。 静态生命表分析结果表明,坡垒种群Ⅱ龄级的个体死亡率最低,Ⅲ龄级的个体死亡率最高,种群存活曲线趋向于Deevey-Ⅲ型;死亡率和消失率变化趋势一致。研究结果表明,坡垒迁地保护取得了初步成功。此外,迁地栽培中应加强对幼苗、幼树的管理,有助于提高其成活率,更多的进入下一龄级的生长和种群的扩大。
Abstract:An investigation of a Hopea hainanensis population was conducted in a 500 m2 plot in the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG), Chinese Academy of Sciences. The diameter-level structure was used instead of the age-level structure to analyze the structural characteristics of the population. At the same time, a static life table was compiled to analyze the survival rate, mortality rate, and disappearance rate of the population. Results showed that the ex situ cultivated H. hainanensis population had no individuals with large diameter, although most of adult individuals are capable of blossoming, fruiting, and naturally regenerating. The seedling density of H. hainanensis was 19 550 plants per hm2, accounting for 86.00% of total individuals. Based on the static life table, the lowest mortality rate was observed in age class Ⅱ, while the highest was observed in age class Ⅲ. The population survival curve was categorized as the Deevey-Ⅲ type. Changes in mortality and loss rate curves showed the same trend. Results indicated that ex situ conservation of H. hainanensis in XTBG has achieved initial success, as evidenced by its population increase and germination stability. Enhanced management of seedlings and saplings could further improve survival rates and promote seedling to sapling, treelet, and tree progression, thereby expanding its population.
-
种群结构是植物种群生态学研究的重要内容,年龄结构分析、静态生命表、存活曲线和生存分析等是进行种群结构和动态分析的重要手段和方法[1-3]。种群龄级结构既是种群数量随时间变化的客观反映,也是种群结构的指标之一,它的研究有助于了解种群的现存状态、受干扰情况及预测种群发展的趋势[4, 5]。对于种群年龄结构的研究,基本上采用立木径级替代,成为龄级最直观的体现[6]。静态生命表和存活曲线是种群数量的动态展现,不仅为种群数量统计提供丰富的指标信息[7, 8],也有助于了解种群数量变化的潜在机制,阐明种群生存的客观规律[9],还可反映各年龄阶段的存活状态[10]。幼苗是森林恢复演替过程中最基本的物质基础[11],也是种群更新的来源。天然更新的成功与否与幼苗的生长和存活密切相关[12, 13]。而幼苗是个体生长最为脆弱、对环境最为敏感时期,幼苗的更新格局能够决定未来物种的组成和结构[14]。因此,在植物种群动态变化中,幼苗常被作为重要的研究对象。研究植物的种群结构与更新,认识种群的生存现状及发展动态,揭示种群的生态特征、生存潜力和濒危机制,对于珍稀濒危植物的保护、种群重建与恢复具有重要意义[15, 16]。
坡垒(Hopea hainanensis Merr. & Chun)是龙脑香科的高大乔木,我国仅在海南省有天然分布,是中国热带雨林的标志性物种之一,其木材材质优良,位于海南硬木之首,也是我国特类木材。坡垒的木材结构紧致细密,质地坚硬,干燥后不易变形,且耐腐蚀和暴晒,是造船的良好木材[17]。正因如此,坡垒被严重采伐,导致其种群数量急剧下降。在野生状态下,种群数量更新缓慢,已从热带雨林的代表种变为偶见种[18]。从20世纪60年代以来,有关单位和学者就已开展坡垒的保护工作。但经过60余年的发展,该种群在野外的生境并没有得到有效改善,种群数量稀少,被列为中国一级保护植物,被《中国植物红皮书》列为濒危种,IUCN评估为濒危(EN)等级,2012年3月国家林草局印发的《全国极小种群野生植物拯救工程规划(2011-2015)》的120种物种中,坡垒名列其中[19]。就地保护是坡垒保护的重要方式,并就坡垒的种群地理分布格局、生境特征对幼苗多度的影响、野生种子的传播及幼苗生长、群落学、致濒原因[20-24]等进行了相关研究。迁地保护作为就地保护的一种补充方式,在珍稀濒危植物的保护中发挥了重要作用。中国科学院西双版纳热带植物园(以下简称“版纳植物园”)、云南省林科院普文试验林场、海南省林业科学研究院等单位开展了坡垒迁地保护研究工作,在种子繁育、适应性、栽培等方面开展了大量的研究工作[25-28]。然而,对于迁地栽培条件下坡垒的自然更新及种群结构仅见于海南省枫木林场迁地栽培的坡垒种群的发育研究报道[29]。
在《生物多样性公约》缔约方大会第15次会议(COP15)之后,迁地保护已被提升到国家战略层面,做好迁地保护是顺应时代潮流,也是践行生态文明建设及做好生物多样保护的重要举措。版纳植物园自1964年开始引种坡垒,开展了一系列的迁地保护研究工作,并于1990年在园内建立了包括坡垒在内的龙脑香科植物迁地保护区。如今,这些坡垒已长成大树,并能完成“种子到种子”的过程。本文通过对版纳植物园迁地栽培的坡垒人工种群结构及幼苗更新调查,采用种群年龄结构、静态生命表、存活曲线等方法,揭示迁地栽培坡垒种群的生存现状及动态趋势,探讨在迁地保护地坡垒的自然更新特征,为迁地保护坡垒林的营造及管护提供科学依据,进而为坡垒的保护提供科学策略。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 研究地概况
研究地点位于版纳植物园内,该园地处勐腊县勐仑镇(21°56'N,101°16'E),海拔534 m,该地区属西南热带季风气候,干湿季节明显,年平均气温 21.8 ℃,终年无霜。根据降水量可分为旱季和雨季,旱季又可分为雾凉季(11 月-翌年 2 月)和干热季(3-4 月)。干热季气候干燥,降水量少,日温差较大;雾凉季降水量虽少,但从夜间到次日中午都会存在大量的浓雾,对旱季植物的水分需求有一定补偿作用。雨季时,气候湿热,水分充足,降水量 1 256 mm,占全年降水量的84%,年均相对湿度为 85%[30]。调查样地位于植物园东区的专家公寓旁的龙脑香科迁地保护区。坡垒于1990年种植,种植规格为2.5 m × 3 m,至调查时林龄为31 a。坡向SE,坡度15°。林分土壤为砖红壤,pH值为5.0左右,坡垒种植后除前3年对其进行除草等抚育管理外,此后只是去除长在坡垒植株个体上的藤蔓植物。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 野外调查
为确切地掌握人工坡垒林的物种组成及坡垒种群的个体数量,根据种群的大小,设置25 m × 20 m的样地,采用相邻格子样方法,将样地分成20个5 m × 5 m的样方。对样地内高度大于 50 cm 的个体进行每木调查,高度小于 2.0 m的幼树测量记录其基径、高度和株数;高度大于 2.0 m 的植株调查记录其基径、胸径、树高等因子。由于坡垒的幼苗密度很大,在样地的四角及中心设置5个2 m × 2 m 的小样方,调查高度小于 50 cm 的幼苗、幼株,记录其基径、高度和株数。
1.2.2 种群立木级结构的划分
年龄结构是种群的重要特征,在相同环境下同一树种的龄级和径级对环境反应具有一致性的特点[31]。根据坡垒的生存环境以及生活史特点,参照前人的研究[32],将坡垒的立木级划分为6个等级,即 Ⅰ 级:幼苗高度(H)<0.5 m;Ⅱ 级:小苗0.5 ≤ H ≤ 1.5 m;Ⅲ 级:幼树H > 1.5 m,DBH < 2.5 cm;Ⅳ 级:小树2.5 cm ≤ DBH <7.5 cm;Ⅴ 级:中树7.5 cm ≤ DBH <15.0 cm;Ⅵ 级:大树DBH ≥ 15.0 cm。在静态生命表中将坡垒的径级代替龄级,6个径级代表6个龄级。
1.2.3 静态生命表
静态生命表可反应种群动态变化,是依据种群在特定时间阶段的年龄结构而建立。根据调查所得的数据以及上述划分的种群立木级划分标准所得到的径级结构来编制坡垒种群的静态生命表,并进行存活率、死亡率和消失率的分析。有关参数的计算如下:
dx=lx−lx+1;ex=Tx/lx;Kx=lnlx−lnlx+1;lx=ax/a0×1000;qx=dx/lx;Lx=(lx+lx+1)/2;Tx=∞∑xlx。 式中,x为龄级;ax,龄级内现有植株存活数;dx,标准化死亡数;ex为生命期望值;Kx为消失率;lx为标准化存活数;qx为死亡率;Lx为存活的个体数或区间寿命;Tx为从x龄级到超过x龄级的个体总数或总寿命。由于本研究中的坡垒人工种群的林龄为31 a,林龄较小。坡垒的种群更新尚未到达径级 Ⅴ,而径级Ⅵ 是最初定植的树种,而非种子自然更新形成。因此,以径级 Ⅰ 到径级 Ⅳ 的个体数编制坡垒种群的静态生命表。
1.2.4 幼苗密度的估算
根据小样方调查的坡垒幼苗及幼树的个体数,求取样方中幼苗个体数的平均值估算幼苗的密度。
1.2.5 人工坡垒林的生长状况
根据调查所得数据,以株高、胸径作为分析人工栽培坡垒生长情况的指标。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 人工坡垒林的树种组成及结构特征
根据样地的植物调查资料,坡垒林的乔木层可分为2层,乔木Ⅰ层主要是坡垒占优势,在该层中混生的其他主要树种有云南黄杞(Engelhardia spicata Lesch.)、泰国黄叶树(Xanthophyllum flavescens Roxburgh),但仅有2株,高度16 ~ 23 m。乔木Ⅱ层除坡垒外,其他树种有潺槁木姜子(Litsea glutinosa (Lour.) C. B. Rob.)、箭毒木(Antiaris toxicaria Lesch.)、海红豆(Adenanthera microsperma Teijs mann & Binnendijk)、柯(Lithocarpus glaber (Thunb.) Nakai)、思茅崖豆(Imbralyx leptobotrya (Dunn) Z. Q. Song)、高檐蒲桃(Syzygium jambos (L.) Alston)、破布木(Cordia dichotoma Forst.)、猴耳环(Archidendron clypearia (Jack) I. C. Nielsen)、菠萝蜜(Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam.)等乔木,高度约3 ~ 5 m,个体数量较少,仅有10 株个体。灌木层高度2 m左右,除坡垒幼树外,其他植物有假鹰爪(Desmos chinensis Lour.)、水麻(Debregeasia orientalis C. J. Chen)、香港大沙叶(Pavetta hongkongensis Bremek.)、萍婆(Sterculia monosperma Ventenat)、椴叶山麻杆(Alchornea tiliifolia (Benth.) Muell. Arg.)、火焰花(Phlogacanthus curviflorus (Wall.) Nees)、弯管花(Chassalia curviflora Thwaites)等,零星分布在坡垒幼树中;草本植物有老挝山姜(Alpinia laosensis Gagnep.)、海芋(Alocasia longiloba Miq.)、叶下珠(Phyllanthus urinaria L.)、小花锥花(Gomphostemma parviflorum Wall.)、广东万年青(Aglaonema modestum Schott ex Engl.)、版纳茶竿竹(Pseudosasa xishuangbannaensis D. Z. Li, Y. X. Zhang & Triplett)、红豆蔻(Alpinia galanga (L.) Willd.)等,多度较小,仅零星生长,高度约0.5 m;藤本植物有山葛(Pueraria montana (Loureiro) Merrill)、白粉藤(Cissus repens Lamk. Encycl.)、乌蔹梅(Causonis japonica (Thunb.) Raf.)、黄花胡椒(Piper flaviflorum C. DC.)、斑果藤(Stixis suaveolens (Roxb.) Pierre)、鸡心藤(Cissus kerrii Craib)、买麻藤(Gnetum montanum Markgr.)、毛车藤(Amalocalyx microlobus Pierre)、苍白秤钩风(Diploclisia glaucescens (Bl.) Diels)、蓝叶藤(Marsdenia tinctoria R. Br.)、柳条省藤(Calamus viminalis Willd.)等。由此可见,人工坡垒林的群落物种组成较为丰富。
2.2 种群的个体数量及径级结构
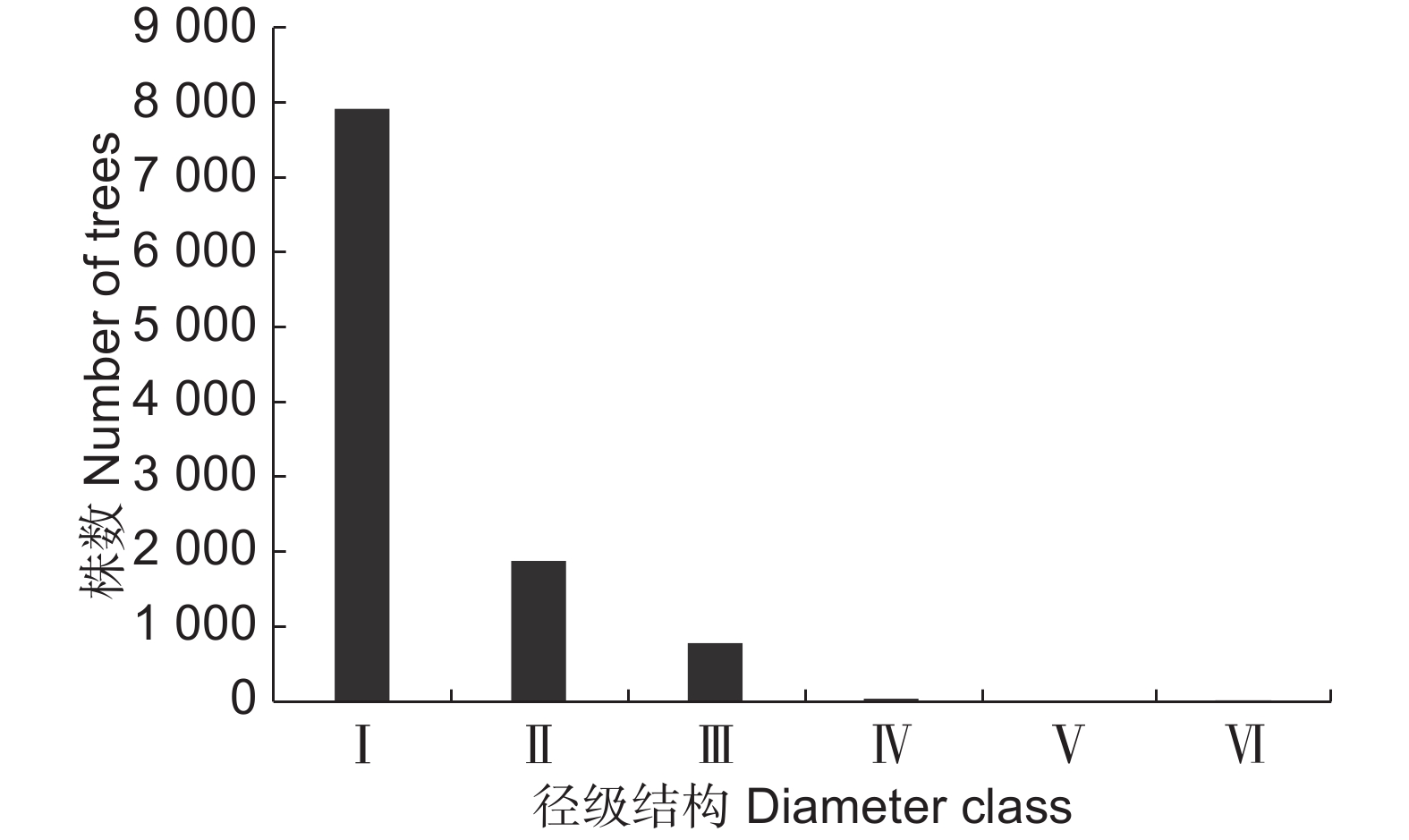
根据样地的调查结果,在500 m2 样地中坡垒总个体数为10 705 株,其径级结构如图1所示。其中径级 Ⅰ 的幼苗个体数量最多,共有7 925 株,占了总数的74.03%,其次为径级 Ⅱ 小苗的个体数,共有1 900 株,占总数的17.75%;再次为径级 Ⅲ 幼树阶段的个体数,总数为800 株,占总数的7.47%;径级 Ⅳ 小树占总数的0.47%。上述结果表明人工栽培的坡垒种群的幼苗更新良好,具备较强的发展和生存潜力。而径级Ⅴ的个体没有,这是因为该人工林林龄只有31 a,属于中龄林,更新的幼苗尚未到达小树阶段。而Ⅵ为1990年定植的母树。
2.3 坡垒种群的静态生命表
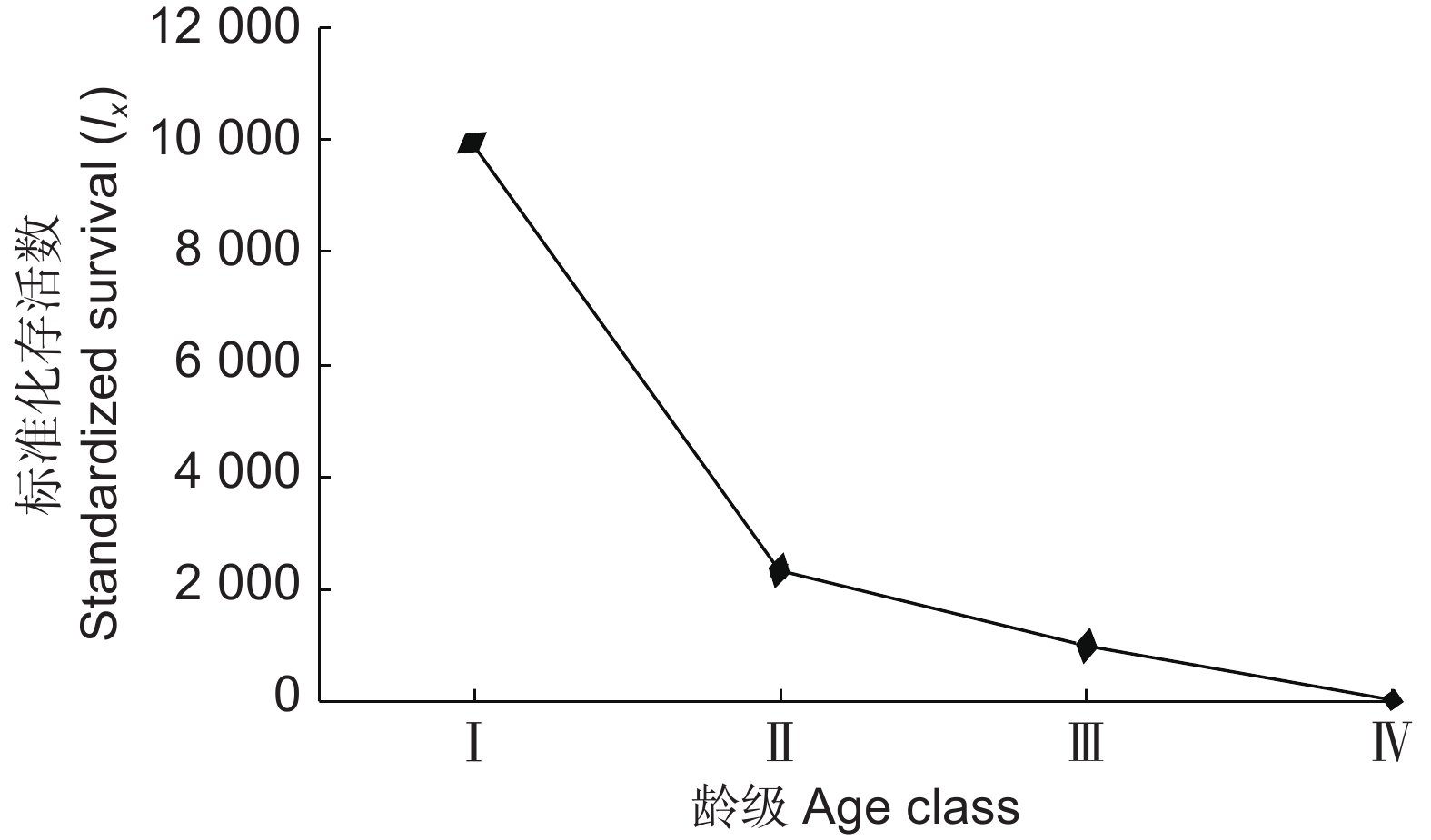
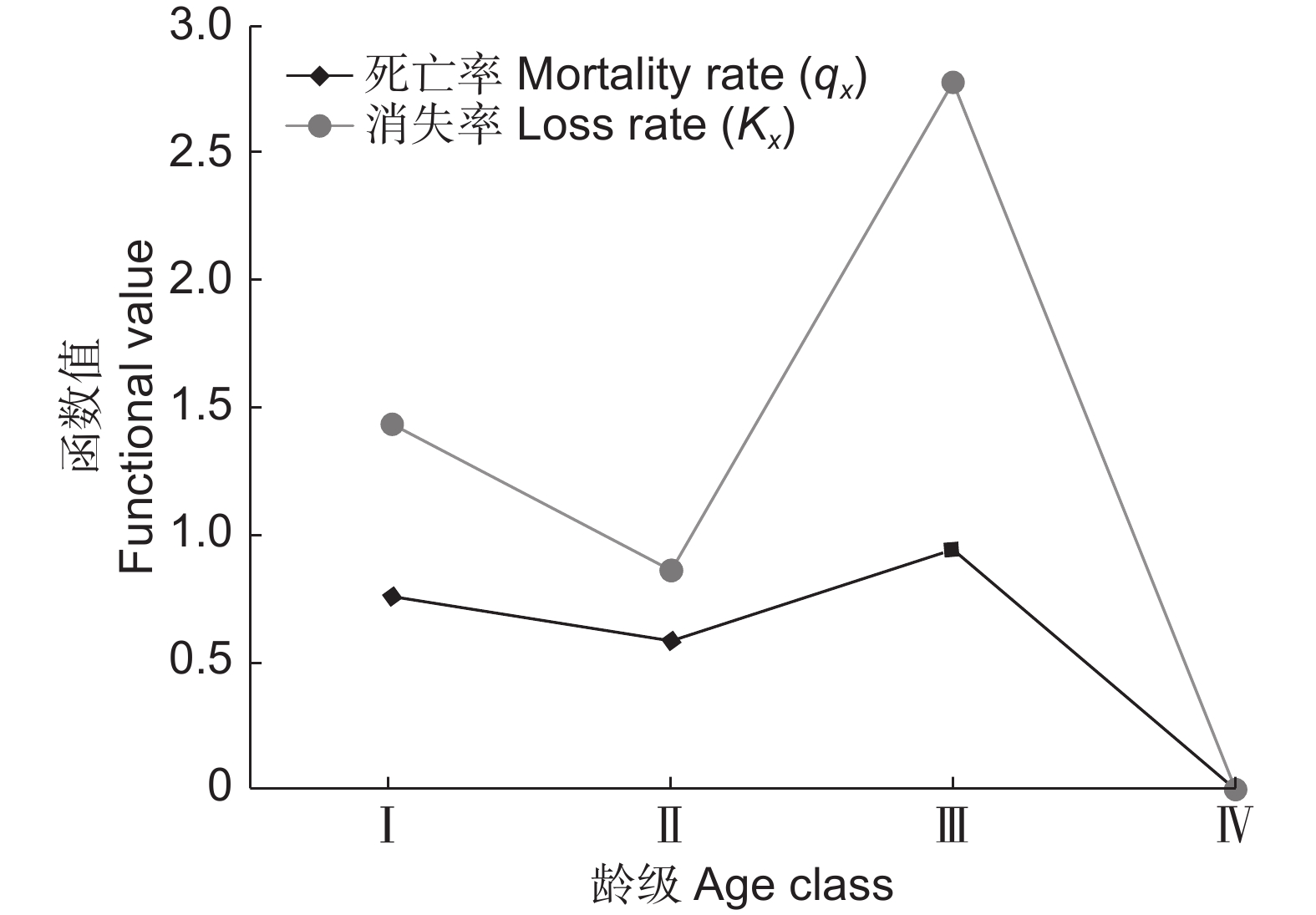
静态生命表反映种群在某一特定时刻的数量特征,并反映种群的生存状态[32]。本研究以径级代替龄级绘制坡垒人工种群的静态生命表(表1)。从坡垒种群静态生命表的各龄级个体数量来看,坡垒的幼苗(Ⅰ 龄级)、小苗(Ⅱ 龄级)的数量占据了群落中个体总数的91.78%,而进入 Ⅲ 龄级的幼苗仅占个体总数的7.47%,且坡垒在 Ⅲ 龄级时的死亡率和消失率最高,分别为0.94和2.78;其次是 Ⅰ 龄级的0.76和1.43;Ⅱ 龄级个体的死亡率及消失率最低,分别为0.58和0.86。这说明人工坡垒种群的幼苗在 Ⅲ 龄级时受到的阻力或竞争力最大,成为幼苗和小苗能否进一步发展为幼树或小树的重要阶段。这一结果表明,坡垒在Ⅰ、Ⅱ 龄级时,生长旺盛,数量庞大,使种群具有一定的更新潜力。
表 1 迁地栽培坡垒种群的静态生命表Table 1. Static life table of ex situ cultivated Hopea hainanensis populationx ax lx lnlx dx qx Lx Tx ex Kx Ⅰ 7925 10 000 9.21 7606 0.76 6197 12394 1.24 1.43 Ⅱ 1900 2 394 7.78 1386 0.58 1701 3402 1.42 0.86 Ⅲ 800 1 008 6.92 945 0.94 536 1071 1.06 2.78 Ⅳ 50 63 4.14 − − 32 63 1.00 − 注:x均为龄级;ax为龄级内现有植株存活数;dx为标准化死亡数;ex为生命期望值;Kx为消失率; lx为标准化存活数;qx为死亡率;Lx为存活的个体数或区间寿命;Tx为从x龄级到超过x龄级的个体总数或总寿命。 Notes: x, age class; ax, surviving numbers observed within each age class; dx, standardized death number; ex, life expectancy; Kx, loss rate; lx, standardized survival number; qx, individual morality rate; Lx, average number of surviving individuals or mortality rate; Tx, total number of surviving individuals in age class x and above. 2.4 坡垒种群的存活曲线
存活曲线可直观的反映种群数量的动态变化,根据静态生命表数据(表1),以立木级为横坐标,标准化存活量(lx)为纵坐标,绘制出坡垒种群的存活曲线(图2)。由图2可知,坡垒种群的存活曲线趋向于Deevey-Ⅲ型,种群早期死亡率较高,曲线斜率较大,一旦生活到某一年龄阶段,死亡率就降低。
2.5 坡垒种群的死亡率和消亡率曲线
以坡垒立木级为横坐标,各龄级的死亡率(qx)和消失率(Kx)为纵坐标,绘制坡垒种群的死亡率和消失率曲线(图3)。由图3可知,死亡率和消失率呈现出一致的变化趋势,均在 Ⅲ 龄级达到顶峰,呈单峰型。结合表1静态生命表可知,坡垒 Ⅰ 龄级幼苗Ⅱ龄级小苗阶段个体储备量较大,Ⅱ 龄级小苗阶段的死亡率和消失率最低,表明坡垒种群在低龄幼苗阶段生活力较强,为维持种群的更新和稳定奠定了基础。Ⅲ 龄级时死亡率达到了高峰,高达94%。消亡率和死亡率的趋势一致,达到2.78和0.94。说明此阶段是坡垒幼苗生长中遇到的生存阻力较大,只有少部分能够存活。
2.6 幼苗、幼树更新
在5个样方内调查到的坡垒幼苗分别为:1 号样方120 株;2 号样方76 株;3号样方60株;4 号样方110 株;5 号样方26 株;其平均密度为19.6 株/米2,即196000 株/公顷2。根据幼苗天然更新的评判标准(表2)[33],表明种群幼苗更新良好。
表 2 天然更新等级评判Table 2. Grade of natural regeneration等级Class 不同胸径株数 Individual number of DBH H ≤ 30 cm 30 < H ≤ 50 cm H > 50 cm 不分高度
Irrespective of height良好 > 5 000 > 3 000 > 2 500 > 4 000 中等 3 000 < N ≤ 5000 1 000 < N ≤ 3 000 500 < N ≤ 2 500 2 000 < N ≤ 4 000 不良 ≤ 3 000 ≤ 1 000 ≤ 500 ≤ 2000 注:DBH为胸径英文首个字母;N代表株数。 Notes: DBH, diameter at breast height; N, number. 2.7 坡垒的生长状况
坡垒是中国海南热带雨林的群落优势树种,高可达60 m。本研究中的坡垒是版纳植物园引种自华南植物园栽培的坡垒收获的种子,经繁育后获得的实生苗,并于1990 年种植于园内的迁地保护区。目前,坡垒共有30 株,其生长势指标如表3所示。
表 3 迁地栽培坡垒的生长状况Table 3. Growth of DBH and height of ex situ cultivated Hopea hainanensis population类别
Type胸径DBH / cm 树高Height / cm 最大
Max最小
Min平均值
Average年均生长量
Annual average growth最高
Max最低
Min平均值
Average年均生长量
Annual average growth指标值 44.40 15.30 26.54 0.85 27.00 13.00 24.13 0.78 由表3可知,在这些坡垒中最小的胸径为15.30 cm,胸径最大的达44.40 cm,约是最小胸径的3倍,总体的平均胸径为26.54 cm,年均生长0.85 cm。在株高的指标中也存在类似的情况,高度最高的树(27 m)是最低树的2倍多,年均生长0.78 m;这说明,虽然栽培的坡垒种群各植株个体长势差异较大,无论其年均胸径生长和高度生长都长势良好,目前栽培的坡垒大部分个体已能开花、结果,且在自然状态下种子萌发良好,说明版纳植物园坡垒的迁地栽培是成功的。
3. 讨论
版纳植物园迁地栽培的坡垒种群的林分组成多样性较高,但坡垒依然是种群中的重要组成树种,这得益于在迁地栽培的早期,为了坡垒能够在新的环境中生存,在其生长的前3年,辅以必要的人工管护措施,如清除杂草、水肥管理及适当的遮荫管理等措施,为迁地栽培的坡垒创造良好的生境。待栽培树苗长大后,降低人工管护强度,清除附生的藤本植物即可。调查中也发现在坡垒种群的混交林中,目前除望天树(Parashorea chinensis Wang Hsie)尚未开花、结果外,其余的3个树种已开花结果。但在林下发现的小苗或小树很少,远低于坡垒的苗木数量,而且在这些树种的林下其他植物也很少,这说明坡垒具有良好的自我更新并形成新群落的能力。
运用植物径级结构代替年龄结构是种群生态学中研究种群结构的常用方法[34],对于坡垒等具有顽拗性种子的植物,采用空间差异代替时间变化的方法是可行的[35]。坡垒种群的径级结构呈倒“J”型,静态生命表分析显示,Ⅰ龄级及Ⅱ龄级阶段的个体数最多,到了 Ⅲ 龄级时死亡率及消失率最大,但 Ⅱ 龄级的期望值最高,具有进一步更新发展的基础。虽然 Ⅳ 龄级个体数量只有2 株,Ⅴ 龄级的个体数量为0,这主要是因为该坡垒种群的林龄较小,栽培的坡垒从最初的开花、结果到调查时不过15年左右的时间,加之坡垒的幼苗和其他大多数的龙脑香科植物一样,即种子萌发后有较长的蹲苗期,延缓了长成大径级个体的进程,致使目前尚未有大径级的个体。在普文试验林场引种栽培的42 a坡垒,仍具有很强的生长势[26]。因此,现有的苗木长成大径级的个体还需要较长的时间。本研究的坡垒种群的存活曲线属Deevey-Ⅲ[29],这与海南岛枫木林场迁地保护的坡垒种群的增长方式(Deevey-Ⅰ 型)有所不同,可能是因为所处的环境不同所致,但都属于增长型。版纳植物园迁地保护的坡垒不仅能开花、结果,实现“种子到种子”的过程,还具有形成新群落的能力,表明迁地保护的坡垒取得了初步成功。
本研究的迁地栽培的坡垒长势良好,与其他迁地保护的坡垒相比,广东树木园引种栽培的相同树龄坡垒的树高年均增长量0.42 m,胸径年均生长量为0.72 m[36],表明版纳植物园迁地栽培的坡垒长势优于广东树木园,这可能是版纳植物园水热及气候条件较好,更适合坡垒的生长。而与同属版纳地区的普文试验林场栽培的42 a(树高年均增长量0.59 m,胸径年均生长量为0.90 m)[37]相比,本研究的树高增长较快,但胸径增长稍慢些,总体而言差异不大,说明普文热林所与版纳植物园均适合坡垒的生长,是开展坡垒迁地保护的理想之地。而低于本园种植于西区的树龄相近的28 a坡垒林(树高年均增长量0.90 m,胸径年均生长量为1.48 cm)[25],这主要是种植方法及管理精细程度不同的结果。本研究所调查的迁地保护地是粗放管理,任其自然更新和生长;而西区的坡垒林则是精细化管理,常清除林下杂草,几乎没有其他植物与其争夺养分、水分等资源,生长初期还施加化学肥料,具有更为良好的生长环境,由此造成了植株个体的株高和胸径生长的差异。表明林分不同的管理方式对其生长具有较大的影响。已有研究表明,光是影响坡垒幼苗的重要环境因子,早期阶段适宜在一定遮荫条件下生长,但在后期(幼苗7-8月后)喜光特性增强[38]。对原生境坡垒影响幼苗生长的生境因子的研究表明,坡度、海拔、土壤pH值、土壤含水量、土壤全P含量及与母树的距离等是坡垒幼苗更新的限制因素[23]。随着海拔、坡度增加到一定程度时,幼苗数量、高度和啃食比例会有所下降[39]。由此说明在迁地保护的坡垒种群中,要在海拔低于800 m、坡度小于30°的环境中,可利于幼苗更新;同时,加强其生长发育过程中的抚育管理,是促进其个体生长和种群更新的有效措施。本研究也进一步证明了版纳植物园及其临近地区适合坡垒生长,不仅能够实现“种子到种子的过程”,还能实现种群的自然更新,是开展坡垒迁地保护及推广种植的重要区域。
4. 建议
坡垒是热带雨林的旗舰树种,在维护群落的稳定与生态安全方面发挥着重要作用,且被列为国家 Ⅰ 级重点保护植物及全国极小种群物种,除了做好就地保护之外,还应加强迁地保护研究工作。版纳植物园的迁地栽培研究结果表明,在引种地坡垒具有良好的适应性,能开花、结果,并且实现“种子到种子”的过程,而且幼苗数量充足,生活力旺盛,具有良好的更新潜力,但也面临着种内、种间以及在光线、养分、空间等资源竞争的压力,这与自然种群的更新情况相似。上述研究结果表明,迁地栽培环境及管理方式对种群更新和个体生长具有重要的作用,迁地栽培中要加强低龄级阶幼苗的管护,并加以必要的人工辅助措施,适当增施磷肥等养分元素,提高幼苗的成活率,促进幼苗的更新,以增加各龄级的个体数量,壮大种群数量,从而维持种群稳定,实现较好的保护。
-
表 1 迁地栽培坡垒种群的静态生命表
Table 1 Static life table of ex situ cultivated Hopea hainanensis population
x ax lx lnlx dx qx Lx Tx ex Kx Ⅰ 7925 10 000 9.21 7606 0.76 6197 12394 1.24 1.43 Ⅱ 1900 2 394 7.78 1386 0.58 1701 3402 1.42 0.86 Ⅲ 800 1 008 6.92 945 0.94 536 1071 1.06 2.78 Ⅳ 50 63 4.14 − − 32 63 1.00 − 注:x均为龄级;ax为龄级内现有植株存活数;dx为标准化死亡数;ex为生命期望值;Kx为消失率; lx为标准化存活数;qx为死亡率;Lx为存活的个体数或区间寿命;Tx为从x龄级到超过x龄级的个体总数或总寿命。 Notes: x, age class; ax, surviving numbers observed within each age class; dx, standardized death number; ex, life expectancy; Kx, loss rate; lx, standardized survival number; qx, individual morality rate; Lx, average number of surviving individuals or mortality rate; Tx, total number of surviving individuals in age class x and above. 表 2 天然更新等级评判
Table 2 Grade of natural regeneration
等级Class 不同胸径株数 Individual number of DBH H ≤ 30 cm 30 < H ≤ 50 cm H > 50 cm 不分高度
Irrespective of height良好 > 5 000 > 3 000 > 2 500 > 4 000 中等 3 000 < N ≤ 5000 1 000 < N ≤ 3 000 500 < N ≤ 2 500 2 000 < N ≤ 4 000 不良 ≤ 3 000 ≤ 1 000 ≤ 500 ≤ 2000 注:DBH为胸径英文首个字母;N代表株数。 Notes: DBH, diameter at breast height; N, number. 表 3 迁地栽培坡垒的生长状况
Table 3 Growth of DBH and height of ex situ cultivated Hopea hainanensis population
类别
Type胸径DBH / cm 树高Height / cm 最大
Max最小
Min平均值
Average年均生长量
Annual average growth最高
Max最低
Min平均值
Average年均生长量
Annual average growth指标值 44.40 15.30 26.54 0.85 27.00 13.00 24.13 0.78 -
[1] 吴明开,沈志君,刘海,吴沿友,何汝态,等. 梵净山自然保护区珙桐天然种群生命表与生存分析[J]. 生态学杂志,2012,31(6):1419−1424. Wu MK,Shen ZJ,Liu H,Wu YY,He RT,et al. Life table and survival analysis of natural Davidia involucrata population in Fanjing Mountain Nature Reserve,Guizhou Province of Southwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2012,31 (6):1419−1424.
[2] 王国严,罗建,徐阿生,庄颖梅. 西藏色季拉山川滇高山栎种群结构与动态[J]. 林业科学研究,2011,24(3):292−299. Wang GY,Luo J,Xu AS,Zhuang YM. Population structure and dynamics of Quercus aquifolioides in Sejila Mountain,Tibet,China[J]. Forest Research,2011,24 (3):292−299.
[3] 吴承祯,洪伟,谢金寿,吴继林. 珍稀濒危植物长苞铁杉种群生命表分析[J]. 应用生态学报,2000,11(3):333−336. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2000.03.003 Wu CZ,Hong W,Xie JS,Wu JL. Life table analysis of Tsuga longibracteata population[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2000,11 (3):333−336. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2000.03.003
[4] Stewart GH,Rose AB. The significance of life history strategies in the developmental history of mixed beech (Nothofagus) forests,New Zealand[J]. Vegetatio,1990,87 (2):101−114. doi: 10.1007/BF00042947
[5] Suzán-Azpiri H,Sánchez-Rámos G,Martı́nez-Avalos JG,Villa-Melgarejo S,Franco M. Population structure of Pinus nelsoni Show,an endemic pinyon pine in Tamaulipas,Mexico[J]. Forest Ecol Manage,2002,165 (1-3):193−203. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1127(01)00617-X
[6] 吴丹妮. 油松主伐保留母树林下更新苗的格局分析[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2019: 15-16. [7] 党海山,张燕君,张克荣,江明喜,张全发. 秦岭巴山冷杉(Abies fargesii)种群结构与动态[J]. 生态学杂志,2009,28(8):1456−1461. Dang HS,Zhang YJ,Zhang KR,Jiang MX,Zhang QF. Population structure and its dynamics of Abies fargesii in Qinling Mountains[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2009,28 (8):1456−1461.
[8] 胡云云,亢新刚,赵俊卉. 长白山地区天然林林木年龄与胸径的变动关系[J]. 东北林业大学报,2009,37(11):38−42. Hu YY,Kang XG,Zhao JH. Variable relationship between tree age and diameter at breast height for natural forests in Changbai mountains[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2009,37 (11):38−42.
[9] 杨凤翔,王顺庆,徐海根,李邦庆. 生存分析理论及其在研究生命表中的应用[J]. 生态学报,1991,11(2):153−158. Yang FX,Wang SQ,Xu HG,Li BQ. The theory of survival analysis and its application to life table[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,1991,11 (2):153−158.
[10] 李艳丽,杨华,亢新刚,邱实. 长白山云冷杉种群结构和动态分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报,2014,36(3):18−25. Li YL,Yang H,Kang XG,Qiu S. Population structures and dynamics of Abies nephrolepis and Picea koraiensis in the Changbai Mountains of northeastern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2014,36 (3):18−25.
[11] 沈国舫. 森林培育学(第4版)[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2001: 85. [12] 郑健,郑勇奇,吴超,张川红,宗亦尘,等. 花楸树的地理分布及天然更新方式[J]. 林业科学,2007,43(12):86−93. Zheng J,Zheng YQ,Wu C,Zhang CH,Zong YC,et al. Geographical distribution and patterns of natural regeneration of Sorbus pohuashanensis[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae,2007,43 (12):86−93.
[13] Ellsworth JW,Harrington RA,Fownes JH. Seedling emergence,growth,and allocation of oriental bittersweet:effects of seed input,seed bank,and forest floor litter[J]. Forest Ecol Manage,2004,190 (2-3):255−264. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2003.10.015
[14] Tíscar PA. Recruitment into the seedling bank of an undisturbed Mediterranean pinewood:increasing forest resistance to changing climates[J]. Forest Ecol Manage,2019,432:591−598. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2018.09.058
[15] Hedrick PW. A standardized genetic differentiation measure[J]. Evolution,2005,59 (8):1633−1638.
[16] Aguilar R,Ashworth L,Galetto L,Aizen MA. Plant reproductive susceptibility to habitat fragmentation:review and synthesis through a meta-analysis[J]. Ecol Lett,2006,9 (8):968−980. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00927.x
[17] 曾祥全,田蜜,黄国宁,冯巧. 坡垒与水垒木材的鉴别[J]. 热带林业,2021,49(1):46−48. Zeng XQ,Tian M,Huang GN,Feng Q. Timber identification of Hopea hainanensis and Pseudostreblus indica[J]. Tropical Forestry,2021,49 (1):46−48.
[18] 黄枢, 沈国舫. 中国造林技术[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1993: 47. [19] 孙卫邦,韩春艳. 论极小种群野生植物的研究及科学保护[J]. 生物多样性,2015,23(3):426−429. doi: 10.17520/biods.2015026 Sun WB,Hang CY. Researches and conservation for plant species with extremely small populations (PSESP)[J]. Biodiversity Science,2015,23 (3):426−429. doi: 10.17520/biods.2015026
[20] 李丹. 海南省野生龙脑香科植物分布格局及种群特征研究[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2016: 5. [21] 裴学军. 海南省霸王岭自然保护区珍稀濒危野生植物坡垒保护研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2016: 28-29. [22] 段左俊,彭文成,黄国宁. 龙脑香科植物致濒原因研究概况[J]. 热带林业,2020,48(4):4−8. Duan ZJ,Peng WC,Huang GN. A survey of research on the endangered causes of dipterocarpaceae plants[J]. Tropical Forestry,2020,48 (4):4−8.
[23] 路兴慧,臧润国,丁易,黄继红,许玥. 极小种群野生植物坡垒的生境特征及其对幼苗多度的影响[J]. 生物多样性,2020,28(3):289−295. doi: 10.17520/biods.2019143 Lu XH,Zang RG,Ding Y,Huang JH,Xu Y. Habitat characteristics and its effects on seedling abundance of Hopea hainanensis,a wild plant with extremely small populations[J]. Biodiversity Science,2020,28 (3):289−295. doi: 10.17520/biods.2019143
[24] 符明期,方燕山,桂慧颖,方发之. 海南黎母山坡垒种群结构及伴生群落特征研究[J]. 热带林业,2019,47(3):9−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0938.2019.03.002 Fu MQ,Fang YS,Gui HY,Fang FZ. Study on the population structure and companion community characteristics of Hopea hainanensis in Limu Mountain,Hainan Province[J]. Tropical Forestry,2019,47 (3):9−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0938.2019.03.002
[25] 肖来云,普正和,张玲. 稀有濒危植物坡垒的迁地保护[J]. 植物资源与环境,1994,3(4):49−54. Xiao LY,Pu ZH,Zhang L. Ex situ conservation of rare and endangered species-Hopea hainanensis[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment,1994,3 (4):49−54.
[26] 刘国栋. 普文试验林场引种的龙脑香科植物[J]. 云南林业科技,1995,2:22−26. Liu GD. The introduction of dipterocarpaceae plants in Puwen experimental forest farm[J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science,1995,2:22−26.
[27] 段左俊,梁居红,陈飞飞,黄川腾. 龙脑香科5个树种在海南的适应性研究[J]. 热带林业,2018,46(3):39−42. Duan ZJ,Liang JH,Chen FF,Huang CT. The research on the adaptability of the five tree species of the family dipterocarpaceae[J]. Tropical Forestry,2018,46 (3):39−42.
[28] 黎国运,韦建杏,陈侯鑫,林玲,董晓娜. 海南坡垒育苗、种植及其抚育技术总结[J]. 热带林业,2020,48(1):36−39. Li GY,Wei JX,Chen HX,Lin L,Dong XN. Technology summary on breed seedlings,planting and tending of Hopea hainanensis[J]. Tropical Forestry,2020,48 (1):36−39.
[29] 张丽,杨小波,农寿千,李东海,李苑菱,宋佳昱. 两种不同保护模式下坡垒种群发育特征[J]. 生态学报,2019,39(10):3740−3748. Zhang L,Yang XB,Nong SQ,Li DH,Li YL,Song JY. Comparative study on population development characteristics of Hopea hainanensis base in two different protection modes[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2019,39 (10):3740−3748.
[30] 西双版纳热带森林生态研究组. 西双版纳勐仑地区气候特征[J]. 热带植物研究,2000(47):62−65. Xishuangbanna Forest Ecology Satiation. The climatic characteristic in Xishuangbanna Mneglun[J]. Tropical Plant Research,2000 (47):62−65.
[31] Frost I,Rydin H. Spatial pattern and size distribution of the animal-dispersed tree Quercus robur in two spruce-dominated forests[J]. É coscience,2000,7 (1):38−44.
[32] 曲仲湘,文振旺,朱克贵. 南京灵谷寺森林现况的分析[J]. 植物学报,1952,1(1):18−49. Qu ZX,Wen ZW,Zhu KG. An analytical study of the forest of the spirit valley,Nanjing[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology,1952,1 (1):18−49.
[33] 国家林业局森林资源管理司. 东北天然林生态采伐更新作业调查设计规程, 2002. [34] 胡璇,徐瑞晶,舒琪,郭雯,张建,等. 海南岛甘什岭特有植物无翼坡垒种群结构与动态[J]. 热带作物学报,2020,41(9):1939−1945. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2020.09.030 Hu X,Xu RJ,Shu Q,Guo W,Zhang J,et al. Population structure and dynamics of Hopea reticulata,a plant endemic to Ganshiling,Hainan Island[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2020,41 (9):1939−1945. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2020.09.030
[35] 王祎玲,张钦弟,郝晓杰,闫桂琴. 山西七里峪茶条槭的种群结构与空间分布格局[J]. 西北植物学报,2012,32(5):1027−1035. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4025.2012.05.028 Wang YL,Zhang QD,Hao XJ,Yan GQ. Structure and spatial distribution of Acer ginnala population in Qiliyu,Shanxi[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2012,32 (5):1027−1035. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4025.2012.05.028
[36] 温小莹,黄芳芳,甘先华,张卫强,黄钰辉,等. 坡垒、青皮在广东树木园的引种表现[J]. 林业与环境科学,2017,33(4):52−56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4427.2017.04.011 Wen XY,Huang FF,Gan XH,Zhang WQ,Huang YH,et al. Introduction performance of Hopea hainanensis and Vatica mangachapoi in Guangdong Tree Park[J]. Forestry and Environmental Science,2017,33 (4):52−56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4427.2017.04.011
[37] 杨德军,邱琼. 海南坡垒引种初报[J]. 江西林业科技,2007(2):27−29. doi: 10.16259/j.cnki.36-1342/s.2007.02.010 Yang DJ,Qiu Q. Preliminary study on introduction of Hopea hainanensis[J]. Jiangxi Forestry Science and Technology,2007 (2):27−29. doi: 10.16259/j.cnki.36-1342/s.2007.02.010
[38] 张丽. 海南坡垒种群特征及不同光强对其幼苗生长的影响研究[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2019: 42-43. [39] 裴学军,周晓芳,刘娜,洪小江,周照骊,成克武. 野生极小种群植物坡垒幼苗分布与母树的关系[J]. 河北农业大学学报,2015,38(3):46−51. doi: 10.13320/j.cnki.jauh.2015.0058 Pei XJ,Zhou XF,Liu N,Hong XJ,Zhou ZL,Cheng KW. Relationship between distribution of Hopea hainanensis seedlings and its seed tree[J]. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei,2015,38 (3):46−51. doi: 10.13320/j.cnki.jauh.2015.0058



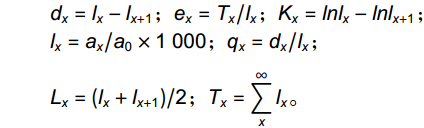
 下载:
下载: