Species composition and flora analysis of seed plants on five uninhabited islands in Pingtan, Fujian Province, China
-
摘要:
基于野外调查和标本鉴定,对福建平潭5个无居民海岛的种子植物进行物种组成分析与地理成分划分,并与不同地区海岛种子植物属的分布区类型进行对比,探讨了5个无居民海岛之间的物种相似性以及与岛屿空间特征参数的关系。结果显示:(1)5个海岛共有种子植物71科179属213种(含种下单位),剔除42个外来物种,共有种子植物65科145属171种,生活型以草本占比最高,其次是灌木、藤本和乔木。(2)在科、属、种水平上,区系类型主要由泛热带分布及其变型组成,热带、亚热带成分占比最高。(3)随着纬度的增加,植物区系具有从热带向温带过渡的特点,体现了海岛植物区系地理成分的纬向分异性。(4)属种相似性上,平潭5个无居民海岛间植物的物种相似度普遍较低。此外,岸线长度、高程和周长面积比等空间参数对海岛物种丰富度影响不显著。
Abstract:Based on field surveys and specimen identification, we analyzed the species composition and geographical distribution of seed plants from five uninhabited islands in Pingtan, Fujian. We compared the distribution patterns of seed plant genera from these islands with those from different regions and explored the species similarity among the five uninhabited islands, as well as the relationship with spatial characteristics of the islands. Results showed the following: (1) The five uninhabited islands contained 213 species of seed plants from 71 families and 179 genera (including infraspecific units). After excluding 42 exotic species, 171 native species from 65 families and 145 genera remained, with herbaceous species comprising the largest proportion, followed by shrubs, lianas, and trees. (2) At the family, genus, and species levels, the prominent distribution types were pan-tropical and its variants, with tropical and subtropical components being the most represented. (3) Flora showed a tropical to temperate zone transition with increasing latitude, reflecting the latitudinal divergence in the geographical components of the island flora. (4) In terms of genus similarity, plant species similarity among the five uninhabited islands was generally low. In addition, spatial parameters, such as shoreline length, elevation, and perimeter/area ratio, also influenced species richness of the islands to some extent.
-
Keywords:
- Uninhabited islands /
- Flora /
- Geographical component /
- Seed plant
-
无居民海岛是指我国海域范围内不用于人口居住的岛屿[1],与有人居住的岛屿数量相比,我国有许多无人居住的岛屿,这些岛屿及周边海域拥有丰富的海洋资源,具有巨大的发展潜力,对我国海洋经济发展和资源合理利用具有重要作用[2]。岛屿植被是岛屿生态系统的重要组成部分,了解岛屿的植物资源对于确定植被的恢复和建设方式具有指导意义[3]。近年来,国内对无居民海岛植被的研究日益增多,主要集中于无居民海岛植物群落的相关环境因子[4-6]、外来入侵植物[7]和海岛开发利用[8-10]等方面。然而,目前对无居民海岛植物物种组成及区系特征的相关研究报道较少。
本研究在实地调查和查阅以往文献的基础上,总结分析了福建平潭5个无居民海岛的种子植物物种组成和地理分布型类型,探索该地区种子植物区系的组成和地理分布,研究结果旨在为保护海岛特色植物群落、促进海岛生态规划和创造海岛优质生态环境提供线索。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 研究区概况
平潭为福建省管辖的综合实验区,位于福建省东部,是福建省第一大岛。平潭属亚热带季风气候,夏季主要为西南风,冬季以东北风为主[11]。本次调查选取包括光幼屿(25°34′54.48″N,119°50′4.56″E)、红山屿(25°34′41.88″N,119°50′27.96″E)、黄门岛(25°27′40.68″N,119°40′ 50.88″E)、姜山岛(25º26′30.12″N,119º48′28.30″E)、龙母屿(25°20′49.26″N,119º41′48.74″E)在内的5座无居民海岛,各岛概况见表1。
表 1 平潭5个无居民海岛基本情况Table 1. Basic information of 5 uninhabited islands in Pingtan岛屿
Island面积
Area / hm²近岸距离
Inshore distance / km周长
Perimeter / m海拔
Altitude / m周长/面积
Perimeter area ratio物种数
Species光幼屿 6.22 22.57 1 075.4 45.1 0.017 77 红山屿 3.07 23.05 1 015.0 33.2 0.033 53 黄门岛 7.18 3.89 1 417.3 24.2 0.020 114 姜山岛 40.24 1.12 4 951.2 22.4 0.012 115 龙母屿 2.88 8.14 993.3 20.8 0.034 102 1.2 调查对象及方法
本研究采用样方法和样线法相结合的技术路线,对平潭5个无居民海岛的植物资源进行详尽的全面踏勘。样方法设置的乔木群落样方面积为20 m×20 m,共22个,四角设置4个5 m×5 m的灌木样方,另外取5个1 m×1 m的草本样方,分别位于样地的四角及中部位置。样线法设置方法为按环岛样线和东西向或南北向沿岛屿中部设置样线的方式,记录样线左右10 m以内出现的植物。随时记录沿路所见植物种类,拍摄照片,对于现场无法识别的植物记录其细节特征,查阅《福建植物志》[12]进行鉴定。依据中国外来入侵物种信息系统(http://www.iplant.cn/ias)和《中国入侵植物名录》[13] 统计外来植物。采用《世界种子植物科的分布区类型》[14]划分种子植物科分布区类型,属、种的分布区类型根据《中国种子植物属的分布区类型》[15] 并结合中国植物志电子版(https://www.iplant.cn/)进行划分。
剔除外来植物后,根据以上方法划分该地种子植物科属种的分布区类型,分析其种子植物区系特征。通过热带属数/温带属数(R/T)研究其区系成分,以平潭5个无居民海岛与其他无居民海岛属的分布区类型为基础,进行聚类分析。采用Jaccard 相似性系数[16],分别计算平潭5个无居民海岛之间的属-种相似性系数,并对岛屿空间特征参数的相关性进行分析。以上数据处理均利用Excel 2016和SPSS 26软件完成。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 平潭5个无居民海岛的种子植物物种组成
调查发现,5个无居民海岛共有种子植物213种(含种下单位,下同),隶属71科179属。其中,被子植物70科178属212种;裸子植物仅1种;单子叶植物10科33属48种,分别占总科、属、种数的14.08%、18.44%和22.54%;双子叶植物61科146属165种,分别占总科、属、种数的85.92%、81.56%和77.46%(表2)。
表 2 平潭5个无居民海岛种子植物物种分类群统计Table 2. Statistics of vascular plant species taxa of 5 uninhabited islands in Pingtan分类群
Plant taxon科数(占比)
No. of families(Percentage / %)属数(占比)
No. of genera(Percentage / %)种数(占比)
No. of species(Percentage / %)裸子植物 1(1.41) 1(0.56) 1(0.47) 被子植物 70(98.59) 178(99.44) 212(99.53) 双子叶植物 61(85.92) 146(81.56) 165(77.46) 单子叶植物 10(14.08) 33(18.44) 48(22.54) 合计 71(100) 179(100) 213(100) 根据整理的种子植物名录,外来草本植物共有42种(19.72%),隶属于20科38属,如鬼针草(Bidens Pilosa L.)、飞扬草(Euphorbia hirta L.)、蟛蜞菊(Wedelia chinensis (L.) Pruski)、牵牛(Pharbitis ni (L.) Roth)和白花地胆草(Elephantopus tomentosus L.)等;原生草本植物共有171种(80.28%),隶属于65科145属。可见,平潭5个无居民海岛的种子植物以原生植物分布为主。
2.2 种子植物生活型统计与分析
植物生活型是植物对环境长期适应的表现形式,体现在外部形态、结构等方面,可反映植物与环境间的关系[17, 18],并揭示植物对环境的生态适应性[19]。由表3可知,植物生活型有乔木、灌木、藤本和草本4种类型。平潭5个无居民海岛的种子植物生活型占比大小依次是草本(59.65%)、灌木(28.07%)、藤本(8.19%)和乔木(4.09%)。草本植物种数最多,其中,多年生草本58种,包括烟豆(Glycine tabacina Benth)、中华补血草(Limonium sinense (Girard) Kuntze)和厚藤(Ipomoea pes-caprae (L.) R. Brown)等;一、二年生植物44种,分别占总种数的21.64%和4.09%,包括画眉草(Eragrostis pilosa (L.) Beauv)、马唐(Digitaria sanguinalis (L.) Scop)和爵床(Justicia procumbens L.)等。
表 3 平潭5个无居民海岛种子植物种子植物生活型统计Table 3. Statistics of life forms of seed plants of 5 uninhabited islands in Pingtan生活型
Life form种数
No. of species占总种数的百分比
Account of total species / %乔木 常绿 2 1.17 落叶 5 2.92 灌木 常绿 31 18.13 落叶 17 9.94 藤本 常绿木质藤本 5 2.92 落叶木质藤本 4 2.34 多年生草质藤本 5 2.92 草本 一年生 37 21.64 二年生 7 4.09 多年生 58 33.92 合计 171 100 2.3 种子植物区系地理成分统计与分析
2.3.1 科分布区类型
在科水平上,平潭5个无居民海岛种子植物65科的地理成分可划分为6个类型4个变型(表4)。其中,世界广布科有29个,占总科数的44.62%,包括菊科、禾本科、蔷薇科、苋科和蝶形花科等。科的地理分布中热带成分占比优势显著,热带性质突出。经统计,热带性质科共28个,占总科数(除世界广布科)的77.78%。热带性质的科主要有大戟科、夹竹桃科、锦葵科和含羞草科等。温带性质的科共8个,包括忍冬科和胡颓子科等,占总科数(除世界广布科)的22.22%。
表 4 平潭5个无居民海岛科、属、种的分布区类型统计Table 4. Distribution pattern statistics of vascular plants families, genera and species on five uninhabited islands in Pingtan分布区类型及其变型
Distribution types and variants科
Families属
Genera种
Species数量
No.占比
Percentage / %数量
No.占比
Percentage / %数量
No.占比
Percentage / %1. 世界分布 29 – 15 – 7 – 2. 泛热带分布 23 63.89 52 40.00 16 9.76 2-1. 热带亚洲-大洋洲和热带美洲分布 1 2.78 2 1.54 1 0.61 2-2. 热带亚洲、非洲和南美洲间断分布 1 2.78 4 3.08 5 3.05 2S. 以南半球为主的泛热带 1 2.78 0 0 0 0 3. 热带亚洲和热带美洲间断分布 1 2.78 4 3.08 7 4.27 4. 旧世界热带分布 1 2.78 14 10.77 6 3.66 4-1. 热带亚洲、非洲和大洋洲间断或星散分布 0 0 2 1.54 3 1.83 5. 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布 0 0 8 6.15 19 11.59 6. 热带亚洲至热带非洲 0 0 2 1.54 4 2.44 7. 热带亚洲(印度-马来西亚)分布 0 0 2 1.54 29 17.68 8. 北温带分布 4 11.11 14 10.78 7 4.27 8-4. 北温带和南温带(全温带)间断分布 3 8.33 3 2.31 3 1.83 9. 东亚和北美洲间断分布 0 0 6 4.62 4 2.44 10. 旧世界温带分布 0 0 4 3.08 4 2.44 10-1. 地中海区、西亚(或中亚)和东亚间断分布 0 0 3 2.31 1 0.61 10-3. 欧亚和南部非洲(有时也在大洋洲)间断分布 0 0 1 0.77 0 0 11. 温带亚洲 0 0 0 0 17 10.37 14. 东亚分布 1 2.78 7 5.38 14 8.54 14-1. 中国-喜马拉雅(SH) 0 0 0 0 3 1.83 14-2. 中国-日本(SJ) 0 0 1 0.77 9 5.49 15. 中国特有分布特有 0 0 1 0.77 12 7.32 合计 65 100 145 100 171 100 2.3.2 属分布区类型
在属水平上,平潭5个无居民海岛的种子植物共145属,其地理成分可划分为12个类型7个变型(表4)。世界广布类型的属有15个,占总属数的10.34%,包括莎草属(Cyperus)、苋属(Amaranthus)和马唐属(Digitaria)等。属的分布区类型中热带成分占主导地位,有90个,占总属数(除世界广布属)的69.24%,热带性质明显,包括大戟属(Euphorbia)、南蛇藤属(Celastrus)、紫珠属(Callicarpa)和马齿苋属(Portulaca)等。温带性质的属共40个,占总属数(除世界广布属)的30.02%,包括山麦冬属(Liriope)、胡枝子属(Lespedeza)、胡颓子属(Elaeagnus)和络石属(Trachelospermum)等。
2.3.3 种分布区类型
在种水平上,平潭5个无居民海岛共有171种种子植物(不含外来植物),其地理成分可划分为13个分布区类型7个变型(表4)。世界广布类型的种有7个,占总种数的4.09%,如莎草属(Cyperus)、苋属(Amaranthus)和堇菜属(Viola)等。种的分布区类型中热带成分占主导地位,热带性质(2~7型)的种有90个,占总种数(除世界广布种)的54.88%,热带性质明显,包括马蹄金(Dichondra micrantha Urban)、紫珠(Callicarpa bodinieri Levl)和算盘子(Glochidion puberum (L.) Hutch)等。温带性质(8~14型)的种共62个,占总种数(除世界广布种)的37.80%,有桑(Morus alba L.)、滨柃(Eurya emarginata (Thunb.) Makino)和络石(Trachelospermum jasminoides (Lindl.) Lem)等。
2.3.4 滨海特有植物
仅分布于岛屿或滨海地区且具有明显岛屿特征的植物被称为滨海特色植物[20]。由于海岛的特殊环境结构,平潭5个无居民海岛分布有较多的滨海特色植物,共14科24属24种。其中,滨海前胡(Peucedanum japonicum Thunb)、滨柃(Eurya emarginata (Thunb.) Makino)、肉叶耳草(Hedyotis coreana (DC.) Neupane & N. Wikstr)和滨海珍珠菜(Lysimachia mauritiana Lam)等植物既适应海岛的气候与土壤,又具有滨海特色与观赏价值,同时具有较高的园林利用价值和极高的生态价值。
2.4 平潭5个无居民海岛与其他海岛种子植物区系比较分析
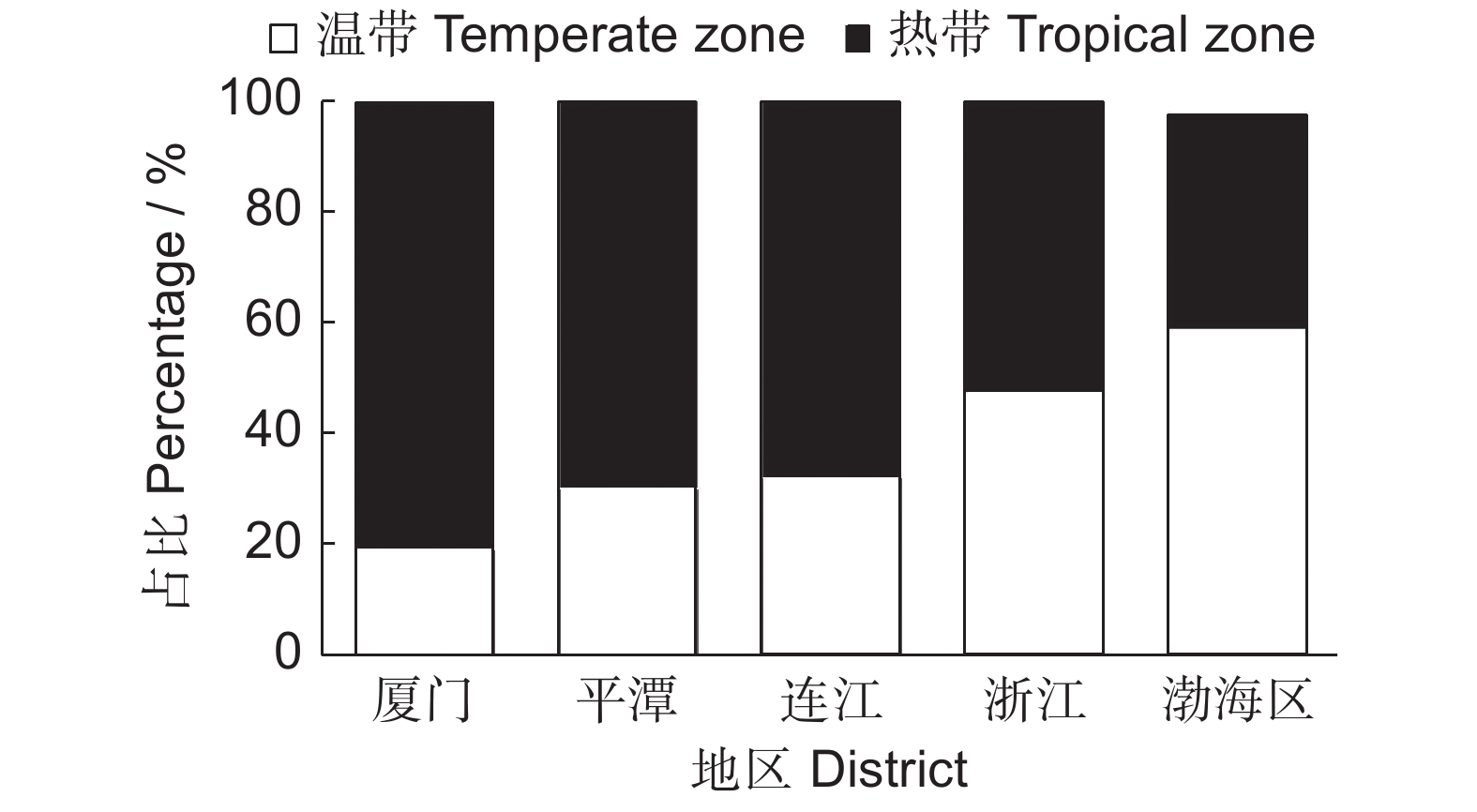
对平潭5个无居民海岛与其他海岛区系进行种子植物属的分布区类型比较,结果见表5。各个地区中泛热带分布型占比较高,为24.03%~40.00%,厦门近岸海域无居民海岛植物区系的R/T值(4.23)远高于其他海岛,热带性质最强烈;纬度相近的平潭和连江无居民海岛的R/T值接近,且均大于2,分别为2.31和2.13,热带优势明显。相反,纬度相对较高的浙江无居民海岛和渤海区9个无居民海岛的热带成分比例稍低,而温带分布比例略高,R/T值最低,仅为1.11和0.66,两者的北温带分布比例则远高于前三者,温带性质趋势明显,符合R/T值的排列顺序。将世界分布属和中国特有属排除后,重新计算这些地区的R/T值(图1)。由图1可知,随着纬度的增加,热带分布型所占比例逐渐降低,而温带分布型占比则逐渐上升,植物区系具有热带向温带过渡的特点,与中国植被类型的分布规律一致[21]。
表 5 平潭与其他地区无居民海岛种子植物属的分布区类型比较Table 5. Comparison of distribution types of seed flora and genera among five uninhabited islands in Pingtan and different island regions分布区
类型
Distribution type平潭(5个)
Pingtan (5)
(25°15′~25°45′N)厦门近岸
Xiamen
(24°25′~24°35′N)连江(5个)
Lianjiang (5)
(26°07′~26°27′N)浙江(5个)
Zhejiang (5)
(28°12′~28°18′N)渤海(9个)
Bohai Sea
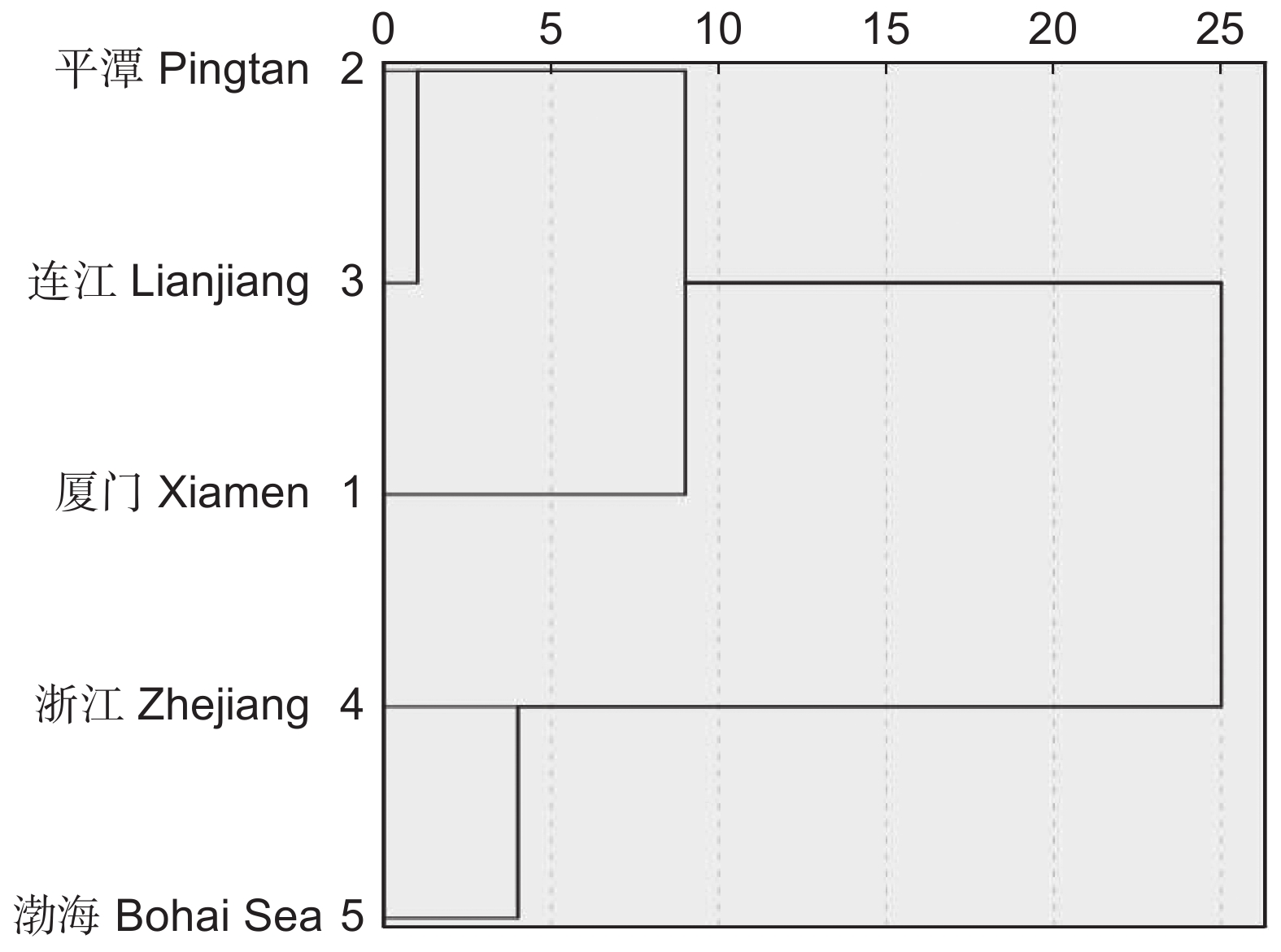
(37°06′~40°55′N)1 10.34 9.35 10.90 12.34 16.67 2 40.00 29.50 36.05 24.03 24.71 3 2.76 11.87 7.48 1.30 0.00 4 11.03 8.63 8.16 7.14 4.71 5 5.52 8.99 6.80 5.19 2.35 6 1.38 6.83 4.08 5.19 3.53 7 1.38 7.19 5.44 3.25 3.53 8 11.72 7.91 13.60 23.38 30.59 9 4.14 3.24 4.08 4.55 5.88 10 5.52 2.16 5.44 4.55 9.41 11 0.00 0.00 0.68 0.64 5.88 12 0.00 0.36 0.00 0.00 2.35 13 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 14 5.52 3.60 8.16 8.44 4.71 15 0.69 0.36 0.00 0.00 2.35 R/T 2.31 4.23 2.13 1.11 0.66 注:1,世界广布;2,泛热带分布;3,热带亚洲和热带美洲分布;4,旧世界热带分布;5,热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布;6,热带亚洲至热带非洲分布;7,热带亚洲分布;8,北温带分布;9,东亚和北美间断分布;10,旧世界温带分布;11,温带亚洲分布;12,地中海及西亚至中亚分布;13,中亚分布;14,东亚分布;15,中国特有分布。 Notes: 1, Cosmopolitan; 2, Pantropic; 3, Tropical Asia & tropical America disjunct; 4, Old world tropical distributed; 5, Tropical Asia to tropical Australasia distributed; 6, Tropical Asia to tropical Africa distributed; 7, Tropical Asia distributed; 8, North temperate distributed; 9, East Asia & North America disjunct; 10, Old world temperate distributed; 11, Temperate Asia; 12, Mediterranea, West Asia to Central Asia; 13, Central Asia; 14, East Asia distributed; 15, Endemic to China. 为进一步探讨平潭5个无居民海岛与其他地区植物区系的相似性,对其属的分布区类型比率进行聚类分析。如图2所示,当欧氏距离约为10时,可将5个地区划分为2组。第1组为厦门近岸海域无居民海岛、平潭5个无居民海岛和连江县5个无居民海岛,3个地区纬度相近,植物热带成分占50%以上;第2组为渤海区9个无居民海岛和浙江5个无居民海岛,其植物热带成分明显减少,占30%左右。
2.5 不同岛屿间植物的物种相似度与空间特征关系
计算平潭5个无居民海岛属相似性系数与种相似性系数。结果显示,5个海岛在属级水平上相似性程度均不高,属的相似性系数大于30%的有光幼屿分别与红山屿(48%)和黄门岛(32%);以及姜山岛分别与龙母屿(47%)和黄门岛(31%);相似性系数小于30%的有黄门岛与红山屿(28%)、姜山岛分别与光幼屿(21%)和红山屿(20%),龙母屿分别与光幼屿(26%)、红山屿(22%)、黄门岛(28%)(附表1
1 ))。相较于属级水平,各个海岛之间在种级水平上的相似性程度有所降低,姜山岛与光幼屿(19%)以及红山屿(17%)之间的相似度均小于20%,说明这3个海岛在种水平上的差异较大(附表
1 ))。分析物种相似性系数Cj与岛屿空间特征的相关性,结果表明,Cj与面积比(δA)(0.577)、岸线长度比(δPer)(0.585)和高程比(δE)(0.591)呈正相关,与周长面积比的比值(δPAR)(−0.602)和近岸距离比(δI)(−0.211)呈负相关,但均不显著。
3. 讨论
3.1 平潭5个无居民海岛种子植物区系特征
平潭5个无居民海岛的种子植物共有71科179属213种,剔除外来物种后,共65科145属171种,与福建种子植物202科1596属4416种相比[22],本研究区域种子植物的科、属 、种数分别占了福建省植物区系的32.18%、9.09%和3.87%。按照生活型进行分类,草本植物占优势,共计102种(59.65%);其次为灌木48种(28.07%);乔木和藤本的种数则较少,分别是7种(4.09%)和14种(8.19%)。
平潭海岛的种子植物区系优势较为明显,含有较多热带科以及亚热带科,区系科、属、种的地理性质均以热带为主,科的热带成分占77.79%,温带成分仅占22.22%;属的热带成分占69.24%,温带成分为30.02%;种的热带成分占54.88%,温带成分为37.80%。种子植物中含有较多的热带科以及亚热带科,与福建省植物区系的特征相符合。科、属的热带成分以泛热带分布为主,种的热带成分以热带亚洲为主;科、属的温带成分以北温带为主,种的温带成分以温带亚洲及东亚分布为主,整体呈现显著的由热带向温带过渡的趋势。通过对平潭与其他地区岛屿的属分布区类型进行对比发现,除浙江和渤海区的无居民海岛外,其余岛屿的R/T值均具有明显的热带性质,符合其所处的亚热带海洋季风气候区的地理位置及热带起源[23],这一结果与相关研究[24]一致。随着纬度的增加,不同海岛植物区系的属级分布类型中,温带分布型逐渐增加,热带分布型占比逐步减少,显示出海岛植物区系地理成分的纬向分异性。
3.2 平潭5个无居民海岛间植物的物种相似度与空间特征关系
分析平潭5个无居民海岛植物间的种相似性系数及其与岛屿空间特征的相关性,发现Cj与面积比、岸线长度比和高程等空间特征均无显著相关性。平潭5个无居民海岛中,物种组成相似性较高的有光幼屿与红山屿、姜山岛与龙母屿、黄门岛与光幼屿,以及姜山岛与黄门岛,但均未超过50%,说明各个岛屿植物间的亲缘关系较远。
通常海岛面积越大,环境异质性越高,物种丰富度也会更高,这是岛屿生物地理学的普遍规律[25, 26]。平潭5个无居民海岛中姜山岛的面积最大,物种数也最多。但面积最小的龙母屿,其物种数却居第3,原因之一可能是龙母屿的灌木、草本能够较好地适应岛屿环境,且草本植物在该岛占绝对优势[27],其生存所需空间比乔木小得多,所以受岛屿面积的制约较小[28, 29];另一方面,尽管平潭5个无居民海岛同属一个气候带,但不同海岛间的物种数存在差异主要是由海岛环境的特殊性决定的[30]。
由于各个岛屿具有独立性,形成了不同的生态环境,并进行长时间的自然选择[31, 32],因此导致各岛屿的植物种类存在差异。本文仅以分布型从宏观层面对平潭5个无居民海岛的种子植物进行了区系分析,没有从微观层面进行探讨,后期对植物区系的研究可考虑土壤因子、地质变化和岛屿间植物竞争生态位等方面的因素。
3.3 平潭5个无居民海岛的保护和利用
海岛植物物种丰富度与人为活动因素紧密相关[33]。有居民海岛由于长期受人为干扰,海岛植被中的原生植被可能被破坏,从而对原生植物的生态位造成威胁,此外,海岛开发也会导致一定程度上原生植物数量的减少和次生植被的增加[34]。相比有居民海岛,无居民海岛植物受人为干扰较小。
平潭5个无居民岛屿的种子植物以原生植物为主,但海岛上的入侵植物也需要重视,如鬼针草(Bidens pilosa L.)、马缨丹(Lantana camara L.)和小蓬草(Conyza canadensis L.)等。为保护当地的物种多样性,避免物种的进一步同质化[35],应建立一个长期稳定的实时更新数据库,开展生态治理研究[36]。针对以上入侵植物,建议制定具有针对性的防控策略,尽可能挖掘其潜在的利用价值[37],做到有效防控与利用。
1 1~2)如需查阅附表内容请登录《植物科学学报》网站(http://www.plantscience.cn)查看本期文章。 -
表 1 平潭5个无居民海岛基本情况
Table 1 Basic information of 5 uninhabited islands in Pingtan
岛屿
Island面积
Area / hm²近岸距离
Inshore distance / km周长
Perimeter / m海拔
Altitude / m周长/面积
Perimeter area ratio物种数
Species光幼屿 6.22 22.57 1 075.4 45.1 0.017 77 红山屿 3.07 23.05 1 015.0 33.2 0.033 53 黄门岛 7.18 3.89 1 417.3 24.2 0.020 114 姜山岛 40.24 1.12 4 951.2 22.4 0.012 115 龙母屿 2.88 8.14 993.3 20.8 0.034 102 表 2 平潭5个无居民海岛种子植物物种分类群统计
Table 2 Statistics of vascular plant species taxa of 5 uninhabited islands in Pingtan
分类群
Plant taxon科数(占比)
No. of families(Percentage / %)属数(占比)
No. of genera(Percentage / %)种数(占比)
No. of species(Percentage / %)裸子植物 1(1.41) 1(0.56) 1(0.47) 被子植物 70(98.59) 178(99.44) 212(99.53) 双子叶植物 61(85.92) 146(81.56) 165(77.46) 单子叶植物 10(14.08) 33(18.44) 48(22.54) 合计 71(100) 179(100) 213(100) 表 3 平潭5个无居民海岛种子植物种子植物生活型统计
Table 3 Statistics of life forms of seed plants of 5 uninhabited islands in Pingtan
生活型
Life form种数
No. of species占总种数的百分比
Account of total species / %乔木 常绿 2 1.17 落叶 5 2.92 灌木 常绿 31 18.13 落叶 17 9.94 藤本 常绿木质藤本 5 2.92 落叶木质藤本 4 2.34 多年生草质藤本 5 2.92 草本 一年生 37 21.64 二年生 7 4.09 多年生 58 33.92 合计 171 100 表 4 平潭5个无居民海岛科、属、种的分布区类型统计
Table 4 Distribution pattern statistics of vascular plants families, genera and species on five uninhabited islands in Pingtan
分布区类型及其变型
Distribution types and variants科
Families属
Genera种
Species数量
No.占比
Percentage / %数量
No.占比
Percentage / %数量
No.占比
Percentage / %1. 世界分布 29 – 15 – 7 – 2. 泛热带分布 23 63.89 52 40.00 16 9.76 2-1. 热带亚洲-大洋洲和热带美洲分布 1 2.78 2 1.54 1 0.61 2-2. 热带亚洲、非洲和南美洲间断分布 1 2.78 4 3.08 5 3.05 2S. 以南半球为主的泛热带 1 2.78 0 0 0 0 3. 热带亚洲和热带美洲间断分布 1 2.78 4 3.08 7 4.27 4. 旧世界热带分布 1 2.78 14 10.77 6 3.66 4-1. 热带亚洲、非洲和大洋洲间断或星散分布 0 0 2 1.54 3 1.83 5. 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布 0 0 8 6.15 19 11.59 6. 热带亚洲至热带非洲 0 0 2 1.54 4 2.44 7. 热带亚洲(印度-马来西亚)分布 0 0 2 1.54 29 17.68 8. 北温带分布 4 11.11 14 10.78 7 4.27 8-4. 北温带和南温带(全温带)间断分布 3 8.33 3 2.31 3 1.83 9. 东亚和北美洲间断分布 0 0 6 4.62 4 2.44 10. 旧世界温带分布 0 0 4 3.08 4 2.44 10-1. 地中海区、西亚(或中亚)和东亚间断分布 0 0 3 2.31 1 0.61 10-3. 欧亚和南部非洲(有时也在大洋洲)间断分布 0 0 1 0.77 0 0 11. 温带亚洲 0 0 0 0 17 10.37 14. 东亚分布 1 2.78 7 5.38 14 8.54 14-1. 中国-喜马拉雅(SH) 0 0 0 0 3 1.83 14-2. 中国-日本(SJ) 0 0 1 0.77 9 5.49 15. 中国特有分布特有 0 0 1 0.77 12 7.32 合计 65 100 145 100 171 100 表 5 平潭与其他地区无居民海岛种子植物属的分布区类型比较
Table 5 Comparison of distribution types of seed flora and genera among five uninhabited islands in Pingtan and different island regions
分布区
类型
Distribution type平潭(5个)
Pingtan (5)
(25°15′~25°45′N)厦门近岸
Xiamen
(24°25′~24°35′N)连江(5个)
Lianjiang (5)
(26°07′~26°27′N)浙江(5个)
Zhejiang (5)
(28°12′~28°18′N)渤海(9个)
Bohai Sea
(37°06′~40°55′N)1 10.34 9.35 10.90 12.34 16.67 2 40.00 29.50 36.05 24.03 24.71 3 2.76 11.87 7.48 1.30 0.00 4 11.03 8.63 8.16 7.14 4.71 5 5.52 8.99 6.80 5.19 2.35 6 1.38 6.83 4.08 5.19 3.53 7 1.38 7.19 5.44 3.25 3.53 8 11.72 7.91 13.60 23.38 30.59 9 4.14 3.24 4.08 4.55 5.88 10 5.52 2.16 5.44 4.55 9.41 11 0.00 0.00 0.68 0.64 5.88 12 0.00 0.36 0.00 0.00 2.35 13 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 14 5.52 3.60 8.16 8.44 4.71 15 0.69 0.36 0.00 0.00 2.35 R/T 2.31 4.23 2.13 1.11 0.66 注:1,世界广布;2,泛热带分布;3,热带亚洲和热带美洲分布;4,旧世界热带分布;5,热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布;6,热带亚洲至热带非洲分布;7,热带亚洲分布;8,北温带分布;9,东亚和北美间断分布;10,旧世界温带分布;11,温带亚洲分布;12,地中海及西亚至中亚分布;13,中亚分布;14,东亚分布;15,中国特有分布。 Notes: 1, Cosmopolitan; 2, Pantropic; 3, Tropical Asia & tropical America disjunct; 4, Old world tropical distributed; 5, Tropical Asia to tropical Australasia distributed; 6, Tropical Asia to tropical Africa distributed; 7, Tropical Asia distributed; 8, North temperate distributed; 9, East Asia & North America disjunct; 10, Old world temperate distributed; 11, Temperate Asia; 12, Mediterranea, West Asia to Central Asia; 13, Central Asia; 14, East Asia distributed; 15, Endemic to China. -
[1] 邹永广,郑向敏. 国内无居民海岛保护与利用研究进展[J]. 经济地理,2013,33(3):176−179. Zou YG,Zheng XM. A review and prospect of research on uninhabited island protection and utilization in China[J]. Economic Geography,2013,33(3):176−179.
[2] 周学锋. 基于建设海洋强国的无居民海岛管理研究[J]. 经济地理,2014,34(1):28−34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8462.2014.01.005 Zhou XF. Management of uninhabited islands based on the construction of strong marine country[J]. Economic Geography,2014,34(1):28−34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8462.2014.01.005
[3] 何雅琴,陈国杰,曾纪毅,肖集泓,邓传远. 平潭大练岛种子植物区系研究[J]. 西南林业大学学报,2022,42(1):37−50. He YQ,Chen GJ,Zeng JY,Xiao JH,Deng CY. Research on seed plant flora of Dalian Island in Pingtan[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University,2022,42(1):37−50.
[4] 肖兰,董标,张琳婷,邓传远,李霞,等. 渤海区无居民海岛植物物种丰富度分布格局[J]. 生物多样性,2022,30(4):21231. doi: 10.17520/biods.2021231 Xiao L,Dong B,Zhang LT,Deng CY,Li X,et al. Distribution pattern of plant species richness of uninhabited islands in the Bohai Sea area[J]. Biodiversity Science,2022,30(4):21231. doi: 10.17520/biods.2021231
[5] 张凯迪,魏艳艳,龚元,郭智娟,赵敏. 浙江沿海无居民海岛植物群落物种组成及多样性[J]. 地球环境学报,2019,10(1):58−68. Zhang KD,Wei YY,Gong Y,Guo ZJ,Zhao M. Floristic composition and diversity of plant communities of the five nonresidential coastal islands of Zhejiang,China[J]. Journal of Earth Environment,2019,10(1):58−68.
[6] 魏艳艳,张凯迪,徐良,赵敏,刘冬燕. 浙江省无居民海岛植物与土壤pH值和养分的关系[J]. 东北林业大学学报,2019,47(11):81−85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2019.11.016 Wei YY,Zhang KD,Xu L,Zhao M,Liu DY. Relationship between plant,and soil pH and nutrients in non-residential islands[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2019,47(11):81−85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2019.11.016
[7] 郑建忠,靳莎,魏凯,邓传远. 平潭无居民海岛外来入侵植物特征分析[J]. 生物安全学报,2023,32(4):348−355. Zheng JZ,Jin S,Wei K,Deng CY. Analysis on the characteristics of invasive alien plants in the uninhabited islands of Pingtan[J]. Journal of Biosafety,2023,32(4):348−355.
[8] 常岭,谭春兰,朱清澄. 无居民海岛开发利用适宜性评价—以上海市九段沙岛为例[J]. 海洋开发与管理,2021,38(3):91−96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2021.03.016 Chang L,Tan CL,Zhu QC. Suitability evaluation of exploitation and utilization in uninhabited islands:a case study in Jiuduansha island of Shanghai[J]. Ocean Development and Management,2021,38(3):91−96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2021.03.016
[9] 傅世锋,吴海燕,蔡晓琼,潘翔,吴剑,陈鹏. 中国无居民海岛开发利用管理现状、问题和对策[J]. 应用海洋学学报,2021,40(4):728−734. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2021.04.021 Fu SF,Wu HY,Cai XQ,Pan X,Wu J,Chen P. Problems and countermeasures of recent development and utilization of uninhabited islands in China[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography,2021,40(4):728−734. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2021.04.021
[10] 吴奕彪,傅世锋,吴海燕,陈凤桂,蔡晓琼,等. 福州市无居民海岛开发利用强度评价及自然地理影响因子[J]. 中国环境科学,2023,43(5):2531−2541. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2023.05.045 Wu YB,Fu SF,Wu HY,Chen FG,Cai XQ,et al. Evaluation of development and utilization intensity of uninhabited islands and geographical influencing factors in Fuzhou[J]. China Environmental Science,2023,43(5):2531−2541. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2023.05.045
[11] 蔡晓禾,廖廓. 福建平潭大风气候特征分析[J]. 闽江学院学报,2011,32(5):130−133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7821.2011.05.031 Cai XH,Liao K. Analysis of climatic characteristics for gale in Pingtan of Fujian[J]. Journal of Minjiang University,2011,32(5):130−133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7821.2011.05.031
[12] 福建植物志编辑委员会. 福建植物志[M]. 福州:科学技术出版社,1959:113−275. [13] 马金双. 中国入侵植物名录[M]. 北京:高等教育出版社,2013:1−299. [14] 吴征镒,周浙昆,李德铢,彭华,孙航. 世界种子植物科的分布区类型系统[J]. 云南植物研究,2003,25(3):245−257. Wu ZY,Zhou ZK,Li DZ,Peng H,Sun H. The areal-types of the world families of seed plants[J]. Acta Botanica Yunnanica,2003,25(3):245−257.
[15] 吴征镒. 中国种子植物属的分布区类型[J]. 云南植物研究,1991(S4):1−139. Wu ZY. The areal-types of Chinese genera of seed plants[J]. Acta Botanica Yunnanica,1991(S4):1−139.
[16] 张镱锂. 植物区系地理研究中的重要参数——相似性系数[J]. 地理研究,1998,17(4):429−434. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.1998.04.014 Zhang YL. Coefficient of similarity:an important parameter in floristic geography[J]. Geographical Research,1998,17(4):429−434. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.1998.04.014
[17] 朱晓旭,温仲明,郑诚,高原,张格语,等. 延河流域不同生活型植物功能性状特征及其对环境变化的响应[J]. 水土保持研究,2023,30(6):328−336. Zhu XX,Wen ZM,Zheng C,Gao Y,Zhang GY,et al. Functional traits of plant life forms and their responses to environmental factors in the Yanhe River Basin[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2023,30(6):328−336.
[18] 张静,才文代吉,谢永萍,李德凯,李海燕,孙海群. 三江源国家公园种子植物区系特征分析[J]. 西北植物学报,2019,39(5):935−947. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2019.05.0935 Zhang J,Caiwen DJ,Xie YP,Li DK,Li HY,Sun HQ. Characteristics on the flora of seed plants in Sanjiangyuan National Park[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2019,39(5):935−947. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2019.05.0935
[19] 曾纪毅,何雅琴,谢艳秋,邓传远. 平潭六个无居民海岛野生植物物种组成及功能性状研究[J]. 四川林业科技,2021,42(6):75−81. Zeng JY,He YQ,Xie YQ,Deng CY. Species composition and functional traits of wild plants in six uninhabited islands of Pingtan district[J]. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology,2021,42(6):75−81.
[20] 陈征海,唐正良,裘宝林. 浙江海岛植物区系的研究[J]. 云南植物研究,1995,17(4):405−412. Chen ZH,Tang ZL,Chiu PL. A study on the flora of the islands of Zhejiang Province[J]. Acta Botanica Yunnanica,1995,17(4):405−412.
[21] 刘利. 中国沿海主要岛屿植物区系的性质及其相互关系与分布格局[J]. 西北植物学报,2015,35(8):1676−1682. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2015.08.1676 Liu L. Phytogeographical patterns,relationships and characters of coastal islands in China[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2015,35(8):1676−1682. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2015.08.1676
[22] 姜必亮,张宏达. 福建种子植物区系地理研究[J]. 广西植物,2000,20(2):117−125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3142.2000.02.003 Jiang BL,Zhang HD. Floristic study of spermatophyte of Fujian Province[J]. Guihaia,2000,20(2):117−125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3142.2000.02.003
[23] 郑建忠,靳莎,邓传远. 平潭北香炉屿种子植物区系及功能性状特征[J]. 北华大学学报(自然科学版),2022,23(5):660−667. Zheng JZ,Jin S,Deng CY. Flora and functional traits of seed plants in Beixianglu Island,Pingtan[J]. Journal of Beihua University (Natural Science),2022,23(5):660−667.
[24] 叶志勇. 福建平潭岛种子植物区系地理及外来植物对其影响[J]. 广西植物,2017,37(3):280−293. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201605040 Ye ZY. Flora of seed plants in Pingtan Island,Fujian and effects of exotic plants[J]. Guihaia,2017,37(3):280−293. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201605040
[25] 肖兰,张琳婷,杨盛昌,郑志翰,姜德刚. 厦门近岸海域无居民海岛植物区系和物种组成相似性[J]. 生物多样性,2018,26(11):1212−1222. doi: 10.17520/biods.2018124 Xiao L,Zhang LT,Yang SC,Zheng ZH,Jiang DG. Flora and species composition similarity of the uninhabited islands in the nearshore Xiamen[J]. Biodiversity Science,2018,26(11):1212−1222. doi: 10.17520/biods.2018124
[26] Kerr JT,Packer L. Habitat heterogeneity as a determinant of mammal species richness in high-energy regions[J]. Nature,1997,385(6613):252−254. doi: 10.1038/385252a0
[27] Webb CO,Ackerly DD,McPeek MA,Donoghue MJ. phylogenies and community ecology[J]. Annu Rev Ecol Syst,2002,33:475−505. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.33.010802.150448
[28] 魏凯. 平潭6个无居民海岛植物群落特征及优势种滨柃(Eurya emarginata)叶片解剖研究[D]. 福州:福建农林大学,2021:17−20. [29] 苏晓飞,袁金凤,胡广,徐高福,于明坚. 千岛湖陆桥岛屿植物群落结构的边缘效应[J]. 应用生态学报,2014,25(1):77−84. Su XF,Yuan JF,Hu G,Xu GF,Yu MJ. Edge effect of the plant community structure on land-bridge islands in the Thousand Island Lake[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2014,25(1):77−84.
[30] 谢艳秋,黄晖,王春晓,何雅琴,江怡萱,等. 福建海岛滨海特有植物种-面积关系及物种丰富度决定因素[J]. 生物多样性,2023,31(5):22345. doi: 10.17520/biods.2022345 Xie YQ,Huang H,Wang CX,He YQ,Jiang YX,et al. Determinants of species-area relationship and species richness of coastal endemic plants in the Fujian islands[J]. Biodiversity Science,2023,31(5):22345. doi: 10.17520/biods.2022345
[31] 吴端聪,肖兰,张琳婷,刘建辉,陈淳,邓传远. 平潭周边海岛植物丰富度、相似度与岛屿空间特征的关系[J]. 亚热带农业研究,2020,16(1):35−41. Wu DC,Xiao L,Zhang LT,Liu JH,Chen C,Deng CY. Relationship between plant richness,similarity,and spatial characteristics of islands around Pingtan[J]. Subtropical Agriculture Research,2020,16(1):35−41.
[32] 张恒庆,唐丽丽,张晓明,李雪,邢军. 大连市5个海岛野生维管束植物多样性研究[J]. 辽宁大学学报(自然科学版),2015,42(4):372−377. Zhang HQ,Tang LL,Zhang XM,Li X,Xing J. Wild vascular plants diversity on five islands,Dalian[J]. Journal of Liaoning University (Natural Science Edition),2015,42(4):372−377.
[33] 徐河山,马丹炜. 鼓浪屿岛种子植物分布区类型初步研究[J]. 四川师范大学学报(自然科学版),2016,39(4):588−592. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8395.2016.04.024 Xu HS,Ma DW. The seed plants areal types in Gulangyu island of Fujian[J]. Journal of Sichuan Normal University (Natural Science),2016,39(4):588−592. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8395.2016.04.024
[34] 刘翔宇,赵慈良,许洺山,梁启明,朱晓彤,等. 中国东部海岛维管植物的beta多样性及其驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性,2019,27(4):380−387. doi: 10.17520/biods.2018235 Liu XY,Zhao CL,Xu MS,Liang QM,Zhu XT,et al. Beta diversity of vascular plants and its drivers in sea-islands of eastern China[J]. Biodiversity Science,2019,27(4):380−387. doi: 10.17520/biods.2018235
[35] 张坚强,张琳婷,赵东铭,吴端聪,白珮珮,邓传远. 珠海淇澳岛次生植被特征及物种多样性[J]. 西北植物学报,2019,39(1):173−184. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2019.01.0173 Zhang JQ,Zhang LT,Zhao DM,Wu DC,Bai PP,Deng CY. Characteristics and species diversity of secondary vegetation on Qi'ao Island,Zhuhai[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2019,39(1):173−184. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2019.01.0173
[36] Yang Q,Weigelt P,Fristoe TS,Zhang ZJ,Kreft H,et al. The global loss of floristic uniqueness[J]. Nat Commun,2021,12(1):7290. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27603-y
[37] 郭亚男,王瑞江. 华南地区外来入侵和归化植物分析[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报,2023,31(5):715−726. Guo YN,Wang RJ. Analysis on the alien invasive and naturalized plants in south China[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany,2023,31(5):715−726.
-
其他相关附件
-
PDF格式
毛玥 附表1、附表2 点击下载(32KB)
-



 下载:
下载: