Niche and interspecific associations of main species in the Acacia confusa Merr. community shrub layer in Fuying Island, Xiapu County
-
摘要:
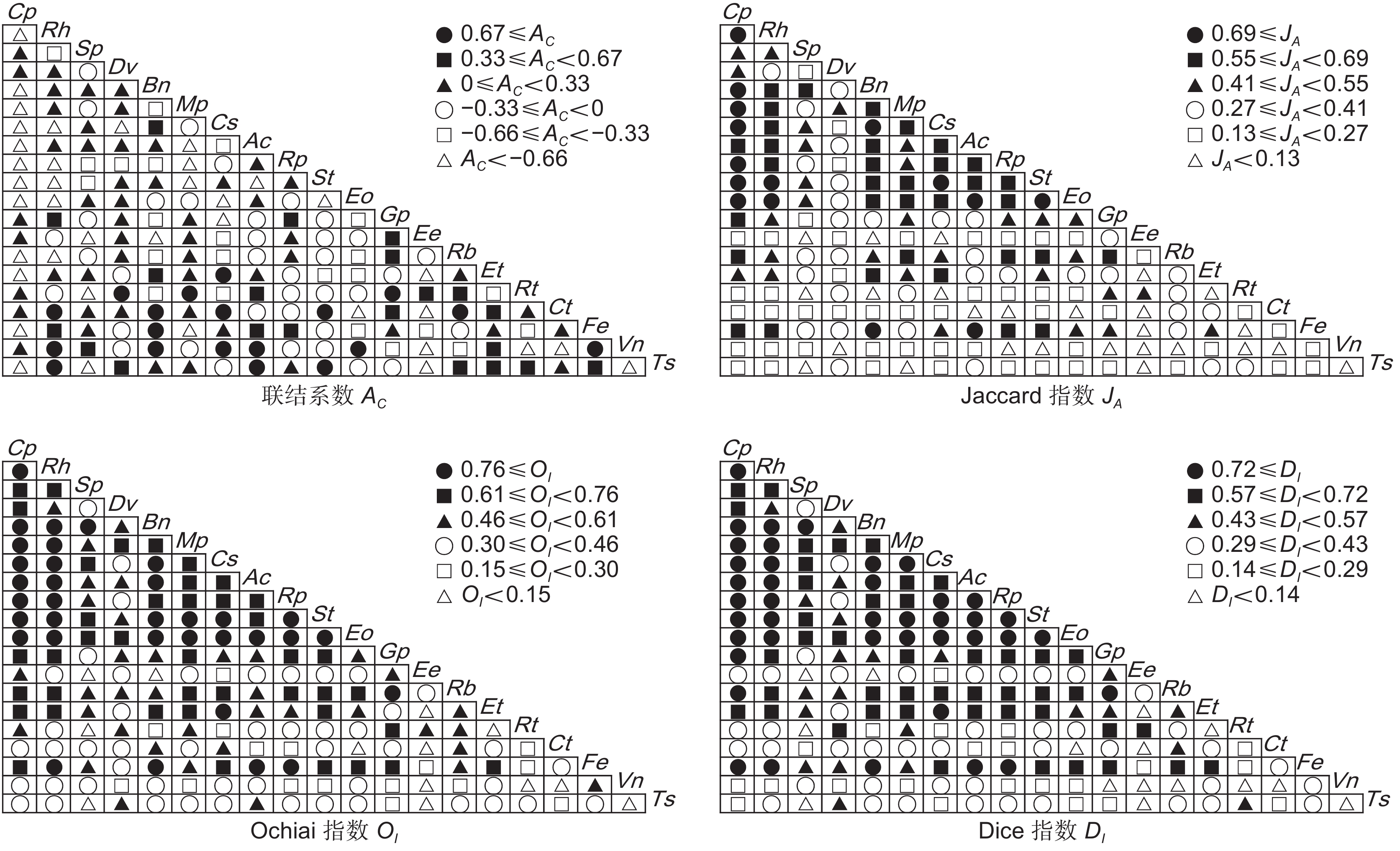
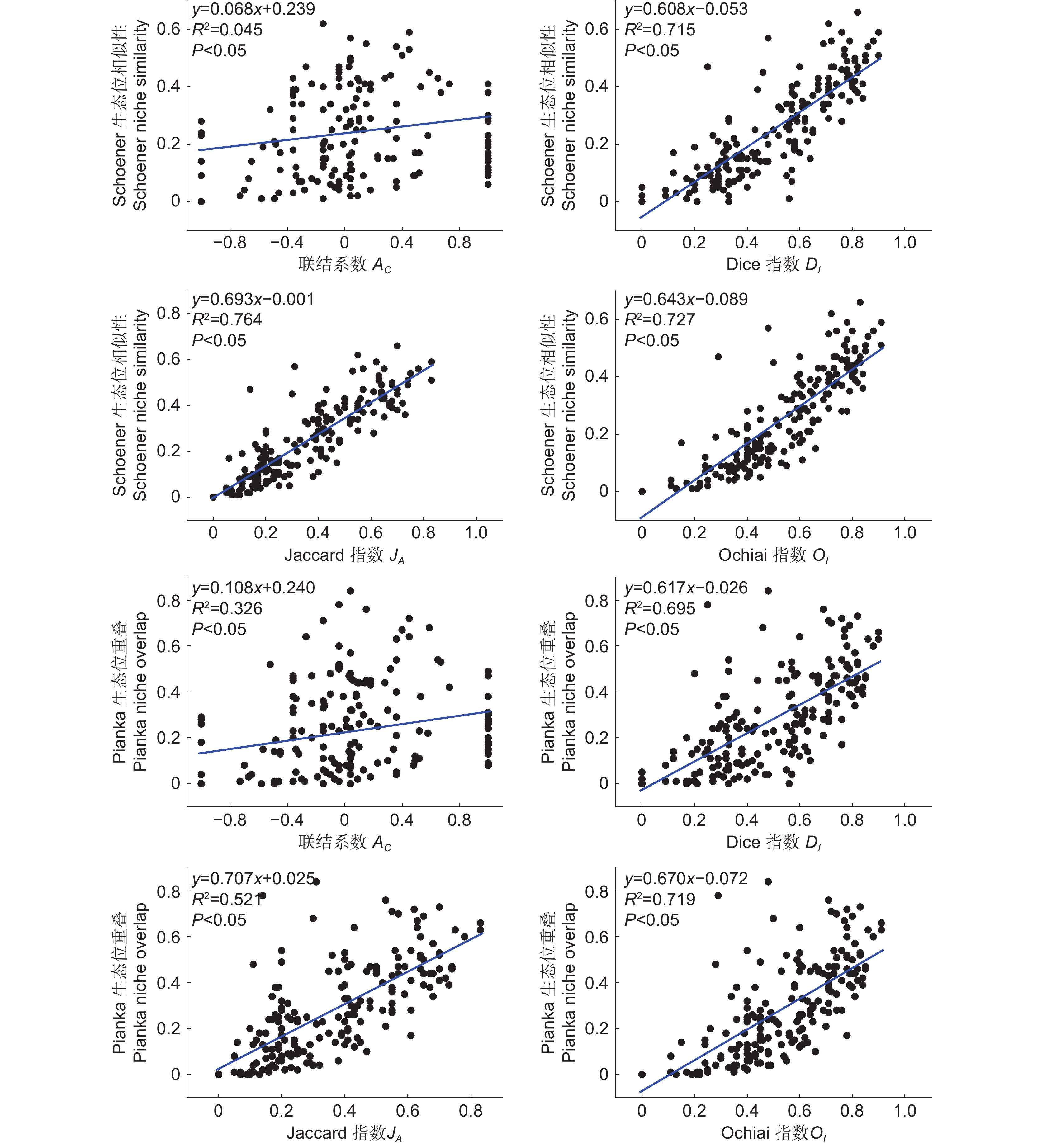
台湾相思(Acacia confusa Merr.)林是霞浦浮鹰岛主要森林群落,为探究其演替动态和共存机制,基于典型样方法,采用生态位测度、方差比率法(VR)、χ2检验和AC联结系数(AC)、Jaccard系数(JA)、Ochiai系数(OI)、Dice系数(DI)检验等方法,对霞浦浮鹰岛台湾相思群落样方灌木层的主要物种生态位与种间联结进行研究。结果显示:(1)杜虹花(Callicarpa pedunculata R. Br.)的重要值和生态位宽度均为最大,在群落灌木层中占据绝对优势。(2)台湾相思群落灌木层主要物种间的生态位相似性和生态位重叠均较小,各物种对资源利用比较充分。(3)物种的生态位宽度越大,其生态位相似性和生态位重叠程度也越高,但不存在绝对的正相关。(4)台湾相思群落灌木层的主要物种总体联结性表现为不显著负联结,群落仍处于动态演替不稳定阶段。(5)种对间正负联结比为0.98,几种联结检验显著率均较低,其种对间联结程度较弱,物种竞争不激烈。(6)联结系数AC、JA、OI、DI指数与生态位相似性和生态位重叠程度之间均呈显著正相关,种间联结越强,其生态位相似性和生态位重叠程度也越高。研究结果表明,霞浦浮鹰岛台湾相思群落灌木层主要物种对环境资源利用较充分,大部分物种间竞争较弱,台湾相思幼苗未能占据绝对优势,群落稳定性较差,存在逆向演替可能,应适当采取人工抚育手段。
Abstract:Acacia confusa Merr. is the dominant forest type on Fuying Island in Xiapu County, China. This study investigated the niche characteristics and interspecific associations of the main species in the A. confusa community shrub layer using data from 92 shrub plots. Niche analysis was conducted using Levins niche breadth (BL), Shannon niche breadth (BS), Schoener niche similarity (Cik), and Pianka niche overlap (Oik). Interspecific associations were examined using the variance ratio (VR), χ2 test, and association (AC), Ochiai (OI), Dice (DI), and Jaccard (JA) coefficients. Results showed that: (1) Among the 20 species analyzed, Callicarpa pedunculata R. Br. exhibited the largest niche breadth and held an absolute competitive advantage in the community. (2) Niche similarity and overlap among species in the shrub layer were low, suggesting efficient resource utilization by each species. (3) Greater niche breadth showed a general correspondence to higher niche similarity and overlap, although this relationship did not show an absolute positive correlation. (4) The W test revealed that the overall interspecific associations were insignificantly negative, reflecting a dynamic stage of succession with instability. (5) The ratio of positive to negative associations among species was 0.98, and the low significance rates across multiple association tests indicated weak interspecific associations and limited competition. (6) The AC, JA, OI, and DI coefficients showed significantly positive correlations with niche similarity and overlap, indicating that stronger positive associations corresponded to greater niche similarity and overlap among species. These findings suggest that the main shrub species within the A. confusa community efficiently utilize environmental resources, with relatively weak interspecies competition. However, young A. taiwanensis trees failed to establish a dominant position in the community. The overall stability of the community is low, with potential for reverse succession. Therefore, targeted artificial management strategies should be adopted.
-
Keywords:
- Xiapu County /
- Acacia confusa forest /
- Niche /
- Interspecific association
-
森林空间结构是根据林木的空间位置和属性,来描述林木间相互关系的空间排列方式。而林木个体的空间分布状态,即分布格局,是研究林木在水平空间相互关系的重要指标,同时也是空间结构的基本特征之一[1]。分布格局的研究方法主要有样方法和距离法,但两种方法均存在局限性。
1999年,有学者提出了由参照树和相邻木组成的描述林分空间结构单元的方法[2]。该方法把林区内任意一棵树和距其最近的4棵相邻树组成的结构小组称为林分空间结构单元。角尺度(Wi)就是基于林分空间结构单元所构建的一个参数,用于描述林木的分布格局[3]。角尺度法主要是通过判断由参照树和相邻木构成的夹角大小,来判断相邻木围绕参照树的均匀性。该方法既可以通过图形来判断分布格局,也可以通过数值来判断,其操作方便,计算简单[4]。林木分布格局在林木和森林的生长演替过程中均发挥直接作用。因此,通过分析森林林分整体的角尺度分布特征,能有效地确定林分演替阶段,了解林分的稳定性。同时,对优势种分布格局进行分析,还能了解优势种与其他物种的关系,如竞争、共生、互助等。
随机木是指Wi=0.50的林木,随机木对应的结构单元称为随机体。该概念是Zhang和Hui[5]在2021年基于角尺度参数提出的。随机木在反映林分整体树种组成和竞争情况等方面具有重要作用。研究发现,随机体比例在天然林中不受地域分布、树种组成、林分结构、格局类型和树木竞争的影响,并由此提出了“随机体-稳定性”假说[6]。但在喀斯特区域,因其特有的“富钙、干旱、瘠薄”等异质生境,加之喀斯特复杂的地质地貌和环境因素,使其成为环境异质性与生物物种多样性的独特响应区。因此,生境异质性强的喀斯特地区天然林中,“随机体-稳定性”假说是否仍然成立,还有待检验。Li等[7]分析了喀斯特地区土壤和岩石两种立地上,不同径阶树木群体以及每种立地上两种生活型树木的随机体分布特征,结果发现随机体的比例和分布受生活型和生境异质性的影响,而与树的大小无关。然而,先前对于随机体在喀斯特地区影响因素的分析,均是以尺度较小的样地作为研究对象,在更大的森林样地尺度中,生活型是否对随机体有影响还不清楚。生境异质性的产生主要有两个原因,一是组成生境的能量和物质在时间或空间上的差异,如生物因素、水分状况等[8],二是区域生态系统运动发展的不平衡性[9]。而不同的环境因子在喀斯特地区中对随机体的影响还未知。此外,立地条件对于林木生长也是一个重要因素[10]。因此,研究喀斯特生境中不同因子对随机体的影响差异具有重要意义。
我国桂西南地区是北热带喀斯特季节性雨林的重要分布区之一,不但包含了从山顶到山坡到洼地的各种地形要素,还包含了水平方向上的高异质性以及垂直方向上的多层性,形成了一系列典型的“峰丛-洼地”生境类型[11, 12]。在喀斯特岩溶山地的地形地貌中,存在着复杂多样的小生境,这些小生境受不同因素的影响而呈现出多样性。此外,在不同的地段、坡向和坡位上,小生境的资源分配和植物组成等方面均存在明显差异。本文基于弄岗喀斯特季节性雨林15-hm2样地的第2次复查数据,从林分整体和优势种角尺度分布特征,以及生活型、生物因子和地形因子对随机体的影响进行分析。研究旨在探讨:(1)基于北热带喀斯特季节性雨林相邻木林分整体和优势种的随机体分布特征;(2)不同生活型树种在空间尺度较大的喀斯特生境中对随机体是否有影响;(3)北热带喀斯特季节性雨林不同环境因子对随机体的影响差异。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 研究区概况
弄岗国家级自然保护区地处广西龙州县与宁明县的交界地带,分弄岗、隆呼、陇瑞3个区,总面积为10 077 hm2。保护区土壤类型为原始石灰土、棕色石灰土、黑色石灰土等。年降水集中在5-9月,降水量分布不均匀,干湿交替较强;年平均温度22 ℃,最低温度13 ℃,最高温度37 ℃~39 ℃。
1.2 样地设置与调查
北热带喀斯特季节性雨林地处弄岗自然保护区弄岗片的弄姆皇(22°25′N,106°57′E)。整个样地南北宽300 m,东西长500 m,海拔为180~370 m,平均海拔260 m,样地坡度范围在3.7°~78.9°,平均坡度41.7°。整个样地生境多样化,属于喀斯特“峰丛-洼地”典型的生境类型,在中国森林生物多样性监测网络中,该样地是唯一的典型热带喀斯特森林监测样地。
根据CTFS全球森林生物多样性监测标准,利用全站仪将15-hm2样地划分成1 500个10 m×10 m的样方。在此基础上,于2011年完成了首次植被调查,对样方内胸径(DBH)≥1 cm个体的名称、胸径、坐标及生长状态等进行了调查并记录。之后,每5年进行一次调查,并于2021年完成第2次复查。本文以2021年的复查数据为依据,选取DBH≥5 cm的个体作为研究对象。
1.3 树种优势度的计算
树种优势度(Dsp)指树种在林分中的数量优势度和空间上的优势度,选取优势度位于前10的物种作为优势种,Dsp的计算公式为:
Dsp=√Dg⋅(1−¯Usp) (1) 式中,Dg表示相对显著度,
ˉUsp 表示树种大小比数均值。Dsp接近1表示非常优势,接近0表示几乎没有优势[13]。树种大小比数均值表达式如下:
¯Usp=1Nsp∑Nspi=1Ui (2) 式中,Nsp表示所观察树种的参照树数量,Ui为树种的第i株树的大小比数值。
1.4 角尺度计算
角尺度(Wi)指的是参照树与4株最近邻木间小于标准角的夹角占比,用下式表示[3]:
Wi=1n∑nj=1Zij (3) 其中:Zij=
1{1(当j个角小于标准角α0)0(否则) 式中,Wi为参照树i的角尺度,n指相邻木个体数,n=4。Zij为参照树i与其相邻木j之间的第j个夹角α与标准角α0之间的大小关系,有两种可能的值,当Zij=1时,表明第j个α角小于标准角,当Zij=0时,表明第j个α角大于标准角。
角尺度均值(
¯W )能够反映一个林分整体的分布情况。其计算公式如下:¯W=1N∑Niwi (4) 优势种角尺度均值用下式表示:
¯Wsp=1Nsp∑Nspi=1 (5) 式中,N为样地林木总株数。当角尺度均值在[0.457,0.517]时为随机分布;大于0.517为聚集分布;小于0.475为均匀分布[14]。角尺度等于0.50的林木被称为随机木,相应林木的结构单元称为随机体[15]。角尺度为0.75或1的林木为聚集木,相应林木结构单元称为聚集体。角尺度为0或0.25的林木被称作均匀木,相应林木的结构单元被称作均匀体。本研究在计算林分整体和优势种角尺度时,设置了5 m缓冲区,并将缓冲区内的林木做相邻木处理,以此消除林木的边缘效应造成的影响。
1.5 Pearson 相关分析
运用Pearson相关分析法,判断随机体与环境因子及环境因子间的相关性。相关系数r计算公式如下:
r=∑(x−ˉx)−(y−ˉy)∑(x−ˉx)2∑(y−ˉy)2 (6) r取值范围为−1~1,当|r|≥0.8,表示两者高度相关;0.5≤|r|<0.8,为中度相关;0.3≤|r|<0.5,表示低相关;当|r|<0.3,表示相关性非常微弱,可视为没有相关性,P<0.05表明有统计学意义。
1.6 环境因子获取
用全站仪获取精确海拔数据,计算每个20 m×20 m样方的平均海拔、坡向、坡度和凹凸度4个地形指标[16-18]。土壤湿度状况以地形湿润指数和干旱度指数为表征,参见Punchi-Manage等[19]的研究。样地内岩石裸露情况采用踏查法进行评估。综上共有7个地形因子。此外,还考查了每个样方内最大胸径、胸高断面积之和、植株个体数和平均胸径4个生物因子,共11个环境因子。
1.7 冗余分析
冗余分析的响应变量由每个样方的随机体个数组成。为了消除林木边缘效应的影响,设置2 m缓冲区,缓冲区内的林木做相邻木处理。解释变量数据包括11个环境因子。冗余分析前,对数据进行标准化处理,并比较自变量的相关系数是否大于7,以此衡量自变量间的共线性。再计算每个变量的方差膨胀因子,当方差膨胀因子<10时,表示无明显的共线性问题[20],可进行冗余分析。采用层次分割方法对冗余分析结果进行变差分解,以获取每个解释变量的校正解释率。
1.8 数据处理
数据分析计算均利用R 4.3.1软件完成,冗余分析在vegan程序包中进行,层次分割采用rdacca.hp程序包[21],利用ForestSAS程序包计算角尺度和大小比数均值[22],Pearson相关系数图在corrplot包中绘制,角尺度分布特征图在ggplot2包中完成,单独效应比例图在Origin 2021软件中绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 林分整体和优势种随机体的比例和分布特征
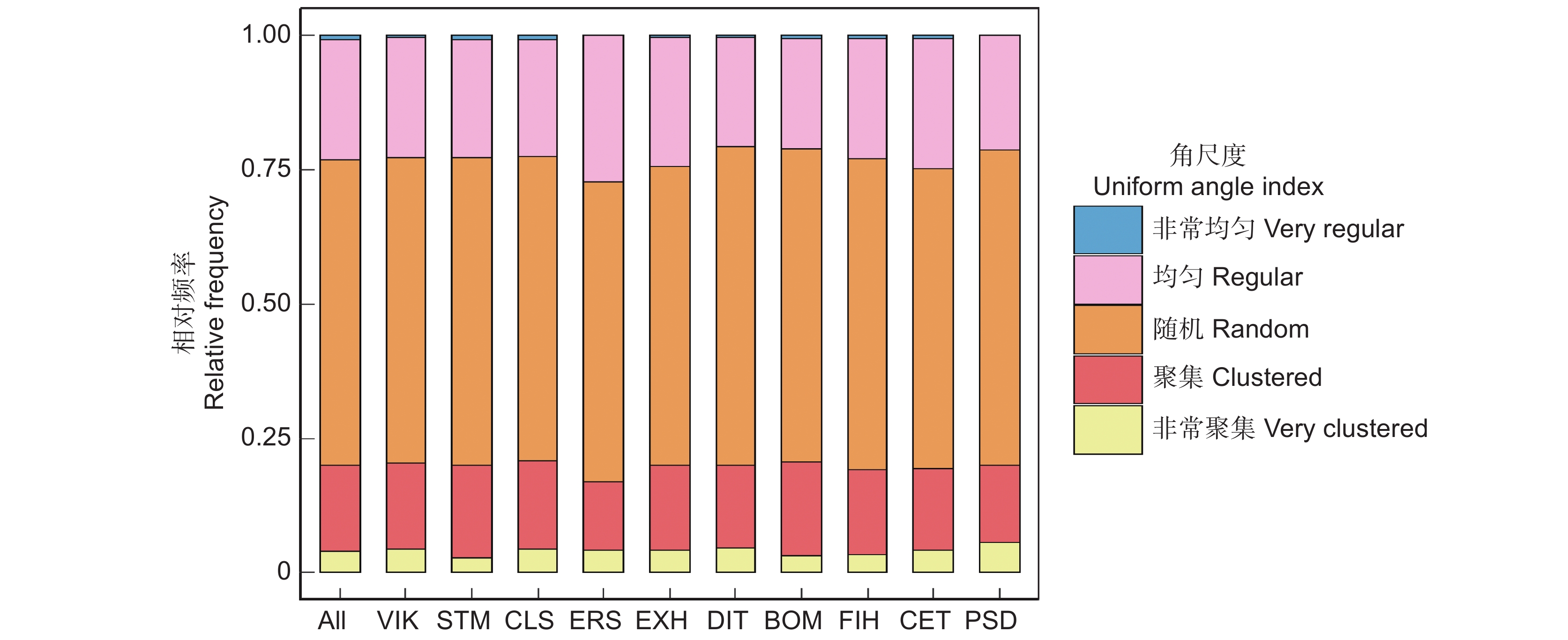
树种优势度位于前10的物种在森林中起关键作用,尤其是闭花木(Cleistanthus sumatranus (Miq.) Muell. Arg.)、苹婆(Sterculia monosperma Ventenat)和广西牡荆(Vitex kwangsiensis P'ei),不仅在数量上占林分整体的绝大多数,其优势度也是最高的,分别为0.262、0.260、0.245,其他树种的优势度均小于0.200。角尺度计算结果表明,林分整体和优势种角尺度均值都在随机分布范围内(表1)。但林分整体和优势种随机木的分布频率均超过0.5,而均匀木和聚集木分布频率均比随机木低,说明样地中大多数林木的最近相邻木处于随机分布,各个优势种的最近相邻木处于随机分布的也占大多数,即随机体占绝对分布(图1)。
表 1 北热带喀斯特季节性雨林树种优势度排名前10的树种Table 1. Top 10 dominant species in northern tropical karst seasonal rainforest树种
Species科名
Family株数
Number of
plants大小比数
Dominance相对显著度
Relative
significance优势度
Advantage
degree角尺度
Uniform angle
index广西牡荆
Vitex kwangsiensis P'ei唇形科 1 645 0.325 0.122 0.286 0.504 苹婆
Sterculia monosperma Ventenat梧桐科 2 426 0.491 0.134 0.262 0.498 闭花木
Cleistanthus sumatranus (Miq.) Muell. Arg.大戟科 3 054 0.530 0.139 0.256 0.504 劲直刺桐
Erythrina stricta Roxb.豆科 242 0.074 0.031 0.171 0.485 蚬木
Excentrodendron tonkinense (A. Chev.)
H. T. Chang et R. H. Miau锦葵科 483 0.367 0.039 0.156 0.498 海南椴
Diplodiscus trichosperma (Merrill) Y. Tang锦葵科 456 0.317 0.033 0.150 0.509 黄梨木
Boniodendron minus (Hemsl.) T. Chen无患子科 404 0.314 0.026 0.133 0.506 对叶榕
Ficus hispida L. f.桑科 676 0.602 0.031 0.110 0.497 假玉桂
Celtis timorensis Span大麻科 414 0.509 0.020 0.099 0.495 鱼骨木
Psydrax dicocca Gaertn.茜草科 252 0.405 0.015 0.094 0.510 林分整体 − 10 052 0.489 − − 0.500 ![]() 图 1 北热带喀斯特季节性雨林林分整体和优势种角尺度分布特征All :林分整体 ;VIK :广西牡荆 ;STM :苹婆;CLS: 闭花木 ; ERS :劲直刺桐; EXH :蚬木 ; DIT :海南椴 ;BOM :黄 梨木 ; FIH :对叶榕 ;CET :假玉桂 ;PSD :鱼骨木。Figure 1. Uniform angle index distribution characteristics of overall stand and dominant species in northern tropical karst seasonal rainforestAll: Entire stand; VIK: Vitex kwangsiensis C. P'ei; STM: Sterculia monosperma Vent; CLS: Cleistanthus sumatranus (Miq.) Müll. Arg.; ERS: Erythrina stricta Roxb.; EXH: Excentrodendron hsienmu (A. Chev.) H. T. Chang et R. H. Miao; DIT: Diplodiscus trichospermus (Merr.) Y. Tang, M. G. Gilbert et Dorr; BOM: Boniodendron minus (Hemsl.) T.C. Chen; FIH: Ficus hispida L. f.; CET: Celtis timorensis Span.; PSD: Psydrax dicocca Gaertn.
图 1 北热带喀斯特季节性雨林林分整体和优势种角尺度分布特征All :林分整体 ;VIK :广西牡荆 ;STM :苹婆;CLS: 闭花木 ; ERS :劲直刺桐; EXH :蚬木 ; DIT :海南椴 ;BOM :黄 梨木 ; FIH :对叶榕 ;CET :假玉桂 ;PSD :鱼骨木。Figure 1. Uniform angle index distribution characteristics of overall stand and dominant species in northern tropical karst seasonal rainforestAll: Entire stand; VIK: Vitex kwangsiensis C. P'ei; STM: Sterculia monosperma Vent; CLS: Cleistanthus sumatranus (Miq.) Müll. Arg.; ERS: Erythrina stricta Roxb.; EXH: Excentrodendron hsienmu (A. Chev.) H. T. Chang et R. H. Miao; DIT: Diplodiscus trichospermus (Merr.) Y. Tang, M. G. Gilbert et Dorr; BOM: Boniodendron minus (Hemsl.) T.C. Chen; FIH: Ficus hispida L. f.; CET: Celtis timorensis Span.; PSD: Psydrax dicocca Gaertn.2.2 不同生活型树种随机体的比例和分布特征
乔木角尺度均值在随机分布范围内,为0.499,随机体占比为57.167%,均匀体占比较小,为23.189%,聚集体次之,为19.644%。灌木角尺度均值为0.519,为聚集分布,随机体占比为59.173%,均匀体占比为19.064%,聚集体为21.763%。乔木和灌木的随机体比例均超过55%,但灌木的聚集体占比高于均匀体。而在乔木中,均匀体占比高于聚集体,表明不同生活型的植物,其随机体比例和分布存在一定的差异(表2)。
表 2 北热带喀斯特季节性雨林不同生活型随机体比例和分布Table 2. Proportion and distribution of random framework among different life forms in northern tropical karst seasonal rainforest生活型
Life style角尺度 Uniform angle index / % 非常均匀
Very regular均匀
Regular随机
Random聚集
Clustered非常聚集
Very clustered角尺度均值
Uniform angle index mean乔木 0.773 22.416 57.167 15.785 3.859 0.499 灌木 0.719 18.345 59.173 16.187 5.576 0.519 2.3 Pearson相关性分析
研究结果显示,随机体与胸高断面积之和、平均海拔、坡度、岩石裸露率、凹凸度、干旱度指数、原有植株个体数之间均存在显著正相关,其中相关性最高的为原有植株个体数,相关系数达0.86;平均海拔和坡度分别与随机体存在低度相关,相关系数分别为0.36和0.31。随机体分别与最大胸径、平均胸径和地形湿润指数存在显著负相关,但与坡向无显著相关性。胸高断面积和最大胸径、坡度和地形湿润指数间也具有较高的相关性,相关系数分别为0.7和−0.72(图2)。
![]() 图 2 北热带喀斯特季节性雨林随机体与环境因子Pearson相关性矩阵图Meanelev:平均海拔;Slope:坡度;Aspect:坡向;Convex:凹凸度;TWI:地形湿润指数;ACH:干旱度指数;RBR:岩石裸露率;ba:胸高断面积之和;Maxdbh:最大胸径;Meandbh:平均胸径。Figure 2. Pearson correlation matrix between random framework and environmental factors in northern tropical karst seasonal rainforestMeanelev: Mean elevation; Slope: Slope; Aspect: Aspect; Convex: Convexity; TWI: Topographic wetness index; ACH: Altitude above channel; RBR: Rock-bareness rate; ba: Total basal area; Maxdbh: Maximum diameter at breast height; Meandbh: Mean diameter at breast height.
图 2 北热带喀斯特季节性雨林随机体与环境因子Pearson相关性矩阵图Meanelev:平均海拔;Slope:坡度;Aspect:坡向;Convex:凹凸度;TWI:地形湿润指数;ACH:干旱度指数;RBR:岩石裸露率;ba:胸高断面积之和;Maxdbh:最大胸径;Meandbh:平均胸径。Figure 2. Pearson correlation matrix between random framework and environmental factors in northern tropical karst seasonal rainforestMeanelev: Mean elevation; Slope: Slope; Aspect: Aspect; Convex: Convexity; TWI: Topographic wetness index; ACH: Altitude above channel; RBR: Rock-bareness rate; ba: Total basal area; Maxdbh: Maximum diameter at breast height; Meandbh: Mean diameter at breast height.2.4 环境因子与随机体的冗余分析及单个解释变量的相对重要性
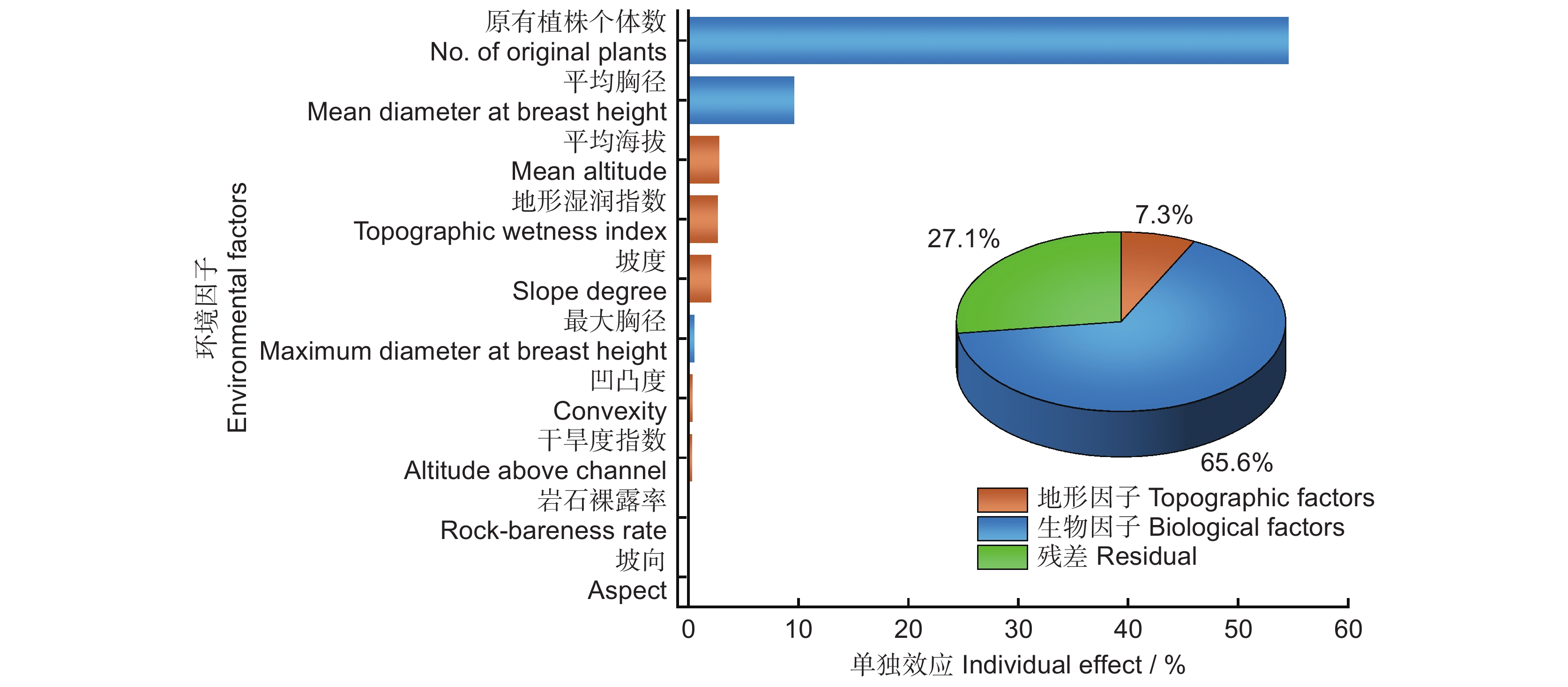
结合环境因子的相关性和方差膨胀因子分析,将胸高断面积之和剔除。对随机体与生物因子和地形因子进行冗余分析,10个环境因子对随机体的解释量R2经校正后为0.729。其中,生物因子解释了65.6%,地形因子解释了7.3%。未被解释的部分占27.1%。根据层次分割法各环境因子单独效应比例排序,随机体的主要影响因素包括原有植株个体数、平均胸径、平均海拔、地形湿润指数和坡度;贡献较小的是最大胸径、坡向、岩石裸露率、凹凸度和干旱度指数(图3)。
3. 讨论
3.1 随机体的分布特征
林木的空间分布格局主要分为随机分布、规则分布和聚集分布,最理想的是随机分布,而随机分布也是天然原始顶极群落中最为显著的结构特征[23]。本研究中,林分整体为随机分布,优势种的角尺度均值也在随机分布范围内,且随机体占比均超过50%。因此,随机体以相似的比例出现在不同树种中,且支持了“随机体-稳定性”假说,与前人研究结果一致[5]。这种结构体相对来说具有较小的生存压力,稳定性高,在竞争情况下不易出现弱势或者不健康的林木,在自然演替过程中存活几率更大[6]。而均匀体和聚集体占比较小,与袁星明等[24]的报道相似。
不同空间分布格局分析方法可能导致结果上的差异。前人研究采用完全随机零模型和泊松异质性零模型对该地区分布格局进行了分析,完全随机零模型结果表明,在小尺度上所有物种均呈聚集分布[25],与本研究结果不一致;然而,当泊松异质性零模型去除生境异质性后,大部分物种表现为随机分布,与本文结果一致。完全随机零模型是基于假设个体随机分布,不受任何因素的干扰而对分布格局进行拟合分析。但在生境异质性强的北热带喀斯特地区,物种的分布显然会受到各种因素的影响。因此,在不考虑任何因素干扰情况下大多数物种呈聚集分布,与本研究结果存在差异。泊松异质性零模型主要用于模拟生境关联,本研究基于相邻木的角尺度法分析林木分布格局,也未直接考虑生境异质性,所以二者结果一致。另外,角尺度法不存在尺度效应,而空间点格局法可以拟合分析不同尺度的林木分布格局,二者各具特点。对于这两种方法,有学者也进行了对比,发现角尺度法在判断分布格局的准确性、有效性和可行性方面优于空间点格局分析[26]。
林分密度是预测林分动态的重要空间信息之一[27]。以往研究表明,种群分布格局对密度具有一定的依赖性,密度越大,聚集强度越高[28]。在本研究中,闭花木的密度最大,聚集程度也是最高的。尽管苹婆与鱼骨木在数量上存在显著差异,但它们在聚集体中所占的比例却几乎相同。这可能是在北热带喀斯特季节性雨林中岩石的裸露率较高,在岩石裸露度高的区域,植物聚集度就会偏低,反之亦然。因此,种群的分布格局与密度无明显的线性关系。
3.2 生活型对随机体的影响
植物生活型的形成是植物在特定环境中趋同适应的结果。灌木主要处于上层乔木树种的林冠下或林隙中,在数量特征和空间分布格局上会受后者的制约与影响[29]。本研究中,乔木分布比灌木多,优势度位于前10的皆为乔木树种,生活型为灌木的树种仅占25.8%。灌木树种相对于乔木树种其聚集体比例更高,分布格局为聚集分布,而乔木树种为随机分布。研究表明,不同生活型的种群聚集度差异很大,从乔木层到灌木层,聚集度逐渐增加,在林下灌丛层中,聚集度最高[25],与本文结果一致。因此随机体分布与树种自身的生物学特性有一定关系。
3.3 环境因子对随机体的影响
随机体受诸多因素的影响,不同因素的影响程度不同。本研究中,植株个体数、平均胸径、平均海拔、地形湿润指数和坡度对随机体的影响较大,而最大胸径、坡向、岩石裸露率、凹凸度和干旱度指数对随机体的影响较小。从相关系数可以看出,植株个体数与随机体呈显著正相关,植株的个体数越多,随机体所占比例越高,群落越稳定。
林木间的竞争是最直观的相互影响关系。在林区,因为森林资源有限,为了生存,林木之间必然要进行争夺[30-32]。林木自身遗传物质的差异,导致了林木自身的竞争能力也不一样。竞争力可以从林木的胸径等属性中反映出来[33]。不同树种之间的竞争强度会影响其生长状况,从而影响其在森林中的分布。此外,强烈的竞争还会造成一些树木的死亡,从而使森林随机体的分布发生改变。本研究中优势种随机体的分布情况不一,既存在随机分布,也存在聚集分布。因此,竞争是影响随机体分布的重要原因之一。
海拔对植物的分布起重要作用,一方面是直接作用,另一方面是对其他非生物资源(如光、温、水、土等)的分配产生影响。然而,在本研究中,地形因子对于随机体分布的解释力度相对较低。尽管如此,在这些地形因子之中,海拔仍然是解释随机体分布最具影响力的因素。在北热带喀斯特季节性雨林中,物种丰富度随着海拔梯度的变化而呈现显著差异[34],物种之间的竞争强度和自疏程度都有所提高,而同种植物之间的聚集程度则有所下降[35]。同时,由于海拔的不同,水热条件也会发生较大的差异,从而使植物在不同海拔有明显的分布差异。在海拔较高的地区,如山顶,其光照强度高、水分缺乏、昼夜温差大、岩石裸露度高、土层薄。而在洼地边缘通常伴有季节性水淹,光照强度较弱[36]。因此,海拔直接或间接影响林木分布[37],造成随机体分布的差异。
4. 结论
本研究分析了北热带喀斯特季节性雨林森林动态监测样地中的随机体分布特征及其影响因素,发现该区林分整体稳定性较高,多数林木处于随机分布状态。其中,闭花木、苹婆和广西牡荆树种占主要优势,且其角尺度对林分整体分布起关键作用。不同生活型植物的随机体分布不同,树种本身生物学特性是影响不同生活型树种随机体分布的原因。不同环境因子对随机体的影响程度不同,原有植株个体数、平均胸径、平均海拔、地形湿润度指数和坡度是随机体的主要驱动因子。
-
表 1 浮鹰岛台湾相思群落样方的基本信息
Table 1 Basic information on Acacia confusa community in Fuying Island
样地编号
No.纬度
Latitude (N)经度
Longitude (E)海拔
Elevation / m坡度
Slope / °坡向
Aspect坡位
Slope positionD1 26°35′36.36″ 120°8′32.80″ 68.9 28.9 西北WN 中坡Ms D2 26°35′37.65″ 120°8′40.85″ 136.2 31.6 西南WS 中坡Ms D3 26°36′6.90″ 120°8′56.99″ 51.5 17.6 西W 中坡Ms D4 26°36′6.56″ 120°8′6.25″ 40.0 30.2 西南WS 中坡Ms D5 26°35′59.68″ 120°8′50.20″ 69.5 13.2 西南WN 中坡Ms D6 26°35′58.89″ 120°8′49.65″ 60.92 23.1 西W 中坡Ms D7 26°35′54.10″ 120°8′45.63″ 70.8 44.7 西北WN 中坡Ms D8 26°35′50.16″ 120°9′23.70″ 291.1 22.2 东南ES 上坡Us D9 26°35′50.24″ 120°9′38.86″ 291.1 27.5 西南WS 上坡Us D10 26°35′47.63″ 120°9′35.20″ 296.3 9.5 东E 上坡Us D11 26°36′6.30″ 120°9′22.16″ 180.6 32.5 北N 中坡Ms D12 26°35′0.75″ 120°8′8.80″ 64.5 29.7 西北WN 中坡Ms D13 26°35′16.21″ 120°8′10.85″ 67.1 36.4 西W 中坡Ms D14 26°35′20.17″ 120°8′8.94″ 33.9 27.2 西南WS 中坡Ms D15 26°35′3.25″ 120°8′40.36″ 73.5 27.0 东南ES 中坡Ms D16 26°34′50.74″ 120°8′40.80″ 35.8 27.6 南S 中坡Ms D17 26°35′59.70″ 120°8′20.58″ 67.6 22.7 北N 中坡Ms D18 26°33′56.29″ 120°7′39.85″ 183.6 23.6 西W 上坡Us D19 26°33′59.66″ 120°7′32.63″ 167.0 19.2 东E 中坡Ms D20 26°34′1.06″ 120°7′27.41″ 205.0 10.2 南S 上坡Us D21 26°33′57.03″ 120°7′45.31″ 210.5 13.4 西W 上坡Us D22 26°34′49.31″ 120°8′47.98″ 35.4 6.3 西北WN 中坡Ms D23 26°34′43.89″ 120°8′41.91″ 24.4 28.9 西W 下坡Ds 表 2 浮鹰岛台湾相思群落灌木层主要物种的重要值与生态位宽度
Table 2 Importance values and niche breadths of main shrub species in Acacia confusa community in Fuying Island
序号
No.种名
Species种名缩写
Abbreviation of
species重要值
Importance
value / %Levins 指数
Niche breadth
Levins (BL)Shannon 指数
Niche breadth
Shannon (BS)1 杜虹花Callicarpa pedunculata R. Br. Cp 12.44 17.08 2.94 2 蓬藟Rubus hirsutus Thunb. Rh 6.55 9.95 2.54 3 珊瑚樱Solanum pseudocapsicum L. Sp 5.21 5.51 1.96 4 车桑子Dodonaea viscosa (L.) Jacq. Dv 4.95 4.36 1.67 5 苎麻Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaudich. Bn 4.88 10.48 2.54 6 鲫鱼胆Maesa perlarius (Lour.) Merr. Mp 3.82 7.35 2.35 7 朴树Celtis sinensis Pers. Cs 3.74 7.13 2.31 8 台湾相思Acacia confusa Merr. Ac 3.67 11.06 2.56 9 茅莓Rubus parvifolius L. Rp 3.08 11.14 2.58 10 雀梅藤Sageretia thea (Osbeck) Johnst. St 3.07 12.80 2.72 11 福建胡颓子Elaeagnus oldhamii Maximowicz Eo 2.96 12.00 2.67 12 算盘子Glochidion puberum (L.) Hutch. Gp 2.90 4.31 1.95 13 滨柃Eurya emarginata (Thunb.) Makino Ee 2.88 3.02 1.26 14 硕苞蔷薇Rosa bracteata Wendl. Rb 2.60 7.76 2.29 15 白簕Eleutherococcus trifoliatus (L.) Hu Et 2.11 4.54 1.83 16 桃金娘Rhodomyrtus tomentosa (Ait.) Hassk. Rt 2.04 1.76 0.88 17 海州常山Clerodendrum trichotomum Thunb. Ct 1.98 2.16 0.87 18 天仙果Ficus erecta Thunb. Fe 1.81 10.50 2.47 19 牡荆Vitex negundo var. Cannabifolia(Sieb.et Zucc.) Hand.-Mazz. Vn 1.53 2.00 0.87 20 乌桕Triadica sebifera (L.) Small Ts 1.50 2.32 0.97 表 3 主要物种总体联结性
Table 3 Overall interspecific associations among main species in shrub layer
方差比率
Variance ratio(VR)检验统计量
Statistic(W)χ2临界值
χ2 threshold(23)检验结果
Results0.87 20.01 13.09,35.17 不显著负联结 -
[1] Ma YM,Li QH,Pan SP,Liu C,Han MS,Brancelj A. Niche and interspecific associations of Pseudoanabaena limnetica–exploring the influencing factors of its succession stage[J]. Ecol Indic,2022,138:108806. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108806
[2] 李锦婷,穆君,申开平,郭云,白小节,等. 小黄花茶群落优势木本植物生态位及种间联结性[J]. 生态学报,2024,44(1):283−294. Li JT,Mu J,Shen KP,Guo Y,Bai XJ,et al. Niche and interspecific association of dominant woody plants in Camellia luteoflora community[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2024,44(1):283−294.
[3] Grinnell J. The niche-relationships of the California thrasher[J]. Auk,1917,34(4):427−433. doi: 10.2307/4072271
[4] Gu L,O’Hara KL,Li WZ,Gong ZW. Spatial patterns and interspecific associations among trees at different stand development stages in the natural secondary forests on the Loess Plateau,China[J]. Ecol Evol,2019,9(11):6410−6421. doi: 10.1002/ece3.5216
[5] 徐满厚,刘敏,翟大彤,刘彤. 植物种间联结研究内容与方法评述[J]. 生态学报,2016,36(24):8224−8233. Xu MH,Liu M,Zhai DT,Liu T. A review of contents and methods used to analyze various aspects of plant interspecific associations[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2016,36(24):8224−8233.
[6] 池源,石洪华,郭振,丁德文. 海岛生态脆弱性的内涵、特征及成因探析[J]. 海洋学报,2015,37(12):93−105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2015.12.010 Chi Y,Shi HH,Guo Z,Ding DW. Connotation,features and causes of island ecological vulnerability[J]. Haiyang Xuebao,2015,37(12):93−105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2015.12.010
[7] 王国明,叶波. 舟山群岛典型植物群落物种组成及多样性[J]. 生态学杂志,2017,36(2):349−358. Wang GM,Ye B. Floristic composition and diversity of typical plant community in Zhoushan Archipelago,East China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2017,36(2):349−358.
[8] 陈越琳,黄阿青,肖集泓,王芳,邓传远,陈凌艳. 福建连江县5个无居民海岛种子植物区系及地理分布研究[J]. 热带作物学报,2024,45(2):424−434. Chen YL,Huang AQ,Xiao JH,Wang F,Deng CY,Chen LY. Seed plant flora and distribution on five uninhabited islands in Lianjiang,Fujian province[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2024,45(2):424−434.
[9] 郑俊鸣,张嘉灵,郑建忠,方笑,邓传远. 中国海岛植被修复的适生植物[J]. 世界林业研究,2017,30(3):86−90. Zheng JM,Zhang JL,Zheng JZ,Fang X,Deng CY. Adaptable plant species for island vegetation restoration[J]. World Forestry Research,2017,30(3):86−90.
[10] 张增可,吴雅华,王齐,季凌波,黄柳菁. 环境因子对海岛植物茎、叶功能性状的影响[J]. 广西植物,2020,40(3):433−442. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201811051 Zhang ZK,Wu YH,Wang Q,Ji LB,Huang LJ. Effects of environmental factors on stem and leaf functional traits of island plants[J]. Guihaia,2020,40(3):433−442. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201811051
[11] 肖君. 福州市主要森林类型林下灌木层生物量和碳密度研究[J]. 林业勘察设计,2023,43(1):1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2180.2023.01.001 Xiao J. Biomass and carbon density of undergrowth in main forest types in Fuzhou[J]. Forestry Prospect and Design,2023,43(1):1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2180.2023.01.001
[12] 刘永安,陈小勇,王友芳,马钰洪,马伍卡. 攀西地区台湾相思适宜育苗容器和基质[J]. 东北林业大学学报,2012,40(10):98−102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2012.10.022 Liu YA,Chen XY,Wang YF,Ma YH,Ma WK. Proper container and growing media for Acacia richii seedlings in Panzhihua and Xichang regions[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2012,40(10):98−102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2012.10.022
[13] 何晨阳,陈珑,王耘籽,周艳芬,李键,等. 低磷胁迫下内生真菌对台湾相思叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版),2022,61(5):872−879. He CY,Chen L,Wang YZ,Zhou YF,Li J,et al. Effects of endophytic fungi on chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of Acacia confusa under low phosphorus stress[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science),2022,61(5):872−879.
[14] 黄猛,丁国昌,赵苗菲,阮少宁,李树斌,黄玉梅. 台湾相思开花结实生物学特性研究[J]. 西南林业大学学报,2019,39(1):80−87. doi: 10.11929/j.swfu.201808006 Huang M,Ding GC,Zhao MF,Ruan SN,Li SB,Huang YM. The biological characteristics of flowering and fruiting in Acacia confusa[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University,2019,39(1):80−87. doi: 10.11929/j.swfu.201808006
[15] 徐华林,袁天天,王蕾,关开朗,廖文波. 广东内伶仃岛台湾相思群落在15年间的演替研究[J]. 生态科学,2016,35(4):12−22. Xu HL,Yuan TT,Wang L,Guan KL,Liao WB. Succession of Acacia confusa communities during fifteen years in Neilingding Island of Guangdong Province,China[J]. Ecological Science,2016,35(4):12−22.
[16] 王国宏,方精云,郭柯,谢宗强,唐志尧,等. 《中国植被志》研编内容与规范[J]. 植物生态学报,2020,44(2):128−178. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2019.0272 Wang GH,Fang JY,Guo K,Xie ZQ,Tang ZY,et al. Contents and protocols for the classification and description of Vegetation Formations,Alliances and Associations of vegetation of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2020,44(2):128−178. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2019.0272
[17] 张金屯. 数量生态学[M]. 2版. 北京:科学出版社,2011:1−372. [18] Shannon CE,Weaver W,Wiener N. The mathematical theory of communication[J]. Phys Today,1950,3(9):31−32. doi: 10.1063/1.3067010
[19] Levins RA. Evolution in Changing Environments:Some Theoretical Explorations. (MPB-2)[M]. Princeton:Princeton University Press,1968:1−100.
[20] Schoener TW. Resource partitioning in ecological communities[J]. Science,1974,185(4145):27−39. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4145.27
[21] Pianka ER. The structure of lizard communities[J]. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst,1973,4:53−74. doi: 10.1146/annurev.es.04.110173.000413
[22] Schluter D. A variance test for detecting species associations,with some example applications[J]. Ecology,1984,65(3):998−1005. doi: 10.2307/1938071
[23] 尚玉昌. 普通生态学[M]. 2版. 北京:北京大学出版社,2002:35−39. [24] 王刚,赵松岭,张鹏云,陈庆诚. 关于生态位定义的探讨及生态位重叠计测公式改进的研究[J]. 生态学报,1984,4(2):119−127. Wang G,Zhao SL,Zhang PY,Chen QC. On the definition of niche and the improved formula for measuring niche overlap[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,1984,4(2):119−127.
[25] 李坤,邢小艺,李逸伦,李晓鹏,李如辰,等. 石林风景区不同石漠化人工修复方式对木本植物群落组成及种群生态位的影响[J]. 生态学报,2020,40(13):4641−4650. Li K,Xing XY,Li YL,Li XP,Li RC,et al. Effect of different artificial restoration methods of Karst rocky desertification on community composition and niche characteristics of woody populations in Shilin scenic area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2020,40(13):4641−4650.
[26] 刘润红,常斌,荣春艳,姜勇,杨瑞岸,等. 漓江河岸带枫杨群落主要木本植物种群生态位[J]. 应用生态学报,2018,29(12):3917−3926. Liu RH,Chang B,Rong CY,Jiang Y,Yang RA,et al. Niche of main woody plant populations of Pterocarya stenoptera community in riparian zone of Lijiang River,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2018,29(12):3917−3926.
[27] 郑俊鸣,李敏,张盟,Tarin MWK,何天友,等. 滨海防护林木麻黄和花吊丝竹混交林群落的种间关联和生态位分析[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报,2021,29(5):465−473. doi: 10.11926/jtsb.4346 Zheng JM,Li M,Zhang M,Tarin MWK,He TY,et al. Interspecific association and niche of mixed forest communities of Casuarina equisetifolia and Dendrocalamus minor var. amoenus in the windbreak of sandy coast[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany,2021,29(5):465−473. doi: 10.11926/jtsb.4346
[28] 马晓迪,姜德刚,刘子琳,王芳,温瑞龙,邓传远. 平潭岛台湾相思群落优势种群生态位研究[J]. 热带作物学报,2022,43(12):2614−2625. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2022.12.024 Ma XD,Jiang DG,Liu ZL,Wang F,Wen RL,Deng CL. Niche of dominant plant populations of Acacia confusa community in Pingtan Island[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2022,43(12):2614−2625. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2022.12.024
[29] 肖集泓,熊宽洪,陈越琳,王春晓,江怡萱,等. 福建琅岐岛台湾相思群落灌木层主要物种生态位与种间联结[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报,2023,31(6):805−815. doi: 10.11926/jtsb.4687 Xiao JH,Xiong KH,Chen YL,Wang CX,Jiang YX,et al. Niche and interspecific association of main species in shrub layer of Acacia confusa community in Langqi Island,Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany,2023,31(6):805−815. doi: 10.11926/jtsb.4687
[30] 李燕芬,铁军,张桂萍,郭华. 山西蟒河国家级自然保护区人工油松林生态位特征[J]. 生态学杂志,2014,33(11):2905−2912. Li YF,Tie J,Zhang GP,Guo H. Niche characteristics of an artificial Pinus tabuliformis forest in Manghe National Nature Reserve of Shanxi[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2014,33(11):2905−2912.
[31] 刘润红,陈乐,涂洪润,梁士楚,姜勇,等. 桂林岩溶石山青冈群落灌木层主要物种生态位与种间联结[J]. 生态学报,2020,40(6):2057−2071. Liu RH,Chen L,Tu HR,Liang SC,Jiang Y,et al. Niche and interspecific association of main species in shrub layer of Cyclobalanopsis glauca community in karst hills of Guilin,southwest China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2020,40(6):2057−2071.
[32] Chai ZZ,Sun CL,Wang DX,Liu WZ. Interspecific associations of dominant tree populations in a virgin old-growth oak forest in the Qinling Mountains,China[J]. Bot Stud,2016,57(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s40529-016-0139-5
[33] 温鑫鸿,王其炳,潘辉,王李睿,陈妍,何东进. 天宝岩柳杉群落主要乔木种群的种间联结性[J]. 森林与环境学报,2022,42(1):1−10. Wen XH,Wang QB,Pan H,Wang LR,Chen Y,He DJ. Interspecific associations of the main tree populations of the Cryptomeria fortunei community in Tianbaoyan[J]. Journal of Forest and Environment,2022,42(1):1−10.
[34] Jonsson BG,Moen J. Patterns in species associations in plant communities:the importance of scale[J]. J Veg Sci,1998,9(3):327−332. doi: 10.2307/3237097
[35] Jiang CC,Fu JQ,Wang YQ,Chai PT,Yang YD,et al. The habitat type and scale dependences of interspecific associations in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest[J]. Forests,2022,13(8):1334. doi: 10.3390/f13081334
[36] 张峰,上官铁梁. 山西翅果油树群落种间关系的数量分析[J]. 植物生态学报,2000,24(3):351−355. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2000.03.018 Zhang F,Shangguan TL. Numerical analysis of interspecific relationships in an Elaeagnus mollis community in Shanxi[J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica,2000,24(3):351−355. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2000.03.018
[37] 许金石,陈煜,王国勋,柴永福,王茂,等. 陕北桥山林区主要木本植物群落种间联结性[J]. 西北植物学报,2014,34(7):1467−1475. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2014.07.1467 Xu JS,Chen Y,Wang GX,Chai YF,Wang M,et al. Interspecific association of dominant woody plant communities in Qiaoshan forest region,Shaanxi[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2014,34(7):1467−1475. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2014.07.1467
[38] 李丘霖,宗秀虹,邓洪平,万海霞,吴洪英,等. 赤水桫椤群落乔木层优势物种生态位与种间联结性研究[J]. 西北植物学报,2017,37(7):1422−1428. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2017.07.1422 Li QL,Zong XH,Deng HP,Wan HX,Wu HY,et al. Niche and interspecific association of dominant species in tree layer of Chishui Alsophila spinulosa community[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2017,37(7):1422−1428. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2017.07.1422
[39] 李帅锋,刘万德,苏建荣,张志钧. 季风常绿阔叶林不同恢复阶段乔木优势种群生态位和种间联结[J]. 生态学杂志,2011,30(3):508−515. Li SF,Liu WD,Su JR,Zhang ZJ. Niches and interspecific associations of dominant tree populations at different restoration stages of monsoonal broad-leaved evergreen forest[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2011,30(3):508−515.
[40] 邓小艳,刘建国,郭朋军,俞存根,张平,等. 小洋山邻近海域主要游泳动物生态位及种间联结性[J]. 海洋学报,2018,40(1):96−105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2018.01.011 Deng XY,Liu JG,Guo PJ,Yu CG,Zhang P,et al. Niche and interspecific association of major nekton in Xiao Yangshan adjacent waters[J]. Haiyang Xuebao,2018,40(1):96−105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2018.01.011
[41] 张东梅,赵文智,罗维成. 荒漠草原带盐碱地优势植物生态位与种间联结[J]. 生态学杂志,2018,37(5):1307−1315. Zhang DM,Zhao WZ,Luo WC. Niche and interspecific association of dominant plant species in saline-alkaline soils of desert steppe zone[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2018,37(5):1307−1315.



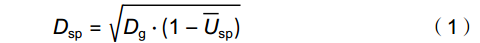
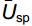



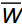


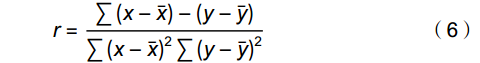
 下载:
下载: